1、spring介绍
2、Spring IoC helloworld
3、依赖注入DI,setter方法注入,构造方法注入
4、bean的实例化方式(三种)
5、Spring 容器类
6、基于xml装配bean---作用域
7、属性注入
8、bean之间的关系
9、p命令空间和SpEL
10、Spring容器中bean的生命周期
11、装配Bean--基于注解Annotation
1、spring介绍 <--返回目录
* 什么是spring:
- Spring是一个开放源代码的设计层面框架,他解决的是业务逻辑层和其他各层的松耦合问题,
因此它将面向接口的编程思想贯穿整个系统应用。Spring是于2003 年兴起的一个轻量级的Java 开发框架,
由Rod Johnson创建。简单来说,Spring是一个分层的JavaSE/EE full-stack(一站式) 轻量级开源框架。
- 轻量级:与EJB对比,依赖资源少,消耗的资源少。
- 分层: 一站式,每一个层都提供的解决方案
web层:struts,spring-MVC
service层:spring
dao层:hibernate,mybatis , jdbcTemplate --> spring-data
* Spring的核心:控制反转(IoC,Inverse of Control)和面向切面编程(AOP,)
* IoC意思:将创建对象的控制权反转给了spring,换一句话说就是,以后对象全部由spring创建
* spring的优点
- 方便解耦,简化开发 (高内聚低耦合)
Spring就是一个大工厂(容器),可以将所有对象创建和依赖关系维护,交给Spring管理
spring工厂是用于生成bean
- AOP编程的支持
Spring提供面向切面编程,可以方便的实现对程序进行权限拦截、运行监控等功能
- 声明式事务的支持
只需要通过配置就可以完成对事务的管理,而无需手动编程
- 方便程序的测试
Spring对Junit4支持,可以通过注解方便地测试Spring程序
- 方便集成各种优秀框架
Spring不排斥各种优秀的开源框架,其内部提供了对各种优秀框架(如:Struts、Hibernate、MyBatis、Quartz等)的直接支持
- 降低JavaEE API的使用难度
Spring 对JavaEE开发中非常难用的一些API(JDBC、JavaMail、远程调用等),都提供了封装,使这些API应用难度大大降低
* spring 体系
2、Spring IoC helloworld <--返回目录
定义 bean
public class HelloWorld { public void sayHi() { System.out.println("hello,你好!!!"); } }
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 装配bean --> <bean id="HelloWorldBeanId" class="com.oy.entity.HelloWorld"/> </beans>
测试类
package com.oy.test; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.oy.entity.HelloWorld; /** * HelloWorld演示: * 1)编写JavaBean类 * 2)配置<bean> * 3)初始化Spring IoC容器 * 4)获取bean实例 * * @author oy * @version 1.0 * @date 2018年12月29日 * @time 上午1:25:43 */ class HelloWorldTest { @Test public void test() { // 初始化Spring IoC容器 ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); // 根据name获取bean实例 HelloWorld hw = (HelloWorld)ctx.getBean("HelloWorldBeanId"); hw.sayHi(); } }
3、依赖注入DI,setter方法注入,构造方法注入 <--返回目录
* DI:Dependency Injection , 依赖注入
* 什么叫依赖?
