一、初识Css
1、概念
- 用于修饰标签。
- 使用css选择器需要关注两点:1、选择哪个选择器 2、如何选择需要使用css样式的标签。
- 在head中添加style标签,在style标签中添加css选择器,就可以将css样式附着到body中的标签上了。
二、选择器
1、选择器种类
(1)id选择器
- head中使用#号定位,在body中的div标签添加id属性,head中写入对应id属性的值,即可将css样式定位到标签上。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <!--样式标签--> <style> /*id选择器*/ #div1{ background-color: red; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="div1">我是个人</div> </body> </html>

(2)class选择器
- head中使用英文.号定位,在body中的div标签添加class属性,head中写入对应class属性的值,即可将css样式定位到标签上。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> .c1{ background-color: green; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="c1">我是绿色</div> </body> </html>

(3)标签选择器
- head中使用标签名div定位,在body中写入标签内容,head中写入对应div标签的值,即可将css样式定位到标签上。
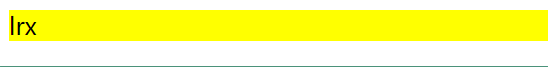
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> div{ background-color: yellow; } </style> </head> <body> <div>lrx</div> </body> </html>
(4)标签层级选择器
- head中使用标签名div里面的span标签定位,在body中写入标签内容,head中写入对应span标签的值,即可将css样式定位到标签上。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> div span{ background-color: yellow; } </style> </head> <body> <div> <span>123</span> </div> </body> </html>

(5)属性选择器
- 在body里面的div标签中加入自定义属性,然后head中通过使用标签名div加中括号,中括号中写全自定义属性名和值的方式,将css样式与标签进行关联。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> div[abc="哈哈哈"]{ background-color: burlywood; } </style> </head> <body> <div abc="哈哈哈">哦哦哦</div> </body> </html>

区别:
- 使用标签选择器时,body中的div标签没有对应的属性,所以body中所有的div标签内容都会被附着这种选择器样式,局限性很高,只有规定了整篇标签都使用同一种样式时才会用到;
- 使用标签层级选择器时,span标签也是没有对应的属性,跟标签选择器的局限性一样,凡是符合div中有span的这个路径的标签,都会被附着相同的样式;
- id选择器和class选择器都会通过标签的属性精确定位。
2、组合选择器种类
(1)id组合选择器
div标签中,在一个HTML标签中不允许出现两个id属性:
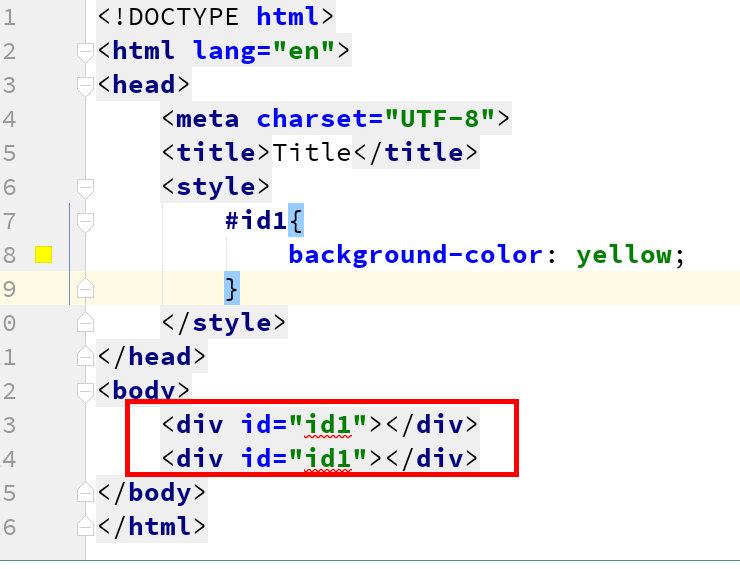
那么如何将两个div标签附着相同的id选择器的css样式呢?可以使用id组合选择器。
- head中使用#号定位,将两个id的属性值同时写在一起,使用英文逗号间隔,在body中的div标签添加id属性,head中写入对应id属性的值,即可将css样式定位到标签上。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> #id1,#id2{ background-color: pink; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="id1"></div> <div id="id2"></div> </body> </html>

(2)class组合选择器
div标签中,在一个HTML标签中可以同时出现两个class属性:

body中可以同时附着多个css样式,只需在body的class属性中写入附着的css样式名,使用一个空格间隔即可:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> .c1{ background-color: blue; } .c2{ width: 100px; height: 100px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="c1 c2">c1</div> <div class="c1">c2</div> </body> </html>

可以看到,第一个标签同时附着了两个css样式。
3、选择器引入方式
(1)在head中通过style标签包裹
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> div[abc="哈哈哈"]{ background-color: burlywood; } </style> </head> <body> <div abc="哈哈哈">哦哦哦</div> </body> </html>
(2)直接在body里面的标签中加入style属性
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <div abc="哈哈哈" style="background-color: burlywood">哦哦哦</div> </body> </html>
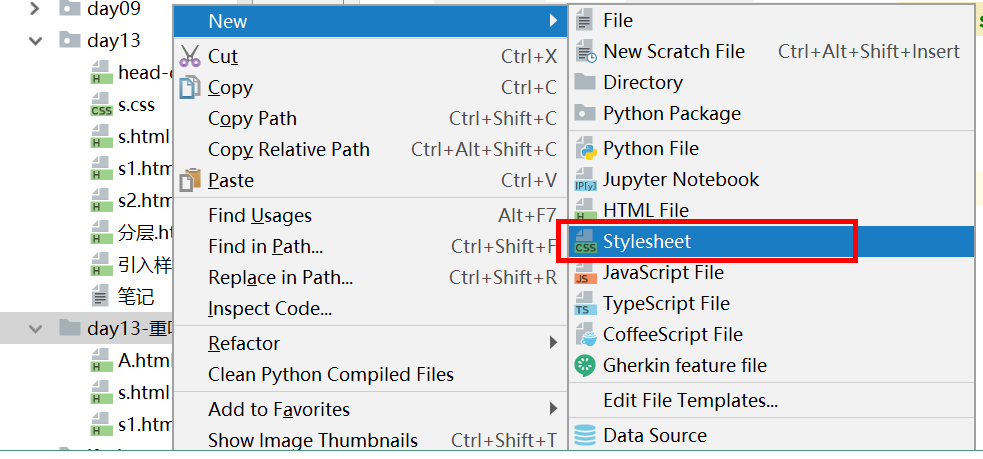
(3)在head中引入css样式表,样式表中的内容与第一种方式在head的style标签中写的内容一样。
- 使用link标签,加入属性rel="stylesheet",和属性href,值为引入的css的路径。
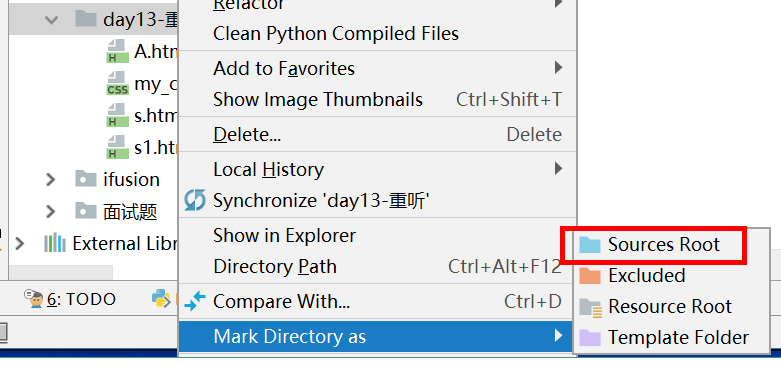
- 如果css文件所在的目录不止一层,需要将引入的css文件所在的文件夹、引入该css文件的html文件和所在的文件夹sources root,避免找不到。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="my_css.css"> </head> <body> <div abc="哈哈哈">哦哦哦</div> </body> </html>

