Expression表达式目录树:一个能拼装能解析的数据结构,语法树。
一、手动拼装表达式目录树
示例1:
/// <summary> /// 展示表达式树,协助用的 /// 编译lambda--反编译C#--得到原始声明方式 /// </summary> public class ExpressionTreeVisualizer { public static void Show() { //lambda表达式声明表达式目录树(快捷方式),是一个数据结构 //不能有语句体,只能是一行,不能有大括号 Expression<Func<int, int, int>> expression = (m, n) => m * n + m + n + 2; //int iResult = expression.Compile().Invoke(23, 34); } }
上面的这种方式是使用lambda表达式快捷的声明表达式目录树,那我们怎么手动拼装这样子的一个表达式目录树呢?
此处我们借助反编译工具ILSpy,编译lambda--反编译C#--得到原始声明方式
反编译示例1后得到的结果如下:
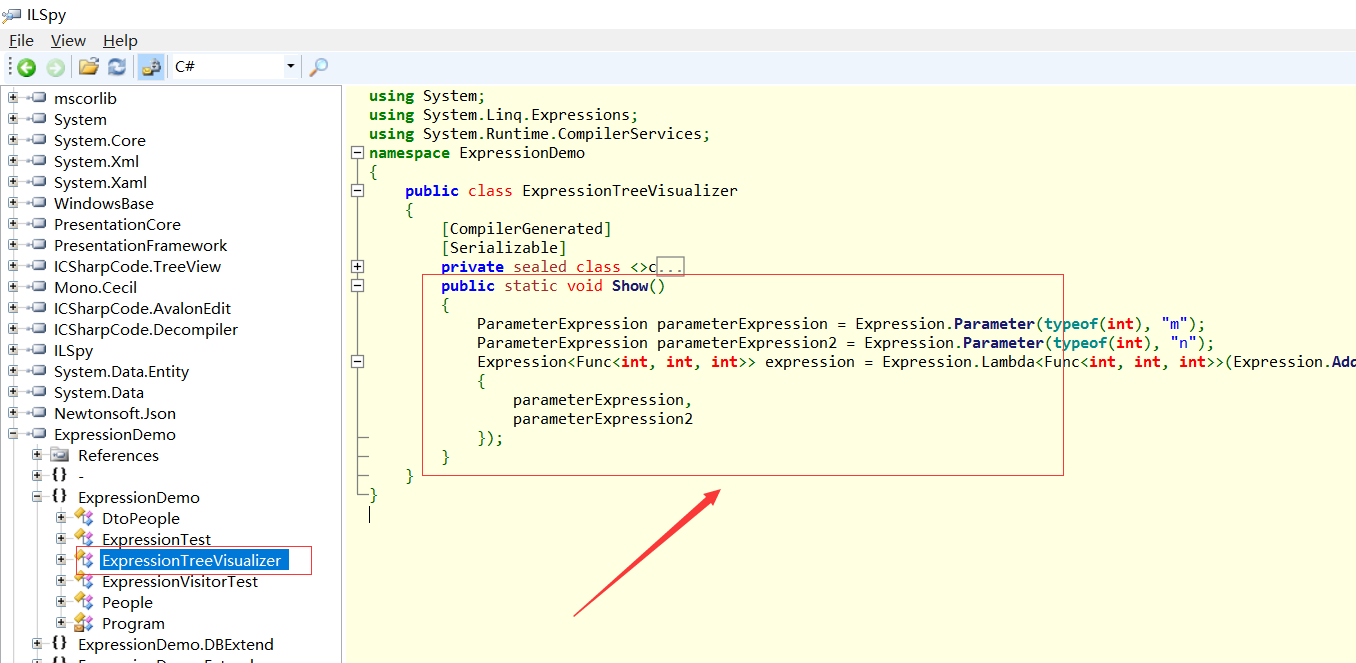
public static void Show() { ParameterExpression parameterExpression = Expression.Parameter(typeof(int), "m"); ParameterExpression parameterExpression2 = Expression.Parameter(typeof(int), "n"); Expression<Func<int, int, int>> expression = Expression.Lambda<Func<int, int, int>>(Expression.Add(Expression.Add( Expression.Add(Expression.Multiply(parameterExpression, parameterExpression2), parameterExpression), parameterExpression2), Expression.Constant(2, typeof(int))), new ParameterExpression[] { parameterExpression, parameterExpression2 }); }
然后根据反编译后得到的结果作为参考,再手动拼装表达式目录树,如下所示:
{ //Expression<Func<int, int, int>> expression = (m, n) => m * n + m + n + 2; //int iResult = expression.Compile().Invoke(23, 34); ParameterExpression m = Expression.Parameter(typeof(int), "m"); ParameterExpression n = Expression.Parameter(typeof(int), "n"); var constant = Expression.Constant(2); var mutiply = Expression.Multiply(m, n); var plus1 = Expression.Add(mutiply, m); var plus2 = Expression.Add(plus1, n); var plus3 = Expression.Add(plus2, constant); Expression<Func<int, int, int>> expression = Expression.Lambda<Func<int, int, int>>(plus3, new ParameterExpression[] { m, n }); int iResult = expression.Compile().Invoke(23, 34); }
运行后就可以发现我们动态的拼装出来了:

示例2:
/// <summary> /// 展示表达式树,协助用的 /// 编译lambda--反编译C#--得到原始声明方式 /// </summary> public class ExpressionTreeVisualizer { public static void Show() { //lambda表达式声明表达式目录树(快捷方式),是一个数据结构 //不能有语句体,只能是一行,不能有大括号 //Expression<Func<int, int, int>> expression = (m, n) => m * n + m + n + 2; //int iResult = expression.Compile().Invoke(23, 34); Expression<Func<People, bool>> lambda = x => x.Id.ToString().Equals("5"); } }
反编译示例2后得到的结果如下:
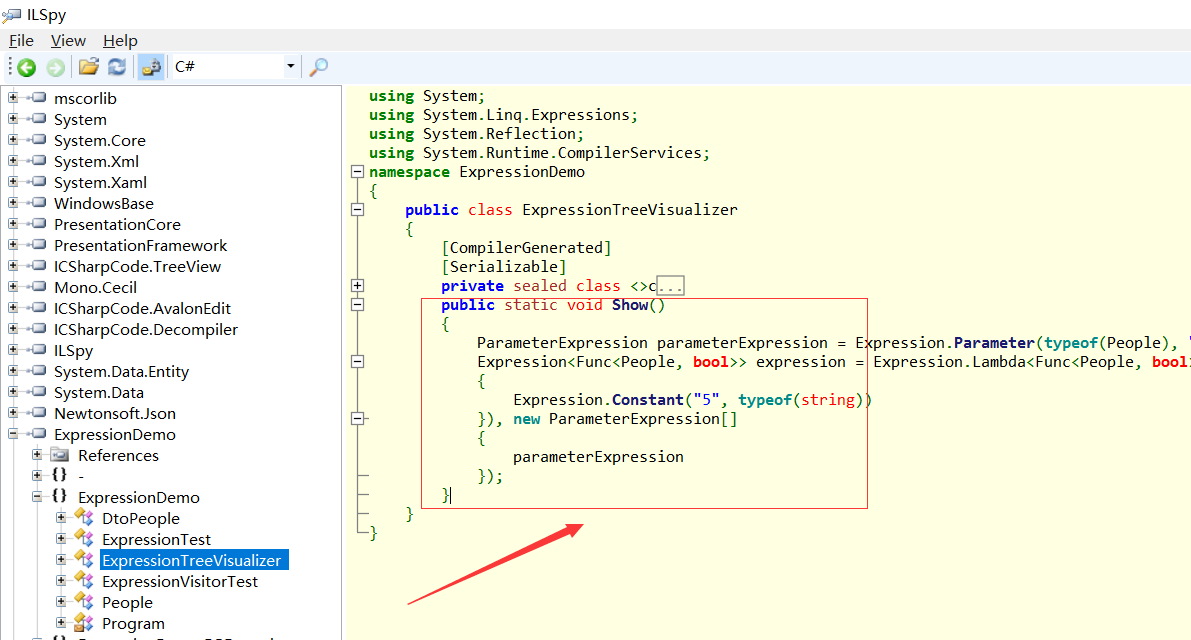
public static void Show() { ParameterExpression parameterExpression = Expression.Parameter(typeof(People), "x"); Expression<Func<People, bool>> expression = Expression.Lambda<Func<People, bool>>(Expression.Call(Expression.Call(Expression.Field(parameterExpression, FieldInfo.GetFieldFromHandle(ldtoken(Id))), (MethodInfo)MethodBase.GetMethodFromHandle(ldtoken(ToString())), new Expression[0]), (MethodInfo)MethodBase.GetMethodFromHandle(ldtoken(Equals())), new Expression[] { Expression.Constant("5", typeof(string)) }), new ParameterExpression[] { parameterExpression }); }
