1.测试代码,一个简单的springboot web项目:地址:https://gitee.com/yangxioahui/demo_mybatis.git
一:tomcat的主要架构:1.如果我们下载了tomcat的安装包,可以在解压后的文件夹看到server.xml文件:

内容如下:
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?> <Server port="8005" shutdown="SHUTDOWN"> <Listener className="org.apache.catalina.startup.VersionLoggerListener" /> <Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.AprLifecycleListener" SSLEngine="on" /> <!--Initialize Jasper prior to webapps are loaded. Documentation at /docs/jasper-howto.html --> <Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.JasperListener" /> <!-- Prevent memory leaks due to use of particular java/javax APIs--> <Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.JreMemoryLeakPreventionListener" /> <Listener className="org.apache.catalina.mbeans.GlobalResourcesLifecycleListener" /> <Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.ThreadLocalLeakPreventionListener" /> <GlobalNamingResources> <Resource name="UserDatabase" auth="Container" type="org.apache.catalina.UserDatabase" description="User database that can be updated and saved" factory="org.apache.catalina.users.MemoryUserDatabaseFactory" pathname="conf/tomcat-users.xml" /> </GlobalNamingResources> <Service name="Catalina"> <Connector port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1" connectionTimeout="20000" redirectPort="8443" /> <Connector port="8009" protocol="AJP/1.3" redirectPort="8443" /> <Engine name="Catalina" defaultHost="localhost"> <Realm className="org.apache.catalina.realm.LockOutRealm"> <Realm className="org.apache.catalina.realm.UserDatabaseRealm" resourceName="UserDatabase"/> </Realm> <Host name="localhost" appBase="webapps" unpackWARs="true" autoDeploy="true"> <Valve className="org.apache.catalina.valves.AccessLogValve" directory="logs" prefix="localhost_access_log." suffix=".txt" pattern="%h %l %u %t "%r" %s %b" /> <Context path="/shop" docBase="D:shopdemoweb" debug="0" reloadable="true"> </Host> </Engine> </Service> </Server>
从server.xml中我们可以分析出如下关系:
上图wrapper是我根据tomcat源码补上去的,在server.xml中并没有体现出来,通过上图,大概分析下他们的关系,记得不要在意每个节点的意思:
由于在java中一切皆对象,所以结合上图我们分析:
一个tomcat对象中会包含一个server对象,一个server对象可以包含多个service对象,一个service对象,可以包含多个connector对象(用于接收TCP连接)和一个Engine对象;
一个Engine可以包含多个Host对象,而每个Host可以包含多个context(我们写的每个项目就是一个context),每个Context会包含多个Wrapper对象,而每个Wrapper都会包含一个servlet;
从Engine节点往下包含它自己,都称为容器Container
伪代码实现如下:
Tomcat tomcat=new Tomcat();
Server server=new Server();
tomcat.setServer(server);
Service service=new Service();
server.addService(service); //存到集合中
Connector connector=new Connector();
service.setConnector(connector);
Engine engine=new Engine();
service.setEngine(engine);
..... 省略
在tomcat中,命名上面的节点都喜欢使用StandardXX,如StandardServer,StandardService;








通过这些节点的类,我们发现Engine节点和其包含的子节点都是继承了ContainerBase这个类,所以为何说Engine这个节点和其子节点都叫做容器的道理了:
我们仔细查看上面的节点类,发现他们都继承了生命周期相关的类:LifecycleMBeanBase:

所以他们都会有对应的生命周期相关方法,这些节点通过生命周期的方法进行串联起来,如tomcat.start()->server.start()->servece.start()->engine.start().........
二.springboot内嵌tomcat源码分析:
有了上面的基础,我们分析springboot内嵌tomcat的源码就比较方便了: 启动项目,debug调试,可以跟踪到内嵌tomcat的源码:

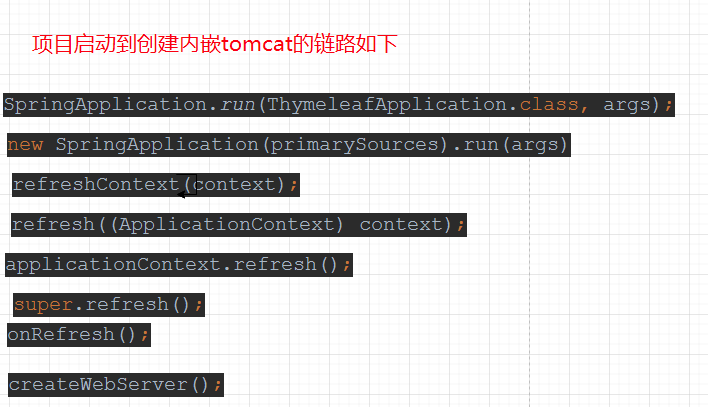
//下面从createWebServer() 开始就是我们要分析的源码了,它在ServletWebServerApplicationContext这个类中
private void createWebServer() { WebServer webServer = this.webServer; //第一次过来,这个为null ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext(); //这个也是null if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) { ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();//获取tomcat工厂 this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());//通过工厂类获取服务器对象。这个是核心 getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("webServerGracefulShutdown", new WebServerGracefulShutdownLifecycle(this.webServer)); getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("webServerStartStop", new WebServerStartStopLifecycle(this, this.webServer)); } else if (servletContext != null) { try { getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext); } catch (ServletException ex) { throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context", ex); } } initPropertySources(); }
上面代码主要是通过web工厂,创建webserver对象,那web工厂有哪些呢?