将css所在的文件夹设置成sourceroot路径:
4、选择器选择顺序优先级
- 优先级顺序:由内而外,由近到远
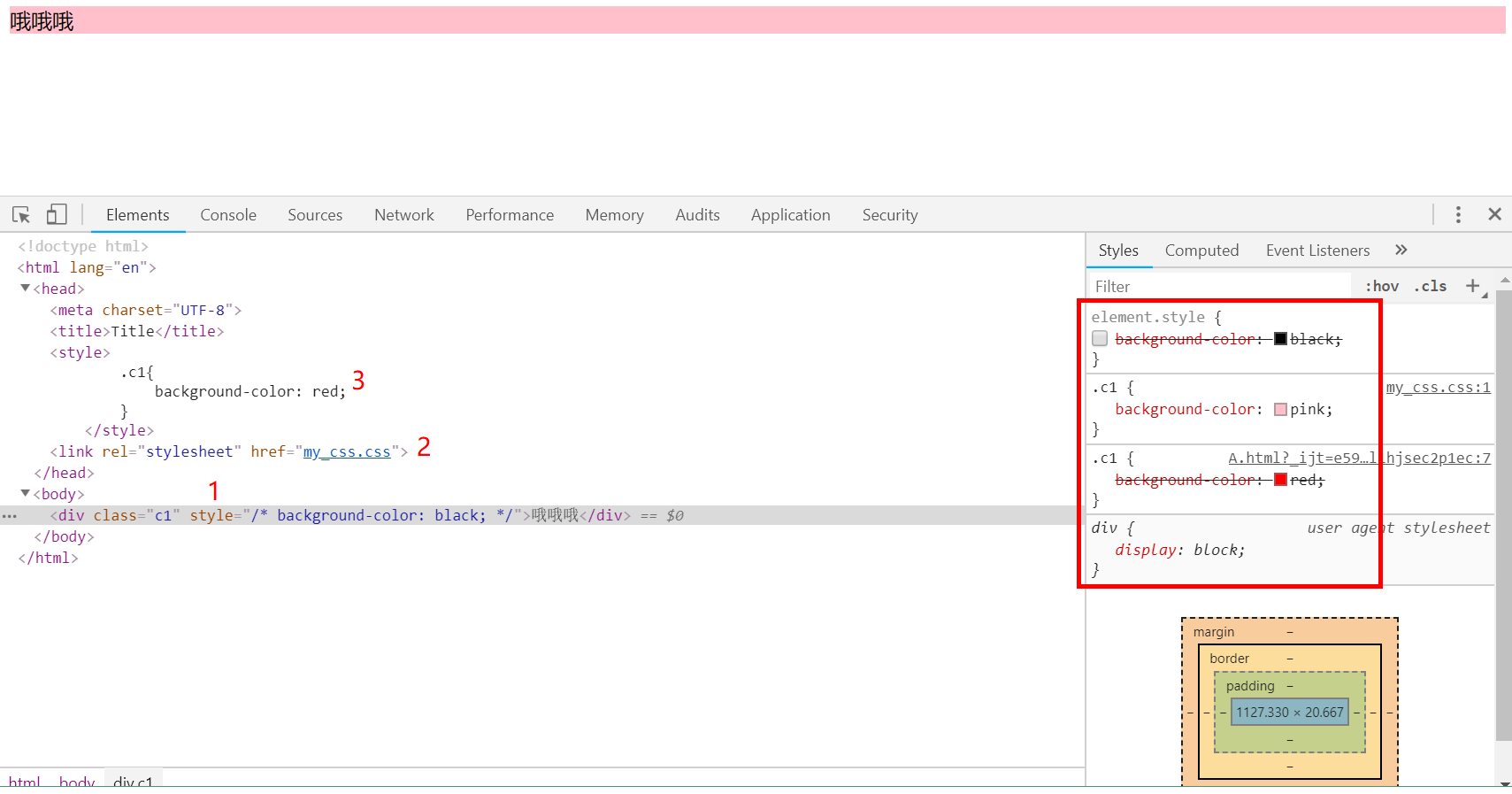
- 由内到外,先id后class最后style

三、CSS属性
1、宽度、高度、背景色
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> .c1{ width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: red; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="c1"></div> </body> </html>

2、字体大小、字体粗细
- 中间使用分号分隔
<body> <div style="font-size:xx-large;font-weight: bolder">哈哈哈</div> </body>

3、边框大小、实线、颜色
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <div style=" 100px;height: 100px;border: 1px solid red;">try a try</div> </body> </html>

4、框中内容水平居中
<body> <div style=" 100px;height: 100px;border: 1px solid red;text-align: center">try a try</div> </body>

5、框中内容垂直居中
- 垂直居中的数值与框的高度数值一致
<body> <div style=" 100px;height: 100px;line-height: 100px;text-align: center;border: 1px solid red">try a try</div> </body>

6、浮动
- 使用float属性
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> .f1{ width: 100px; height: 48px; background-color: red; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="f1"></div> <div class="f1" style="background-color: black"></div> <div class="f1" style="background-color: green"></div> </body> </html>
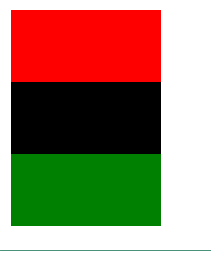
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> .f1{ width: 100px; height: 48px; background-color: red; float: left; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="f1"></div> <div class="f1" style="background-color: black"></div> <div class="f1" style="background-color: green"></div> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> .f1{ width: 100px; height: 48px; background-color: red; float: left; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="f1"></div> <div class="f1" style="background-color: black"></div> <div class="f1" style="background-color: green;float: right"></div> </body> </html>

- 由于每个电脑的宽高不一致,所以使用固定高度,宽度采用百分比的方式。(注意:高度不可以使用百分比的方式,因为不显示)
<body> <div style=" 30%; height: 100px;background-color: red">sdfs</div> </body>

7、行内标签与块级标签相互转换
- 使用属性style="display"即可实现
(1)块级标签转成行内标签
- 使用style="display:inline"属性
<body> <div style="display: inline">sdfs</div> </body>

