MySQL version: 5.7.X
对查询进行优化, 应尽量避免全表扫描, 首先应考虑在 where 及 order by 涉及的列上建立索引.
导致索引失效的操作:
- 应尽量避免在 where 子句中使用 != 或 <> 操作符, 否则将引擎放弃使用索引而进行全表扫描.
- 应尽量避免在 where 子句中对字段进行 null 值判断, 否则将导致引擎放弃使用索引而进行全表扫描, 如:
select id from t where num is null -- 可以在num上设置默认值0, 确保表中num列没有null值, 然后这样查询: select id from t where num=0
- 应尽量避免在 where 子句中使用 or 来连接条件, 否则将导致引擎放弃使用索引而进行全表扫描, 如:
select id from t where num=10 or num=20 -- 可以这样查询: select id from t where num=10 union all select id from t where num=20
- 尽量避免使用 左 like, 否则将导致引擎放弃使用索引而进行全表扫描.
- 应尽量避免在 where 子句中使用 in 和 not in, 否则会导致全表扫描, 如:
select id from t where num in(1,2,3) -- 对于连续的数值, 能用 between 就不要用 in 了: select id from t where num between 1 and 3
- 如果在 where 子句中使用参数, 也会导致全表扫描. 因为SQL只有在运行时才会解析局部变量, 但优化程序不能将访问计划的选择推迟到运行时;
它必须在编译时进行选择. 然而, 如果在编译时建立访问计划, 变量的值还是未知的, 因而无法作为索引选择的输入项. 如下面语句将进行全表扫描:
select id from t where num=@num -- 可以改为强制查询使用索引: select id from t with(index(索引名)) where num=@num
- 应尽量避免在 where 子句中对字段进行表达式操作, 这将导致引擎放弃使用索引而进行全表扫描. 如:
select id from t where num/2=100 -- 应改为: select id from t where num=100*2
- 在使用索引字段作为条件时, 如果该索引是复合索引, 那么必须使用到该索引中的第一个字段作为条件时才能保证系统使用该索引, 否则该索引将不会被使用.
- 避免数据类型的隐式转换(例如:查询的参数与字段类型不匹配), 隐式转换会导致索引失效. Type Conversion in Expression Evaluation
drop table if exists tb_t1; create table tb_t1(r_id int not null, c1 varchar(20) not null, primary key(r_id), key index_c1(c1))engine=innodb; insert into tb_t1 values(1, '1'),(2, '2'); explain select * from tb_t1 where c1=2; +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | tb_t1 | NULL | index | index_c1 | index_c1 | 82 | NULL | 2 | 50.00 | Using where; Using index | +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------+ explain select * from tb_t1 where c1='2'; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | tb_t1 | NULL | ref | index_c1 | index_c1 | 82 | const | 1 | 100.00 | Using index | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------+
其他 SQL 规范:
- 避免使用子查询, 把子查询优化为 join 操作. 子查询的结果集无法使用索引; 子查询会产生临时表操作, 如果子查询数据量大则严重影响效率.
- 在两个结果集中明显不会有重复值时使用 UNION ALL 而不是 UNION, 因为 UNION 会把所有数据放到临时表中进行去重操作.
- update/delete 语句, where 子句中必须使用到索引, 否则会锁表.
-- 查看事务隔离级别 select @@global.tx_isolation, @@session.tx_isolation, @@tx_isolation; +-----------------------+------------------------+----------------+ | @@global.tx_isolation | @@session.tx_isolation | @@tx_isolation | +-----------------------+------------------------+----------------+ | READ-COMMITTED | READ-COMMITTED | READ-COMMITTED | +-----------------------+------------------------+----------------+ drop table if exists tb_t1; create table tb_t1(r_id int not null, c1 varchar(20) not null, primary key(r_id))engine=innodb; insert into tb_t1 values(1, '1'),(2, '2');
-- session 1 -- 设置事务隔离级别为"可重复读" set session tx_isolation='repeatable-read'; begin; update tb_t1 set c1='a' where c1 = '1';
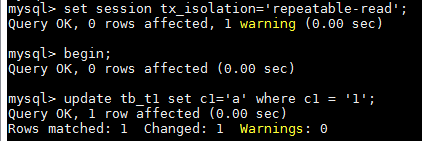
-- session 2; -- 设置事务隔离级别为"可重复读" set session tx_isolation='repeatable-read'; begin; update tb_t1 set c1='b' where c1 = '2';