它最重要的作用就是用来:检查一个图是否存在环。
#define VERTICES 6
void Init(int parent[], int rank[])
{
for (int i = 0; i < VERTICES; ++i) {
parent[i] = -1;
rank[i] = 0; // 代表当前树高
}
}
int FindRoot(int x, int parent[])
{
int x_root = x;
while (parent[x_root] != -1) {
x_root = parent[x_root];
}
return x_root;
}
int Union(int x, int y, int parent[], int rank[])
{
int x_root = FindRoot(x, parent);
int y_root = FindRoot(y, parent);
if(x_root == y_root) {
return 0;
}
else {
// parent[x_root] = y_root;
if ( rank[x_root] > rank[y_root] ) {
parent[y_root] = x_root;
}
else if ( rank[x_root] < rank[y_root] ) {
parent[x_root] = y_root;
}
else {
parent[x_root] = y_root;
++rank;
}
return 1;
}
}
int main()
{
int parent[VERTICES] = {0};
int rank[VERTICES] = {0};
int edges[6][2] = {
{0, 1}, {1, 2}, {1, 3},
{2, 4}, {3, 4}, {2, 5}
};
Init(parent, rank);
for(int i = 0; i < 6; ++i) {
int x = edges[i][0];
int y = edges[i][1];
if(Union(x, y, parent, rank) == 0) {
printf("Cycle detected!
");
exit(0);
}
}
printf("No cycle found.
");
return 0;
}
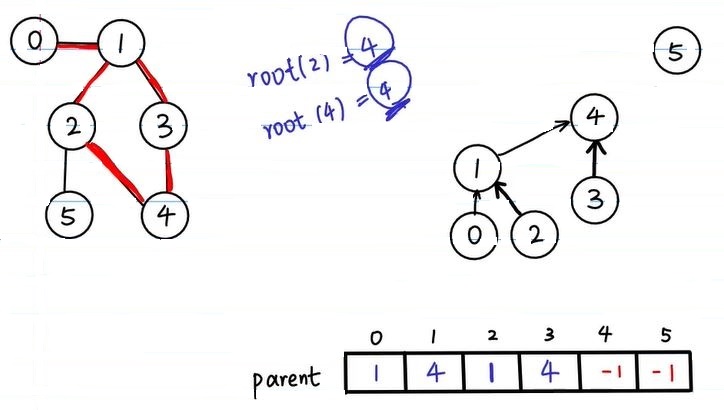
上面是一种路径压缩的思路,即根据 rank 数组,将较矮的树连接到较高的树上。
也有另一种路径压缩的方法,如下
int FindRoot(int x, int parent[])
{
int x_root = x;
while( x != parent[x]) {
x = parent[x]; // 此时 x 为根节点
}
// 进行路径压缩, 把所有非根节点的父节点都改为x
while(-1 != parent[x_root])
{
int z = x_root; // 先记录该节点
x_root = parent[x_root]; // a指向父节点
parent[z] = x; // 修改子节点的父亲
}
return x;
}