1、自动配置原理
2、@Conditional派生注解(Spring注解版原生的@Conditional作用)
3、demo
1、自动配置原理 <--返回目录
1)SpringBoot启动的时候加载主配置类,开启了自动配置功能 @EnableAutoConfiguration
2)@EnableAutoConfiguration 作用:
利用EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector给容器中导入一些组件?
可以查看selectImports()方法的内容;
List configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);获取候选的配置
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames() 扫描所有jar包类路径下 META‐INF/spring.factories 把扫描到的这些文件的内容包装成properties对象 从properties中获取到EnableAutoConfiguration.class类(类名)对应的值,然后把他们添加在容器中
将 类路径下 META-INF/spring.factories 里面配置的所有EnableAutoConfiguration的值加入到了容器中:
# Auto Configure org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration= org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.amqp.RabbitAutoConfiguration, ...
每一个这样的 xxxAutoConfiguration类都是容器中的一个组件,都加入到容器中;用他们来做自动配置;
3)每一个自动配置类进行自动配置功能;
4)以HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(Http编码自动配置)为例解释自动配置原理:
@Configuration //表示这是一个配置类,以前编写的配置文件一样,也可以给容器中添加组件 @EnableConfigurationProperties(HttpEncodingProperties.class) //启动指定类的 //ConfigurationProperties功能;将配置文件中对应的值和HttpEncodingProperties绑定起来;并把 //HttpEncodingProperties加入到ioc容器中 @ConditionalOnWebApplication //Spring底层@Conditional注解(Spring注解版),根据不同的条件,如果 //满足指定的条件,整个配置类里面的配置就会生效; 判断当前应用是否是web应用,如果是,当前配置类生效 @ConditionalOnClass(CharacterEncodingFilter.class) //判断当前项目有没有这个类CharacterEncodingFilter;SpringMVC中进行乱码解决的过滤器; @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.http.encoding", value = "enabled", matchIfMissing = true) //判断配置文件中是否存在某个配置 spring.http.encoding.enabled;如果不存在,判断也是成立的 //即使我们配置文件中不配置pring.http.encoding.enabled=true,也是默认生效的; public class HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration { //他已经和SpringBoot的配置文件映射了 private final HttpEncodingProperties properties; //只有一个有参构造器的情况下,参数的值就会从容器中拿 public HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(HttpEncodingProperties properties) { this.properties = properties; } @Bean //给容器中添加一个组件,这个组件的某些值需要从properties中获取 @ConditionalOnMissingBean(CharacterEncodingFilter.class) //判断容器没有这个组件? public CharacterEncodingFilter characterEncodingFilter() { CharacterEncodingFilter filter = new OrderedCharacterEncodingFilter(); filter.setEncoding(this.properties.getCharset().name()); filter.setForceRequestEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(Type.REQUEST)); filter.setForceResponseEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(Type.RESPONSE)); return filter; }
根据当前不同的条件判断,决定这个配置类是否生效?
一但这个配置类生效;这个配置类就会给容器中添加各种组件;这些组件的属性是从对应的properties类中获取的,这些类里面的每一个属性又是和配置文件绑定的;
5)所有在配置文件中能配置的属性都是在xxxxProperties类中封装者‘;配置文件能配置什么就可以参照某个功能对应的这个属性类
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.http.encoding") //从配置文件中获取指定的值和bean的属性进行绑定 public class HttpEncodingProperties { public static final Charset DEFAULT_CHARSET = Charset.forName("UTF‐8");
精髓:
1)SpringBoot启动会加载大量的自动配置类
2)我们看我们需要的功能有没有SpringBoot默认写好的自动配置类;
3)我们再来看这个自动配置类中到底配置了哪些组件;(只要我们要用的组件有,我们就不需要再来配置了)
4)给容器中自动配置类添加组件的时候,会从properties类中获取某些属性。我们就可以在配置文件中指定这些属性的值;
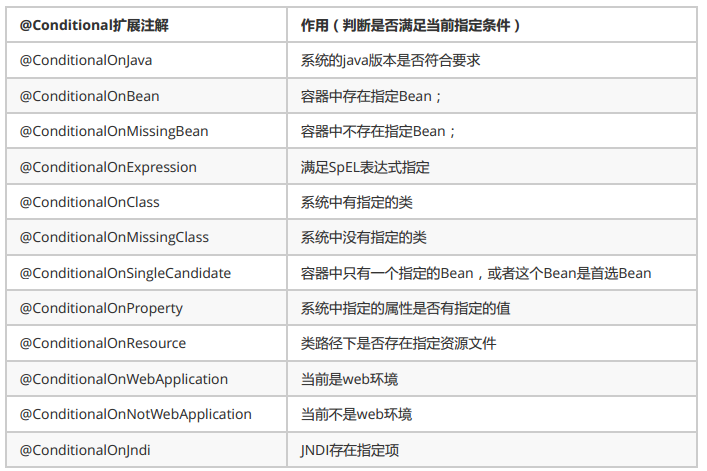
2、@Conditional派生注解(Spring注解版原生的@Conditional作用) <--返回目录
作用:必须是@Conditional指定的条件成立,才给容器中添加组件,配置配里面的所有内容才生效;
3、demo <--返回目录
项目结构

pom.xml

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.1.2.RELEASE</version> <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <groupId>com.oy</groupId> <artifactId>SpringBoot10-autoconfig</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>SpringBoot10-autoconfig</name> <description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description> <properties> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
启动类 Application

package com.oy; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; @SpringBootApplication public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args); } }
A 类
package com.oy.config; /** * @author oy * @version 1.0 * @date 2019年1月19日 * @time 上午7:33:32 */ public class A { }
AProperties
package com.oy.config; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; /** * @author oy * @version 1.0 * @date 2019年1月19日 * @time 上午7:34:35 */ @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "a") public class AProperties { private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass()); private String username; private String password; public AProperties() { logger.info("实例化AProperties============="); } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } }
MyAutoConfiguration
package com.oy.config; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnClass; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource; import com.oy.entity.User; /** * @author oy * @version 1.0 * @date 2019年1月19日 * @time 上午7:32:44 */ @PropertySource({"classpath:a.properties"}) @Configuration //在IoC容器中添加一个AProperties类型的Bean,该Bean绑定了属性文件中的属性 @EnableConfigurationProperties({AProperties.class}) // 当类路径下有A这个类,本自动配置类才会生效 @ConditionalOnClass(A.class) public class MyAutoConfiguration { private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass()); private AProperties properties; // 如果本自动配置类生效,将自动调用该有参构造进行实例化,AProperties由容器注入 public MyAutoConfiguration(AProperties properties) { logger.info("配置类MyAutoConfiguration实例化========start========="); logger.info("properties:" + properties.getUsername() + "---" + properties.getPassword()); logger.info("配置类MyAutoConfiguration实例化======== end ========"); this.properties = properties; } @Bean User user() { logger.info("Bean user实例化=================="); User user = new User(); user.setUsername(properties.getUsername()); user.setPassword(properties.getPassword());
logger.info(user.toString()); return user; } }
a.properties
a.username=zhangsan
a.password=abc
application.properties
a.username=zhangsan111
a.password=abc111
a.properties中的配置为默认配置,application.properties为个性化配置。个性化配置会覆盖默认配置。
启动打印日志:

---