同理我们根据反编译后得到的结果作为参考,再手动拼装表达式目录树,如下所示:
{ //Expression<Func<People, bool>> lambda = x => x.Id.ToString().Equals("5"); ParameterExpression parameterExpression = Expression.Parameter(typeof(People), "x"); var constantExp = Expression.Constant("5"); FieldInfo field = typeof(People).GetField("Id"); var fieldExp = Expression.Field(parameterExpression, field); var toString = typeof(int).GetMethod("ToString", new Type[] { }); var toStringExp = Expression.Call(fieldExp, toString, new Expression[0]); var equals = typeof(string).GetMethod("Equals", new Type[] { typeof(string) }); var equalsExp = Expression.Call(toStringExp, equals, new Expression[] { constantExp }); Expression<Func<People, bool>> expression = Expression.Lambda<Func<People, bool>>(equalsExp, new ParameterExpression[] { parameterExpression }); bool bResult = expression.Compile()(new People() { Id = 5, Name = "浪子天涯", Age = 20 }); }
运行结果如下:
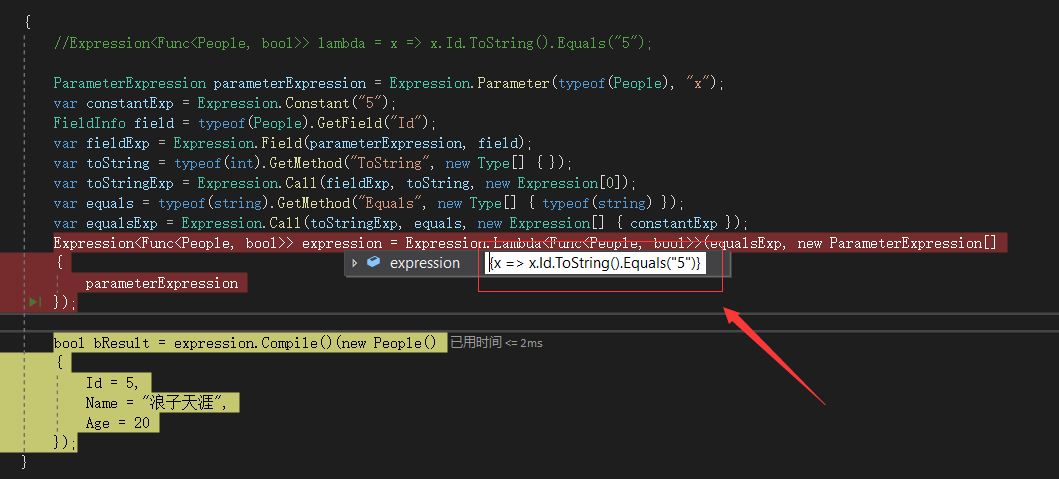
手动拼装表达式目录树的目的:
1、使用lambda表达式声明表达式目录树(快捷方式)这是硬编码,硬编码就无法做到动态,但是我们可以借助手动拼装表达式目录树来动态生成硬编码。
2、表达式目录树可以转换成委托,手动拼装表达式目录树就相当于可以动态生成委托。
3、表达式目录树是一个能拼装能解析的数据结构,语法树。手动拼装成功后,后面就可以根据实际需要去解析表达式目录树完成相应的操作。
二、表达式目录树应用场景
下面我们来看个简单的例子:
需求:一个Web应用通过前端收集用户的输入成为Dto,然后将Dto转换成领域模型并持久化到数据库中。也就是说在实际的软件开发项目中,我们的“业务逻辑”常常需要我们对同样的数据进行各种变换。
解决这个问题我们的常规做法是:使用AutoMapper来完成Dto与Model之间的实体映射。
此处引发一个思考:如果让我们自己来完成实体映射,那么我们有哪些解决思路呢?
