1. 概述
1.1 说明
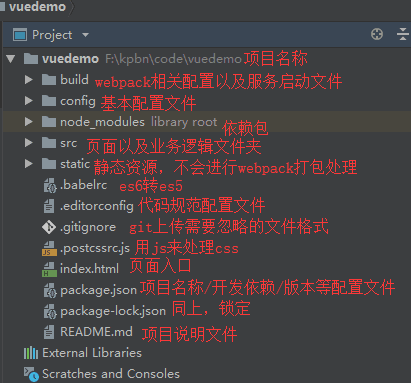
使用vue-cli快速创建的vue项目目录如下:
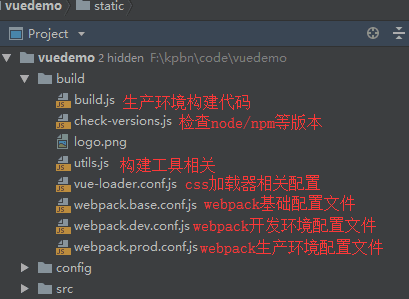
1.2 build
1.3 config
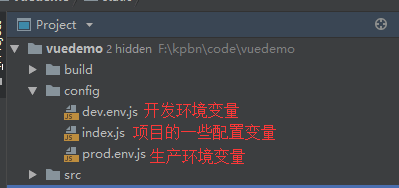
config文件夹下的文件目录如下:
1.4 .editorconfig
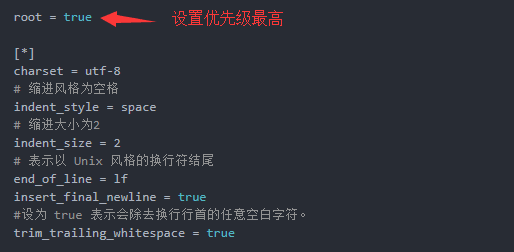
代码规范化编辑可以帮助我们简单整洁的展示代码结构,而.editorconfig文件就是对代码规范设置的一个文档。使用编辑器/IDE打开项目时编辑器会自动寻找.editorconfig文件,然后根据其内容配置去显示相关的项目代码文件。
2. 项目页面开发
2.1 index.html
项目页面入口(可删除),通常是进行根节点功能设置,如需要引用静态资源文件夹static中的文件时,建议在index.html中进行引入;手机端文件在此文件中更改viewport等。
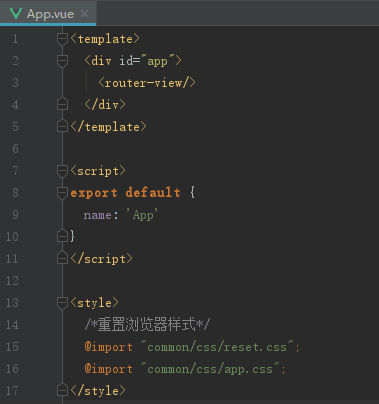
2.2 App.vue
app.vue时项目的主组件,所有页面都是在app.vue下切换的(基于此组件,若多页面的则不是)。其中<router-view/>是子路由视图。
2.3 main.js
main.js是入口文件,主要作用是初始化vue实例并使用需要的插件。使用某些插件使用Vue.use(xxx)。

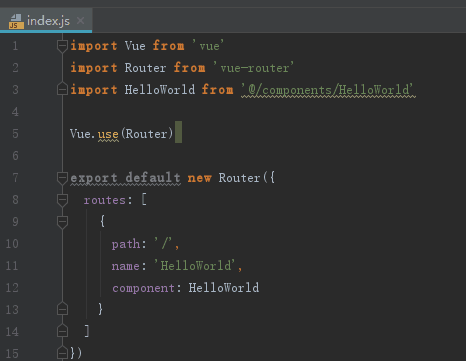
2.4 router
路由配置文件,地址为src>router>index.js。可进行自定义配置,然后引入到main.js中,加入至vue实例。
2.5 store(vuex)
自己增加文件,作用为数据仓库,对项目中公用数据进行设置存储。

3. webpack
webpack是当下最热门的前端资源模块化管理工具和打包工具,可以将很多松散的模块按照一定的规则打包成符合生产环境的前端资源,同时具有按需加载,等到实际需要的时候进行异步加载。通过loader的转换,在项目中任何形式的资源都可以被理解为模块,比如img,css,js等。
3.1 webpack.base.conf.js
'use strict'
const path = require('path')
const utils = require('./utils')
const config = require('../config')
const vueLoaderConfig = require('./vue-loader.conf')
function resolve (dir) {
return path.join(__dirname, '..', dir)
}
module.exports = {
context: path.resolve(__dirname, '../'),
//******入口******
entry: {
app: './src/main.js'
},
//输出文件,打包到哪里,配置来源于config文件夹配置
output: {
//config>index.js下的build中的assetsRoot,即dist文件夹
path: config.build.assetsRoot,
//导出文件的文件名
filename: '[name].js',
//生产模式或开发模式下的html,js等文件内部引用的公共路径(config>index.js下的build或dev)
publicPath: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production'
? config.build.assetsPublicPath
: config.dev.assetsPublicPath
},
//文件解析
resolve: {
//自动解析确定的扩展名,使导入模块时不带扩展名(import a from a.vue,后缀名省略)
extensions: ['.js', '.vue', '.json'],
alias: {
// 创建import 或 require的别名
'vue$': 'vue/dist/vue.esm.js',
// 用@来代替src,引用路径时使用
'@': resolve('src'),
}
},
//项目中不同类型的模块处理规则
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /.vue$/,//vue 文件后缀
loader: 'vue-loader',//使用vue-loader进行处理
options: vueLoaderConfig//对vue-loader做的额外选项配置
},
{
test: /.js$/,//js文件后缀
loader: 'babel-loader',// 使用babel-loader进行处理
// 必须处理包含src test的文件夹
include: [resolve('src'), resolve('test'), resolve('node_modules/webpack-dev-server/client')]
},
{
test: /.(png|jpe?g|gif|svg)(?.*)?$/,//图片后缀
loader: 'url-loader',//使用url-loader处理
//对loader做的额外配置
options: {
limit: 10000,//小于10kb的以base64进行引用
// 文件名为name ,7位hash值,扩展名
name: utils.assetsPath('img/[name].[hash:7].[ext]')