这里我们用的是tomcat,所以webserver工厂就自然是TomcatServletWebServerFactory,之后就看它是如何创建tomcat的

@Override public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) { if (this.disableMBeanRegistry) { Registry.disableRegistry(); } Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat(); //创建tomcat对象了 File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null) ? this.baseDirectory : createTempDir("tomcat"); tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath()); Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol); //创建connector了,根据之前tomcat架构分析,这里的connector最终会包含在service里 connector.setThrowOnFailure(true); tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector); //这里获取service,获取不到,就会创建,然后设置到Connector到service中 customizeConnector(connector); tomcat.setConnector(connector); tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);//获取Host节点,获取不到就会创建Host configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());//创建Engine,在里面会将Host设置到Engine里面 for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) { tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector); } prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);//创建Connext,在里面会将Context设置到host里面 return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);//启动各个组件的生命周期的方法 }
上面的方法,主要是创建tomcat的架构的各种主件,并且将它们的关系串联起来,之后就调用组件的生命周期方法:
分析几个重要的方法,在tomcat中,通过tomcat.getXX主件,获取不到,内部会创建1. tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector); //由于创建service之前需要创建server,因为server节点是包含service的:
public Service getService() { return getServer().findServices()[0]; } public Server getServer() { if (server != null) { return server; } System.setProperty("catalina.useNaming", "false"); server = new StandardServer(); //创建server节点了 initBaseDir(); // Set configuration source ConfigFileLoader.setSource(new CatalinaBaseConfigurationSource(new File(basedir), null)); server.setPort( -1 ); Service service = new StandardService(); //创建service节点了 service.setName("Tomcat"); server.addService(service); //将service节点加到server节点中 return server; }

2.tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false); //根据tomcat架构分析,创建Host前一定会创建Engine

3.prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers); 这里开始创建Context节点了,并将其加到Host中
protected void prepareContext(Host host, ServletContextInitializer[] initializers) { File documentRoot = getValidDocumentRoot(); TomcatEmbeddedContext context = new TomcatEmbeddedContext();//继承于StandardContext if (documentRoot != null) { context.setResources(new LoaderHidingResourceRoot(context)); } context.setName(getContextPath()); context.setDisplayName(getDisplayName()); context.setPath(getContextPath()); File docBase = (documentRoot != null) ? documentRoot : createTempDir("tomcat-docbase"); context.setDocBase(docBase.getAbsolutePath()); context.addLifecycleListener(new FixContextListener()); context.setParentClassLoader((this.resourceLoader != null) ? this.resourceLoader.getClassLoader() : ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader()); resetDefaultLocaleMapping(context); addLocaleMappings(context); try { context.setCreateUploadTargets(true); } catch (NoSuchMethodError ex) { // Tomcat is < 8.5.39. Continue. } configureTldSkipPatterns(context); WebappLoader loader = new WebappLoader(); loader.setLoaderClass(TomcatEmbeddedWebappClassLoader.class.getName()); loader.setDelegate(true); context.setLoader(loader); if (isRegisterDefaultServlet()) { addDefaultServlet(context); //context中添加servelet,这里添加的并不是我们业务代码创建的servlet,而是默认的 } if (shouldRegisterJspServlet()) { addJspServlet(context); // addJasperInitializer(context); } context.addLifecycleListener(new StaticResourceConfigurer(context)); ServletContextInitializer[] initializersToUse = mergeInitializers(initializers); host.addChild(context); //将Context添加到Host节点 configureContext(context, initializersToUse); postProcessContext(context); }
4.我们看看servlet如何添加到Context中的

至此,tomcat架构的主要主件已经被串起来了,接下来要分析的是主件的生命周期启动过程:

protected TomcatWebServer getTomcatWebServer(Tomcat tomcat) { return new TomcatWebServer(tomcat, getPort() >= 0, getShutdown()); } public TomcatWebServer(Tomcat tomcat, boolean autoStart, Shutdown shutdown) { Assert.notNull(tomcat, "Tomcat Server must not be null"); this.tomcat = tomcat; this.autoStart = autoStart; this.gracefulShutdown = (shutdown == Shutdown.GRACEFUL) ? new GracefulShutdown(tomcat) : null; initialize(); //开始初始化 } private void initialize() throws WebServerException { logger.info("Tomcat initialized with port(s): " + getPortsDescription(false)); synchronized (this.monitor) { try { addInstanceIdToEngineName(); Context context = findContext(); context.addLifecycleListener((event) -> { if (context.equals(event.getSource()) && Lifecycle.START_EVENT.equals(event.getType())) { // Remove service connectors so that protocol binding doesn't // happen when the service is started. removeServiceConnectors(); } }); // Start the server to trigger initialization listeners this.tomcat.start(); //开始启动主件的生命周期方法 // We can re-throw failure exception directly in the main thread rethrowDeferredStartupExceptions(); try { ContextBindings.bindClassLoader(context, context.getNamingToken(), getClass().getClassLoader()); } catch (NamingException ex) { // Naming is not enabled. Continue } // Unlike Jetty, all Tomcat threads are daemon threads. We create a // blocking non-daemon to stop immediate shutdown startDaemonAwaitThread(); } catch (Exception ex) { stopSilently(); destroySilently(); throw new WebServerException("Unable to start embedded Tomcat", ex); } } }
从这里开始this.tomcat.start();将会是我们要重点关注的逻辑了:
我们知道tomcat架构第一个主件是server,所以肯定接下来是server.start()