(2)行内标签转成块级标签
- 使用style=display:block属性
<body> <span style="display: block">sdfs</span> </body>
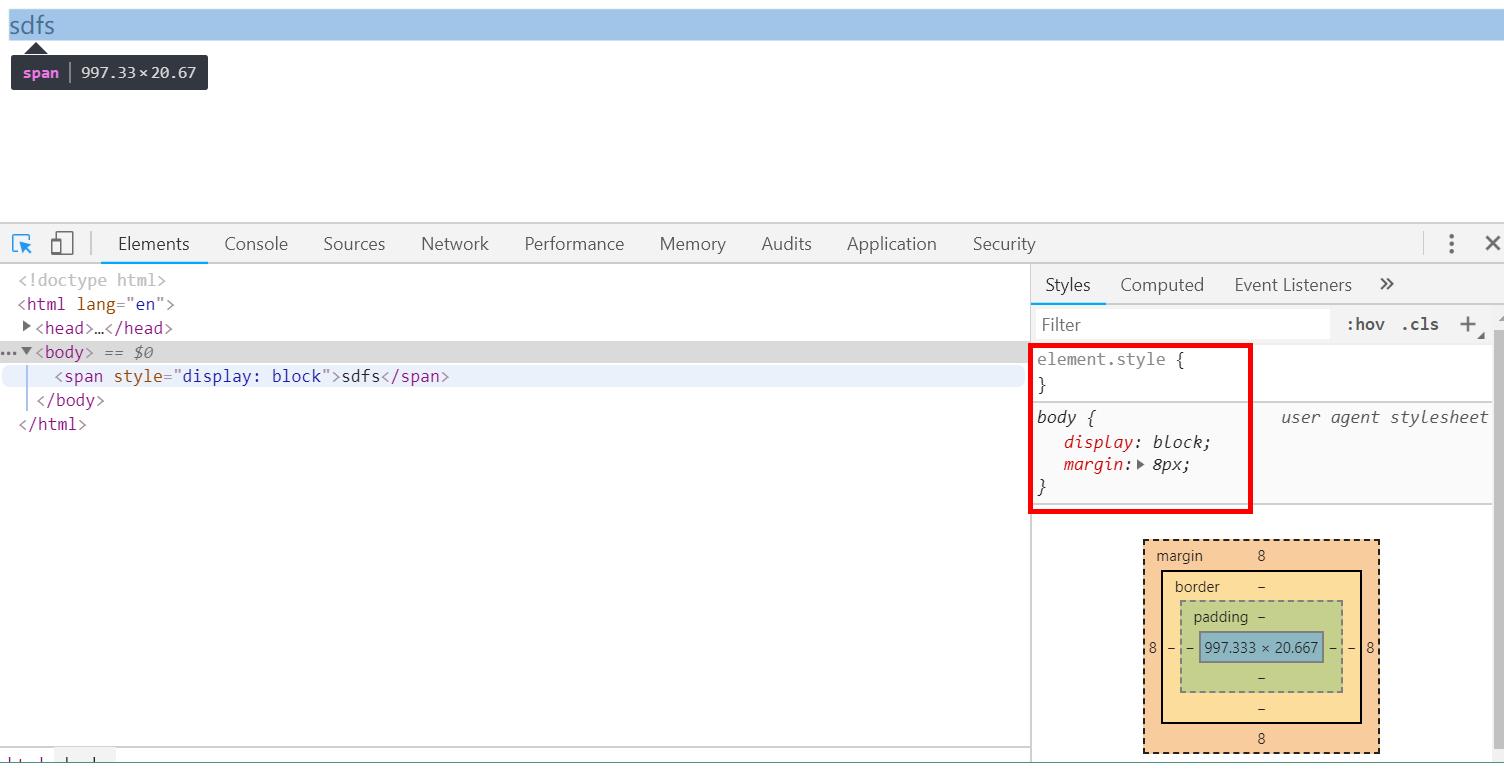
注意:
行内标签是不可以使用宽度、高度、外边距、内边距属性的,即:不识别span标签里面的这些属性,因为span标签本身是有多大占多大。
<body> <span style="100px;height: 100px">sdfs</span> </body>

