数据库:
数据库就是存储数据的仓库
为了方便数据的存储和管理,它将数据按照特定的规律存储在磁盘上,通过数据库的管理系统,可以有效的管理存储在数据库中的数据;
mysql数据库的优点:
1.多语言的支持
2.可以移植性好,
3.免费开源,
4.高效
5.支持大量数据的存储和查询
sql语言:
就是结构化查询语言 数据管理系统通过sql语言来管理数据库中的数据
其中
DDL语句:create alter drop
DML语句:update select delect insert
DCL语句:是数据库控制功能 用来设置或更改数据库中用户和角色的权限的语句 包含revoke deny grant等
mysql常用命令:
显示所有数据库:show databases
选定数据库:use name
显示数据库中所有表:show tables
放弃正在输入的命令:c
显示命令清单:h
退出mysql:q
查看mysql服务器状态信息:s
创建数据库:create database+数据库名
显示数据库结构:show create database+数据库名
删除数据库:drop database+数据库名
mysql -u账号 -p密码
mysql的安装:yum安装 rpm安装 源码安装
mysql的连接和登陆:
1)mysql自带的sql客户端连接
mysql -h host -p 3306 -u user -ppassword
-h:当连接mysql服务器不在同一台主机时,填写主机名或ip地址 默认的是localhost;
-P:访问mysql服务器的端口,默认是3306;
-u:登录服务器的用户名;
-p:登录服务器的密码;
注意:密码如果写在命令行时一定不要有空格
2)图形化界面管理工具连接
navicat ,sqlyag。。。
mysql的数据类型:
数据类型是数据的一种属性,可以决定数据的存储格式,有效范围和相应的限制
包含:
1)整数类型 int
2)浮点数类型 float
3)定点数类型 decimal
4)日期和时间类型
date: ‘YYYY-MM-DD’
time:'HH:ii:ss’
year:就是date和time混合一起
5)字符串类型
char
varchar
text
6)二进制类型 bit
数据库
为数据库授权:grant 权限 on 数据库对象 to 用户
例子:增加一个超级用户,拥有所有权限,只允许本地登录
grant all on *.* 'zyy'@'localhost' identified by '12345' with grant option;
取消数据库权限:
revoke 权限 on 数据库对象 from 用户
例子;取消zyy的超级用户权限
revoke all on *.* zyy@localhost ;
为数据库设置密码:
1>使用set password
set password for zyy=password(‘12345’);
2>使用update语句
update user set password=password(‘12345’) where user=‘zyy’;
3>删除用户
delect from user where user=‘zyy’;
表:
主键:唯一标示一条记录,不能有重复的,不允许为空,主键只能有一个
外键:表的外键是令一表的主键,外键可以重复,也可以为空,一个表可以有多个外键
表的常用命令:
创建表:create table+表名(表内容)
查看表结构:desc+表名或者show create table+表名
修改表名:alter table 旧表名 rename 新表名
修改数据类型:alter table 表名 modify 属性名 数据类型 或者 alter table 旧表名change 旧属性名 新属性名数据类型![]()
![]()
增加表内的字段:alter table 表名 add 属性名 数据类型
![]()
增加表的外键:alter table 表名 add constriaint 外键的字段名 deferenges 外表表名

删除表的外键约束:alter table表名 drop foreign key 外键别名
![]()
删除字段:alter table 表名 drop 字段名
删除表:drop table 表名
常见的唯一性约束:
主码约束(主键):primary key
唯一性约束:unique
非空值约束:not null
用于整数列自增长:auto_increment
无符号整数:unsigend
默认值约束:default default_value
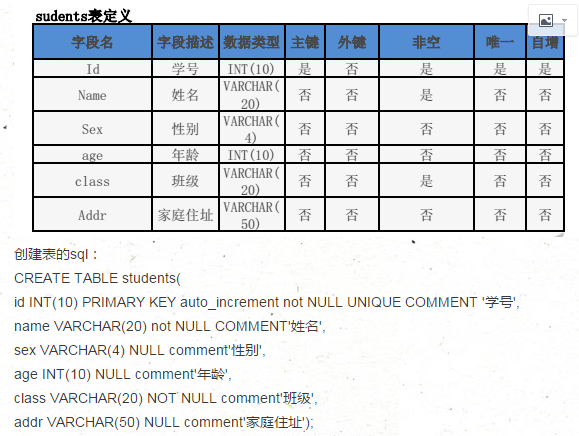
创建表例子:
数据
数据的常用命令:
为表内所有字段插入数据:insert into 表名 values(插入内容)
![]()
为表的指定字段插入内容:insert into 表名(属性)values(值)
![]()
查询结果插入表中:insert into 表名1(属性1)
select 属性2 from表名2where 表达式

