ReentrantLock
可重入
可中断
可限时
公平锁
简单示例
class ReentrantLockTest implements Runnable{
private static ReentrantLock reentrantLock = new ReentrantLock();
private static int i=0;
@Override
public void run() {
for (int j=0;j<10000;j++){
reentrantLock.lock();
try {
i++;
}finally {
reentrantLock.unlock();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ReentrantLockTest reentrantLockTest = new ReentrantLockTest();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(reentrantLockTest);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(reentrantLockTest);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
System.out.println(i);
}
}
可重入
可重入锁的基本原理:锁也是一个类。
类的内部lock()方法,当线程第一个需要获取锁的时候,将当前线程保存到类中,并且将锁的状态设置为false,计数器+1,下次当某一个线程来获取锁的时候,lock()方法while循环判断,如果是不是当前线程并且锁的状态是false,就等待(并且一直尝试获取锁),如果是当前线程或者锁的状态为true,就继续加锁,计数器+1;
类的内部unlock()方法,首先判断是不是当前线程调用unlock方法(不是抛出异常),调用成功就将计数器-1,如果计数器=0,就将锁设置为true,此时其他的线程可以来获取锁了,否则只有当前线程才可以获取锁。
class ReentrantLockTest implements Runnable{
private static ReentrantLock reentrantLock = new ReentrantLock();
private static int i=0;
@Override
public void run() {
for (int j=0;j<10000;j++){
reentrantLock.lock();
reentrantLock.lock();
try {
i++;
}finally {
reentrantLock.unlock();
reentrantLock.unlock();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ReentrantLockTest reentrantLockTest = new ReentrantLockTest();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(reentrantLockTest);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(reentrantLockTest);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
System.out.println(i);
}
}
可中断
当一个线程处于死锁或者长期等待状态,可以将该线程强制中断;
class DeadLockChecker{
private final static ThreadMXBean mxBean= ManagementFactory.getThreadMXBean();
private static Runnable runnable = new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
long[] deadlockedThreads = mxBean.findDeadlockedThreads();
if (deadlockedThreads!=null){
ThreadInfo[] threadInfo = mxBean.getThreadInfo(deadlockedThreads);
for (Thread t:Thread.getAllStackTraces().keySet()){
for (int i=0;i<threadInfo.length;i++){
if (t.getId()==threadInfo[i].getThreadId()){
t.interrupt();
}
}
}
}
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
};
public static void check(){
Thread thread = new Thread(runnable);
//设置守护线程;
thread.setDaemon(true);
thread.start();
}
}
class ReentrantLockTest implements Runnable{
private static ReentrantLock reentrantLock1 = new ReentrantLock();
private static ReentrantLock reentrantLock2 = new ReentrantLock();
private static int i=0;
private int x;
public ReentrantLockTest(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
@Override
public void run() {
//为了构造死锁
try {
if (x==1){
//和reentrantLock1.lock()差不多,都是加锁,但是lockInterruptibly()可以响应中断
reentrantLock1.lockInterruptibly();
Thread.sleep(500);
reentrantLock2.lockInterruptibly();
}
else {
reentrantLock2.lockInterruptibly();
Thread.sleep(500);
reentrantLock1.lockInterruptibly();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
//可以处理其他的事情
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (reentrantLock1.isHeldByCurrentThread()){
reentrantLock1.unlock();
}
if (reentrantLock2.isHeldByCurrentThread()){
reentrantLock2.unlock();
}
System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread().getId()+"退出");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ReentrantLockTest reentrantLockTest = new ReentrantLockTest(1);
ReentrantLockTest reentrantLockTest2 = new ReentrantLockTest(2);