- is a:是一个,继承;子类继承父类==>子类is a 父类
- has a:有一个,成员变量,依赖。
public B {
private A a; //B类依赖A类
}
* 注入:通过setter方法进行另一个对象实例设置
public B {
private A a; //B类依赖A类
public A setA(A a) {
this.a = a; //注入
}
}
* 例如:
class BookServiceImpl{
//之前开发:接口 = 实现类 (service和dao耦合)
//private BookDao bookDao = new BookDaoImpl();
//spring之后 (解耦:service实现类使用dao接口,不知道具体的实现类,后面使用setter注入实现类)
private BookDao bookDao;
setter方法
}
模拟spring执行过程
创建service实例:BookService bookService = new BookServiceImpl() -->IoC <bean>
创建dao实例:BookDao bookDao = new BookDaoImple() -->IoC
将dao设置给service:bookService.setBookDao(BookDao); -->DI <property>
People
package com.oy.entity; /** * @author oy * @version 1.0 * @date 2018年12月29日 * @time 上午7:32:23 */ public class People { private Integer id; private String name; private Integer age; public People() { System.out.println("调用People的无参构造。。。"); } public People(Integer id, String name, Integer age) { super(); System.out.println("调用People的有参构造。。。"); this.id = id; this.name = name; this.age = age; } // getXxx 和 setXxx }
PeopleTest
package com.oy.test; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.oy.entity.People; /** * 2种依赖注入方法: * 1.setter方法注入 * 2.构造方法注入 * * @author oy * @version 1.0 * @date 2018年12月29日 * @time 上午7:37:57 */ public class PeopleTest { @SuppressWarnings("resource") @Test public void test1() { // 初始化Spring IoC容器 ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); // 根据name获取bean实例 // =====测试依赖注入:setter方法注入===== People p = (People)ctx.getBean("people"); System.out.println(p.getId() + "---" + p.getName() + "---" + p.getAge()); // =====测试依赖注入:构造方法注入===== // 通过索引 People p2 = (People)ctx.getBean("people2"); System.out.println(p2.getId() + "---" + p2.getName() + "---" + p2.getAge()); // 通过类型 People p3 = (People)ctx.getBean("people3"); System.out.println(p3.getId() + "---" + p3.getName() + "---" + p3.getAge()); // 通过索引和类型 People p4 = (People)ctx.getBean("people4"); System.out.println(p4.getId() + "---" + p4.getName() + "---" + p4.getAge()); } }
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- ==========依赖注入:使用setter方法========== --> <!-- 装配bean过程: IoC容器初始化时,调用People类的无参构造创建bean实例, 然后调用People类的setter方法给属性注入值 --> <bean id="people" class="com.oy.entity.People"> <!-- 依赖注入:使用setter方法注入 --> <property name="id" value="1"></property> <property name="name" value="张三1"></property> <property name="age" value="15"></property> </bean> <!-- ==========依赖注入:使用构造方法========== --> <!-- 装配bean过程: IoC容器初始化时,调用People类的有参构造创建bean实例 --> <bean id="people2" class="com.oy.entity.People"> <!-- 依赖注入:使用有参构造注入 --> <!-- 通过索引 --> <constructor-arg index="0" value="2"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg index="1" value="李四2"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg index="2" value="25"></constructor-arg> </bean> <bean id="people3" class="com.oy.entity.People"> <!-- 依赖注入:使用有参构造注入 --> <!-- 通过类型 --> <constructor-arg type="Integer" value="3"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg type="String" value="李四3"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg type="Integer" value="35"></constructor-arg> </bean> <bean id="people4" class="com.oy.entity.People"> <!-- 依赖注入:使用有参构造注入 --> <!-- 通过类型和索引 --> <constructor-arg index="0" type="Integer" value="4"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg index="1" type="String" value="李四4"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg index="2" type="Integer" value="45"></constructor-arg> </bean> </beans>
4、bean的实例化方式(三种) <--返回目录
方式一:默认构造 <bean id="" class=""> 必须提供默认构造
方式二:静态工厂
方式三:实例工厂
PeopleFactory
package com.oy.entity; /** * 定义了一个非静态工厂 * @author oy * @version 1.0 * @date 2018年12月29日 * @time 上午8:10:25 */ public class PeopleFactory { public People createPeople() { People p = new People(); p.setId(5); p.setName("李四5"); p.setAge(55); return p; } }
PeopleStaticFactory
