Smart Pointer
std::unique_ptr - single ownership
std::shared_ptr - shared ownership
std::weak_ptr - temp / no ownership
为什么使用智能指针?
void bar(Entity* e) { // who owns e? // How long is e's life cycle? // Should I delete e? } void foo() { Entity* e = new Entity(); e->DoSomething(); bar(e); } foo(); // out of scope, memory leak
void bar(std::unique_ptr<Entity> e) { // bar owns e // e will be automatically destoryed } void foo() { auto e = std::unique_ptr<Entity>(); e->DoSomething(); bar(std::move(e)); } foo(); // no memory leak
1、创建unique_ptr
1 std::unique_ptr<Entity> e1 = new Entity(); //non-assignable 2 std::unique_ptr<Entity> e1(new Entity()); //OK 3 std::unique_ptr<Entity> e1 = std::make_unique<Entity>(); //preferred 4 auto e2 = std::make_unique<Entity>(); //preferred 5 std::unique_ptr<Entity> e2 = e1; //non-copyable 6 std::unique_ptr<Entity> e2 = std::move(e1); //moveable, transfer ownership 7 foo(std::move(e1)); //transfer ownership
Example:
1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <memory> 4 #include <string> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 class Entity { 9 public: 10 Entity() { puts("Entity created!"); } 11 ~Entity() { puts("Entity destoried!"); } 12 }; 13 14 void ex1() { 15 puts("------------"); 16 puts("Entering ex1"); 17 { 18 puts("Entering ex1::scope1"); 19 auto e1 = make_unique<Entity>(); 20 puts("Leaveing ex1::scope1"); 21 } 22 puts("Entering ex1"); 23 } 24 25 void foo(unique_ptr<Entity>) { 26 puts("Entering foo"); 27 puts("leaving foo"); 28 } 29 30 void ex2() { 31 puts("------------"); 32 puts("Entering ex2"); 33 auto e1 = make_unique<Entity>(); 34 foo(move(e1)); 35 // e1 was destoried. 36 puts("Leaving ex2"); 37 } 38 39 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) { 40 ex1(); 41 ex2(); 42 return 0; 43 }
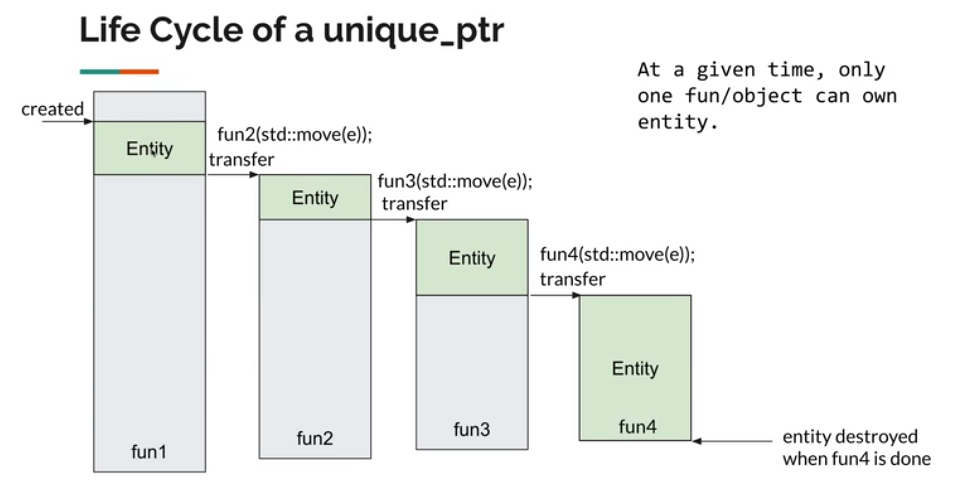
2、unique_ptr的生命周期
创建shared_ptr
1 std::shared_ptr<Entity> e1 = std::make_shared<Entity>(); // preferred 2 std::shared_ptr<Entity> e1(new Entity()); // OK 3 auto e1 = std::make_shared<Entity>(); // preferred 4 std::shared_ptr<Entity> e2 = e1; // copyable,use_count+1 5 std::shared_ptr<Entity> e2 = std::move(e1); // moveable, use_count remains 6 foo(std::move(e1)); // use_count remains 7 foo(e1); // use_count+1
example:
#include <cstdio> #include <iostream> #include <memory> #include <string> using namespace std; class Entity { public: Entity() { puts("Entity created!"); } ~Entity() { puts("Entity destoried!"); } }; oid ex3() { puts("-------------"); puts("Entering ex3"); auto e1 = make_shared<Entity>(); cout << e1.use_count() << endl; { puts("Entering ex3::scope1"); auto e2 = e1; cout << e1.use_count() << endl; auto e3 = move(e2); cout << e1.use_count() << endl; puts("Leaving ex3:scope1"); } cout << e1.use_count() << endl; puts("Leaving ex3"); } int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) { // ex1(); // ex2(); ex3(); return 0; }
out:

shared_ptr的生命周期
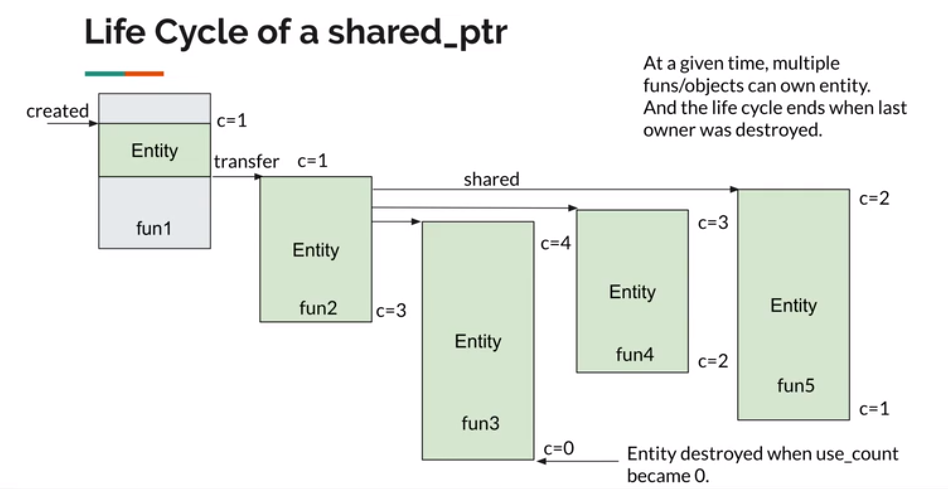
在fun1中创建了shared_ptr,transfer给fun2后引用计数还是1,在func2中用多线程调用了fun3,fun4,fun5,shared给它们
小结:
1.尽量使用智能指针而不是裸指针
2.优先使用unique_ptr
unique_ptr
正常情况下分配与释放动态内存:
#include <iostream> #include <memory> #include <string> using namespace std; int main(void) { string *str = new(string("hello world")); delete str; //需要手动去释放
return 0; }
使用智能指针unique_ptr
unique_ptr<string> pointer(new string("hello world")); // pointer是一个栈变量,在栈变量被回收后动态内存也会被回收 cout << *pointer << ' ';