epoll可以用单进程单线程实现高并发
首先我们可以实现单进程单线程实现高并发(模拟非阻塞IO请求)
服务端
//服务端
public class BlockNIOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//获取通道
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//切换非阻塞模式
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//绑定端口
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8090));
//获取选择器
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//将该通道注册到select中,让select监听该通道的连接是否准备就绪
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = null;
//通过选择器轮询获取已经准备就绪的事件
while (selector.select()>0){
iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
SelectionKey selectionKey = iterator.next();
//如果获取的是准备连接就绪的事件
if (selectionKey.isAcceptable()){
System.out.println("有客户端已经准备好连接了....");
//开始接受连接客户端
SocketChannel accept = serverSocketChannel.accept();
//切换非阻塞模式
accept.configureBlocking(false);
//将通道注册到selector中,让select监听该通道的数据是否准备就绪
accept.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
else if (selectionKey.isReadable()){
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
Random random = new Random();
int i = random.nextInt(100);
String path = "C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\"+i+".txt";
FileChannel fileChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get(path), StandardOpenOption.READ, StandardOpenOption.WRITE, StandardOpenOption.CREATE);
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while (socketChannel.read(byteBuffer)!=-1){
byteBuffer.flip();
fileChannel.write(byteBuffer);
byteBuffer.clear();
}
byteBuffer.put("数据已经接受完毕...".getBytes());
byteBuffer.flip();
socketChannel.write(byteBuffer);
fileChannel.close();
socketChannel.close();
System.out.println("写入数据成功....");
}
//取消选择键
iterator.remove();
}
}
}
}
客户端
//客户端
public class BlockNIOClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//获取通道
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8090));
FileChannel fileChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\x.txt"), StandardOpenOption.READ);
//System.out.println("模拟10秒之后发送数据...");
//可以开启两个客户端,一个睡10秒发送数据(先请求),一个不用睡眠(后请求),发现,必须等第一个用户处理完毕之后,第二个用户才可以被处理
//Thread.sleep(20000);
//分配缓冲区大小
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//读取本地文件发送到服务器
while (fileChannel.read(byteBuffer)!=-1){
byteBuffer.flip();
socketChannel.write(byteBuffer);
byteBuffer.clear();
}
//告诉服务器,我的数据已经发送完毕
socketChannel.shutdownOutput();
//接受服务器返回来的消息
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
int len =-1;
while ((len=socketChannel.read(byteBuffer))!=-1){
byteBuffer.flip();
stringBuffer.append(new String(byteBuffer.array(),0,len));
byteBuffer.clear();
}
System.out.println(stringBuffer);
socketChannel.close();
fileChannel.close();
}
}
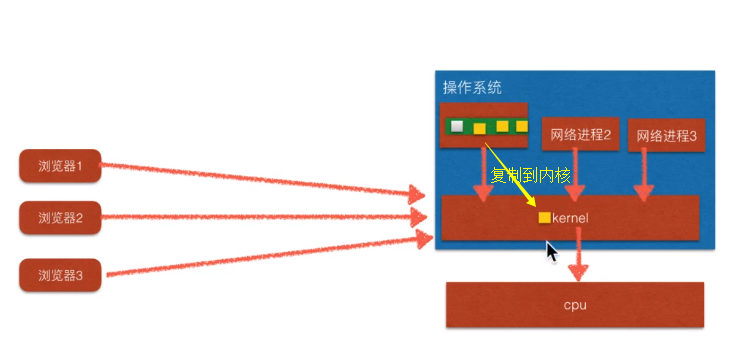
假如有三个连接到来了,一个socker通道监听连接是否到来(白色方格),三个socker通道是因为连接到来了,被注册到select中监听数据是否到来(黄色方格),此时select不断的遍历,首先select将其中的一个socker通道(在linux中是fd(int)文件描述符)复制一份到操作系统(这一步是性能的瓶颈所在,让操作提供来看看我这个通道有没有数据到来,或者连接请求的到来),此时操作系统(内核)还会执行别的应用进程,什么执行我们这个检测操作是由操作系统决定(又浪费了一部分时间)。然后一步一步将select选择器中的所有的socket通道全部遍历(select选择器中的socker通道数目越多,性能越差),有的socker通道不活跃,也被检测了,就非常损耗性能。
图中绿色的是select选择器(维护了socker通道),处于应用层,放在用户空间
epoll
epoll有一段特殊的内存空间(操作系统和应用程序共用)
图中绿色的是epoll选择器(维护了socker通道,实现方式是红黑树和链表),处于应用程序和内核共享空间
epoll的第一个优点:不需要额外的复制操作

epoll的第一个优点:采用事件通知,取代了之前的轮询(select)