一. Pod 是什么
pod在k8s里能够运行的最小的逻辑端元 一个pod代表集群运行的一个进程
1个pod里面可以运行单个或者多个容器 他们共享 UTS NET IPC volume 名称空间 隔离了 USER PID Mount
pod中的容器共享ip hostname ipc 他们可以通过localhost 互相发现 他们之间可以通过ipc通讯
pod中的容器也有访问共享volume的权限 这些volume也会被定义成pod的一部分被挂载到pod的容器中应用成文件系统
可以把Pod理解成豌豆荚 容器为豆粒

一个pod里运行多个容器 又叫边车(SideCar)模式
二. 使用pod
通常把pod分为两类
1.自主式pod 这种pod本身是不能自我修复的 当pod被创建后 pod会一直在那个节点 直到pod进程被删除或者因为缺少资源被调度到其他节点 自主式pod运行的节点发生故障或者因为资源不足驱逐pod pod不会被调度其他节点
2.控制器管理的pod kubernetes通过controller控制器来创建管理pod pod的标签能匹配controller控制器的标签 当运行pod的节点发生故障时 控制器会把pod调度到其他节点 pod被删除 控制器会根据清单上pod的数量来运行pod controller控制器能控制pod的副本(水平扩展) 滚定升级 自愈
Deployment
DaemonSet
ReplicaSet
StatefulSet
job
Cronjob
Pod的终止
因为Pod作为在集群的节点上运行的进程,所以在不再需要的时候能够优雅的终止掉是十分必要的(比起使用发送KILL信号这种暴力的方式)。用户需要能够放松删除请求,并且知道它们何时会被终止,是否被正确的删除。用户想终止程序时发送删除pod的请求,在pod可以被强制删除前会有一个宽限期,会发送一个TERM请求到每个容器的主进程。一旦超时,将向主进程发送KILL信号并从API server中删除。如果kubelet或者container manager在等待进程终止的过程中重启,在重启后仍然会重试完整的宽限期。
示例流程如下:用户发送删除pod的命令,默认宽限期是30秒;
在Pod超过该宽限期后API server就会更新Pod的状态为“dead”;
在客户端命令行上显示的Pod状态为“terminating”;
跟第三步同时,当kubelet发现pod被标记为“terminating”状态时,开始停止pod进程:
如果在pod中定义了preStop hook,在停止pod前会被调用。如果在宽限期过后,preStop hook依然在运行,第二步会再增加2秒的宽限期;
向Pod中的进程发送TERM信号;
跟第三步同时,该Pod将从该service的端点列表中删除,不再是replication controller的一部分。关闭的慢的pod将继续处理load balancer转发的流量;
过了宽限期后,将向Pod中依然运行的进程发送SIGKILL信号而杀掉进程。
Kublete会在API server中完成Pod的的删除,通过将优雅周期设置为0(立即删除)。Pod在API中消失,并且在客户端也不可见。
删除宽限期默认是30秒。 kubectl delete命令支持 —grace-period=选项,允许用户设置自己的宽限期。如果设置为0将强制删除pod。在kubectl>=1.5版本的命令中,你必须同时使用 --force 和 --grace-period=0 来强制删除pod。
kubectl delete pod podname --force --grace-period=0
Pod的强制删除是通过在集群和etcd中将其定义为删除状态。当执行强制删除命令时,API server不会等待该pod所运行在节点上的kubelet确认,就会立即将该pod从API server中移除,这时就可以创建跟原pod同名的pod了。这时,在节点上的pod会被立即设置为terminating状态,不过在被强制删除之前依然有一小段优雅删除周期。
三. 创建pod
三种方式
陈述时
声明式
[root@master ~]# kubectl explain pod
KIND: Pod
VERSION: v1
DESCRIPTION:
Pod is a collection of containers that can run on a host. This resource is
created by clients and scheduled onto hosts.