Thread thread1 = new Thread(reentrantLockTest);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(reentrantLockTest2);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
//检查死锁,中断死锁(可以放在thread1和thread2前面,任何位置)
DeadLockChecker.check();
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
System.out.println(i);
}
}
可限时
class ReentrantLockTest implements Runnable{
private static ReentrantLock reentrantLock = new ReentrantLock();
@Override
public void run() {
try {
//表示当某一个线程过来获取锁,最多等待2秒,如果这个锁还没有被释放,直接跳过,不需要在等待,可以执行其他的事情了
if (reentrantLock.tryLock(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS)){
System.out.println("线程 "+Thread.currentThread().getId()+" get lock succeed");
Thread.sleep(3000);
}
else {
System.out.println("线程 "+Thread.currentThread().getId()+" get lock filed");
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//会执行两次xx,一次yy,所以我们需要判断reentrantLock是否是当前线程所有,
//否则会抛出异常,原因在于有一个线程没有获取锁所以释放不了,就抛出异常;
System.out.println("xx");
if (reentrantLock.isHeldByCurrentThread()){
System.out.println("yy");
reentrantLock.unlock();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ReentrantLockTest reentrantLockTest = new ReentrantLockTest();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(reentrantLockTest);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(reentrantLockTest);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
System.out.println("end");
}
}
公平锁
性能较非公平锁差很多,它要处理排队的问题,如果没有特殊的需要,不考虑公平锁
一般情况下,先申请锁的线程未必先获取锁,而公平锁可以保证先申请锁的线程一定先获得锁
condition
await()方法会使当前线程等待,同时释放当前锁,当其地接程中使用signal0时成者signalAll0方法时,线程会重新获得锁并把继续执行。或者当线程别中断时,也能跳出等待,这和Object.wait0方法很相似。
singal()方法用于唤醒一个在等待中的线程,相对的singalAll()方法会唤醒所有等待的线程。这和Obejct.notify0方法很类似。
class ReentrantLockTest implements Runnable{
private static ReentrantLock reentrantLock = new ReentrantLock();
private static Condition condition = reentrantLock.newCondition();
@Override
public void run() {
try {
reentrantLock.lock();
condition.await();
System.out.println("thread is going on");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
reentrantLock.unlock();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ReentrantLockTest reentrantLockTest = new ReentrantLockTest();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(reentrantLockTest);
thread1.start();
//让主线程睡2秒,然后进行condition.signal();通知子线程继续执行
Thread.sleep(2000);
reentrantLock.lock();
condition.signal();
reentrantLock.unlock();
thread1.join();
System.out.println("end");
}
}
信号量
Semaphore是一个并发工具类,用来控制可同时并发的线程数,其内部维护了一组虚拟许可,通过构造器指定许可的数量,每次线程执行操作时先通过acquire方法获得许可,执行完毕再通过release方法释放许可。如果无可用许可,那么acquire方法将一直阻塞,直到其它线程释放许可。
对比线程池
使用Seamphore,你创建了多少线程,实际就会有多少线程进行执行,只是可同时执行的线程数量会受到限制。但使用线程池,你创建的线程只是作为任务提交给线程池执行,实际工作的线程由线程池创建,并且实际工作的线程数量由线程池自己管理。
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/mryang125/article/details/81490783
class ReentrantLockTest implements Runnable{
private final static Semaphore signal = new Semaphore(5);
@Override
public void run() {
try {
signal.acquire();
//模拟耗时操作
System.out.println("线程 "+Thread.currentThread().getId()+" done");
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
signal.release();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//主线程会中断
//ReentrantLockTest reentrantLockTest = new ReentrantLockTest();
//Thread thread1=null;
//for (int i=0;i<20;i++){
//thread1 = new Thread(reentrantLockTest);
//thread1.start();
//}
//thread1.join();
//System.out.println("end");
//主线程不会中断