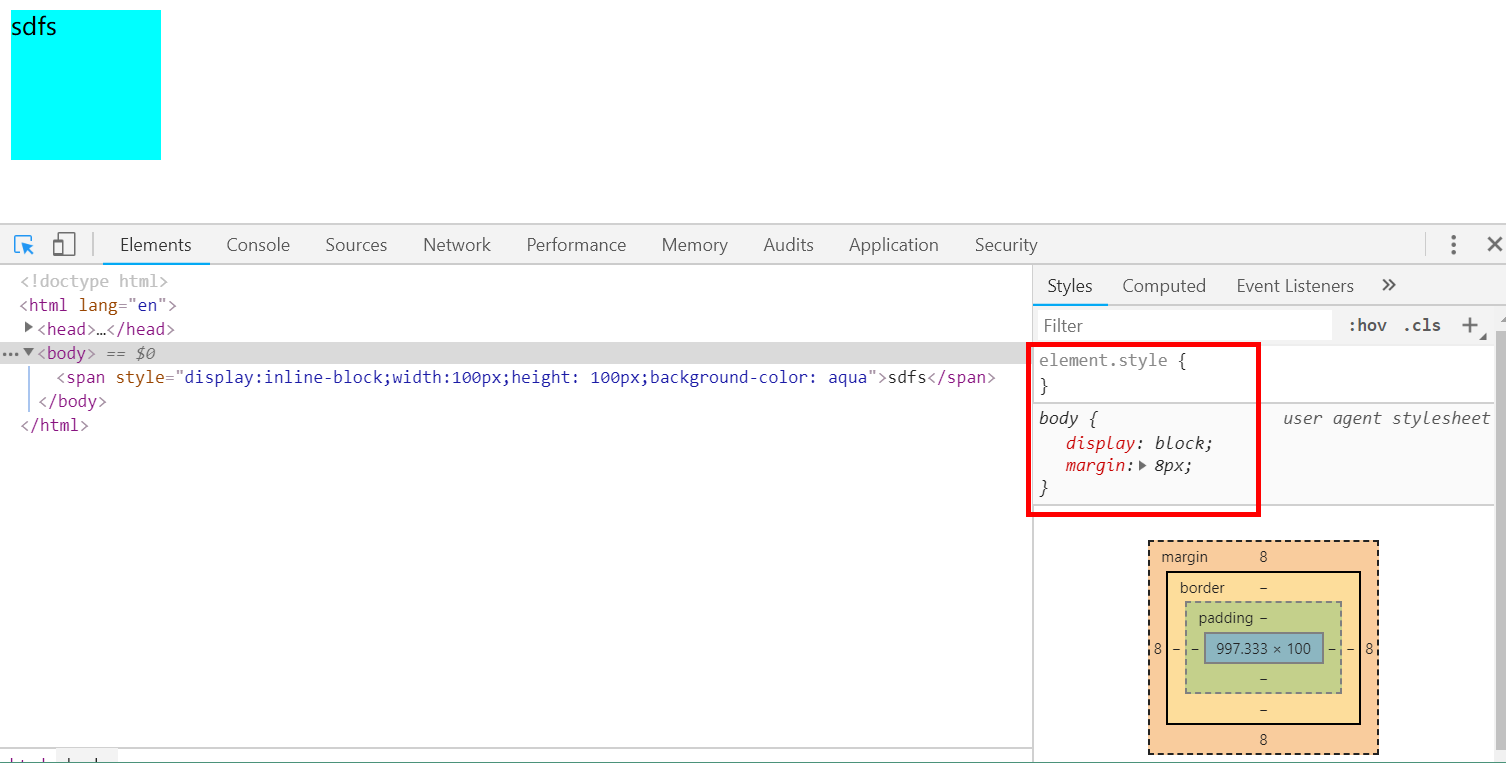
(3)在块级标签中使宽、高这些属性生效
- 在span标签中使用style=display:inline-block属性即可。
<body> <span style="display:inline-block;100px;height: 100px;background-color: aqua">sdfs</span> </body>
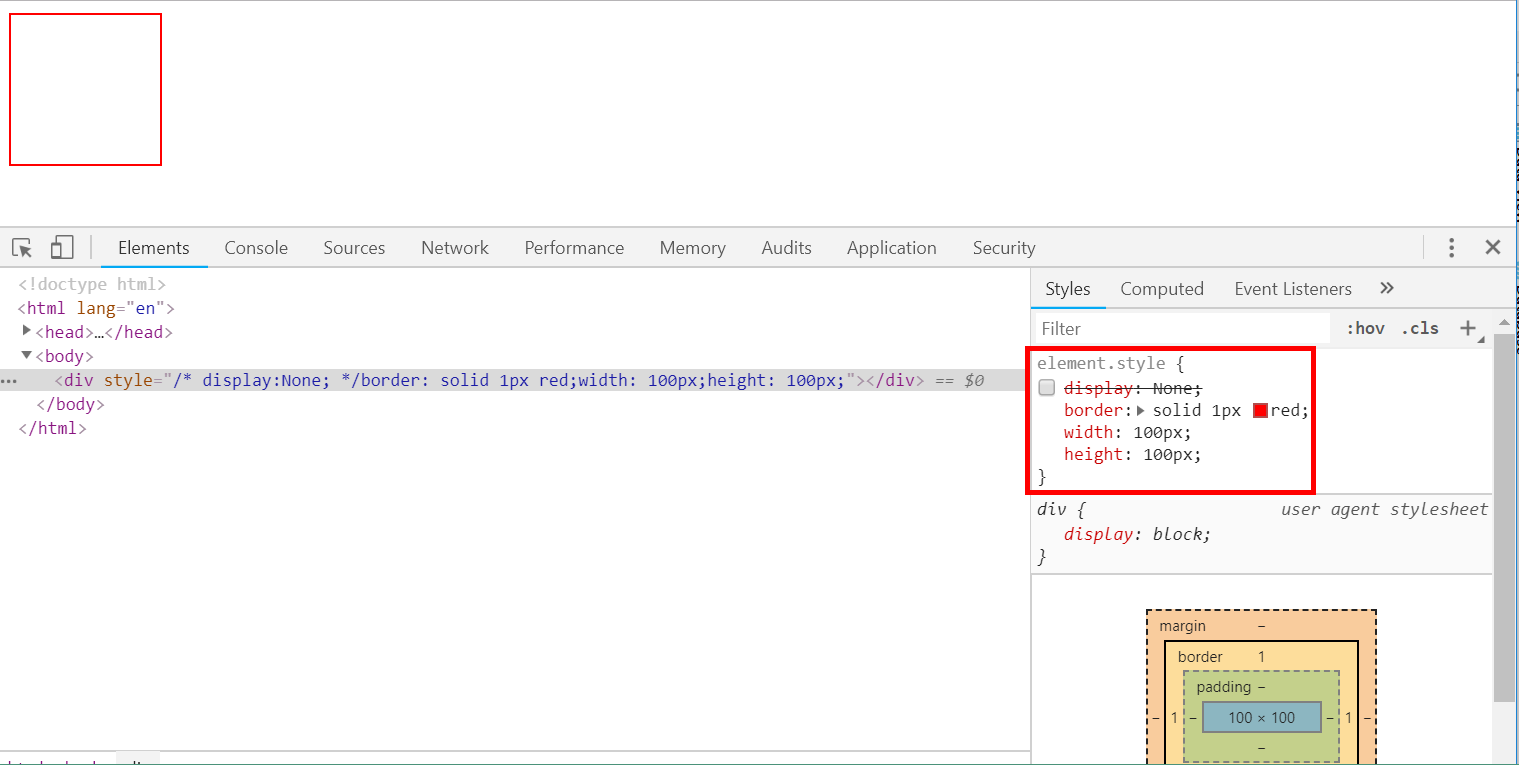
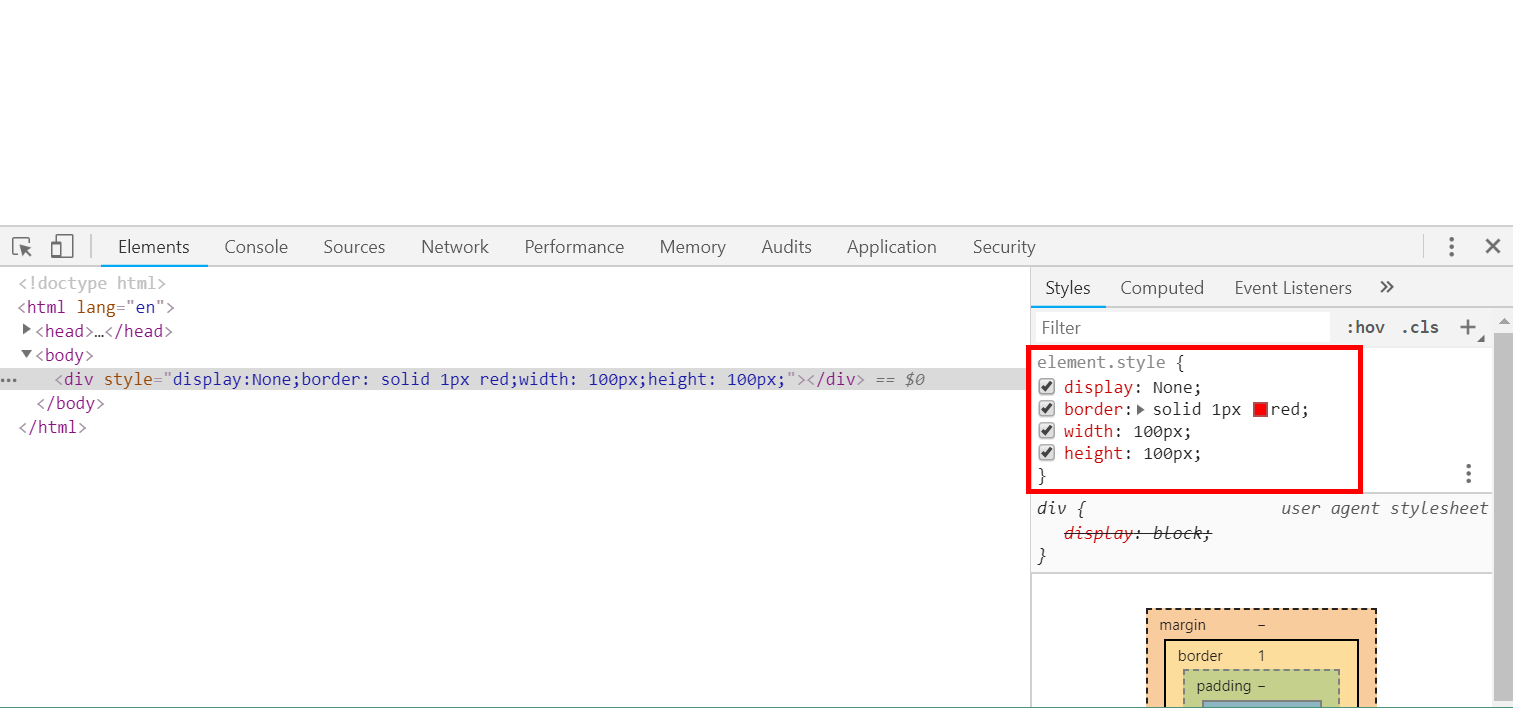
8、隐藏页面信息
- 使用style=display:none属性即可。
<body> <div style="display:None;border: solid 1px red; 100px;height: 100px"></div> </body>
9、边距属性
(1)外边距
-
使用style=margin-top属性
- 不改变自身,针对外层进行像素移动,指的是自身对外层的距离
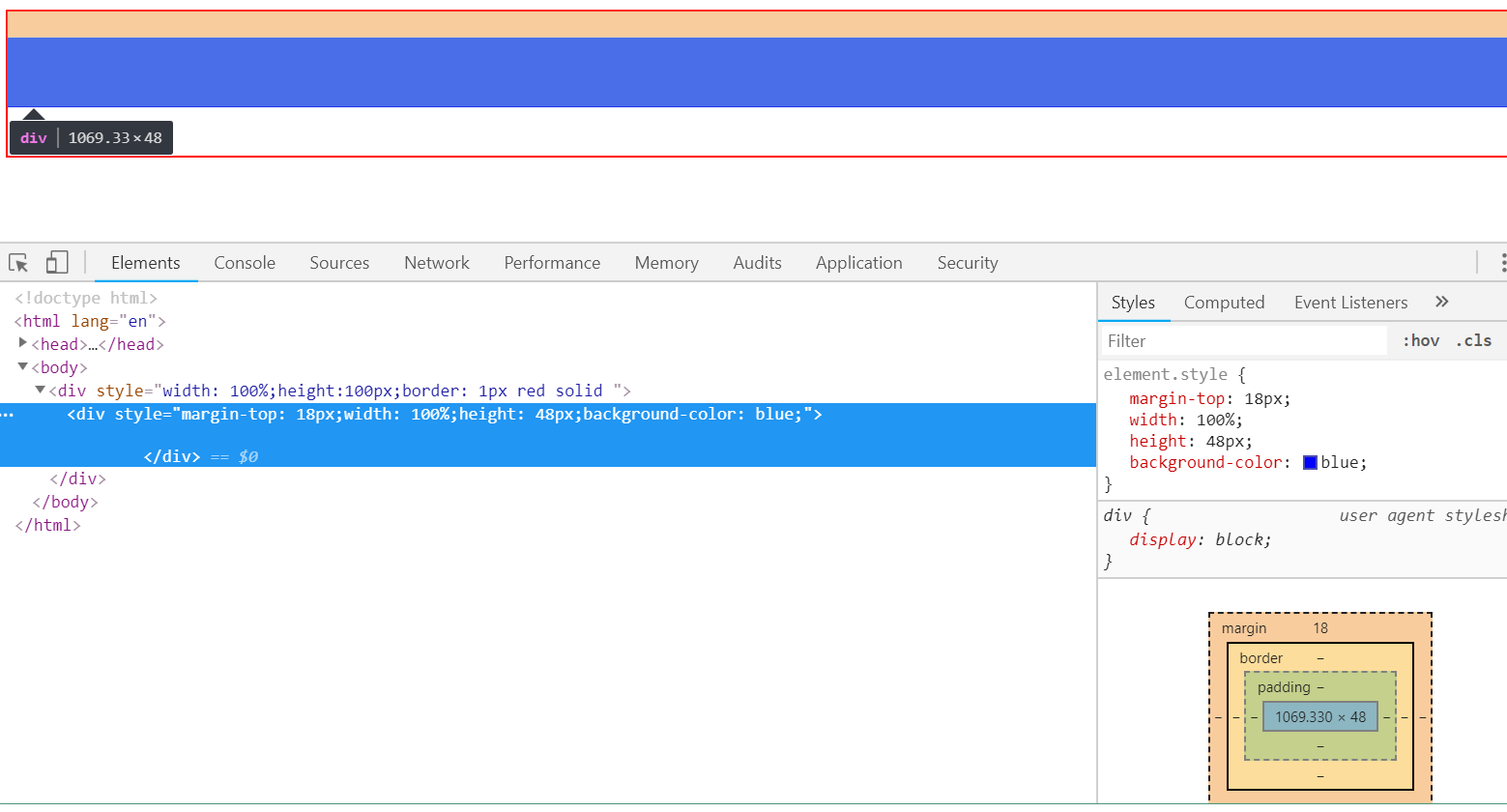
<body> <div style=" 100%;height:100px;border: 1px red solid "> <div style="margin-top:1px; 100%;height: 48px;background-color: blue"></div> </div> </body>