package com.oy.entity; /** * 静态工厂 * @author oy * @version 1.0 * @date 2018年12月29日 * @time 上午8:25:21 */ public class PeopleStaticFactory { public static People createPeople() { People p = new People(); p.setId(6); p.setName("李四6"); p.setAge(66); return p; } }
测试类
package com.oy.test; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.oy.entity.People; /** * bean的实例化方式 : * 1.无参构造 * <bean id="" class=""> 或 使用setter方法注入属性时都是调用无参构造来实例化bean * 2.有参构造 * 使用构造方法注入属性时调用有参构造 * 3.非静态工厂 * 4.静态工厂 */ public class PeopleTest { @SuppressWarnings("resource") @Test public void test1() { // 初始化Spring IoC容器 ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); // =====测试bean的实例化方式:非静态工厂===== People p5 = (People)ctx.getBean("people5"); System.out.println(p5.getId() + "---" + p5.getName() + "---" + p5.getAge()); // =====测试bean的实例化方式:静态工厂===== People p6 = (People)ctx.getBean("people6"); System.out.println(p6.getId() + "---" + p6.getName() + "---" + p6.getAge()); } }
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- ==========bean的实例化方式:使用非静态工厂========== --> <bean id="peopleFactory" class="com.oy.entity.PeopleFactory"/> <!-- 装配bean过程: IoC容器初始化时,调用factory-bean实例的createPeople()方法 --> <bean id="people5" factory-bean="peopleFactory" factory-method="createPeople"/> <!-- ==========bean的实例化方式:使用静态工厂========== --> <!-- 装配bean过程: IoC容器初始化时,调用静态工厂的createPeople()方法 --> <bean id="people6" class="com.oy.entity.PeopleStaticFactory" factory-method="createPeople"/> </beans>
5、Spring 容器类 <--返回目录
* api整体了解,之后不使用,在学习过程需要使用,所以了解即可。
* BeanFactory :这是一个工厂,用于生成任意bean。
- 【采取延迟加载,第一次getBean时才会初始化Bean】
* ApplicationContext:是BeanFactory的子接口,功能更强大。
- (国际化处理、事件传递、Bean自动装配、各种不同应用层的Context实现)。
- 【当配置文件被加载,就进行对象实例化】
* ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 用于加载classpath(类路径、src)下的xml
加载xml运行时位置 --> /WEB-INF/classes/*.xml
* FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 用于加载指定盘符下的xml
一般加载xml运行时位置 --> /WEB-INF/*.xml
也就是说如果xml文件放在/WEB-INF/*.xml,可以使用FileSystemXmlApplicationContext
通过java web ServletContext.getRealPath() 获得具体盘符
6、基于xml装配bean---作用域 <--返回目录
* 作用域:用于确定spring创建bean实例个数
* 取值:
- singleton 单例,默认值。
- prototype 多例,每执行一次getBean将获得一个实例。例如:struts整合spring,配置action多例。
* 如何配置:<bean id="" class="" scope="singleton|prototype">
7、属性注入 <--返回目录

public class Dog { private String name; public Dog() { System.out.println("调用Dog的无参构造。。。"); } // getXxx和setXxx }
public class People { private Integer id; private String name; private Integer age; private Dog dog; private List<String> hobbies = new ArrayList<String>(); private Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>(); private Properties props = new Properties(); public People() { System.out.println("调用People的无参构造。。。"); } public People(Integer id, String name, Integer age) { super(); System.out.println("调用People的有参构造。。。"); this.id = id; this.name = name; this.age = age; } // getXxx和setXxx }
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 依赖注入:属性是基本数据类型 --> <bean id="people" class="com.oy.entity.People"> <property name="id" value="1"></property> <property name="name" value="张三1"></property> <property name="age" value="15"></property> </bean> <!-- 依赖注入:属性是bean,注入外部bean --> <bean id="people2" class="com.oy.entity.People"> <property name="id" value="1"></property> <property name="name" value="张三1"></property> <property name="age" value="15"></property> <property name="dog" ref="dog"></property> </bean> <!-- dog配置在people2后面也是可以的 --> <bean id="dog" class="com.oy.entity.Dog"> <property name="name" value="jack"></property> </bean> <!-- 依赖注入:属性是bean,注入内部bean --> <bean id="people3" class="com.oy.entity.People"> <property name="id" value="1"></property> <property name="name" value="张三1"></property> <property name="age" value="15"></property> <property name="dog"> <bean class="com.oy.entity.Dog"> <property name="name" value="tom"></property> </bean> </property> </bean> <!-- 依赖注入:属性是bean,注入null --> <bean id="people4" class="com.oy.entity.People"> <property name="id" value="1"></property> <property name="name" value="张三1"></property> <property name="age" value="15"></property> <property name="dog"> <null></null> </property> </bean> <!