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(20);
ReentrantLockTest reentrantLockTest1 = new ReentrantLockTest();
for (int i=0;i<20;i++){
executorService.submit(reentrantLockTest1);
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
ReadWriteLock
读读之间不会堵塞
读会堵塞写,写也会堵塞读
写写之间堵塞
ReentrantReadWriteLock reentrantReadWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock(); ReentrantReadWriteLock.ReadLock readLock = reentrantReadWriteLock.readLock(); ReentrantReadWriteLock.WriteLock writeLock = reentrantReadWriteLock.writeLock();
CountDownLatch
class T implements Runnable{
static final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(10);
private final static T t = new T();
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("等待子线程 "+Thread.currentThread().getId()+" 执行完毕");
countDownLatch.countDown();
System.out.println(countDownLatch.getCount());
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
for (int i=0;i<10;i++){
executorService.submit(t);
}
countDownLatch.await();
System.out.println("所有的子线程执行完毕,主线程继续执行");
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
CyclicBarrier
CountDownLatch 同步计数器,主要用于线程间的控制,但计数无法被重置,如果需要重置计数,请考虑使用 CyclicBarrier 。
可以循环复用,比CountDownLatch功能更加强大
class T{
static CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(10, new BarrierRun(false));
public static class soldier implements Runnable{
String soldierName;
public soldier(String soldierName) {
this.soldierName=soldierName;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
//等待所有的士兵(线程)到齐
System.out.println("士兵 "+soldierName+" 到齐");//执行10次
//所有的线程到达完毕之后,执行一次CyclicBarrier(int parties, Runnable barrierAction)中barrierAction的run方法
cyclicBarrier.await();//执行1次
System.out.println("士兵 "+soldierName+" 开始工作");
//等待所有的士兵(线程)到齐
cyclicBarrier.await();
System.out.println("士兵 "+soldierName+" 继续开始工作");
cyclicBarrier.await();
//可以继续await()
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static class BarrierRun implements Runnable{
boolean flag;
public BarrierRun( boolean flag) {
this.flag = flag;
}
@Override
public void run() {
if (flag){
System.out.println("所有士兵完成任务");
}else{
System.out.println("所有的士兵集合完毕");
this.flag = true;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread[] threads = new Thread[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
String s = String.valueOf(i);
threads[i] = new Thread(new soldier(s));
threads[i].start();
}
}
}
LockSupport
底层实现
线程中断不会抛出异常,能够响应中断,但不抛出异常。
中断响应的结果是,park0函数的返回,可以从Thread.interupted0想到中断标志
测试过程中:如果我中断thread1不知道为什么
class T{
private static Object object = new Object();
public static class ChangeObjectThread extends Thread{
public ChangeObjectThread(String name) {
super.setName(name);
}
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (object){
System.out.println("in "+getName());
//如果LockSupport没有获取许可(unpark),就将该线程挂起
LockSupport.park();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ChangeObjectThread thread1 = new ChangeObjectThread("thread1");
thread1.start();
ChangeObjectThread thread2 = new ChangeObjectThread("thread2");
thread2.start();
//无论线程先执行unpark还是先执行park,线程都不会堵塞(unpark让该线程获取一个许可)
LockSupport.unpark(thread1);
LockSupport.unpark(thread2);
System.out.println("unpark不会堵塞unpark");
}
}
BlockingQueue
接口
性能不高
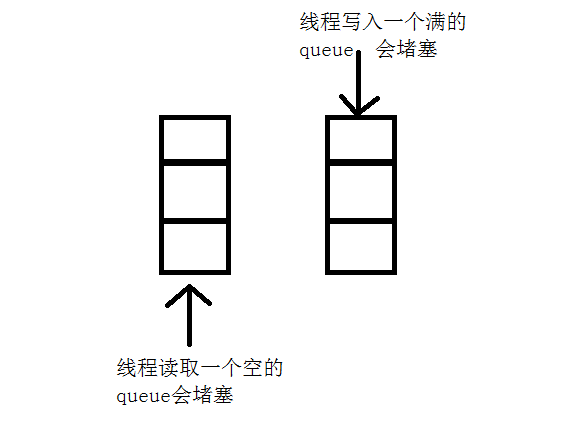
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/jackyuj/archive/2010/11/24/1886553.html
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
/**
* @author jackyuj
