引用:https://blog.csdn.net/T2080305/article/details/84651873
https://blog.csdn.net/T2080305/article/details/84651873
https://blog.csdn.net/rambler_designer/article/details/78144808
ArrayList
创建对象:
[ArrayList<要存储元素的数据类型> 变量名 = new ArrayList<要存储元素的数据类型>();
]
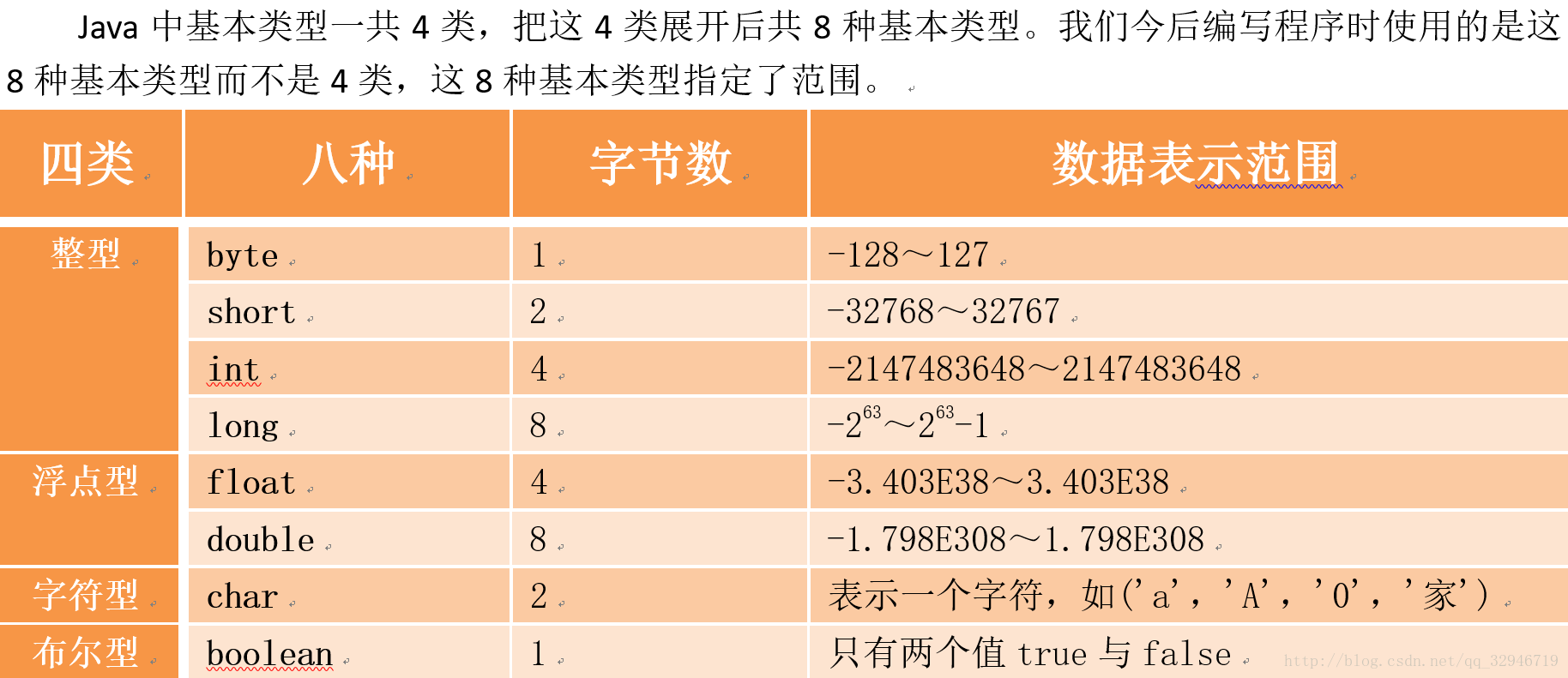
基本数据类型 对应的引用数据类型表示形式
byte Byte
short Short
Int Integer
long Long
float Float
double Double
char Character
boolean Boolean
从数组创建一个 ArrayList
String[] stringArray = { "a", "b", "c", "d", "e" };
ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<String>(Arrays.asList(stringArray));
增加元素到链表中
boolean add(Element e) //增加指定元素到链表尾部.
boolean add(int index, Element e) //增加指定元素到链表指定位置.
boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) //将指定collection中的所有元素插入到ArrayList中
boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) //从指定的位置开始,将指定collection 中的所有元素插入到ArrayList中
从链表中删除元素
void clear() //从链表中删除所有元素.
