 在web 里面叫tabs 选项卡。
在web 里面叫tabs 选项卡。这里从基本的开始:
场景:ContainerActivity 自动添加一个afragment ,ContainerActivity 页面有个按钮 ,点击按钮替换成bfragment。
ContainerActivity 代码: 这里有个按钮,和 FrameLayout
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".fragment.ContainerActivity"> <Button android:id="@+id/btn_chang" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="50dp" android:text="更换fragment"/> <FrameLayout android:id="@+id/fl_container" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" /> </RelativeLayout>
后台代码: 在create里面 通过 getSupportFragmentManager实例化得到 fragment 开启了beginTransaction后面add了一个 aFragment (本质是个类 对象 有对应的xml布局文件),
这里我也不理解为啥要开启事务,学习的是时候看别人都是这样写的,很奇怪
public class ContainerActivity extends AppCompatActivity { Fragment aFragment; Fragment bFragment; Button btn_chang; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_container); /*实例化 aFragment*/ /*如何向fragment 传递参数*/ aFragment=AFragment.newInstance("我是aFragment参数"); /*点击事件*/ btn_chang=findViewById(R.id.btn_chang); btn_chang.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { if (bFragment==null){ bFragment=new BFragment(); } getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction().replace(R.id.fl_container,bFragment).commitAllowingStateLoss();; } }); /*aFragment 添加到 activity 重点记得调用 commit这里使用commitAllowingStateLoss 横屏竖屏宽容性错误 */ getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction().add(R.id.fl_container,aFragment,"A").commitAllowingStateLoss(); } }
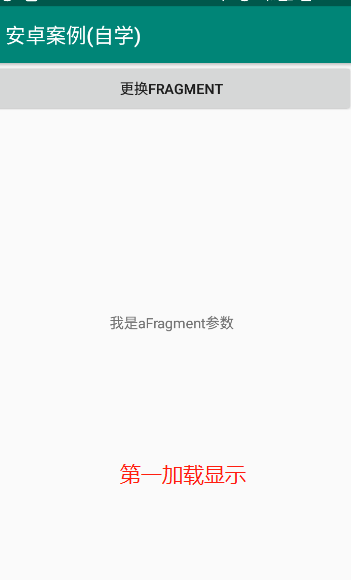
aFragment里面就一个行文字显示 没什么解释的
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:gravity="center"> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv_title" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="我是a fragment" android:gravity="center_horizontal"/> </LinearLayout>

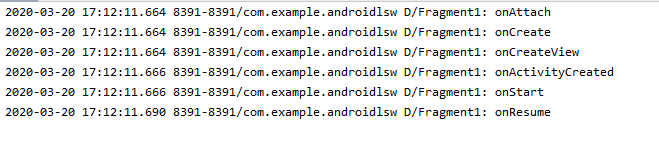
生命周期:(在前端框架也有各种生命周期 个人粗暴理解 在什么时候干什么事,这帮家伙定义的好的)没什么好的说的 实现所有方法 ,打印 看日志
package com.example.androidlsw.fragment; import android.app.Activity; import android.content.Context; import android.os.Bundle; import android.util.Log; import android.view.LayoutInflater; import android.view.View; import android.view.ViewGroup; import androidx.fragment.app.Fragment; import com.example.androidlsw.R; public class Fragment1 extends Fragment { public static final String TAG = "Fragment1"; @Override public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) { Log.d(TAG, "onCreateView"); return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment1, container, false); } @Override public void onAttach(Context context) { super.onAttach(context); Log.d(TAG, "onAttach"); } @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); Log.d(TAG, "onCreate"); } @Override public void onActivityCreated(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState); Log.d(TAG, "onActivityCreated"); } @Override public void onStart() { super.onStart(); Log.d(TAG, "onStart"); } @Override public void onResume() { super.onResume(); Log.d(TAG, "onResume"); } @Override public void onPause() { super.onPause(); Log.d(TAG, "onPause"); } @Override public void onStop() { super.onStop(); Log.d(TAG, "onStop"); } @Override public void onDestroyView() { super.onDestroyView(); Log.d(TAG, "onDestroyView"); } @Override public void onDestroy() { super.onDestroy(); Log.d(TAG, "onDestroy"); } @Override public void onDetach() { super.onDetach(); Log.d(TAG, "onDetach"); } }
这里使用一个小技巧在 android studio logcat页面新建一个过滤;名字上面的TAG
如图:
启动打印:
安home键:

在打开:

返回back

看到这里,我相信大多数朋友已经非常明白了,因为这和Activity的生命周期太相似了。只是有几个Activity中没有的新方法,这里需要重点介绍一下:
onAttach方法:Fragment和Activity建立关联的时候调用。
onCreateView方法:为Fragment加载布局时调用。
onActivityCreated方法:当Activity中的onCreate方法执行完后调用。
onDestroyView方法:Fragment中的布局被移除时调用。
onDetach方法:Fragment和Activity解除关联的时候调用。
activity生命周期https://www.cnblogs.com/nylcy/p/6500832.html
使用场景:
第一次学习我也很苦恼为什么安卓设计出来这么一套, 引出(比如你在某a app 正在打游戏 或者做一些事),来了电话, 或者在一个输入框 ,突然按下home 在打开 之前的输入的内容不见了。
这些都是和生命周期有关系。 个人猜测是因为手机是单窗口, 当打开某一个运用后,其他的app运用,假死,系统设计 从资源,硬件使用角度回收资源, 提高性能,但是增加复杂度,开发成本。
也不知道理解对不对。