*/
public class BlockingQueueTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 声明一个容量为10的缓存队列
BlockingQueue<String> queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<String>(10);
Producer producer1 = new Producer(queue);
Producer producer2 = new Producer(queue);
Producer producer3 = new Producer(queue);
Consumer consumer = new Consumer(queue);
// 借助Executors
ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
// 启动线程
service.execute(producer1);
service.execute(producer2);
service.execute(producer3);
service.execute(consumer);
// 执行10s
Thread.sleep(10 * 1000);
producer1.stop();
producer2.stop();
producer3.stop();
Thread.sleep(2000);
// 退出Executor
service.shutdown();
}
}
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* 消费者线程
*
* @author jackyuj
*/
public class Consumer implements Runnable {
public Consumer(BlockingQueue<String> queue) {
this.queue = queue;
}
public void run() {
System.out.println("启动消费者线程!");
Random r = new Random();
boolean isRunning = true;
try {
while (isRunning) {
System.out.println("正从队列获取数据...");
String data = queue.poll(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if (null != data) {
System.out.println("拿到数据:" + data);
System.out.println("正在消费数据:" + data);
Thread.sleep(r.nextInt(DEFAULT_RANGE_FOR_SLEEP));
} else {
// 超过2s还没数据,认为所有生产线程都已经退出,自动退出消费线程。
isRunning = false;
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
} finally {
System.out.println("退出消费者线程!");
}
}
private BlockingQueue<String> queue;
private static final int DEFAULT_RANGE_FOR_SLEEP = 1000;
}
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* 生产者线程
*
* @author jackyuj
*/
public class Producer implements Runnable {
public Producer(BlockingQueue queue) {
this.queue = queue;
}
public void run() {
String data = null;
Random r = new Random();
System.out.println("启动生产者线程!");
try {
while (isRunning) {
System.out.println("正在生产数据...");
Thread.sleep(r.nextInt(DEFAULT_RANGE_FOR_SLEEP));
data = "data:" + count.incrementAndGet();
System.out.println("将数据:" + data + "放入队列...");
if (!queue.offer(data, 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
System.out.println("放入数据失败:" + data);
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
} finally {
System.out.println("退出生产者线程!");
}
}
public void stop() {
isRunning = false;
}
private volatile boolean isRunning = true;
private BlockingQueue queue;
private static AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger();
private static final int DEFAULT_RANGE_FOR_SLEEP = 1000;
}
ConcurrentLinkedQueue
高性能线程间通讯
ConcurrentLinkedQueue concurrentLinkedQueue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue();
concurrentLinkedQueue.add("s");
Object remove = concurrentLinkedQueue.remove();
对于高并发我们还可以采用CAS无锁
乐观锁的实现原理,当前版本号是不是我预期的版本号,如果是就进行修改,并且修改是原子性。
CAS只能对一个变量进行原子操作,如果需要的变量需要同时进行的话,有一个办法就是将变量打包。
CAS存在ABA的问题:假设线程1从内存中取出了A,线程2也从内存中取出了A,并且将值修改为B,最后又改为A,当线程1去更新值得时候发现内存中的数据和线程备份数据相同,可以更新;但是此时内存中的值其实发生了变化的,只不过又变回去了;
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/gosaint/p/9045494.html
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(1); int i = atomicInteger.addAndGet(1);
内部实现:Unsafe.getUnsafe().getAndAddInt(this, valueOffset, delta) + delta;
如何实现高并发无锁缓存?
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/xybelieve1990/article/details/70313076
java代码实现
首先对1条数据添加一个字段(version,lastTime等),用于进行乐观锁控制。对1条数据进行修改,首先获取这个数据(获取version,lastTime),如果想对这条数据进行修改的时候,version或者lastTime需要作为where查询条件。