-- 依赖注入:属性是List集合 --> <bean id="people5" class="com.oy.entity.People"> <property name="id" value="1"></property> <property name="name" value="张三1"></property> <property name="age" value="15"></property> <property name="hobbies"> <list> <value>吃饭</value> <value>睡觉</value> <value>打豆豆</value> </list> </property> </bean> <!-- 依赖注入:属性是Map集合 --> <bean id="people6" class="com.oy.entity.People"> <property name="id" value="1"></property> <property name="name" value="张三1"></property> <property name="age" value="15"></property> <property name="map"> <map> <entry key="key1" value="value1"/> <entry key="key2" value="value2"/> </map> </property> </bean> <!-- 依赖注入:属性是Properties --> <bean id="people7" class="com.oy.entity.People"> <property name="id" value="1"></property> <property name="name" value="张三1"></property> <property name="age" value="15"></property> <property name="props"> <props> <prop key="username">张三</prop> <prop key="password">123</prop> </props> </property> </bean> </beans>
测试类
package com.oy.test; import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.oy.entity.People; /** * 测试依赖注入 * 属性的类型分为: * 1.基本数据类型 * 2.bean * 通过ref引用注入外部bean * 注入内部bean * 注入null * 3.List集合 (数组Array类似) * 4.Map集合 * 5.Properties类型 * * @author oy * @version 1.0 * @date 2018年12月29日 * @time 上午8:57:22 */ class PeopleTest { ApplicationContext ctx = null; @BeforeEach void setUp() throws Exception { ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); } /** * 依赖注入:属性是基本数据类型 */ @Test void test1() { People p = (People)ctx.getBean("people"); System.out.println(p.getId() + "---" + p.getName() + "---" + p.getAge()); } /** * 依赖注入:属性是bean,注入外部bean */ @Test void test2() { People p2 = (People)ctx.getBean("people2"); System.out.println(p2.getId() + "---" + p2.getName() + "---" + p2.getAge() + "---" + p2.getDog().getName()); } /** * 依赖注入:属性是bean,注入内部bean */ @Test void test3() { People p3 = (People)ctx.getBean("people3"); System.out.println(p3.getId() + "---" + p3.getName() + "---" + p3.getAge() + "---" + p3.getDog().getName()); } /** * 依赖注入:属性是bean,注入null */ @Test void test4() { People p4 = (People)ctx.getBean("people4"); System.out.println(p4.getId() + "---" + p4.getName() + "---" + p4.getAge() + "---" + p4.getDog()); } /** * 依赖注入:属性是List集合 */ @Test void test5() { People p5 = (People)ctx.getBean("people5"); System.out.println(p5.getId() + "---" + p5.getName() + "---" + p5.getAge() + "---" + p5.getHobbies()); } /** * 依赖注入:属性是Map集合 */ @Test void test6() { People p6 = (People)ctx.getBean("people6"); System.out.println(p6.getId() + "---" + p6.getName() + "---" + p6.getAge() + "---" + p6.getMap()); } /** * 依赖注入:属性是Properties */ @Test void test7() { People p7 = (People)ctx.getBean("people7"); System.out.println(p7.getId() + "---" + p7.getName() + "---" + p7.getAge() + "---" + p7.getProps().getProperty("username") + p7.getProps().getProperty("password")); } }
8、bean之间的关系 <--返回目录
public class People { private Integer id; private String name; private Integer age; private String className; public People() { System.out.println("调用People的无参构造。。。"); } // getXxx和setXxx @Override public String toString() { return "People [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", className=" + className + "]"; } }
public class User { private Integer id; private String username; private String password; public User() { System.out.println("调用User的无参构造。。。"); } // getXxx和setXxx @Override public String toString() { return "User [id=" + id + ", username=" + username + ", password=" + password + "]"; } }