我们继续跟进,server.start(); //这里开始要注意了,主件的start()方法是在父类LifecycleBase 中的,因此,后续的主件调用也是调用父类的start方法
@Override public final synchronized void start() throws LifecycleException { if (LifecycleState.STARTING_PREP.equals(state) || LifecycleState.STARTING.equals(state) || LifecycleState.STARTED.equals(state)) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { Exception e = new LifecycleException(); log.debug(sm.getString("lifecycleBase.alreadyStarted", toString()), e); } else if (log.isInfoEnabled()) { log.info(sm.getString("lifecycleBase.alreadyStarted", toString())); } return; } if (state.equals(LifecycleState.NEW)) { init(); //第一次进来先调用初始化,运用多态的思想,具体逻辑由子类实现 } else if (state.equals(LifecycleState.FAILED)) { stop(); } else if (!state.equals(LifecycleState.INITIALIZED) && !state.equals(LifecycleState.STOPPED)) { invalidTransition(Lifecycle.BEFORE_START_EVENT); } try { setStateInternal(LifecycleState.STARTING_PREP, null, false); startInternal(); //初始化完,开始调用内部的start方法 if (state.equals(LifecycleState.FAILED)) { // This is a 'controlled' failure. The component put itself into the // FAILED state so call stop() to complete the clean-up. stop(); } else if (!state.equals(LifecycleState.STARTING)) { // Shouldn't be necessary but acts as a check that sub-classes are // doing what they are supposed to. invalidTransition(Lifecycle.AFTER_START_EVENT); } else { setStateInternal(LifecycleState.STARTED, null, false); } } catch (Throwable t) { // This is an 'uncontrolled' failure so put the component into the // FAILED state and throw an exception. handleSubClassException(t, "lifecycleBase.startFail", toString()); } }
从上面方法可知,所有主件都会先调用int()-> startInternal();
我们继续跟进startInternal();

service.start(); 最终也是调用父类的对应方法,跟进去看看

我们只要看startInternal();方法即可
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException { if(log.isInfoEnabled()) log.info(sm.getString("standardService.start.name", this.name)); setState(LifecycleState.STARTING); // Start our defined Container first if (engine != null) { synchronized (engine) { engine.start(); //这里启动engine->启动host->context } } synchronized (executors) { for (Executor executor: executors) { executor.start(); } } //----- 走到下面的代码说明上面的容器节点都执行完生命周期了------------------ mapperListener.start(); //启动监听器,这个是重点,因为servlet交给tomcat是在这里做的 // Start our defined Connectors second synchronized (connectorsLock) { for (Connector connector: connectors) { // If it has already failed, don't try and start it if (connector.getState() != LifecycleState.FAILED) { connector.start(); //启动连接器,这里也是重点,这个是初始化NIO的服务端,开始监听客户端请求 } } } }
通过上面的service的start()方法,我们发现其会调用容器的start方法,之后调用mapperListener的start方法,最后调用Connector的start()方法,开始监听服务。我们一个个看:
1.engine.start(),之后也是调用父类的方法,所以只要看startInternal(); 从这里开始都是容器的启动,实现
@Override protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException { // Start our subordinate components, if any logger = null; getLogger(); Cluster cluster = getClusterInternal(); if (cluster instanceof Lifecycle) { ((Lifecycle) cluster).start(); } Realm realm = getRealmInternal(); if (realm instanceof Lifecycle) { ((Lifecycle) realm).start(); } // Start our child containers, if any Container children[] = findChildren(); //获取子容器,这里的子容器 List<Future<Void>> results = new ArrayList<>(); for (Container child : children) { results.add(startStopExecutor.submit(new StartChild(child))); //使用线程池启动子容器StartChild实现了Callable接口 } MultiThrowable multiThrowable = null; for (Future<Void> result : results) { try { result.get(); } catch (Throwable e) { log.error(sm.getString("containerBase.threadedStartFailed"), e); if (multiThrowable == null) { multiThrowable = new MultiThrowable(); } multiThrowable.add(e); } } if (multiThrowable != null) { throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("containerBase.threadedStartFailed"), multiThrowable.getThrowable()); } // Start the Valves in our pipeline (including the basic), if any if (pipeline instanceof Lifecycle) { ((Lifecycle) pipeline).start(); } setState(LifecycleState.STARTING); // Start our thread if (backgroundProcessorDelay > 0) { monitorFuture = Container.getService(ContainerBase.this).getServer() .getUtilityExecutor().scheduleWithFixedDelay( new ContainerBackgroundProcessorMonitor(), 0, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS); } }
startStopExecutor.submit(new StartChild(child));//容器的启动会调用该方法

Host的启动,会调用Context的启动,逻辑跟前面一样


Context的启动会调用Wrapper的启动
之后的Wrapper的start();后续就不分析了,现在小结生命周期的流程:

1.问题:tomcat接收到Http请求后,如何通过url找到对应的servlet的?
回答上述问题,先看看service的生命周期调用中,调用了mapperListener.start();我们看看它做了啥? 因为mapperListener也是实现生命周期接口的,所以我们看其:
startInternal();方法:
@Override public void startInternal() throws LifecycleException { setState(LifecycleState.STARTING); Engine engine = service.getContainer(); if (engine == null) { return; } findDefaultHost(); addListeners(engine); Container[] conHosts = engine.findChildren(); for (Container conHost : conHosts) { Host host = (Host) conHost; if (!LifecycleState.NEW.equals(host.getState())) { // Registering the host will register the context and wrappers registerHost(host); //根进这个方法 } } }
private void registerHost(Host host) { String[] aliases = host.findAliases(); mapper.addHost(host.getName(), aliases, host); for (Container container : host.findChildren()) { if (container.getState().isAvailable()) { registerContext((Context) container); //跟进这里,因为Context包含了wrapper,而Wrapper包含了Servlet,servlet是有对应的映射路径的 } } // Default host may have changed findDefaultHost(); if(log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug(sm.getString("mapperListener.registerHost", host.getName(), domain, service)); } }
private void registerContext(Context context) { String contextPath = context.getPath(); if ("/".equals(contextPath)) { contextPath = ""; } Host host = (Host)context.getParent(); WebResourceRoot resources = context.getResources(); String[] welcomeFiles = context.findWelcomeFiles(); List<WrapperMappingInfo> wrappers = new ArrayList<>(); for (Container container : context.findChildren()) { prepareWrapperMappingInfo(context, (Wrapper) container, wrappers); //将wrapper封装成WrapperMappingInfo } mapper.addContextVersion(host.getName(), host, contextPath, context.getWebappVersion(), context, welcomeFiles, resources, wrappers); //加到Mapper对象中 }

通过上图可知,经过prepareWrapperMappingInfo()方法,将Context容器中的所有Wrapper都封装成了WrapperMappingInfo对象了:
之后我们根据mapper.addContextVersion() 方法: 省略部分代码后:下面的代码存在Mapper这个类中
protected void addWrapper(ContextVersion context, String path, Wrapper wrapper, boolean jspWildCard, boolean resourceOnly) { synchronized (context) { if (path.endsWith("/*")) { // Wildcard wrapper //如果匹配的路径是通配符 String name = path.substring(0, path.length() - 2); MappedWrapper newWrapper = new MappedWrapper(name, wrapper, jspWildCard, resourceOnly); MappedWrapper[] oldWrappers = context.wildcardWrappers; MappedWrapper[] newWrappers = new MappedWrapper[oldWrappers.length + 1]; if (insertMap(oldWrappers, newWrappers, newWrapper)) { context.wildcardWrappers = newWrappers; //加到ContextVersion 的WildcardWrapper数组中 int slashCount = slashCount(newWrapper.name); if (slashCount > context.nesting) { context.nesting = slashCount; } } } else if (path.startsWith("*.")) { // Extension wrapper //如果是拓展名结尾的映射路径 String name = path.substring(2); MappedWrapper newWrapper = new MappedWrapper(name, wrapper, jspWildCard, resourceOnly); MappedWrapper[] oldWrappers = context.extensionWrappers; MappedWrapper[] newWrappers = new MappedWrapper[oldWrappers.length + 1]; if (insertMap(oldWrappers, newWrappers, newWrapper)) { context.extensionWrappers = newWrappers; //加到ContextVersion 的extensionWrappers数组中 } } else if (path.equals("/")) { // Default wrapper MappedWrapper newWrapper = new MappedWrapper("", wrapper, jspWildCard, resourceOnly); context.defaultWrapper = newWrapper; //默认的,我们这个的是默认的 } else { // Exact wrapper final String name; if (path.length() == 0) { // Special case for the Context Root mapping which is // treated as an exact match name = "/"; } else { name = path; } MappedWrapper newWrapper = new MappedWrapper(name, wrapper, jspWildCard, resourceOnly); MappedWrapper[] oldWrappers = context.exactWrappers; MappedWrapper[] newWrappers = new MappedWrapper[oldWrappers.length + 1]; if (insertMap(oldWrappers, newWrappers, newWrapper)) { context.exactWrappers = newWrappers; //ContextVersion 的精确匹配的exactWrappers 数组中 } } } }
通过上面的分析,我们可以清晰的看到,Servlet的路径不一样,最后存到ContextVersion中的数组也是不一样,分为:通配符匹配,拓展名匹配,默认匹配,精确匹配,我们看看ContextVersion对象:

我们已经知道Mapper的内部类存有所有的servlet包装类,并且也根据不同的路径分类了,那接下来,我们分析下请求过来时,如何查找对应的servlet: 还是在Mapper这个类
private final void internalMapWrapper(ContextVersion contextVersion, CharChunk path, MappingData mappingData) throws IOException { int pathOffset = path.getOffset(); int pathEnd = path.getEnd(); boolean noServletPath = false; int length = contextVersion.path.length(); if (length == (pathEnd - pathOffset)) { noServletPath = true; } int servletPath = pathOffset + length; path.setOffset(servletPath); // Rule 1 -- Exact Match //精确匹配 匹配到的wrapper会存到mappingData MappedWrapper[] exactWrappers = contextVersion.exactWrappers; internalMapExactWrapper(exactWrappers, path, mappingData); // Rule 2 -- Prefix Match //通配符匹配 匹配到的wrapper会存到mappingData boolean checkJspWelcomeFiles = false; MappedWrapper[] wildcardWrappers = contextVersion.wildcardWrappers; if (mappingData.wrapper == null) { internalMapWildcardWrapper(wildcardWrappers, contextVersion.nesting, path, mappingData); if (mappingData.wrapper != null && mappingData.jspWildCard) { char[] buf = path.getBuffer(); if (buf[pathEnd - 1] == '/') { /* * Path ending in '/' was mapped to JSP servlet based on * wildcard match (e.g., as specified in url-pattern of a * jsp-property-group. * Force the context's welcome files, which are interpreted * as JSP files (since they match the url-pattern), to be * considered. See Bugzilla 27664. */ mappingData.wrapper = null; checkJspWelcomeFiles = true; } else { // See Bugzilla 27704 mappingData.wrapperPath.setChars(buf, path.getStart(), path.getLength()); mappingData.pathInfo.recycle(); } } } if(mappingData.wrapper == null && noServletPath && contextVersion.object.getMapperContextRootRedirectEnabled()) { // The path is empty, redirect to "/" path.append('/'); pathEnd = path.getEnd(); mappingData.redirectPath.setChars (path.getBuffer(), pathOffset, pathEnd - pathOffset); path.setEnd(pathEnd - 1); return; } // Rule 3 -- Extension Match //拓展名匹配 匹配到的wrapper会存到mappingData MappedWrapper[] extensionWrappers = contextVersion.extensionWrappers; if (mappingData.wrapper == null && !checkJspWelcomeFiles) { internalMapExtensionWrapper(extensionWrappers, path, mappingData, true); } // Rule 4 -- Welcome resources processing for servlets //欢迎页匹配 if (mappingData.wrapper == null) { boolean checkWelcomeFiles = checkJspWelcomeFiles; if (!checkWelcomeFiles) { char[] buf = path.getBuffer(); checkWelcomeFiles = (buf[pathEnd - 1] == '/'); } if (checkWelcomeFiles) { for (int i = 0; (i < contextVersion.welcomeResources.length) && (mappingData.wrapper == null); i++) { path.setOffset(pathOffset); path.setEnd(pathEnd); path.append(contextVersion.welcomeResources[i], 0, contextVersion.welcomeResources[i].length()); path.setOffset(servletPath); // Rule 4a -- Welcome resources processing for exact macth internalMapExactWrapper(exactWrappers, path, mappingData); // Rule 4b -- Welcome resources processing for prefix match if (mappingData.wrapper == null) { internalMapWildcardWrapper (wildcardWrappers, contextVersion.nesting, path, mappingData); } // Rule 4c -- Welcome resources processing // for physical folder if (mappingData.wrapper == null && contextVersion.resources != null) { String pathStr = path.toString(); WebResource file = contextVersion.resources.getResource(pathStr); if (file != null && file.isFile()) { internalMapExtensionWrapper(extensionWrappers, path, mappingData, true); if (mappingData.wrapper == null && contextVersion.defaultWrapper != null) { mappingData.wrapper = contextVersion.defaultWrapper.object; mappingData.requestPath.setChars (path.getBuffer(), path.getStart(), path.getLength()); mappingData.wrapperPath.setChars (path.getBuffer(), path.getStart(), path.getLength()); mappingData.requestPath.setString(pathStr); mappingData.wrapperPath.setString(pathStr); } } } } path.setOffset(servletPath); path.setEnd(pathEnd); } } /* welcome file processing - take 2 * Now that we have looked for welcome files with a physical * backing, now look for an extension mapping listed * but may not have a physical backing to it. This is for * the case of index.jsf, index.do, etc. * A watered down version of rule 4 */ if (mappingData.wrapper == null) { boolean checkWelcomeFiles = checkJspWelcomeFiles; if (!checkWelcomeFiles) { char[] buf = path.getBuffer(); checkWelcomeFiles = (buf[pathEnd - 1] == '/'); } if (checkWelcomeFiles) { for (int i = 0; (i < contextVersion.welcomeResources.length) && (mappingData.wrapper == null); i++) { path.setOffset(pathOffset); path.setEnd(pathEnd); path.append(contextVersion.welcomeResources[i], 0, contextVersion.welcomeResources[i].length()); path.setOffset(servletPath); internalMapExtensionWrapper(extensionWrappers, path, mappingData, false); } path.setOffset(servletPath); path.setEnd(pathEnd); } } // Rule 7 -- Default servlet //默认servlet匹配,“/” 开头的匹配,springmvc的dispatcherServlet就是这种 if (mappingData.wrapper == null && !checkJspWelcomeFiles) { if (contextVersion.defaultWrapper != null) { mappingData.wrapper = contextVersion.defaultWrapper.object; mappingData.requestPath.setChars (path.getBuffer(), path.getStart(), path.getLength()); mappingData.wrapperPath.setChars (path.getBuffer(), path.getStart(), path.getLength()); mappingData.matchType = MappingMatch.DEFAULT; } // Redirection to a folder char[] buf = path.getBuffer(); if (contextVersion.resources != null && buf[pathEnd -1 ] != '/') { String pathStr = path.toString(); // Note: Check redirect first to save unnecessary getResource() // call. See BZ 62968. if (contextVersion.object.getMapperDirectoryRedirectEnabled()) { WebResource file; // Handle context root if (pathStr.length() == 0) { file = contextVersion.resources.getResource("/"); } else { file = contextVersion.resources.getResource(pathStr); } if (file != null && file.isDirectory()) { // Note: this mutates the path: do not do any processing // after this (since we set the redirectPath, there // shouldn't be any) path.setOffset(pathOffset); path.append('/'); mappingData.redirectPath.setChars (path.getBuffer(), path.getStart(), path.getLength()); } else { mappingData.requestPath.setString(pathStr); mappingData.wrapperPath.setString(pathStr); } } else { mappingData.requestPath.setString(pathStr); mappingData.wrapperPath.setString(pathStr); } } } path.setOffset(pathOffset); path.setEnd(pathEnd); }
至此,我们分析完了,servlet如何存到tomcat中,同时tomcat如何通过url查询对应的servlet:
最后我们回去看看Connector的启动流程,看看它又干了啥?

