<1>map
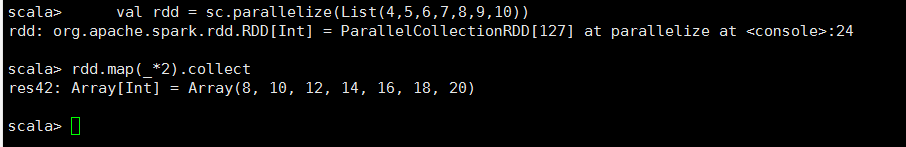
/**
* Return a new RDD by applying a function to all elements of this RDD.
* 一对一的进行RDD的转换操作,并且产生一个新的RDD储存所有的elements
*/
def map[U: ClassTag](f: T => U): RDD[U]
<2>filter
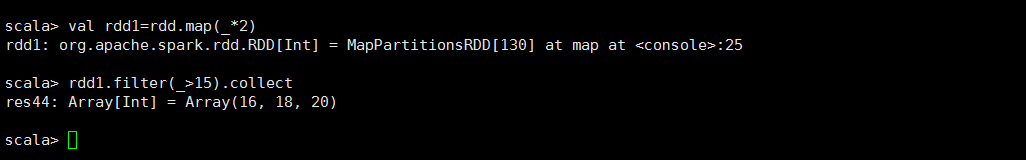
/** * Return a new RDD containing only the elements that satisfy a predicate. * 过滤的RDD转换操作 */ def filter(f: T => Boolean): RDD[T]
<3>flatMap
因为笔者在flatMap这个算子上吃亏比较多 这里会给出两个个案例
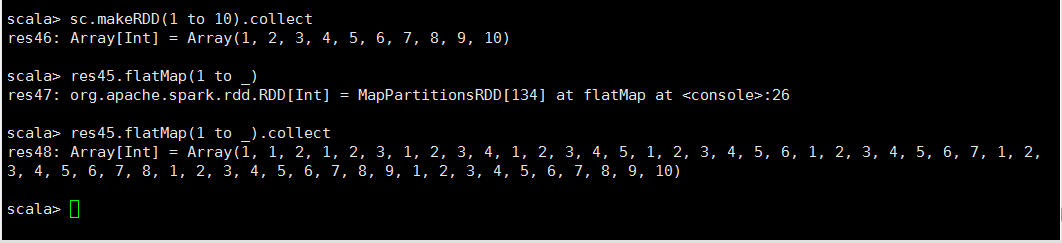
NO.1
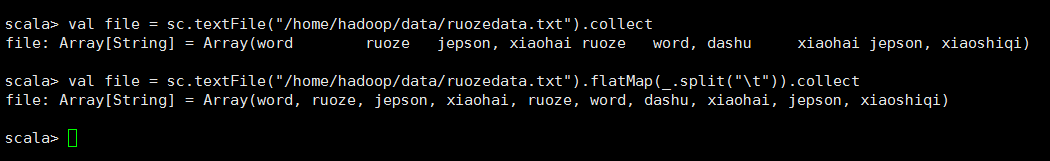
NO.2(这个使用方法是我在实现wc的时候使用的)
/** * 通过一个算法将RDD多维化,但是输出却是平面的类型 */ def flatMap[U: ClassTag](f: T => TraversableOnce[U]): RDD[U]
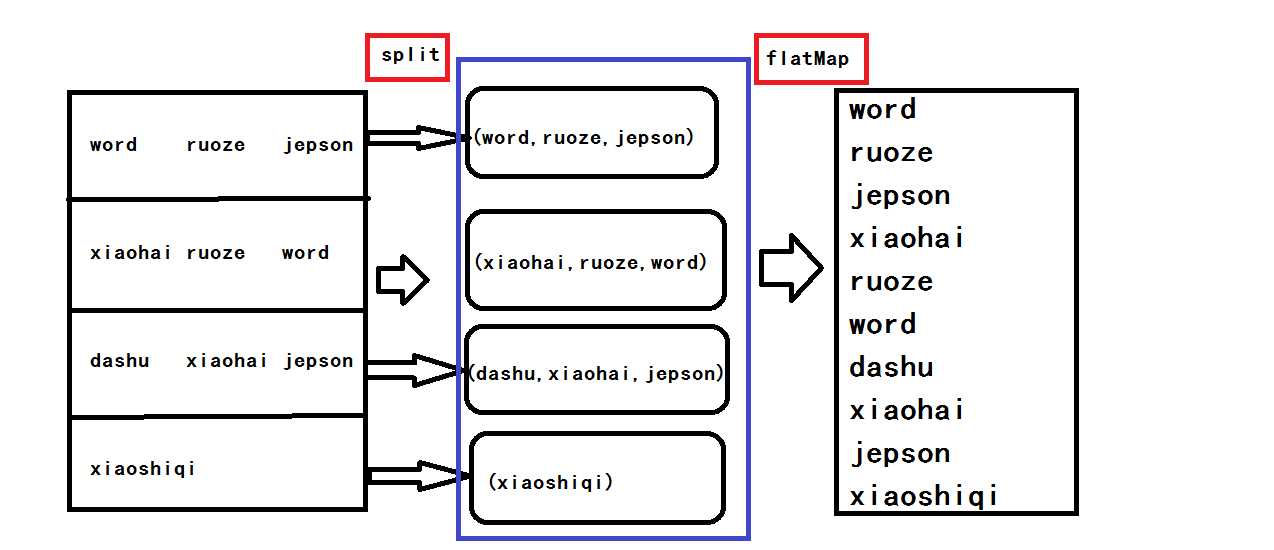
flatMap算子与Map算子的关系: flatMap方法先执行的是map(集合、迭代器来操作), 再执行的flatten,flatten起作用的前提是:它之前的map操作使集合中 装的元素变成了集合。因此,flatMap内部才经常搭配split使用,正是因 为split操作后可以生成集合 NO.2解释,testFile读入文件以后,在flatMap读取数据的时候是一行一行的读取的,就相当于一行为一个元素,读入第一行的数据会用tab分割,然后再读入第二行第三行