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- bean之间的关系:继承 --> <bean id="peopleParent" class="com.oy.entity.People" abstract="true"> <property name="age" value="18"></property> <property name="className" value="高三1班"></property> </bean> <bean id="zhangsan" parent="peopleParent" depends-on="user"> <property name="id" value="1"></property> <property name="name" value="zhangsan"></property> <property name="age" value="19"></property> </bean> <bean id="lisi" parent="peopleParent"> <property name="id" value="2"></property> <property name="name" value="lisi"></property> </bean> <bean id="user" class="com.oy.entity.User"> <property name="id" value="1"></property> <property name="username" value="zhangsan"></property> <property name="password" value="123"></property> </bean> </beans>
测试类
package com.oy.test; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.oy.entity.People; import com.oy.entity.User; /** * bean之间的关系: * 1.继承 * 定义抽象bean:<bean id="parent" class="" abstract="true"> * 继承:<bean id="" parent="parent"> * * 2.依赖 * <bean id="bean1" class="" depends-on="bean2"/> * bean1依赖bean2,bean2必须要在bean1之前初始化 * * 3.引用 ref * <bean id="" class=""> * <property name="dog" ref="dog"/> * </bean> * * @author oy * @version 1.0 * @date 2018年12月29日 * @time 上午10:51:26 */ public class PeopleTest { ApplicationContext ctx = null; @Before public void before() { ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); } /** * bean之间的关系:继承 */ @Test public void test1() { People zhangsan = (People)ctx.getBean("zhangsan"); System.out.println(zhangsan); People lisi = (People)ctx.getBean("lisi"); System.out.println(lisi); } /** * bean之间的关系:依赖 * Spring IoC容器初始化bean是按配置文件从上到下 * 需求:假设初始化<bean id="zhangsan">这个bean之前,必须先初始化<bean id="user">, * 便认为<bean id="zhangsan">依赖<bean id="user"> * 配置:<bean id="zhangsan" depends-on="user"> */ @Test public void test2() { People zhangsan = (People)ctx.getBean("zhangsan"); System.out.println(zhangsan); People lisi = (People)ctx.getBean("lisi"); System.out.println(lisi); User user = (User)ctx.getBean("user"); System.out.println(user); } }
9、p命令空间和SpEL <--返回目录
public class Address { private Integer id; private String addrName; public String fun() { return "abc"; } // getXxx和setXxx }
public class Customer { private String cname = "jack"; private Double pi; private Address address; private String addressName; private String str; // getXxx和setXxx }
public class Student { private Integer id; private String name; private Integer age; private Address address; // getXxx和setXxx }
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="student1" class="com.oy.entity.Student"> <property name="id" value="1"></property> <property name="name" value="张三"></property> <property name="age" value="10"></property> <property name="address" ref="address"></property> </bean> <!-- 使用P命名空间 --> <bean id="student2" class="com.oy.entity.Student" p:id="2" p:name="张三2" p:age="20" p:address-ref="address"> </bean> <bean id="address" class="com.oy.entity.Address" p:id="1" p:addrName="深圳"> </bean> <!-- 使用SpEL --> <bean id="customer" class="com.oy.entity.Customer"> <!-- <property name="cname" value="#{'李四'}"></property> --> <!-- 如果customer.cname?为null,不再调用后面方法 --> <property name="cname" value="#{customer.cname?.toUpperCase()}"></property> <property name="pi" value="#{T(Math).PI}"></property> <property name="address" value="#{address}"></property> <property name="addressName" value="#{address.addrName}"></property> <property name="str" value="#{address.fun()}"></property> </bean> </beans>
测试类
package com.oy.test; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.oy.entity.Customer; import com.oy.entity.Student; /** * P命名空间 * 1)P命名空间使用前提,必须添加命名空间。 * 2)对"setter方法注入"进行简化,替换<property name="属性名" value/ref="属性值">, * 在<bean p:属性名="普通值" p:属性名-ref="引用值"> * * SpEL: * 1)对<property>进行统一编程,所有的内容都使用value * 2)<property name="" value="#{表达式}"> * #{123}、#{'jack'} : 数字、字符串 * #{beanId} :另一个bean引用 * #{beanId.propName} :操作数据 * #{beanId.toString()} :执行方法 * #{T(类).