鼠标选中蓝色的内标签,然后点击右侧的margin-top数值,使用键盘的上下键,可以移动蓝色内标签:

鼠标点击标签代码,可以看到黄色部分就是内标签距离外层的距离:
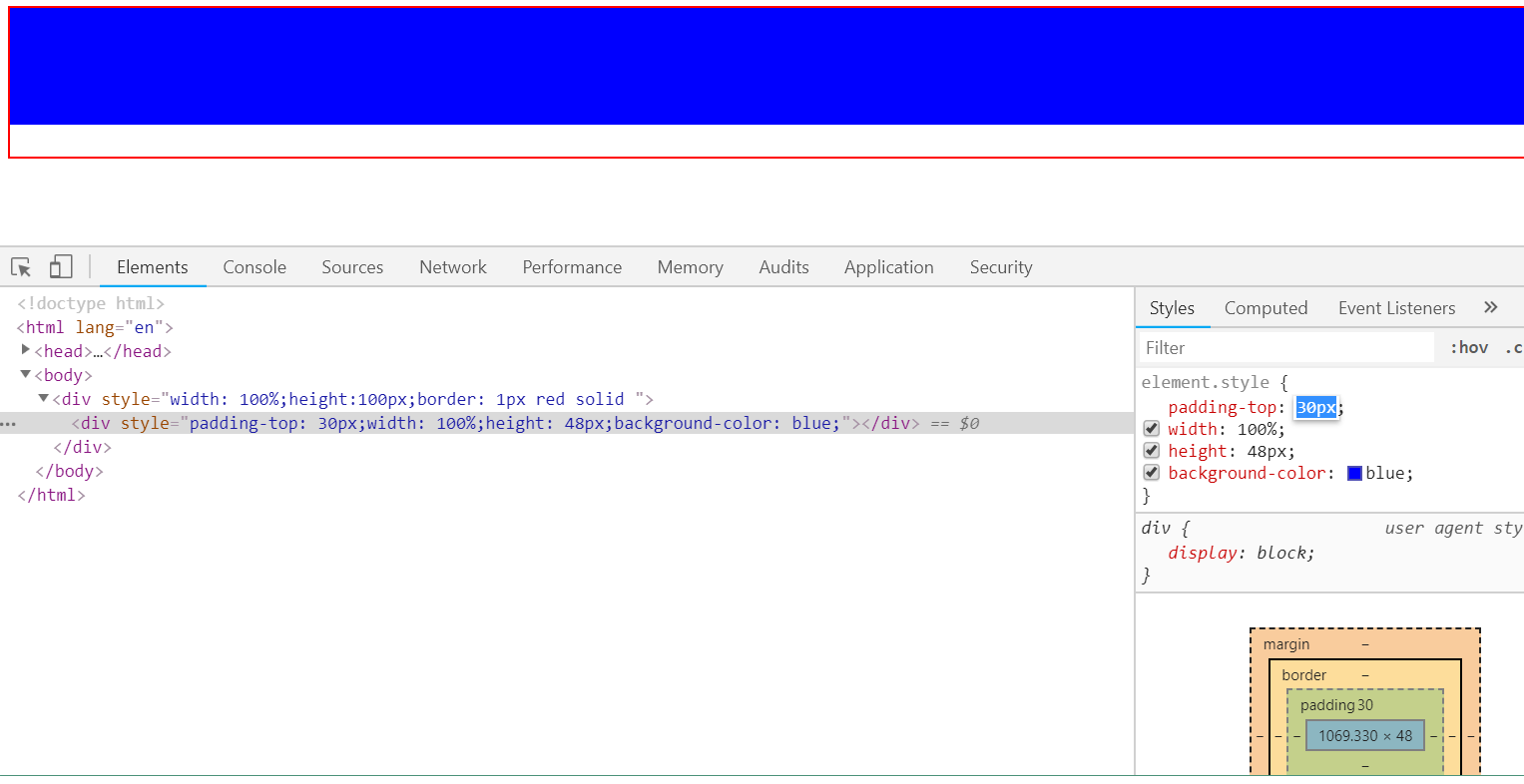
(2)内边距
-
使用style=padding-top属性
- 改变自身,增加或减少自己的面积
<body> <div style=" 100%;height:100px;border: 1px red solid "> <div style="padding-top:1px; 100%;height: 48px;background-color: blue"></div> </div> </body>
9、分层
在写div标签时,默认有一个8px的margin属性,即与上侧、左侧、右侧都留有间距:
<body> <div style=" 100%;height:100px;background-color: green"> </div> </body>