,split以后会返回一个集合,也就是说每一行当作一个元素输入,这一行经过分割以后就会生成一个集合,最后再经过扁平化把得到的几个集合放进一个数组里
<4>mapPartitions
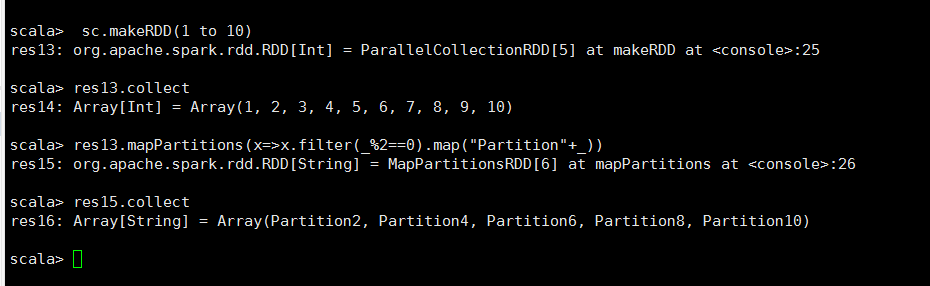
/** * 将RDD进行分块操作,使该RDD区域的所有元素执行此命令 */ def mapPartitions[U: ClassTag]( f: Iterator[T] => Iterator[U], preservesPartitioning: Boolean = false): RDD[U]
<5>mapPartitionsWithIndex
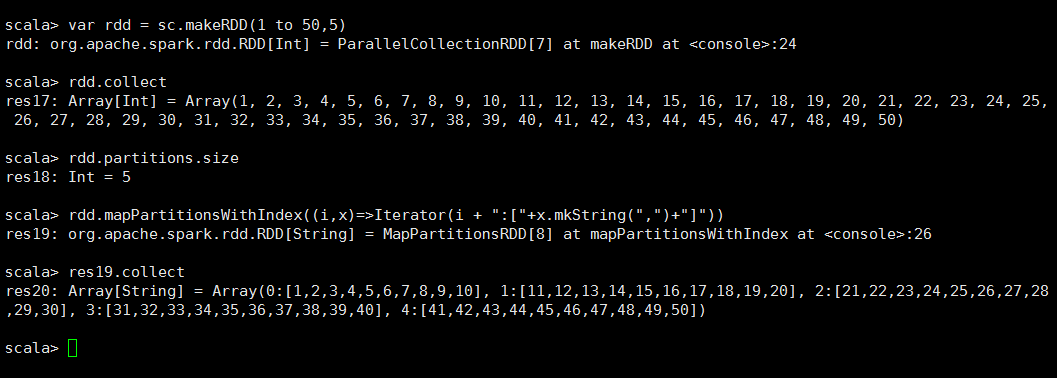
/** *在mapPartitions基础上增加了一个index的索引参数 *在创建RDD的时候也可以手动设置Partitions的数量 *看如下操作 */ def mapPartitionsWithIndex[U: ClassTag]( f: (Int, Iterator[T]) => Iterator[U], preservesPartitioning: Boolean = false): RDD[U]
<6>union
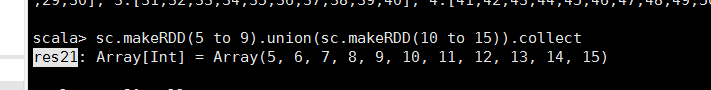
/** * 联合一个RDD,返回一个组合的RDD,但是两个RDD的类型得一样 */ def union(other: RDD[T]): RDD[T]
<7>reduceByKey
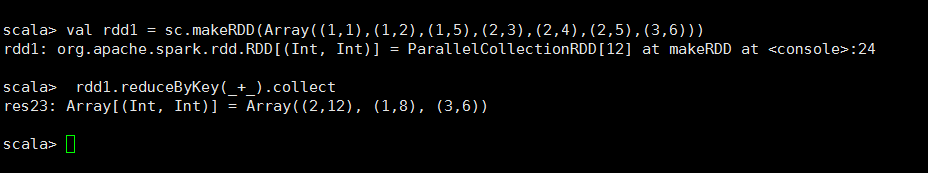
/** * 根据Key进行聚合操作 */ def reduceByKey(func: (V, V) => V): RDD[(K, V)]
<8>groupByKey