静态字段|静态方法} :静态方法或字段 * * @author oy * @version 1.0 * @date 2018年12月30日 * @time 上午12:15:58 */ public class StudentTest { ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = null; @Before public void setUp() throws Exception { ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); } @After public void tearDown() throws Exception { ctx.close(); } /** * 测试P命名空间 */ @Test public void test() { Student stu1 = (Student)ctx.getBean("student1"); System.out.println(stu1); Student stu2 = (Student)ctx.getBean("student2"); System.out.println(stu2); } /** * 测试SpEL */ @Test public void test2() { Customer customer = (Customer)ctx.getBean("customer"); System.out.println(customer.getCname()); System.out.println(customer.getPi()); System.out.println(customer.getAddress()); System.out.println(customer.getAddressName()); System.out.println(customer.getStr()); } }
10、Spring容器中bean的生命周期 <--返回目录
* 1.bean的初始化方法和销毁方法:
* 容器加载配置文件初始化后,将调用People的无参构造进行bean实例化,
* 然后调用bean实例的初始化方法 init-method="myInit"。
* 什么时候调用销毁方法 destroy-method="myDestroy"?容器关闭时,且bean是单例的。
* 2.BeanPostProcessor接口: 后处理Bean
* spring 提供一种机制,只要实现此接口BeanPostProcessor,并将实现类提供给spring容器,
* spring容器将自动执行,在容器每个bean的初始化方法前执行before(),在容器每个bean初始化方法后执行after()。
* 3.模拟Spring IoC实例化bean的过程,即bean的生命周期:
A a =new A(); --> 调用无参构造创建对象 a = B.before(a); --> 将a的实例对象传递给后处理bean,可以生成代理对象并返回。 a.init(); --> 调用bean的初始化方法 a = B.after(a); a.addUser(); //生成代理对象,目的是在目标方法前后执行(例如:开启事务、提交事务、性能监控) a.destroy()
Spring容器中bean的生命周期
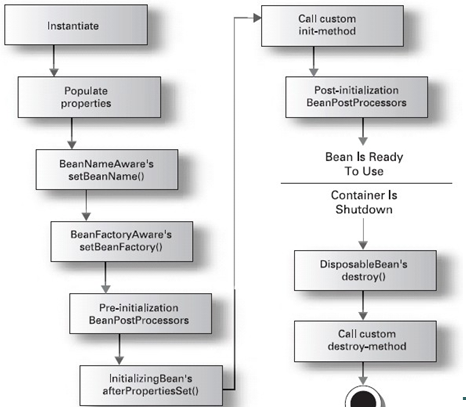
1、instantiate bean对象实例化 2、populate properties 封装属性 3、如果Bean实现BeanNameAware 执行 setBeanName 4、如果Bean实现BeanFactoryAware 或者 ApplicationContextAware 设置工厂 setBeanFactory 或者上下文对象 setApplicationContext 5、如果存在类实现 BeanPostProcessor(后处理Bean) ,执行postProcessBeforeInitialization 6、如果Bean实现InitializingBean 执行 afterPropertiesSet 7、用<bean init-method="myInit"> 指定初始化方法 myInit 8、如果存在类实现 BeanPostProcessor(处理Bean),执行postProcessAfterInitialization 9、执行业务处理(执行目标方法) 10、如果Bean实现 DisposableBean 执行 destroy 11、调用<bean destroy-method="myDestroy"> 指定销毁方法 myDestroy
IPeople
public interface IPeople { public void add(); public void delete(); }
People
public class People implements IPeople{ private Integer id; private String name; private Integer age; private String className; public People() { System.out.println(); System.out.println("==========调用People无参构造=========="); } public void myInit() { System.out.println("调用People初始化方法。。。"); } public void myDestroy() { System.out.println("调用People销毁方法。。。"); } @Override public void add() { System.out.println("调用People目标方法:add()。。。"); long sum = 0; for (int j = 0; j < 1000; j++) { sum = 0; for (long i = 0; i < 100000; i++) { sum += i; } } System.out.println(sum); } @Override public void delete() { System.out.println("调用People目标方法:delete()。。。"); long sum = 0; for (int j = 0; j < 1000; j++) { sum = 0; for (long i = 0; i < 100000; i++) { sum += i; } } System.out.println(sum); } // getXxx和setXxx }
IUserService
public interface IUserService { public void add(); public void delete(); }
UserServiceImpl
public class UserServiceImpl implements IUserService{ private Integer id; private String username; private String password; public UserServiceImpl() { System.out.println(); System.out.println("==========调用UserServiceImpl无参构造=========="); } public void myInit() { System.out.println("调用UserServiceImpl初始化方法。。。"); } public void myDestroy() { System.out.println("调用UserServiceImpl销毁方法。。。"); } @Override public void add() { System.out.println("调用UserServiceImpl目标方法:add()。。。"); } @Override public void delete() { System.out.println("调用UserServiceImpl目标方法:delete()。。。"); } // getXxx和setXxx }
StudentService
public interface StudentService { void add(); }
StudentServiceImpl
