编写一个C程序,第一个步骤称为预处理,预处理在代码编译之前,进行一些文本性质的操作,删除注释、插入被include的文件、定义替换由#define定义的符号,以及确定代码的部分内容是否应该按照条件编译
共有五个预处理指令:
预定义指令:define
条件编译:#if, #elif,#else,#endif,#ifdef,#ifndef
文件包含#include
编译错误:#error指令
#progma指令
一、预定义指令:define
#define name stuff
define为数值命名一个符号,每当有name出现时,就会被替换成stuff。多行命名可以用分隔开每行。define机制包括一个规定,允许把参数替换到文本中,称为宏(macro).
#define name(paramater-list) stuff
其中parameter-list是由逗号分隔的符号列表,可以出现在stuff中。name和左括号直接不可以有空格,不然会被当做stuff一部分处理。
#define MUT(x, y) x *y
如果MUT(3+1, 1+2)会被展开成:
3+1 * 1+ 2
为了避免宏展开时,参数中操作符或邻近操作符之间作用,导致意外,应该使用括号将宏参数括起来。
#define MUT(x, y) (x) *(y)
#define替换
预处理时,字符串常量的值并不进行检查,所以如果需要把宏参数,插入到字符串中,有两种方法:
1.该方法只可以用于字符串参数,利用字符串相邻自动链接特性。
#include <stdio.h>
#define PRINT(FORMAT, VALUE) printf("The FORMAT is "FORMAT"
", VALUE)
int main()
{
PRINT("%d", 10);
return 0;
}
该方法只可以用于字符串。运行:

2.利用define预处理的宏参数进行转换,#arg被替换成arg代表的参数的字符串形式"arg"。
#include <stdio.h>
#define PRINT(FORMAT, VALUE) printf("The "#VALUE" value is "FORMAT"
", VALUE)
int main()
{
int x = 1;
PRINT("%d", x + 10);//x+10被替换成"x+10"
return 0;
}
运行:

宏与函数:
#define MAX(x,y) ((x) > (y) ? (x) : (y))
表达式中求较大值,利用宏来实现的优点是,宏是无类型的,但是会在每一处调用进行展开。宏还可以做一些函数无法实现的
#define MALLOC(n, type) ((type *)malloc(sizeof (type) * (n)))
申请n个type类型的内存空间
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MALLOC(n, type) ((type *)malloc(sizeof (type) * (n)))
int main()
{
char *str;
str = MALLOC(10, char);
strcpy(str, "yang");
printf("%s", str);
return 0;
}
运行:

带副作用的宏:
如果宏参数在宏定义中出现次数超过一次,这个参数如果具有副作用,那么这个宏带有副作用。
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX(x, y) ((x) > (y) ? (x) : (y))
int main()
{
int x = 1;
int y = 2;
printf("%d", MAX(++x, ++y));
return 0;
}
运行:++具有副作用

#undef 移除一个宏定义
#include <stdio.h>
#define NUM 100
int main()
{
printf("%d",NUM);
#undef NUM
printf("%d", NUM);//此处将报错,以及移除宏定义了
return 0;
}
运行:

二、条件编译:#if, #elif,#else,#endif,#ifdef,#ifndef
利用条件编译,可以选择代码一部分是正常编译还是完全忽略。
#include <stdio.h>
#define DEBUG 1
//#if对后面的表达式求值,如果非零(真)那么运行
#if DEBUG
#define NUM -100
#else
#define NUM 100
#endif
int main()
{
printf("%d",NUM);
return 0;
}
还支持#elif, 运行:

是否被定义:#ifdef , #ifndef
#ifdef DEBUG
#define NUM -100
#else
#define DEBUG 1
#define NUM 100
#endif
三、 文件包含#include
#include指令使另一个文件的内容被加入,被编译。当应用系统函数库文件时,使用中括号
#include <file.h>
当引入本地文件时,使用双引号
#include "file.h"
编译器先在本地查找头文件,如果找不到再去系统标准位置查找。
如果一个头文件,被多个文件包含,多个文件直接互相包含,会导致多次包含。可以使用条件编译,使头文件只被包含一次。
#ifndef __HEADFILE_H #define __HEADFILE_H //然后进行函数的声明等等 #endif
这样头文件,就只会被包含一次。但预处理器仍将读取这个文件,只是文件内容会被忽略。
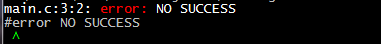
四、#error指令
用于编译时生成错误信息
#ifndef SUCCESS #error NO SUCCESS #endif
五、#progma指令
因编译器而异,允许一些编译选项或其他方式无法实现的一些处理方式。如把汇编插入到C代码中