E remove(int index) //删除链表中指定位置的元素.
boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) //根据重写Predicate类的test方法选择删除集合中的元素
boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) //移除ArrayList中Collection所包含的所有元素
boolean remove(Object o) //移除ArrayList中首次出现的指定元素(如果存在则移除并返回true,否则返回false)
获取链表中的元素
E get(int index) //获取链表中指定位置处的元素.
Object[] toArray() //获取一个数组,数组中所有元素是链表中的元素.(即将链表转换为一个数组)
<T> T[] toArray(T[] a) //构造一个数组
List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) //获取从fromIndex到toIndex位置的元素
修改某个元素
E set(int index, E element) //将链表中指定位置上的元素替换成新元素。
搜索元素
boolean contains(Object o) //如果链表包含指定元素,返回true.
int indexOf(Object o) //返回元素在链表中**第一次**出现的位置,如果返回-1,表示链表中没有这个元素。
int lastIndexOf(Object o) //返回元素在链表中**最后一次**出现的位置,如果返回-1,表示链表中没有这个元素。
检查链表是否为空
boolean isEmpty() //返回true表示链表中没有任何元素. 判断逻辑是size == 0
获取链表大小
int size() //返回链表长度(链表包含元素的个数).
反转链表/排序链表
Collections.reverse(arrayList);
//sort方法:最大的问题,没办法sort list部分,只能用array
Comparator c = new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if((int)o1<(int)o2)
return 1;
//注意!!返回值必须是一对相反数,否则无效。jdk1.7以后就是这样。
//else return 0; //无效
else return -1;
}
};
Collections.sort(listStr);
list01.sort(c);//笔试时经常使用Java7,list并没有sort方法,请使用Collections.sort()
Collections.sort(list02,c);
数组
声明数组
String[] aArray = new String[5];
String[] bArray = {"a","b","c", "d", "e"};
String[] cArray = new String[]{"a","b","c","d","e"};
转成String
String intArrayString = Arrays.toString(intArray);//不推荐,输出[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
char[] t = new char[]{'a','b','c'};
String s = new String(t);//输出“abc”
合并数组
int[] combinedIntArray = ArrayUtils.addAll(intArray, intArray2);
把数组中的元素用指定的分隔符连接起来
String j = StringUtils.join(new String[] { "a", "b", "c" }, ", ");//输出a, b, c
反转数组
ArrayUtils.reverse(intArray);
移除数组中的元素
int[] removed = ArrayUtils.removeElement(intArray, 3);//create a new array
复制
1.arraycopy(sourceArray,int index1,copyArray,index2,int length):从sourceArray的index1位置开始,后面length个元素,放到copyArray数组从index2的位置
int []a = {1,2,3,4,5};
int []b = {6,7,8,9,10};
System.arraycopy(a, 2, b, 3, 2);//b为6 7 8 3 4
2.copyOf(float []original,int newLength):从数组的第一个元素开始复制,复制长度为length,若长度超过数组原长,则超出元素为默认值0,返回一个数组
int []a = {11,22,33,44,55};
int []b = Arrays.copyOf(a, 7);//11 22 33 44 55 0 0
3.copyOfRange(double []original,int from,int to)
int []a = {55,33,44,22,11};
int []b = Arrays.copyOfRange(a, 1, 4);//[33, 44, 22]
sort
sort(doule a[]);//将数组按升序全排序
sort(doule a[],int start,int end);//从索引为start到索引为end-1的位置,升序排序
在数组中查找一个数
binarySearch(double [] a,double number);//返回要寻找的数number的索引,若没查找到,则返回一个负数