package com.oy.entity; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware; public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService,BeanNameAware,ApplicationContextAware { private String beanName; private ApplicationContext applicationContext; // 无参构造 public StudentServiceImpl() { System.out.println(); System.out.println("==========调用StudentServiceImpl无参构造=========="); } // 初始化方法 public void myInit() { System.out.println("调用StudentServiceImpl初始化方法。。。"); } // 销毁方法 public void myDestroy() { System.out.println("调用StudentServiceImpl销毁方法。。。"); } // 目标方法 public void add() { System.out.println("调用StudentServiceImpl目标方法:add()。。。"); } /** * 在bean实例化过程中,调用此方法,将beanName注入给bean实例, * 那么可以在此方法外面定义一个属性beanName,将注入的beanName保存起来, * 从而其他方法也可以用。 */ @Override public void setBeanName(String beanName) { this.beanName = beanName; System.out.println("给StudentServiceImpl注入属性值beanName:" + this.beanName); } /** * 给StudentServiceImpl注入属性值applicationContext。 * 打印applicationContext类型名称 */ @Override public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { this.applicationContext = applicationContext; System.out.println("给StudentServiceImpl注入属性值applicationContext:" + this.applicationContext.getClass().getName()); } }
Spring后处理 BeanPostProcessor 的实现类 BeanPostProcessorImpl
package com.oy.entity; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor; public class BeanPostProcessorImpl implements BeanPostProcessor { public BeanPostProcessorImpl() { System.out.println(); System.out.println("==========调用BeanPostProcessorImpl无参构造=========="); } @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { System.out.println("前处理方法,beanName为:" + beanName); return bean; } /** * 参数bean:目标对象,即被代理的bean对象 * 参数beanName:被代理对象的名字,即bean的id属性值 */ @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { System.out.println("后处理方法,bean的类型为:" + bean.getClass().getName()); // 通过beanName过滤,对不同的bean进行处理 if ("userService".equals(beanName)) { // 生成jdk代理 return Proxy.newProxyInstance( BeanPostProcessorImpl.class.getClassLoader(), bean.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() { @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { System.out.println("===开启事务==="); Object obj = method.invoke(bean, args); System.out.println("===提交事务==="); return obj; } }); } else if ("people".equals(beanName)) { // 生成jdk代理 return Proxy.newProxyInstance( BeanPostProcessorImpl.class.getClassLoader(), bean.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() { @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { //System.out.println(proxy.getClass().getName()); // com.sun.proxy.$Proxy6 long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); Object obj = method.invoke(bean, args); long time = System.currentTimeMillis() - start; System.out.println("方法" + method.getName() + "()共耗时:" + time + "毫秒"); return obj; } }); } else { // 直接返回bean,不生成代理对象 return bean; } } }
DisPosableBeanImpl
public class DisPosableBeanImpl implements DisposableBean { public DisPosableBeanImpl() { System.out.println(); System.out.println("==========调用DisPosableBeanImpl无参构造=========="); } @Override public void destroy() throws Exception { System.out.println(""); System.out.println(""); System.out.println("Spring IoC容器关闭。。。"); } }
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="people" class="com.oy.entity.People" init-method="myInit" destroy-method="myDestroy"></bean> <bean id="userService" class="com.oy.entity.UserServiceImpl" init-method="myInit" destroy-method="myDestroy"></bean> <bean id="stuServiceId" class="com.oy.entity.StudentServiceImpl" init-method="myInit" destroy-method="myDestroy"></bean> <!-- 将后处理BeanPostProcessor接口的实现类注册到Spring容器 --> <!-- spring将首先初始化该bean,与在xml配置的位置无关 --> <bean class="com.oy.entity.BeanPostProcessorImpl"/> <!-- 将DisPosableBean接口的实现注册到Spring容器 --> <bean id="disPosableBeanImpl" class="com.oy.entity.DisPosableBeanImpl"/> </beans>
测试类