FIELDS:
apiVersion <string>
APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation of an
object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest internal
value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources
kind <string>
Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this object
represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client submits
requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds
metadata <Object>
Standard object's metadata. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#metadata
spec <Object>
Specification of the desired behavior of the pod. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status
声明式必须存在的四个字段
apiVersion
kind
metadata
spec
apiVersion
[root@master ~]# kubectl api-resources
NAME SHORTNAMES APIVERSION NAMESPACED KIND
bindings v1 true Binding
componentstatuses cs v1 false ComponentStatus
configmaps cm v1 true ConfigMap
endpoints ep v1 true Endpoints
events ev v1 true Event
limitranges limits v1 true LimitRange
namespaces ns v1 false Namespace
nodes no v1 false Node
persistentvolumeclaims pvc v1 true PersistentVolumeClaim
persistentvolumes pv v1 false PersistentVolume
pods po v1 true Pod
podtemplates v1 true PodTemplate
replicationcontrollers rc v1 true ReplicationController
resourcequotas quota v1 true ResourceQuota
secrets v1 true Secret
serviceaccounts sa v1 true ServiceAccount
services svc v1 true Service
mutatingwebhookconfigurations admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1 false MutatingWebhookConfiguration
validatingwebhookconfigurations admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1 false ValidatingWebhookConfiguration
customresourcedefinitions crd,crds apiextensions.k8s.io/v1 false CustomResourceDefinition
apiservices apiregistration.k8s.io/v1 false APIService
controllerrevisions apps/v1 true ControllerRevision
daemonsets ds apps/v1 true DaemonSet
deployments deploy apps/v1 true Deployment
replicasets rs apps/v1 true ReplicaSet
statefulsets sts apps/v1 true StatefulSet
tokenreviews authentication.k8s.io/v1 false TokenReview
localsubjectaccessreviews authorization.k8s.io/v1 true LocalSubjectAccessReview
selfsubjectaccessreviews authorization.k8s.io/v1 false SelfSubjectAccessReview
selfsubjectrulesreviews authorization.k8s.io/v1 false SelfSubjectRulesReview
subjectaccessreviews authorization.k8s.io/v1 false SubjectAccessReview
horizontalpodautoscalers hpa autoscaling/v1 true HorizontalPodAutoscaler
cronjobs cj batch/v1beta1 true CronJob
jobs batch/v1 true Job
certificatesigningrequests csr certificates.k8s.io/v1 false CertificateSigningRequest
leases coordination.k8s.io/v1 true Lease
bgpconfigurations crd.projectcalico.org/v1 false BGPConfiguration
bgppeers crd.projectcalico.org/v1 false BGPPeer
blockaffinities crd.projectcalico.org/v1 false BlockAffinity
clusterinformations crd.projectcalico.org/v1 false ClusterInformation
felixconfigurations crd.projectcalico.org/v1 false FelixConfiguration
globalnetworkpolicies crd.projectcalico.org/v1 false GlobalNetworkPolicy
globalnetworksets crd.projectcalico.org/v1 false GlobalNetworkSet
hostendpoints crd.projectcalico.org/v1 false HostEndpoint
ipamblocks crd.projectcalico.org/v1 false IPAMBlock
ipamconfigs crd.projectcalico.org/v1 false IPAMConfig
ipamhandles crd.projectcalico.org/v1 false IPAMHandle
ippools crd.projectcalico.org/v1 false IPPool
kubecontrollersconfigurations crd.projectcalico.org/v1 false KubeControllersConfiguration
networkpolicies crd.projectcalico.org/v1 true NetworkPolicy
networksets crd.projectcalico.org/v1 true NetworkSet
endpointslices discovery.k8s.io/v1beta1 true EndpointSlice
events ev events.k8s.io/v1 true Event
ingresses ing extensions/v1beta1 true Ingress