准备测试用的实体和Dto:
/// <summary> /// 实体 /// </summary> public class People { public int Age { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public int Id; } /// <summary> /// Dto /// </summary> public class DtoPeople { public int Age { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public int Id; }
第1种解决思路:硬编码
People people = new People() { Id = 1, Name = "测试", Age = 22 }; for (int i = 0; i < 1_000_000; i++) { DtoPeople dtoPeople = new DtoPeople() { Id = people.Id, Name = people.Name, Age = people.Age }; }
第2种解决思路:反射
/// <summary> /// 反射映射 /// </summary> public class ReflectionMapper { /// <summary> /// 实体转换 /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="T">传入类型</typeparam> /// <typeparam name="TResult">返回值类型</typeparam> /// <param name="tIn">传入参数</param> /// <returns>转换好的实体</returns> public static TResult Trans<T, TResult>(T tIn) { TResult tOut = Activator.CreateInstance<TResult>(); foreach (var itemOut in tOut.GetType().GetProperties()) { var propIn = tIn.GetType().GetProperty(itemOut.Name); itemOut.SetValue(tOut, propIn.GetValue(tIn)); } foreach (var itemOut in tOut.GetType().GetFields()) { var fieldIn = tIn.GetType().GetField(itemOut.Name); itemOut.SetValue(tOut, fieldIn.GetValue(tIn)); } return tOut; } }
第3种解决思路:序列化反序列化
/// <summary> /// 使用第三方序列化反序列化工具 /// </summary> public class SerializeMapper { /// <summary> /// 实体转换 /// </summary> public static TResult Trans<T, TResult>(T tIn) { return JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<TResult>(JsonConvert.SerializeObject(tIn)); } }
第4种解决思路:表达式目录树 + 字典缓存
/// <summary> /// 生成表达式目录树 字典缓存 /// </summary> public class ExpressionMapper { /// <summary> /// 字典缓存--hash分布 /// </summary> private static Dictionary<string, object> _dic = new Dictionary<string, object>(); /// <summary> /// 实体转换 /// </summary> public static TResult Trans<T, TResult>(T tIn) { string key = string.Format("funckey_{0}_{1}", typeof(T).FullName, typeof(TResult).FullName); if (!_dic.ContainsKey(key)) { ParameterExpression parameterExpression = Expression.Parameter(typeof(T), "p"); List<MemberBinding> memberBindingList = new List<MemberBinding>(); foreach (var item in typeof(TResult).GetProperties()) { MemberExpression property = Expression.Property(parameterExpression, typeof(T).GetProperty(item.Name)); MemberBinding memberBinding = Expression.Bind(item, property); memberBindingList.Add(memberBinding); } foreach (var item in typeof(TResult).GetFields()) { MemberExpression property = Expression.Field(parameterExpression, typeof(T).GetField(item.Name)); MemberBinding memberBinding = Expression.Bind(item, property); memberBindingList.Add(memberBinding); } MemberInitExpression memberInitExpression = Expression.MemberInit(Expression.New(typeof(TResult)), memberBindingList.ToArray()); Expression<Func<T, TResult>> lambda = Expression.Lambda<Func<T, TResult>>(memberInitExpression, new ParameterExpression[] { parameterExpression }); Func<T, TResult> func = lambda.Compile(); //调用Compile方法将表达式转换成委托 _dic[key] = func; //拼装是一次性的 } return ((Func<T, TResult>)_dic[key]).Invoke(tIn); } }
第5种解决思路:表达式目录树 + 泛型缓存(泛型缓存特点:为不同类型的组合去缓存一个结果。)
