常见的居中定位
一般我们定位都会使用到position这个属性
position:static | relative | absolute | fixed | center | page | sticky
1、position:static;
static 这个定位我们称之为静态定位,默认元素都是静态的定位,对象遵循常规流。此时4个定位偏移属性不会被应用,也就是使用left,right,bottom,top将不会生效。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <title></title> <style> div{ background: #555555; width: 200px; height: 200px; } .div1{ position: static; left: 500px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="div1"></div> </body> </html>
结果:
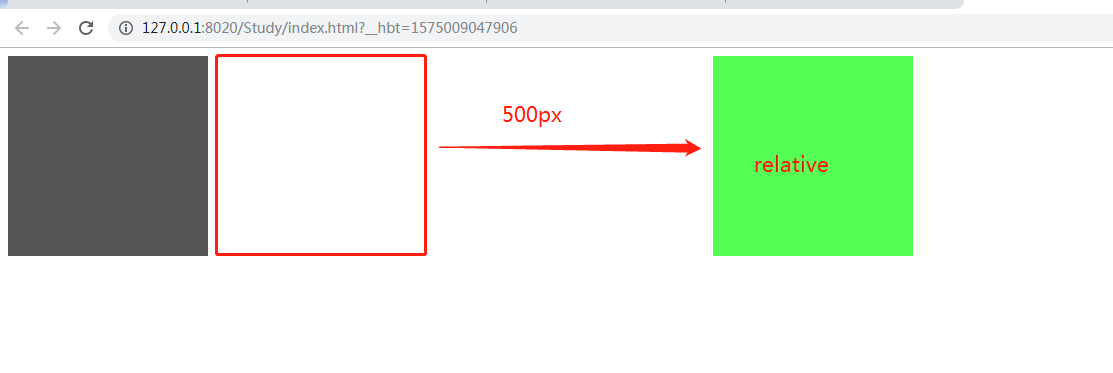
2、position: relative : 生成相对定位的元素,相对于其正常位置进行定位。元素位置还是处于正常流中,但是本身可以脱离原来位置。left,right,bottom,top将根据自身位置产生变化。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <title></title> <style> div{ display: inline-block; width: 200px; height: 200px; } .div1{ background: #555555; position: static; left: 500px; } .div2{ background: #55ff55; position: relative; left: 500px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="div1"></div> <div class="div2"></div> </body> </html>
结果:
3、position:absolute:生成绝对定位的元素,相对于 static 定位以外的第一个父元素进行定位。元素脱离正常流,出现浮动。元素的位置通过 "left", "top", "right" 以及 "bottom" 属性进行规定
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <title></title> <style> body>div{ width: 200px; height: 200px; } .div1{ background: #555555; margin: 0 auto; position: static; } .div-son1{ position: absolute; background: #ff5555; width: 100px; height: 100px; } .div-son2{ position: absolute; background: #5555ff; width: 100px; height: 100px; left: 20px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="div1"> <!--当父元素为static定位,一但使用了left、top、bottom、right,元素就向上会寻找父节点不是static的元素--> <div class="div-son1"></div> <div class="div-son2"></div> </div> </body> </html>
结果:

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <title></title> <style> body>div{ width: 200px; height: 200px; } .div1{ background: #555555; margin: 0 auto; position: relative; } .div-son1{ position: absolute; background: #ff5555; width: 100px; height: 100px; } .div-son2{ position: absolute; background: #5555ff; width: 100px; height: 100px; left: 20px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="div1"> <!-- 绝对定位,是绝对于父元素的,不受其他元素的影响 --> <div class="div-son1"></div> <div class="div-son2"></div> </div> </body> </html>
结果:

4、position: fixed ;生成固定定位的元素,相对于浏览器窗口进行定位。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <title></title> <style> .div1{ height: 2000px; } #fixed{ position: fixed; top: 300px; background: #ff00ff; height: 100px; width: 100%; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="div1"></div> <div id="fixed"></div> </body> </html>
结果:滚动滚动条div也一直地固定在页面

5、居中定位:水平居中-margin:0 auto;
.div1{ height: 200px; width: 200px; margin: 0 auto; background: #ff0000; }
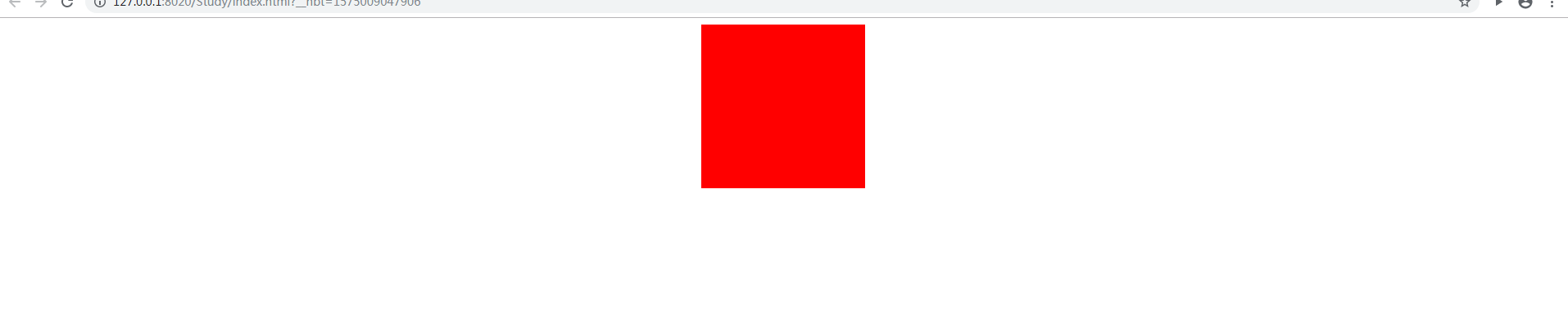
6、垂直居中
.div1{ height: 200px; width: 200px; position: absolute; bottom: 0; top: 0; margin: auto; background: #ff0000; }

8、中间居中
.div1{ height: 200px; width: 200px; position: absolute; top: 50%; left: 50%; margin-top: -100px; margin-bottom: -100px; background: #ff0000; }
.div1{ height: 200px; width: 200px; position: absolute; bottom: 0; top: 0; right: 0; left: 0; margin: auto; background: #ff0000; }