flowschemas flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1beta1 false FlowSchema
prioritylevelconfigurations flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1beta1 false PriorityLevelConfiguration
ingressclasses networking.k8s.io/v1 false IngressClass
ingresses ing networking.k8s.io/v1 true Ingress
networkpolicies netpol networking.k8s.io/v1 true NetworkPolicy
runtimeclasses node.k8s.io/v1 false RuntimeClass
poddisruptionbudgets pdb policy/v1beta1 true PodDisruptionBudget
podsecuritypolicies psp policy/v1beta1 false PodSecurityPolicy
clusterrolebindings rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 false ClusterRoleBinding
clusterroles rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 false ClusterRole
rolebindings rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 true RoleBinding
roles rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 true Role
priorityclasses pc scheduling.k8s.io/v1 false PriorityClass
csidrivers storage.k8s.io/v1 false CSIDriver
csinodes storage.k8s.io/v1 false CSINode
storageclasses sc storage.k8s.io/v1 false StorageClass
volumeattachments storage.k8s.io/v1 false VolumeAttachment
四. pod 调度
[root@master ~]# kubectl get pod -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
nginx-ds-qjlph 1/1 Running 0 111s 172.7.166.129 node1 <none> <none>
nginx-ds-rtp7s 1/1 Running 0 111s 172.7.104.1 node2 <none> <none>
STATUS相位
Running Pending(未调度成功,或者处于下载镜像的过程中) Succeeeded(成功终止) Failed(失败) Unknown(kubelet丢失) CrashLoopBackOff/Error(容器内部错误)
五. pod_env port
格式
[root@master ~]# kubectl explain pods.spec.containers.env
RESOURCE: env <[]Object>
FIELDS:
name <string> -required-
value <string>
示例
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: mysql-5.7
labels:
type: db
spec:
containers:
- name: mysql
image: mysql:5.7
env:
- name: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD
value: "!QAZxsw2"
ports:
- containerPort: 3306
name: mysql-tcp
protocol: TCP
hostPort: 3306
wordpress mysql5.7
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: wordpress
labels:
type: db
spec:
containers:
- name: mysql
image: mysql:5.7
env:
- name: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD
value: "!QAZxsw2"
- name: MYSQL_DATABASE
value: wordpress
- name: wordpress
image: wordpress
ports:
- containerPort: 80
hostPort: 8080
env:
- name: WORDPRESS_DB_HOST
value: "127.0.0.1"
- name: WORDPRESS_DB_USER
value: "root"
- name: WORDPRESS_DB_PASSWORD
value: "!QAZxsw2"
- name: WORDPRESS_DB_NAME
value: wordpress
六. container command args
command相当于entrypoint
args相当于cmd
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: mypod
labels:
app: mypod
release: canary
spec:
containers:
- name: demoapp
image: ikubernetes/demoapp:v1.0
command: ["/bin/sh","-c"]
args: ["echo 11 && sleep 1000"]
[root@master ~]# kubectl exec -it mypod -- sh
[root@mypod /]# ps -ef
PID USER TIME COMMAND
1 root 0:00 sleep 1000
14 root 0:00 sh
20 root 0:00 ps -ef
七. LivenessProbe ReadinessProbe
1.使用示范
spec:
containers:
- name: …
image: …
livenessProbe:
exec <Object> # 命令式探针
httpGet <Object> # http GET类型的探针
tcpSocket <Object> # tcp Socket类型的探针
initialDelaySeconds <integer> # 发起初次探测请求的延后时长
periodSeconds <integer> # 请求周期
timeoutSeconds <integer> # 超时时长
successThreshold <integer> # 成功阈值
failureThreshold <integer> # 失败阈值
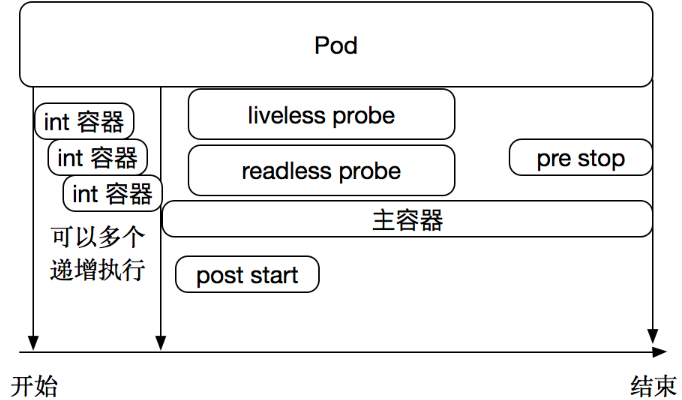
探针是由 kubelet 对容器执行的定期诊断。要执行诊断,kubelet 调用由容器实现的Handler。其存活性探测的方法有以下三种:
- ExecAction:在容器内执行指定命令。如果命令退出时返回码为 0 则认为诊断成功。
- TCPSocketAction:对指定端口上的容器的 IP 地址进行 TCP 检查。如果端口打开,则诊断被认为是成功的。
- HTTPGetAction:对指定的端口和路径上的容器的 IP 地址执行 HTTP Get 请求。如果响应的状态码大于等于200 且小于 400,则诊断被认为是成功的。
LivenessProbe:周期性检测,检测未通过时,kubelet会根据restartPolicy的定义来决定是否会重启该容器;未定义时,Kubelet认为只容器未终止,即为健康;
设置exec探针
[root@master ~]# kubectl explain pod.spec.containers.livenessProbe.exec
KIND: Pod
VERSION: v1
............