/// <summary> /// 生成表达式目录树 泛型缓存 /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="T">传入参数类型</typeparam> /// <typeparam name="TResult">返回值类型</typeparam> public class ExpressionGenericMapper<T, TResult> { /// <summary> /// 泛型缓存 /// </summary> private static Func<T, TResult> _func = null; /// <summary> /// 静态构造函数(只会被调用一次) /// </summary> static ExpressionGenericMapper() { ParameterExpression parameterExpression = Expression.Parameter(typeof(T), "p"); List<MemberBinding> memberBindingList = new List<MemberBinding>(); foreach (var item in typeof(TResult).GetProperties()) { MemberExpression property = Expression.Property(parameterExpression, typeof(T).GetProperty(item.Name)); MemberBinding memberBinding = Expression.Bind(item, property); memberBindingList.Add(memberBinding); } foreach (var item in typeof(TResult).GetFields()) { MemberExpression property = Expression.Field(parameterExpression, typeof(T).GetField(item.Name)); MemberBinding memberBinding = Expression.Bind(item, property); memberBindingList.Add(memberBinding); } MemberInitExpression memberInitExpression = Expression.MemberInit(Expression.New(typeof(TResult)), memberBindingList.ToArray()); Expression<Func<T, TResult>> lambda = Expression.Lambda<Func<T, TResult>>(memberInitExpression, new ParameterExpression[] { parameterExpression }); _func = lambda.Compile();//拼装是一次性的 } /// <summary> /// 实体转换 /// </summary> public static TResult Trans(T t) { return _func(t); } }
下面我们来测试下这5种方案的性能:
/// <summary> /// 性能测试 /// </summary> public static void MapperTest() { People people = new People() { Id = 1, Name = "测试", Age = 22 }; long common = 0; long generic = 0; long cache = 0; long reflection = 0; long serialize = 0; //硬编码 { Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch(); watch.Start(); for (int i = 0; i < 1_000_000; i++) { DtoPeople dtoPeople = new DtoPeople() { Id = people.Id, Name = people.Name, Age = people.Age }; } watch.Stop(); common = watch.ElapsedMilliseconds; } //反射 { Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch(); watch.Start(); for (int i = 0; i < 1_000_000; i++) { DtoPeople dtoPeople = ReflectionMapper.Trans<People, DtoPeople>(people); } watch.Stop(); reflection = watch.ElapsedMilliseconds; } //序列化反序列化 { Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch(); watch.Start(); for (int i = 0; i < 1_000_000; i++) { DtoPeople dtoPeople = SerializeMapper.Trans<People, DtoPeople>(people); } watch.Stop(); serialize = watch.ElapsedMilliseconds; } //表达式目录树 + 字典缓存 { Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch(); watch.Start(); for (int i = 0; i < 1_000_000; i++) { DtoPeople dtoPeople = ExpressionMapper.Trans<People, DtoPeople>(people); } watch.Stop(); cache = watch.ElapsedMilliseconds; } //表达式目录树 + 泛型缓存 { Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch(); watch.Start(); for (int i = 0; i < 1_000_000; i++) { DtoPeople dtoPeople = ExpressionGenericMapper<People, DtoPeople>.Trans(people); } watch.Stop(); generic = watch.ElapsedMilliseconds; } Console.WriteLine($"common = { common} ms"); Console.WriteLine($"reflection = { reflection} ms"); Console.WriteLine($"serialize = { serialize} ms"); Console.WriteLine($"cache = { cache} ms"); Console.WriteLine($"generic = { generic} ms"); //性能比AutoMapper还要高 }
来看下运行结果:

从运行结果可以看出硬编码的性能是最高的,其次就是我们的表达式目录树 + 泛型缓存,这2个的性能几乎是同一个数量级的。
小结:
1、既需要考虑动态(通用),又要保证性能(硬编码)---动态生成硬编码---表达式目录树拼装(动态生成委托)(得到的就是硬编码)。
2、如果使用反射来实现某个功能时性能不高,可以考虑使用表达式目录树拼装来实现这个功能(动态生成委托)。
3、不能将具有语句体的Lambda表达式转换为表达式目录树。(即只能是一行且不能有大括号)
反编译工具ILSpy:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1ngh2AK9HrKLVLi8ng8vcrQ 提取码:c9x5