package com.oy.test; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.oy.entity.IPeople; import com.oy.entity.IUserService; /** * bean的生命周期: * 1.bean的初始化方法和销毁方法 * <bean id="" class="" init-method="" destroy-method=""/> * 2.BeanPostProcessor接口: 后处理Bean * * @author oy * @version 1.0 * @date 2018年12月29日 * @time 上午10:51:26 */ public class PeopleTest { ApplicationContext ctx = null; @Before public void before() { ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); } /** * 1.bean的初始化方法和销毁方法: * 容器加载配置文件初始化后,将调用People的无参构造进行bean实例化, * 然后调用bean实例的初始化方法 init-method="myInit"。 * 什么时候调用销毁方法 destroy-method="myDestroy"?容器关闭时,且bean是单例的。 * 2.BeanPostProcessor接口: 后处理Bean * spring 提供一种机制,只要实现此接口BeanPostProcessor,并将实现类提供给spring容器, * spring容器将自动执行,在容器每个bean的初始化方法前执行before(),在容器每个bean初始化方法后执行after()。 * 3.模拟Spring IoC实例化bean的过程,即bean的生命周期: A a =new A(); --> 调用无参构造创建对象 a = B.before(a); --> 将a的实例对象传递给后处理bean,可以生成代理对象并返回。 a.init(); --> 调用bean的初始化方法 a = B.after(a); a.addUser(); //生成代理对象,目的是在目标方法前后执行(例如:开启事务、提交事务、性能监控) a.destroy() * @throws Exception */ @Test public void test1() throws Exception { System.out.println("=======容器初始化完毕======="); IPeople p = (IPeople)ctx.getBean("people"); //目标方法 p.add(); p.delete(); // 容器关闭时,调用销毁方法 destroy-method="myDestroy",要保证bean是单例的。 //ctx.getClass().getMethod("close").invoke(ctx); // 事实上,close()方法是ClassPathXmlApplicationContext类中提供的 // 使用多态(子类对象指向父类引用),不能直接调用子类特有的方法 // 向下强转 ((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext)ctx).close(); } @Test public void test2() throws Exception { System.out.println("=======容器初始化完毕======="); IUserService u = (IUserService)ctx.getBean("userService"); //目标方法 u.add(); u.delete(); // 容器关闭时,调用销毁方法 destroy-method="myDestroy",要保证bean是单例的。 ((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext)ctx).close(); } }
package com.oy.test; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.oy.entity.StudentService; /** * @author oy * @version 1.0 * @date 2019年1月1日 * @time 上午3:26:32 */ public class StudentTest { ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = null; @Before public void setUp() throws Exception { ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); } @After public void tearDown() throws Exception { System.out.println(); System.out.println("===========销毁IoC容器==========="); ctx.close(); } /* 测试结果: ==========调用BeanPostProcessorImpl无参构造========== ==========调用DisPosableBeanImpl无参构造========== 前处理方法,beanName为:disPosableBeanImpl 后处理方法,bean的类型为:com.oy.entity.DisPosableBeanImpl ==========调用People无参构造========== 前处理方法,beanName为:people 调用People初始化方法。。。 后处理方法,bean的类型为:com.oy.entity.People ==========调用UserServiceImpl无参构造========== 前处理方法,beanName为:userService 调用UserServiceImpl初始化方法。。。 后处理方法,bean的类型为:com.oy.entity.UserServiceImpl ==========调用StudentServiceImpl无参构造========== 给StudentServiceImpl注入属性值beanName:stuServiceId 给StudentServiceImpl注入属性值applicationContext:org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 前处理方法,beanName为:stuServiceId 调用StudentServiceImpl初始化方法。。。 后处理方法,bean的类型为:com.oy.entity.StudentServiceImpl 调用StudentServiceImpl目标方法:add()。。。 ===========销毁IoC容器=========== 调用StudentServiceImpl销毁方法。。。 调用UserServiceImpl销毁方法。。。 调用People销毁方法。。。 Spring IoC容器关闭。。。 */ @Test public void test() { StudentService studentService = (StudentService)ctx.getBean("stuServiceId"); studentService.add(); } }
11、装配Bean--基于注解Annotation <--返回目录
注解使用前提:添加schema命名空间,让spring扫描含有注解的类
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 【xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"】 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd 【http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">】 <!-- 组件扫描,扫描含有注解的类 base-package:指定包 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.oy"></context:component-scan> </beans>
@Component取代<bean class=""/>
@Component("userDaoid")取代<bean id="userDaoId" class="UserDaoImpl"/>
在UserDaoImpl类定义中添加注解@Component("userDaoId")===>这就相当于在配置文件中写了<bean id="userDaoId" class="UserDaoImpl"/>
* web开发,提供3个@Component注解衍生注解(功能一样)取代<bean class="">
@Repository :dao层
@Service:service层
@Controller:web层
* 依赖注入,给私有字段设置,也可以给setter方法设置
普通值:@Value("")
引用值:
方式1:按照【类型】注入
@Autowired
方式2:按照【名称】注入1
@Autowired
@Qualifier("名称")
方式3:按照【名称】注入2
@Resource[("名称")]
* 注意:
@Resource不写名称,就是根据【类型】注入
@Resource是JDK提供的,jdk1.5没有
@Autowired是由spring提供的
* 生命周期
初始化:@PostConstruct
销毁: @PreDestroy
* 作用域
@Scope("prototype") 多例