更新数据:update 表名 set 属性1=取值1 属性2=取值2 where 条件表达式
删除数据:delect from where 条件表达式
例子:delect from students where name=‘zyy’;
select * from students
基本查询语句:select 属性 from 表名 where 条件表达式
单表查询:就是从一张表中查询所需要的数据
查询所有字段:使用‘*’代表所有字段
select * from 表名
查询指定字段:select name from students
设置查询条件:例子:select name from students where id=1;
多表查询:在多张表中查询所需要的数据,一般查询的这几张表中都有一个相同的字段关联这几张表
join关键字来连接:
left join:左连接,就是连接两张表,以左边表的数据匹配右边表的数据, 如果左边表的数据右边没有,就会显示左边表中的全部数据,右边表中不同的部分不显示;
right join:右连接,就是连接两张表,以右边表的数据匹配左边表的数据,如果右边表的数据左边表没有,就会显示右边表的全部数据,左边表中不同的部分不显示;
inner join:内连接。连接两张表,匹配两张表的中数据,只会显示匹配的数据;
为表起别名:使用关键字as
例子:select name from students as a ,qdd as b where a.id=b.id;
带in关键字查询:in关键字可以判断某个字段是否在指定的集合中;
例子:select * from students where id in(1,2);
带or的多关键字查询:使用or就是之言满足值几个查询条件中的一个即可
例子:select * from students where id=1 or id=2;
带and的多条件查询:使用and就是同时满足所有查询条件才会被查询出来;
例子: select * from students where name='zyy' and id>10;
带between and的范围查询:是指某个字段是否在指定的范围内;
例子: select * from students where score between 50 and 100;
带like的字符匹配查询:
%通配符:包含零个或者多个字符组成的任意字符串
_下划线通配符:任意一个字符
例子:select * from students where name like '赵%';
select * from students where name like '赵_';
查询空值: is null来判断字段是否为空
例子:select * from students where name is null;
对查询结果进行排序: asc升序 desc是降序 默认是升序 使用order by
例子; select * from students where sex=‘女' order by score;
查询多少之间: select * from 表名 limit 1,5
limit:不顾头只顾尾
例子:select * from blk limit 1.5 查询第一行之后的五条信息
select * from blk lmit 5 查询5条信息
聚合函数查询:用group by 关键字与集合函数一起使用
包含:count()统计记录条数
例子:select count(*) from students;
sum()用来计算字段值的总和
例子:select sum(score)总成绩 from students;
avg()用来计算字段的平均值
例子:select students.name,avg(b.score) from students a,score b where a.id=b.id1;
max()用来查询字段的最大值
例子:select a.name,max(b.score) from students a,score b where a.id=b.id1;
min()用来查询字段的最小值
例子:select max(score)最高分,min(score)最低分 from score;
group by子句:
group by 关键字可以将查询结果按照某个字段或多个字段进行分组
group by 属性名 having 条件表达式
group by 与聚合函数:
例子:统计每个班的人数(students ,class两个表)
select b.class_name班级名称 ,count(b.student_id)学生人数 from students a,class b where a.id=b.student_id group by b.class_name;
group by 与having 子句;
例子:查询2班男生女生人数(students ,class两个表)
select a.sex,count(b.id) from students a,class b where a.id=b.student_id group by a.sex having b.class_name=2;
合并结果集:
使用union将多个select语句查询结果集组成一个结果集
例子:有学生表和教师表,要查出所有学生和教师
select name,sex from students union select teacher_name,sex from teacher

子查询:
如果一个select语句能够返回一个值或者一列值,且该select语句嵌套在另一个sql语句中,那么该select语句成为子查询
例子:把成绩高于60分的改为天才
update students set name='天才'where id in(select a.student_id from score a where a.score>60);
例子:把没有提过bug的人员查出来
select a.name from user a where id not in(select b.create_by from bug b) and a.id<1;
比较运算符:
‘=’ ‘!=’ ‘>=’ ‘<=’ ‘<’ ‘>’