首先看一道典型题
public class Test { static int x, y, z; static { int x = 5;//局部变量 x--; } static { x--; } public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("x=" + x); z--; method(); System.out.println("result:" + (z + y + ++z)); } public static void method() { y = z++ + ++z; } }//结果输出为x = -1 , y = 0,z=2
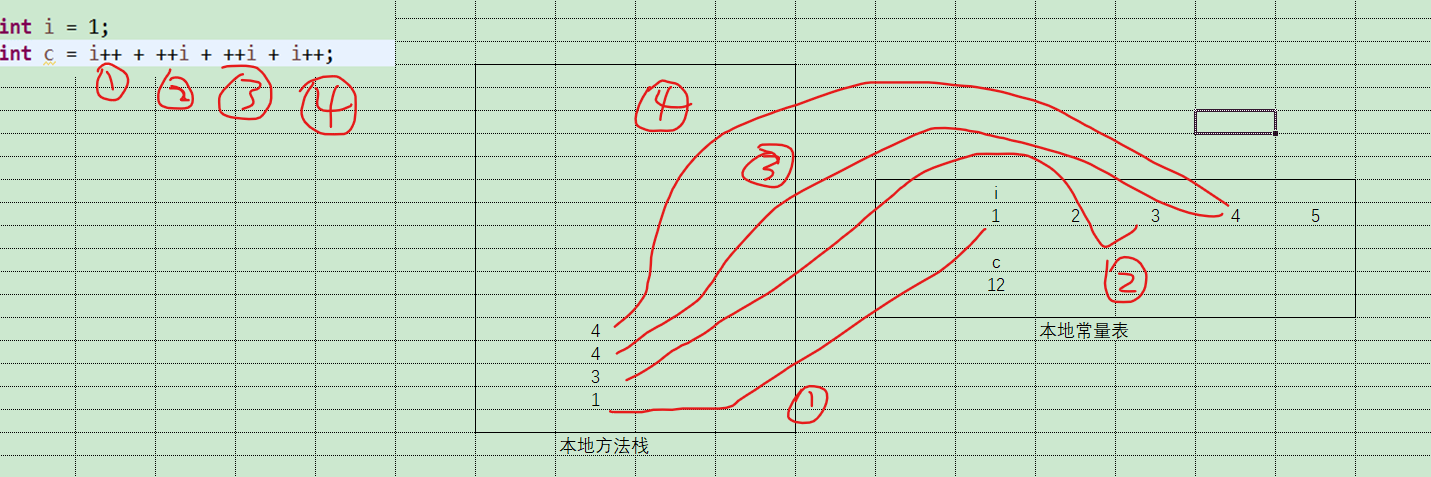
如上图,JVM中存在本地常量表和本地方法栈俩块区域,进行运算时,变量是存放在常量表中,当运行i++时,JVM会先将i的值推进方法栈中,然后再给i+1,如第一步
当运行++i时,JVM会先将i+1,然后再将值推入方法栈,如第二步