}
},
{
test: /.(mp4|webm|ogg|mp3|wav|flac|aac)(?.*)?$/,
loader: 'url-loader',
options: {
limit: 10000,
name: utils.assetsPath('media/[name].[hash:7].[ext]')
}
},
// 字体文件
{
test: /.(woff2?|eot|ttf|otf)(?.*)?$/,
loader: 'url-loader',
options: {
limit: 10000,
name: utils.assetsPath('fonts/[name].[hash:7].[ext]')
}
}
]
},
node: {
// prevent webpack from injecting useless setImmediate polyfill because Vue
// source contains it (although only uses it if it's native).
setImmediate: false,
// prevent webpack from injecting mocks to Node native modules
// that does not make sense for the client
dgram: 'empty',
fs: 'empty',
net: 'empty',
tls: 'empty',
child_process: 'empty'
}
}
3.2 开发环境相关
3.2.1 webpack.dev.conf.js
module: {
// 通过传入一些配置来获取rules配置,此处都为true,表示都生成
rules: utils.styleLoaders({ sourceMap: config.dev.cssSourceMap, usePostCSS: true })
}
3.2.2 styleLoaders/cssLoader(until.js)
styleLoader配置:
exports.styleLoaders = function (options) {
const output = [];//返回数组,数组中保存的是针对各种类型的样式文件的处理方式
// 调用cssLoaders方法返回各类型的样式对象(css:loader)
const loaders = exports.cssLoaders(options);
// 遍历loaders
for (const extension in loaders) {
//根据遍历获得的key(extension) 来得到value (loader)
const loader = loaders[extension]
output.push({
test: new RegExp('\.' + extension + '$'),//处理文件的类型
use: loader// 用loader来处理,loader来自loaders【extension】
})
}
return output
}
exports.cssLoaders = function (options) {
options = options || {}
const cssLoader = {
loader: 'css-loader',
// options 是 css-loader的选项配置
options: {
sourceMap: options.sourceMap// 根据参数是否要生成sourceMap文件
}
}
const postcssLoader = {
loader: 'postcss-loader',
options: {
sourceMap: options.sourceMap
}
}
// generate loader string to be used with extract text plugin 生成loader
function generateLoaders (loader, loaderOptions) {
// 默认的loader是css-loader
const loaders = options.usePostCSS ? [cssLoader, postcssLoader] : [cssLoader]
if (loader) {
loaders.push({
loader: loader + '-loader',
// 将loaderOptions和sourceMap组成一个对象
options: Object.assign({}, loaderOptions, {
sourceMap: options.sourceMap
})
})
}
// Extract CSS when that option is specified
// (which is the case during production build)
if (options.extract) {
// ExtractTextPlugin 分离js中引入的css文件
return ExtractTextPlugin.extract({
use: loaders,// 处理loader
fallback: 'vue-style-loader'// 没有被提取分离时使用的loader
})
} else {
return ['vue-style-loader'].concat(loaders)
}
}
// https://vue-loader.vuejs.org/en/configurations/extract-css.html
//返回css类型对应的loader组成的对象 generateLoaders()来生成loader
return {
css: generateLoaders(),