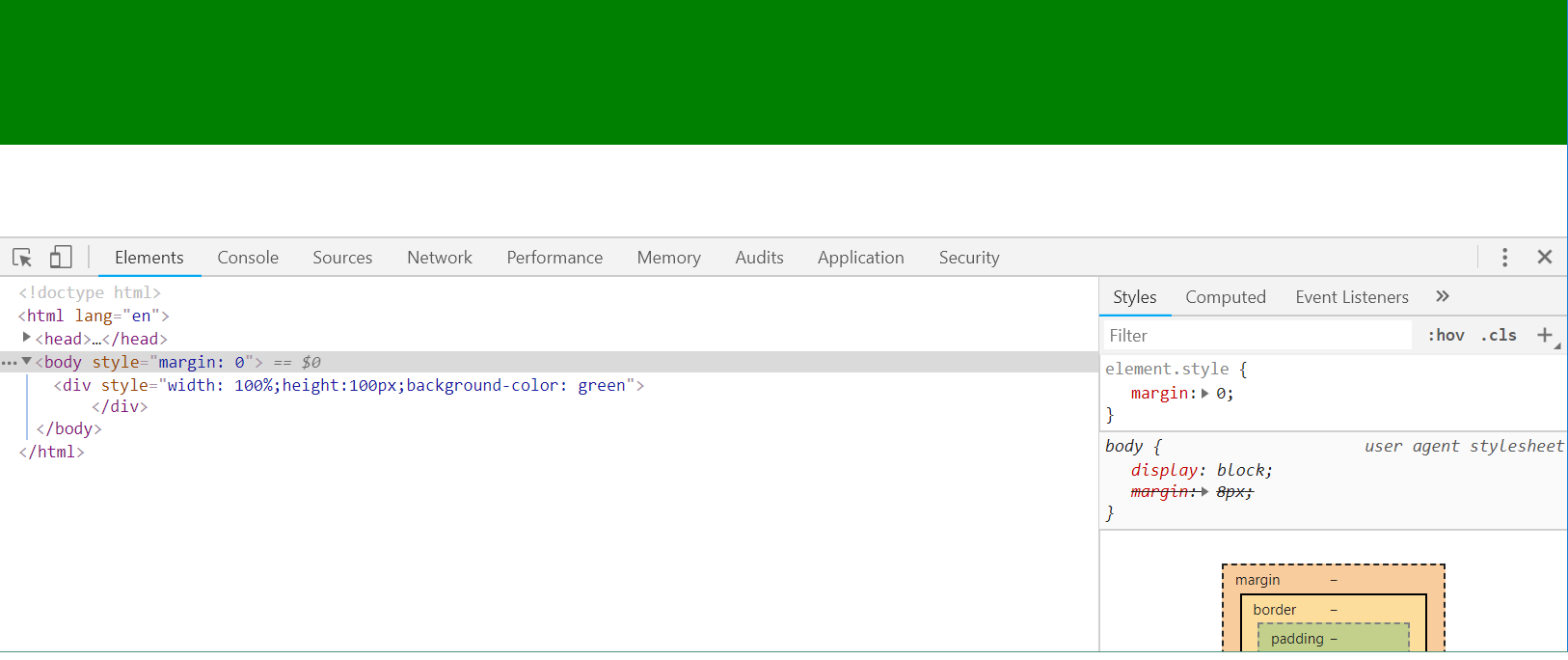
如果想顶格显示,就在body标签中加入属性:style=margin:0
<body style="margin: 0"> <div style=" 100%;height:100px;background-color: green"> </div> </body>
(1)绝对定位
- 在样式中使用position:fixed内容
<head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> .c1{ height:100px; background-color: green; position:fixed; top:0; left:0; right:0; } </style> </head> <body style="margin: 0"> <div class="c1"> <div style=" 100px;height:1000px;background-color: black"></div> </div> </body> </html>
这样绿色条就不会再随鼠标滚动了:

<body style="margin: 0"> <div class="c1"> <div style=" 100px;height:1000px;background-color: black"></div> <div style="position:fixed;right:0;bottom:0; 48px;height:48px;background-color: black"></div> </div> </body>

(2)相对定位
- 在样式中使用position:relative和position:absolute内容
- 在想要固定的div标签中加入position:relative属性,同时在针对这个标签做相对位置的div标签中加入position:absolute属性,并在这个div标签中加入相对位置的坐标,比如写入left、right、top、bottom的数值
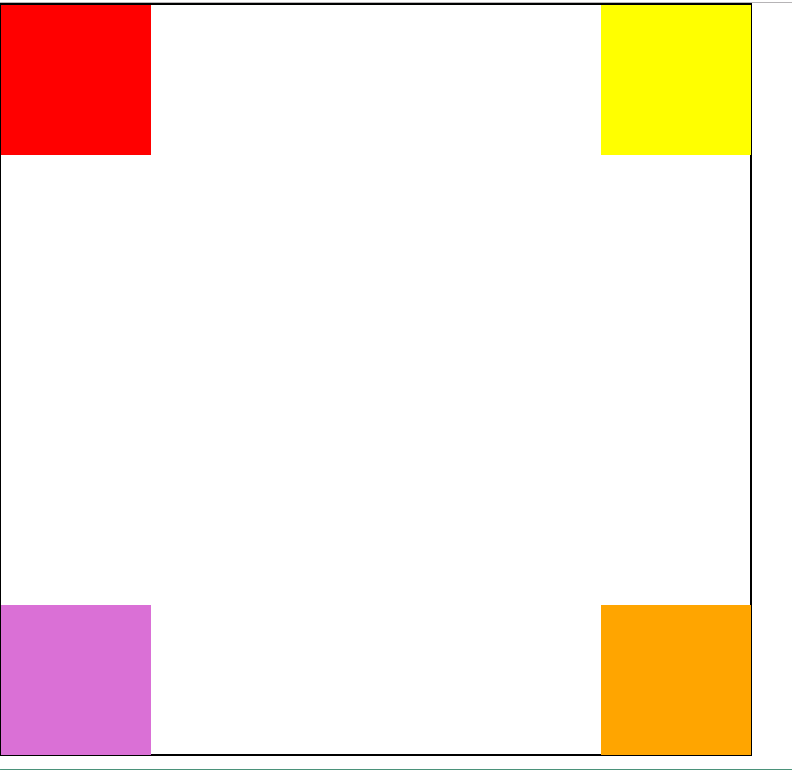
<body style="margin: 0"> <div style="position: relative; 500px;height:500px;border:solid 1px black"> <div style="left:0;top:0;position:absolute; 100px;height:100px;background-color: red"></div> <div style="left:0;bottom:0;position: absolute; 100px;height:100px;background-color: orchid"></div> <div style="right:0;top:0;position:absolute; 100px;height:100px;background-color: yellow"></div> <div style="right:0;bottom:0;position: absolute; 100px;height:100px;background-color: orange"></div> </div> </body>