debug发现,并不是在上面图所示进行Connector进行start(),我们打断点到Connector这个类的startInternal():


继承根进:
public final void start() throws Exception { if (bindState == BindState.UNBOUND) { bindWithCleanup(); bindState = BindState.BOUND_ON_START; } startInternal(); } @Override public void startInternal() throws Exception { if (!running) { running = true; paused = false; if (socketProperties.getProcessorCache() != 0) { processorCache = new SynchronizedStack<>(SynchronizedStack.DEFAULT_SIZE, socketProperties.getProcessorCache()); } if (socketProperties.getEventCache() != 0) { eventCache = new SynchronizedStack<>(SynchronizedStack.DEFAULT_SIZE, socketProperties.getEventCache()); } if (socketProperties.getBufferPool() != 0) { nioChannels = new SynchronizedStack<>(SynchronizedStack.DEFAULT_SIZE, socketProperties.getBufferPool()); } // Create worker collection if (getExecutor() == null) { createExecutor(); } initializeConnectionLatch(); // Start poller thread poller = new Poller(); // 这里是重点,该类实现了Runnable Thread pollerThread = new Thread(poller, getName() + "-ClientPoller"); pollerThread.setPriority(threadPriority); pollerThread.setDaemon(true); pollerThread.start(); //通过线程启动poller这个Runnable startAcceptorThread(); //这里也是重点 } }
//我们先看看Poller这个类:
先来补充下NIO的几个组件知识: Selector选择器,会监听注册到该监听器的SocketChannel的各种事件
我们回到Poller来,先看其构造器,然后看其run()方法:
public class Poller implements Runnable { private Selector selector; private final SynchronizedQueue<PollerEvent> events = new SynchronizedQueue<>();//栈结构,用于存储selector监听到的事件 private volatile boolean close = false; // Optimize expiration handling private long nextExpiration = 0; private AtomicLong wakeupCounter = new AtomicLong(0); private volatile int keyCount = 0; public Poller() throws IOException { this.selector = Selector.open(); //创建选择器,NIO的重要主件之一
}
//省略了部分代码 public void run() { // Loop until destroy() is called while (true) { boolean hasEvents = false; try { if (!close) { hasEvents = events();//判断是否有注册事件 if (wakeupCounter.getAndSet(-1) > 0) { // If we are here, means we have other stuff to do // Do a non blocking select keyCount = selector.selectNow(); } else { keyCount = selector.select(selectorTimeout); } wakeupCounter.set(0); } if (close) { events(); timeout(0, false); try { selector.close(); } catch (IOException ioe) { log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.nio.selectorCloseFail"), ioe); } break; } } catch (Throwable x) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(x); log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.nio.selectorLoopError"), x); continue; } // Either we timed out or we woke up, process events first if (keyCount == 0) { hasEvents = (hasEvents | events()); } Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = keyCount > 0 ? selector.selectedKeys().iterator() : null; //选择器开始监听事件 // Walk through the collection of ready keys and dispatch // any active event. while (iterator != null && iterator.hasNext()) { SelectionKey sk = iterator.next(); NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper = (NioSocketWrapper) sk.attachment(); // Attachment may be null if another thread has called // cancelledKey() if (socketWrapper == null) { iterator.remove(); } else { iterator.remove(); processKey(sk, socketWrapper);//如果有事件过来就会 这个是重点,服务器接收到客户端连接事件后就会调用该方法处理客户端的连接 } } // Process timeouts timeout(keyCount,hasEvents); } getStopLatch().countDown(); }
//根据看看events():下图当envents这个栈有事件时,其会调用events.poll()方法弹出一个事件,如果是注册事件,就会注册到Selector中:

小结:poller实现了Runnable 接口,其run()方法会进行客户端各种连接事件,而其evens这个栈结构用于存储ServerSocketChannel.accept()接收到的SocketChannel封装成的事件:
那么:到底是谁将客户端的连接压入Poller的events栈的呢?我们回到下面的代码:


这里有个acceptor主件,跟poller一样,它也实现了Runnable:看看其源码:
acceptor = new Acceptor<>(this); //该方法传入了this(AbstractEndpoint),而this是包含了Poller的,所以Acceptor接收的客户端才能交给Poller;
我们分析下其run方法:
@Override public void run() { int errorDelay = 0; // Loop until we receive a shutdown command while (endpoint.isRunning()) { // Loop if endpoint is paused while (endpoint.isPaused() && endpoint.isRunning()) { state = AcceptorState.PAUSED; try { Thread.sleep(50); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // Ignore } } if (!endpoint.isRunning()) { break; } state = AcceptorState.RUNNING; try { //if we have reached max connections, wait endpoint.countUpOrAwaitConnection(); // Endpoint might have been paused while waiting for latch // If that is the case, don't accept new connections if (endpoint.isPaused()) { continue; } U socket = null; try { // Accept the next incoming connection from the server // socket socket = endpoint.serverSocketAccept(); } catch (Exception ioe) { // We didn't get a socket endpoint.countDownConnection(); if (endpoint.isRunning()) { // Introduce delay if necessary errorDelay = handleExceptionWithDelay(errorDelay); // re-throw throw ioe; } else { break; } } // Successful accept, reset the error delay errorDelay = 0; // Configure the socket if (endpoint.isRunning() && !endpoint.isPaused()) { // setSocketOptions() will hand the socket off to // an appropriate processor if successful if (!endpoint.setSocketOptions(socket)) { endpoint.closeSocket(socket); } } else { endpoint.destroySocket(socket); } } catch (Throwable t) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t); String msg = sm.getString("endpoint.accept.fail"); // APR specific. // Could push this down but not sure it is worth the trouble. if (t instanceof Error) { Error e = (Error) t; if (e.getError() == 233) { // Not an error on HP-UX so log as a warning // so it can be filtered out on that platform // See bug 50273 log.warn(msg, t); } else { log.error(msg, t); } } else { log.error(msg, t); } } } state = AcceptorState.ENDED; }
@Override public void run() { int errorDelay = 0; // Loop until we receive a shutdown command while (endpoint.isRunning()) { // Loop if endpoint is paused while (endpoint.isPaused() && endpoint.isRunning()) { state = AcceptorState.PAUSED; try { Thread.sleep(50); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // Ignore } } if (!endpoint.isRunning()) { break; } state = AcceptorState.RUNNING; try { //if we have reached max connections, wait endpoint.countUpOrAwaitConnection(); // Endpoint might have been paused while waiting for latch // If that is the case, don't accept new connections if (endpoint.isPaused()) { continue; } U socket = null; try { // Accept the next incoming connection from the server // socket socket = endpoint.serverSocketAccept(); //接收客户端的请求,后续会根据,这个方法会一直阻塞,这也就是为何我们启动springweb项目,不会自动关掉的原因了 } catch (Exception ioe) { // We didn't get a socket endpoint.countDownConnection(); if (endpoint.isRunning()) { // Introduce delay if necessary errorDelay = handleExceptionWithDelay(errorDelay); // re-throw throw ioe; } else { break; } } // Successful accept, reset the error delay errorDelay = 0; // Configure the socket if (endpoint.isRunning() && !endpoint.isPaused()) { // setSocketOptions() will hand the socket off to // an appropriate processor if successful if (!endpoint.setSocketOptions(socket)) {//如果接收到了客户端请求,那么就会调用该方法 endpoint.closeSocket(socket); } } else { endpoint.destroySocket(socket); } } catch (Throwable t) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t); String msg = sm.getString("endpoint.accept.fail"); // APR specific. // Could push this down but not sure it is worth the trouble. if (t instanceof Error) { Error e = (Error) t; if (e.getError() == 233) { // Not an error on HP-UX so log as a warning // so it can be filtered out on that platform // See bug 50273 log.warn(msg, t); } else { log.error(msg, t); } } else { log.error(msg, t); } } } state = AcceptorState.ENDED; }

我们根进看看: endpoint.setSocketOptions(socket)
@Override protected boolean setSocketOptions(SocketChannel socket) { NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper = null; try { // Allocate channel and wrapper NioChannel channel = null; if (nioChannels != null) { channel = nioChannels.pop(); } if (channel == null) { SocketBufferHandler bufhandler = new SocketBufferHandler( socketProperties.getAppReadBufSize(), socketProperties.getAppWriteBufSize(), socketProperties.getDirectBuffer()); if (isSSLEnabled()) { channel = new SecureNioChannel(bufhandler, selectorPool, this); } else { channel = new NioChannel(bufhandler); } } NioSocketWrapper newWrapper = new NioSocketWrapper(channel, this); channel.reset(socket, newWrapper); connections.put(socket, newWrapper); socketWrapper = newWrapper; // Set socket properties // Disable blocking, polling will be used socket.configureBlocking(false); socketProperties.setProperties(socket.socket()); socketWrapper.setReadTimeout(getConnectionTimeout()); socketWrapper.setWriteTimeout(getConnectionTimeout()); socketWrapper.setKeepAliveLeft(NioEndpoint.this.getMaxKeepAliveRequests()); socketWrapper.setSecure(isSSLEnabled()); poller.register(channel, socketWrapper);//在这里将会将接收到的客户端封装成事件,存到Poller的envens栈中 return true; } catch (Throwable t) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t); try { log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.socketOptionsError"), t); } catch (Throwable tt) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(tt); } if (socketWrapper == null) { destroySocket(socket); } } // Tell to close the socket if needed return false; }
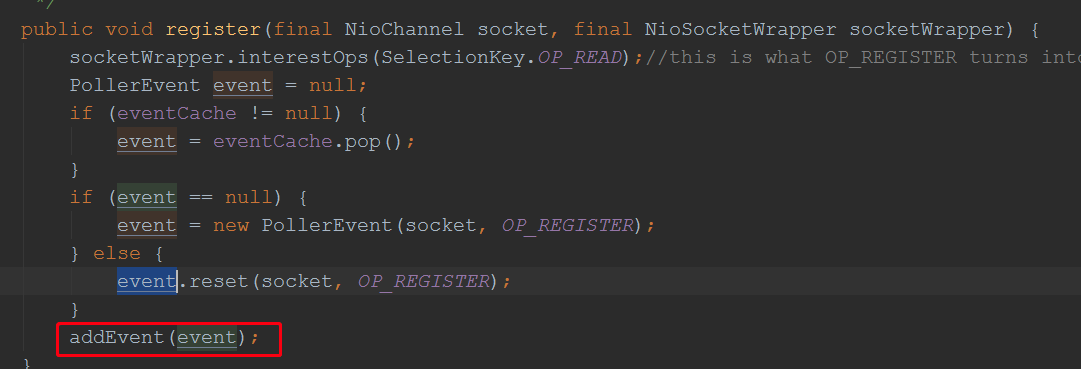
//小结上面的流程:

//最后通过调用Controller的方法,看看整个调用链条:

前面分析过,Poller的run方法会处理监听到的事件,所以,我们打个断点在该方法里:
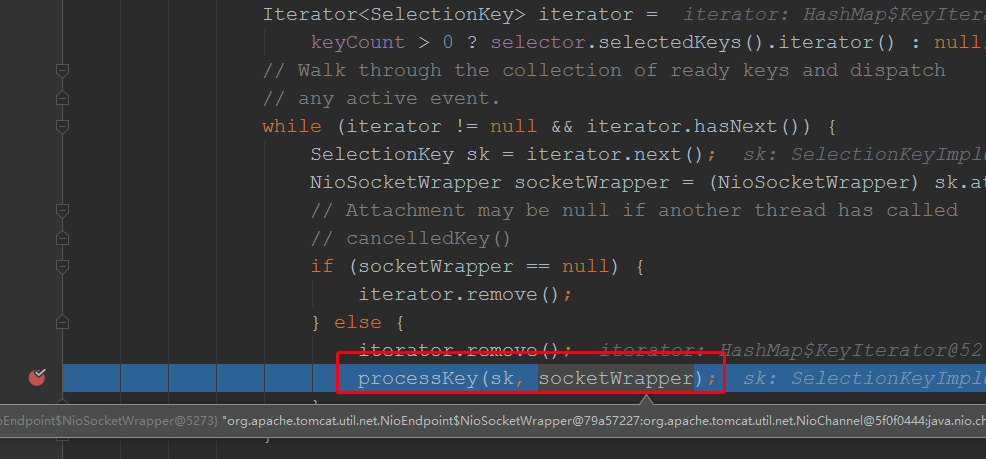
根进去:

public boolean processSocket(SocketWrapperBase<S> socketWrapper,
SocketEvent event, boolean dispatch) {
try {
if (socketWrapper == null) {
return false;
}
SocketProcessorBase<S> sc = null;
if (processorCache != null) {
sc = processorCache.pop();
}
if (sc == null) {
sc = createSocketProcessor(socketWrapper, event); //将客户端封装成sc,sc实现了Runnable接口
} else {
sc.reset(socketWrapper, event);
}
Executor executor = getExecutor();
if (dispatch && executor != null) {
executor.execute(sc); //最终交给了一个线程池处理了
} else {
sc.run();
}
} catch (RejectedExecutionException ree) {
getLog().warn(sm.getString("endpoint.executor.fail", socketWrapper) , ree);
return false;
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
// This means we got an OOM or similar creating a thread, or that
// the pool and its queue are full
getLog().error(sm.getString("endpoint.process.fail"), t);
return false;
}
return true;
}
所以接下来看看:SocketProcessorBase的run方法:
@Override public final void run() { synchronized (socketWrapper) { // It is possible that processing may be triggered for read and // write at the same time. The sync above makes sure that processing // does not occur in parallel. The test below ensures that if the // first event to be processed results in the socket being closed, // the subsequent events are not processed. if (socketWrapper.isClosed()) { return; } doRun(); } }
继续跟踪doRun();

一直到这里,我们可以看到,最终会调用Mapper的方法去找到对应的Servlet的,前面已经分析过Mapper有个根据url获取Servelet包装类的放法,并将其存到MappingData中,我们跟进去:





Pipeline最后一个基本都是xxxValue:

@Override public final void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException { // Disallow any direct access to resources under WEB-INF or META-INF MessageBytes requestPathMB = request.getRequestPathMB(); if ((requestPathMB.startsWithIgnoreCase("/META-INF/", 0)) //这些判断就说明了,为何前端不能直接访问WEB-INF的内容了 || (requestPathMB.equalsIgnoreCase("/META-INF")) || (requestPathMB.startsWithIgnoreCase("/WEB-INF/", 0)) || (requestPathMB.equalsIgnoreCase("/WEB-INF"))) { response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND); return; } // Select the Wrapper to be used for this Request Wrapper wrapper = request.getWrapper();//前面分析过了,Servlet存到了Request中,这里获取出来 if (wrapper == null || wrapper.isUnavailable()) { response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND); return; } // Acknowledge the request try { response.sendAcknowledgement(); } catch (IOException ioe) { container.getLogger().error(sm.getString( "standardContextValve.acknowledgeException"), ioe); request.setAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION, ioe); response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR); return; } if (request.isAsyncSupported()) { request.setAsyncSupported(wrapper.getPipeline().isAsyncSupported()); } wrapper.getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);//调用Servlet处理请求 }


至此分析完毕整个调用流程