FIELDS:
command <[]string>
Command is the command line to execute inside the container, the working
directory for the command is root ('/') in the container's filesystem. The
command is simply exec'd, it is not run inside a shell, so traditional
shell instructions ('|', etc) won't work. To use a shell, you need to
explicitly call out to that shell. Exit status of 0 is treated as
live/healthy and non-zero is unhealthy.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
labels:
test: liveness-exec
name: liveness-exec
spec:
containers:
- name: liveness-exec-demo
image: busybox
args: ["/bin/sh","-c","touch /tmp/healthy;sleep 60;rm -rf /tmp/healthy;sleep 600"]
livenessProbe:
exec:
command: ["test","-e","/tmp/healthy"]
设置HTTP探针
[root@master ~]# kubectl explain pod.spec.containers.livenessProbe.httpGet
KIND: Pod
VERSION: v1
.........
FIELDS:
host <string>
Host name to connect to, defaults to the pod IP. You probably want to set
"Host" in httpHeaders instead.
httpHeaders <[]Object>
Custom headers to set in the request. HTTP allows repeated headers.
path <string>
Path to access on the HTTP server.
port <string> -required-
Name or number of the port to access on the container. Number must be in
the range 1 to 65535. Name must be an IANA_SVC_NAME.
scheme <string>
Scheme to use for connecting to the host. Defaults to HTTP.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
labels:
test: liveness-http
name: liveness-http
spec:
containers:
- name: liveness-http-demo
image: nginx:1.12-alpine
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 80
lifecycle:
postStart:
exec:
command: ["/bin/sh","-c","echo healthy > /usr/share/nginx/html/healthy"]
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /healthy
port: http
scheme: HTTP
设置TCP探针
[root@master ~]# kubectl explain pod.spec.containers.livenessProbe.tcpSocket
KIND: Pod
VERSION: v1
----------------
FIELDS:
host <string>
Optional: Host name to connect to, defaults to the pod IP.
port <string> -required-
Number or name of the port to access on the container. Number must be in
the range 1 to 65535. Name must be an IANA_SVC_NAME.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
labels:
test: liveness-tcp
name: liveness-tcp
spec:
containers:
- name: liveness-tcp-demo
image: nginx:1.12-alpine
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 80
livenessProbe:
tcpSocket:
port: http
上面的资源清单文件,向Pod IP的80/tcp端口发起连接请求,并根据连接建立的状态判断Pod存活状态。
每次探测都将获得以下三种结果之一:
成功:容器通过了诊断。
失败:容器未通过诊断。
未知:诊断失败,因此不会采取任何行动。
Kubelet 可以选择是否执行在容器上运行的两种探针执行和做出反应:
1. `livenessProbe:`指示容器是否正在运行。如果存活探测失败,则 kubelet 会杀死容器,并且容器将受到其 重启策略 的影响。如果容器不提供存活探针,则默认状态为 Success。
2.` readinessProbe:`指示容器是否准备好服务请求。如果就绪探测失败,端点控制器将从与 Pod 匹配的所有 Service 的端点中删除该 Pod 的 IP 地址。初始延迟之前的就绪状态默认为 Failure。如果容器不提供就绪探针,则默认状态为 Success。
ReadinessProbe:周期性检测,检测未通过时,与该Pod关联的Service,会将该Pod从Service的后端可用端点列表中删除;直接再次就绪,重新添加回来。未定义时,只要容器未终止,即为就绪;
StartupProbe:便于用户使用同livenessProbe不同参数或阈值;
2.LivenessProbe readinessProbe使用场景
LivenessProbe
