写一个按照下面方式调用都能正常工作的 sum 方法
console.log(sum(2,3)); // Outputs 5 console.log(sum(2)(3)); // Outputs 5
从这个输出的角度,我们需要求出函数的参数的和。
1 function add(x){ 2 var fir = arguments[0]; 3 if (arguments.length ==2) { 4 return arguments[0]+ arguments[1]; 5 }else{ 6 return function(sec){ 7 return fir + sec; 8 } 9 } 10 } 11 add(2)(3); 12 add(2,3);
这是我们需要缩写的sum函数。
后面遇到一个新的问题,实现如下语法的功能:
var a = add(2)(3)(4); //9 输出:
输出: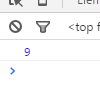
还有一个更高级的做法:
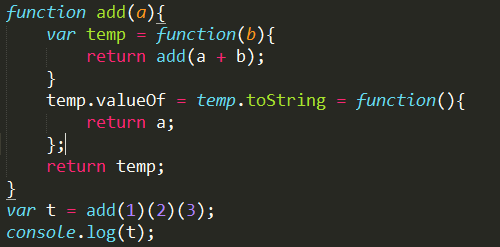 最后输出:
最后输出: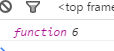
这种方式对于add(1)和add(1)(2)也能达到效果,但对add(1,2)没效果。但需要理解下。
还有一个终极版本:
1 function add(){ 2 var args = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments); 3 var fn = function(){ 4 var arg_fn = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments); 5 return add.apply(null,args.concat(arg_fn)); 6 } 7 fn.valueOf = function(){ 8 return args.reduce(function(a,b){ 9 return a + b; 10 }) 11 } 12 return fn; 13 } 14 15 console.log(add(1)); 16 console.log(add(1,2)(3)); 17 console.log(add(1,2)(3)(4)); 18 console.log(add(1)(2)(3)(4)(5));
在这里使用到了Array.prototype.slice.call()方法,这种方法其实也可以单独写一篇文章了。这里就不在详述。