position本身就是分层的概念,如果有两个div标签,没有进行属性设置,内容就会重合:
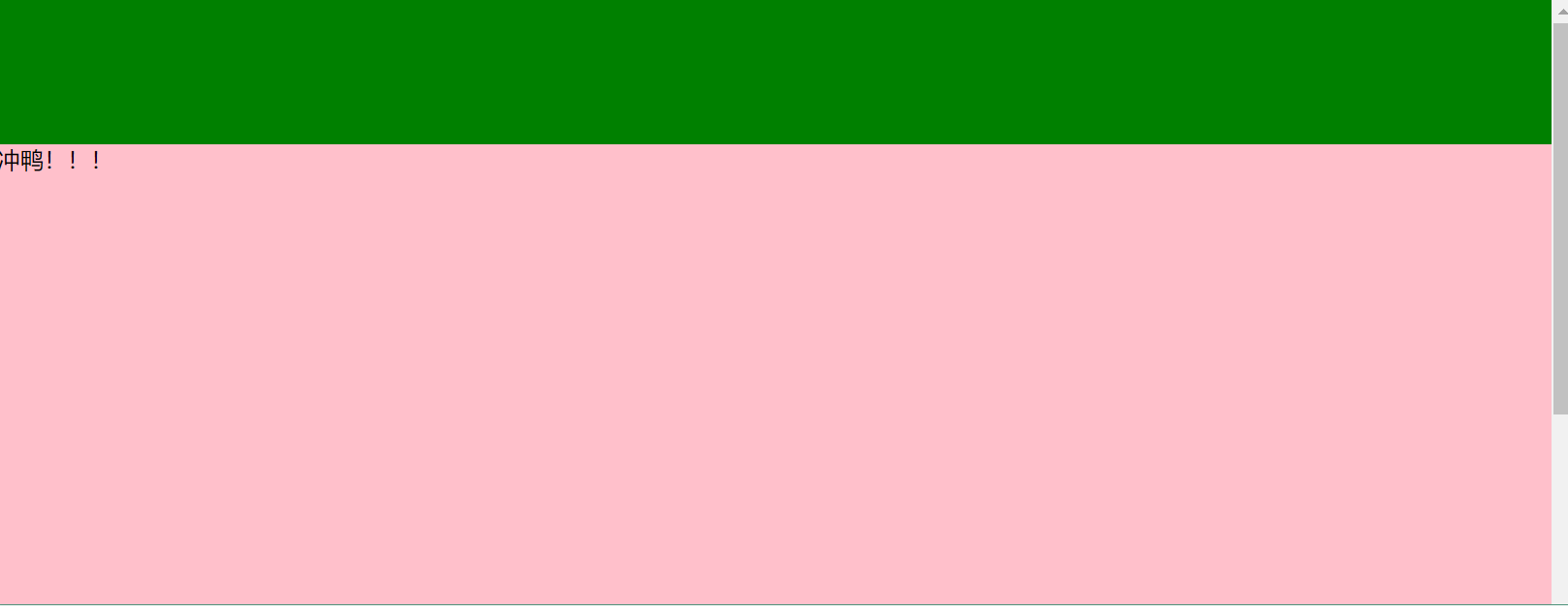
<html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> .c1{ height:100px; background-color: green; position:fixed; top:0; left:0; right:0; } </style> </head> <body style="margin: 0"> <div class="c1"></div> <div style="100%;height: 1000px;border: 1px red solid"> 冲鸭!!! </div> </body> </html>

这时只需使用margin-top属性即可:
<html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> .c1{ height:100px; background-color: green; position:fixed; top:0; left:0; right:0; } </style> </head> <body style="margin: 0"> <div class="c1"></div> <div style="margin-top:100px;100%;height: 1000px;background-color: pink"> 冲鸭!!! </div> </body> </html>

(3)分层优先级
- 使用属性style="z-index",按照z-index的数值大小分层显示,即:数值大的显示在上层,数值小的显示在下层。
- z-index要与position:relative连用才能起作用。
<body style="margin: 0"> <div style="position:relative; 200px;height: 200px;border: solid 1px red"> <div style="z-index: 10;position:absolute;200px;height:200px;background-color:orange"></div> <div style="z-index: 9;position:absolute;200px;height:200px;background-color: yellow"></div> </div> </body>

10、小手鼠标
- 使用input标签的style="cursor: pointer"属性
<input type="button" value="登录" style="cursor: pointer">
鼠标悬浮到按钮上时,显示的是小手。
- 使用input标签的style="cursor: move"属性
<input type="button" value="登录" style="cursor: move">
鼠标悬浮到按钮上时,显示的是移动图标。
- 使用input标签的style="cursor: crosshair"属性
<input type="button" value="登录" style="cursor: crosshair">
鼠标悬浮到按钮上时,显示的是十字截图图标。
11、overflow滚动条
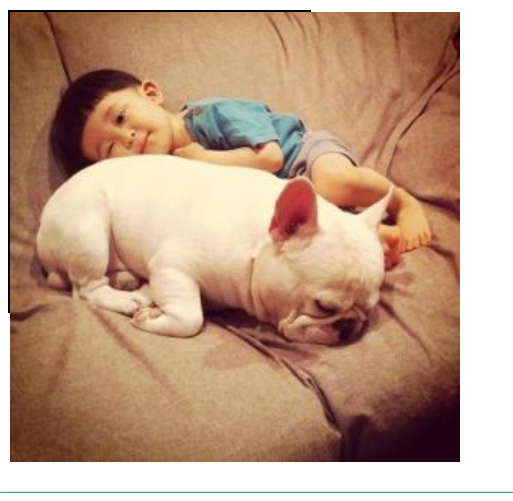

上图中图片将黑色边框挡住了
(1)图片截取
- 在外层div标签中使用style="overflow:hidden"属性
- 当图片或内容大于外层div时,自动截取图片
<div style="overflow:hidden;200px;height:200px;border:solid black 1px;"> <img src="http://ui.imdsx.cn/static/image/dsx.jpg"> </div>
使用hidden后:

(2)增加滚动条
- 在外层div标签中使用style="overflow:scroll"属性
- 无论图片大小,都增加滚动条
<div style="overflow:scroll;200px;height:200px;border:solid black 1px;"> <img src="http://ui.imdsx.cn/static/image/dsx_Small.jpg"> </div>

(3)自动增加滚动条
- 在外层div标签中使用style="overflow:auto"属性
- 当图片大小超过外层div边框时,增加滚动条
<div style="overflow:auto;200px;height:200px;border:solid black 1px;"> <img src="http://ui.imdsx.cn/static/image/dsx_Small.jpg"> </div>

12、背景图
(1)背景图(默认堆叠)
- 使用style=“background-image:url()”属性
<div style="background-image:url('http://ui.imdsx.cn/static/image/dsx_Small.jpg'); 500px;height: 500px;border: solid black 1px"> </div>