| 如果容器中的进程能够在遇到问题或不健康的情况下自行崩溃,则不一定需要存活探针; kubelet 将根据 Pod 的restartPolicy 自动执行正确的操作。 |
| 如果希望容器在探测失败时被杀死并重新启动,那么请指定一个存活探针,并指定restartPolicy 为 Always 或 OnFailure。 |
| 如果要仅在探测成功时才开始向 Pod 发送流量,请指定就绪探针。在这种情况下,就绪探针可能与存活探针相同,但是 spec 中的就绪探针的存在意味着 Pod 将在没有接收到任何流量的情况下启动,并且只有在探针探测成功后才开始接收流量。 |
| 如果您希望容器能够自行维护,您可以指定一个就绪探针,该探针检查与存活探针不同的端点。 |
| 请注意,如果您只想在 Pod 被删除时能够排除请求,则不一定需要使用就绪探针;在删除 Pod 时,Pod 会自动将自身置于未完成状态,无论就绪探针是否存在。当等待 Pod 中的容器停止时,Pod 仍处于未完成状态。 |
八 Pod的重启策略
Pod的重启策略
PodSpec 中有一个 restartPolicy 字段,可能的值为 Always、OnFailure 和 Never。默认为 Always。 restartPolicy 适用于 Pod 中的所有容器。restartPolicy 仅指通过同一节点上的 kubelet 重新启动容器。失败的容器由 kubelet 以五分钟为上限的指数退避延迟(10秒,20秒,40秒...)重新启动,并在成功执行十分钟后重置。pod一旦绑定到一个节点,Pod 将永远不会重新绑定到另一个节点。
九 资源需求和资源限制
在Docker的范畴内,我们知道可以对运行的容器进行请求或消耗的资源进行限制。而在Kubernetes中,也有同样的机制,容器或Pod可以进行申请和消耗的资源就是CPU和内存。CPU属于可压缩型资源,即资源的额度可以按照需求进行收缩。而内存属于不可压缩型资源,对内存的收缩可能会导致无法预知的问题。
资源的隔离目前是属于容器级别,CPU和内存资源的配置需要Pod中的容器spec字段下进行定义。其具体字段,可以使用"requests"进行定义请求的确保资源可用量。也就是说容器的运行可能用不到这样的资源量,但是必须确保有这么多的资源供给。而"limits"是用于限制资源可用的最大值,属于硬限制。
在Kubernetes中,1个单位的CPU相当于虚拟机的1颗虚拟CPU(vCPU)或者是物理机上一个超线程的CPU,它支持分数计量方式,一个核心(1core)相当于1000个微核心(millicores),因此500m相当于是0.5个核心,即二分之一个核心。内存的计量方式也是一样的,默认的单位是字节,也可以使用E、P、T、G、M和K作为单位后缀,或者是Ei、Pi、Ti、Gi、Mi、Ki等形式单位后缀。
| 资源需求举例: |
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
resources:
requests:
memory: "128Mi"
cpu: "200m"
上面的配置清单中,nginx请求的CPU资源大小为200m,这意味着一个CPU核心足以满足nginx以最快的方式运行,其中对内存的期望可用大小为128Mi,实际运行时不一定会用到这么多的资源。考虑到内存的资源类型,在超出指定大小运行时存在会被OOM killer杀死的可能性,于是该请求值属于理想中使用的内存上限。
| 资源限制举例: |
容器的资源需求只是能够确保容器运行时所需要的最少资源量,但是并不会限制其可用的资源上限。当应用程序存在Bug时,也有可能会导致系统资源被长期占用的情况,这就需要另外一个limits属性对容器进行定义资源使用的最大可用量。CPU是属于可压缩资源,可以进行自由地调节。而内存属于硬限制性资源,当进程申请分配超过limit属性定义的内存大小时,该Pod将会被OOM killer杀死。如下:
[root@k8s-master ~]# vim memleak-pod.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: memleak-pod
labels:
app: memleak
spec:
containers:
- name: simmemleak
image: saadali/simmemleak
resources:
requests:
memory: "64Mi"
cpu: "1"
limits:
memory: "64Mi"
cpu: "1"
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl apply -f memleak-pod.yaml
pod/memleak-pod created
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get pods -l app=memleak
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
memleak-pod 0/1 OOMKilled 2 12s
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get pods -l app=memleak
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
memleak-pod 0/1 CrashLoopBackOff 2 28s
Pod资源默认的重启策略为Always,在memleak因为内存限制而终止会立即重启,此时该Pod会被OOM killer杀死,在多次重复因为内存资源耗尽重启会触发Kunernetes系统的重启延迟,每次重启的时间会不断拉长,后面看到的Pod的状态通常为"CrashLoopBackOff"。
这里还需要明确的是,在一个Kubernetes集群上,运行的Pod众多,那么当节点都无法满足多个Pod对象的资源使用时,是按照什么样的顺序去终止这些Pod对象呢??
Kubernetes是无法自行去判断的,需要借助于Pod对象的优先级进行判定终止Pod的优先问题。根据Pod对象的requests和limits属性,Kubernetes将Pod对象分为三个服务质量类别:
| Guaranteed:每个容器都为CPU和内存资源设置了相同的requests和limits属性的Pod都会自动归属于该类别,属于最高优先级。 |
| Burstable:至少有一个容器设置了CPU或内存资源的requests属性,单不满足Guaranteed类别要求的资源归于该类别,属于中等优先级。 |
| BestEffort:未对任何容器设置requests属性和limits属性的Pod资源,自动归于该类别,属于最低级别。 |
顾名思义,最低级别,死得越快!