/** * 延时处理,但是实际开发,reduceBykey用的更多,将key相同的value聚集到一起 */ def groupByKey(partitioner: Partitioner): RDD[(K, Iterable[V])]
<9>combineByKey
def combineByKey[C]( createCombiner: V => C, mergeValue: (C, V) => C, mergeCombiners: (C, C) => C, numPartitions: Int): RDD[(K, C)]
<10>aggregateByKey
/** *在SeqOP中先讲同一个partition内的key值相同情况下各自取出max(value) *然后再对rdd内所有的partition进行同样的操作 *最后在CombOP中进行聚合操作 */ def aggregateByKey[U: ClassTag](zeroValue: U, partitioner: Partitioner)(seqOp: (U, V) => U, combOp: (U, U) => U): RDD[(K, U)]

<11>foldByKey
//是aggregateByKey的简化版 def foldByKey( zeroValue: V, partitioner: Partitioner)(func: (V, V) => V): RDD[(K, V)]
<12>sortByKey

//根据Key进行排序,但是如果不支持key的排序操作就会继承withOrdering接口实现compare方法,实现key的大小判定 def sortByKey(ascending: Boolean = true, numPartitions: Int = self.partitions.length) : RDD[(K, V)]
<13>sortBy

//比sortByKey更灵活 def sortBy[K]( f: (T) => K, ascending: Boolean = true, numPartitions: Int = this.partitions.length) (implicit ord: Ordering[K], ctag: ClassTag[K]): RDD[T]
<14>join
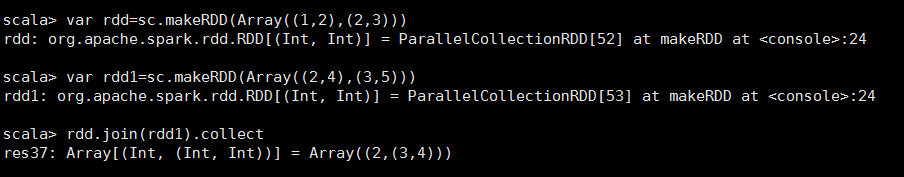

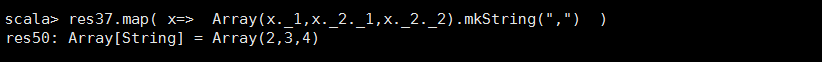
//连接两个RDD然后 //JOIN 只留下双方都有的KEY //left JOIN 留下左边RDD的数据 //right JOIN 留下右边RDD的数据 def join[W](other: RDD[(K, W)], partitioner: Partitioner): RDD[(K, (V, W))]
<15>Coalesce
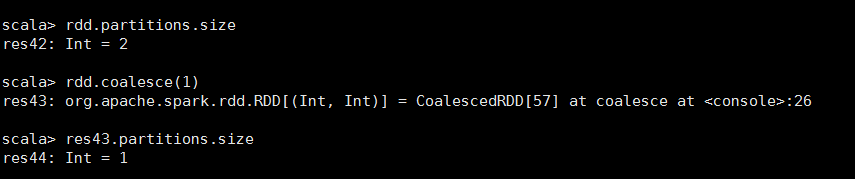
//当RDD数远远大于节点数时,就会把小的数据集放到一个节点上,减小计算压力 def coalesce(numPartitions: Int, shuffle: Boolean = false, partitionCoalescer: Option[PartitionCoalescer] = Option.empty) (implicit ord: Ordering[T] = null) : RDD[T]
<16>repartition
//给数据混洗进行重新分区 def repartition(numPartitions: Int)(implicit ord: Ordering[T] = null): RDD[T]