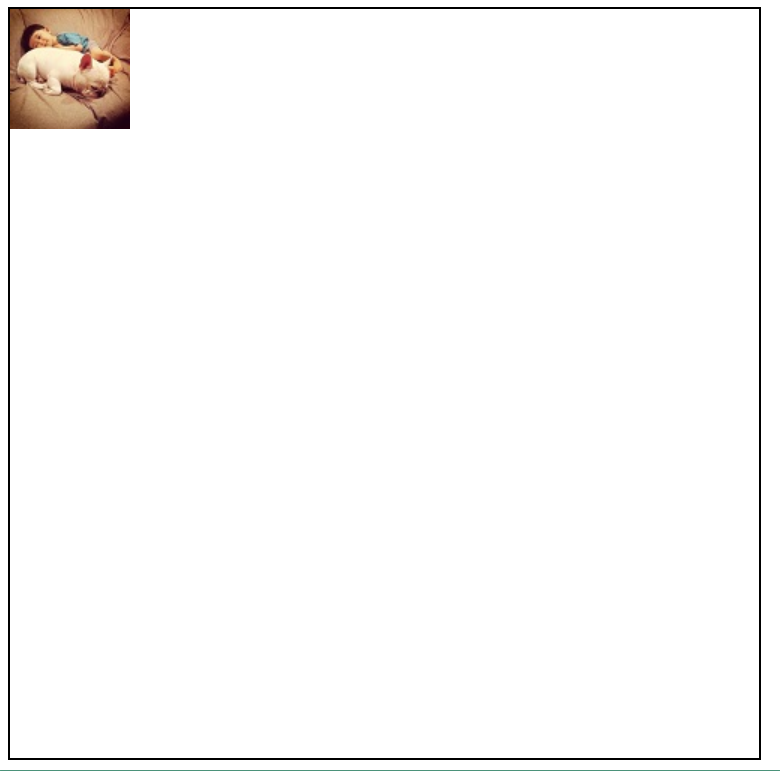
(2)背景图不堆叠
- 使用style=“background-repeat: no-repeat”属性
<div style="background-repeat:no-repeat;background-image: url('http://ui.imdsx.cn/static/image/dsx_Small.jpg'); 500px;height: 500px;border: solid black 1px"> </div>
(3)背景图横向堆叠
- 使用style=“background-repeat:repeat-x”属性
<div style="background-repeat:repeat-x;background-image: url('http://ui.imdsx.cn/static/image/dsx_Small.jpg'); 500px;height: 500px;border: solid black 1px"> </div>

(4)背景图纵向堆叠
- 使用style=“background-repeat:repeat-y”属性
<body> <div style="background-repeat:repeat-y;background-image: url('http://ui.imdsx.cn/static/image/dsx_Small.jpg'); 500px;height: 500px;border: solid black 1px"> </div> </body>

repeat的作用:
图片越大越占空间,如果背景图是一个渐变色的图,那么可以只使用一张小图,然后以某种方式堆叠即可。
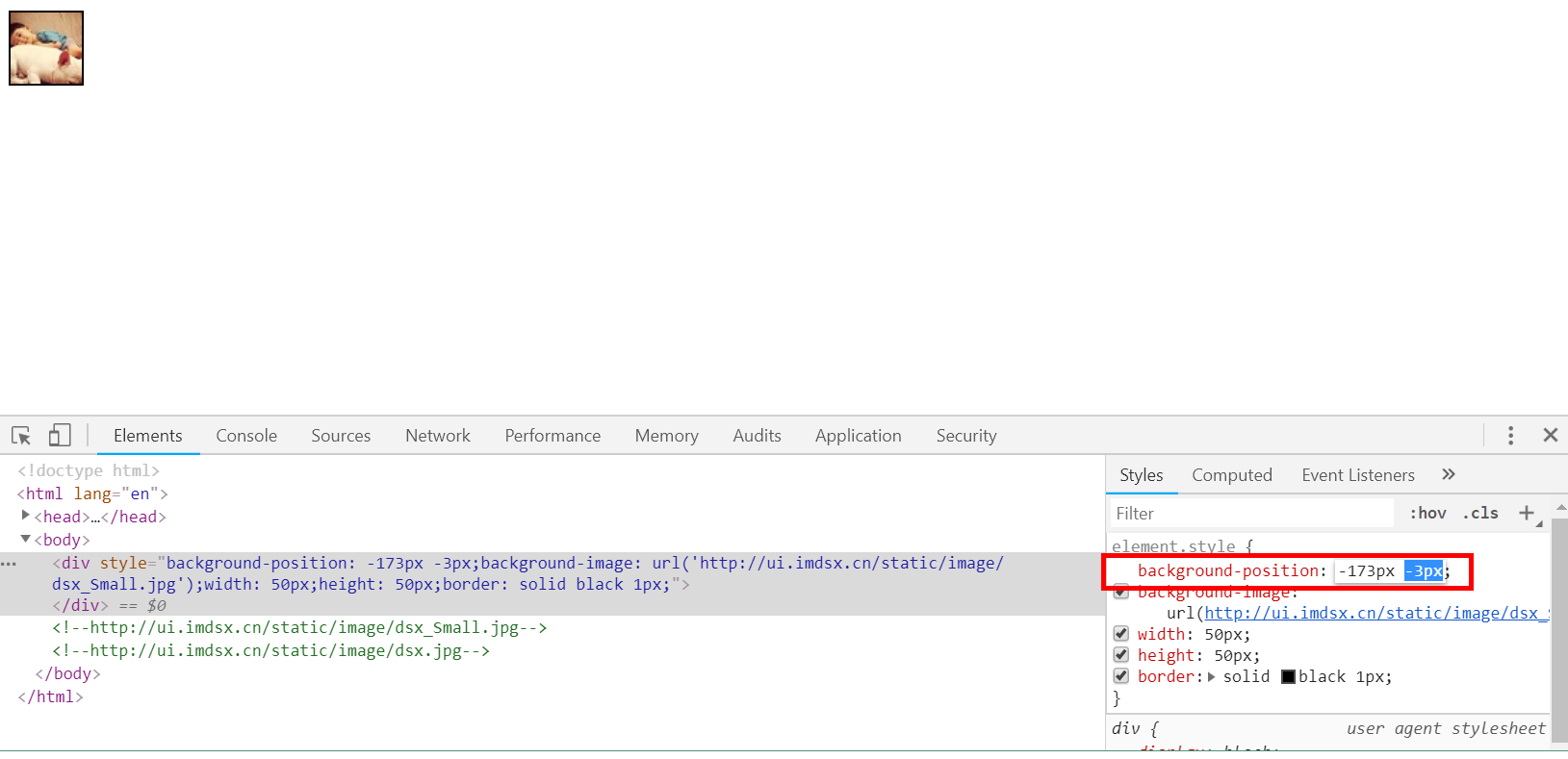
(5)背景图-POSITION
- 使用style="background-position"属性
- 作用:只使用一张大图,通过改变position的x、y坐标来引入图片,实际整个HTML页面是一整张大图,这张大图画了所有的图标
<body> <div style="background-position: 1px 1px;background-image: url('http://ui.imdsx.cn/static/image/dsx_Small.jpg'); 50px;height: 50px;border: solid black 1px"> </div> </body>
13、鼠标悬浮时显示
- 使用hover属性
- 该属性必须要在head中使用
.hover:hover{
background-color: red;
color: black;
151px
}
- 不悬浮和悬浮的样式都要在head中使用,放在body中就不能按顺序执行了
<head> <style> .hover:hover{ background-color: red; color: black; width: 151px } .hover_content{ height: 48px; width: 150px; border: 1px solid red; text-align: center; line-height: 48px; color: lightcyan } </style> </head> <body> <div class="hover hover_content">侯宁讲笑话么?</div> </body>