postcss: generateLoaders(),
less: generateLoaders('less'),
sass: generateLoaders('sass', { indentedSyntax: true }),
scss: generateLoaders('sass'),
stylus: generateLoaders('stylus'),
styl: generateLoaders('stylus')
}
}
webpack.dev.conf.js下的plugins。
plugins: [
//定义全局变量
new webpack.DefinePlugin({
'process.env': require('../config/dev.env')
}),
// 热更新插件
new webpack.HotModuleReplacementPlugin(),
//在热加载时直接返回更新文件名,而不是文件的id。
new webpack.NamedModulesPlugin(), // HMR shows correct file names in console on update.
// 不触发错误,即编译后运行的包正常运行
new webpack.NoEmitOnErrorsPlugin(),
// https://github.com/ampedandwired/html-webpack-plugin
// 自动生成html文件,比如编译后文件的引用
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
filename: 'index.html',// 生成的文件名
template: 'index.html',// 模板
inject: true
}),
// copy custom static assets
//将资源进行复制的插件
new CopyWebpackPlugin([
{
from: path.resolve(__dirname, '../static'),
to: config.dev.assetsSubDirectory,
ignore: ['.*']
}
])
]
3.3.1 webpack.prod.conf.js
生产环境下的webpack配置,通过merge方法合并webpack.base.conf.js基础配置。
const merge = require('webpack-merge')
const baseWebpackConfig = require('./webpack.base.conf')
const webpackConfig = merge(baseWebpackConfig, {
module: {
},
devtool: false,
output: {},
plugins: []
})
3.3.2 webpack.prod.conf.js——module
module主要是针对css的处理,调用了utils.styleLoaders
module: {
rules: utils.styleLoaders({
sourceMap: config.build.productionSourceMap,
extract: true,
usePostCSS: true
})
}
3.3.3 webpack.prod.conf.js——output
输出文件的文件目录/文件名等的设置
output: {
path: config.build.assetsRoot,//导出文件目录
filename: utils.assetsPath('js/[name].[chunkhash].js'), //导出的文件名
chunkFilename: utils.assetsPath('js/[id].[chunkhash].js')//非入口文件的文件名,而又需要被打包出来的文件命名配置,如按需加载的模块
}
3.3.4 webpack.prod.conf.js——plugins(插件)
plugins: [
// http://vuejs.github.io/vue-loader/en/workflow/production.html
new webpack.DefinePlugin({
'process.env': env// 配置全局环境为生产环境
}),
// js压缩插件
new UglifyJsPlugin({
uglifyOptions: {
// 压缩配置
compress: {
warnings: false//不显示警告
}
},
sourceMap: config.build.productionSourceMap,// 是否生成sourceMap文件
parallel: true
}),
// extract css into its own file 将js中引入css分离插件
new ExtractTextPlugin({
filename: utils.assetsPath('css/[name].[contenthash].css'),// 分离出来的css文件名
allChunks: true,
}),
// 压缩提取出的css,并解决ExtractTextPlugin分离出的js重复问题(多个文件引用同一个css文件)
new OptimizeCSSPlugin({
cssProcessorOptions: config.build.productionSourceMap
? { safe: true, map: { inline: false } }
: { safe: true }
}),
//生成html的插件,引入css文件和js文件
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
filename: config.build.index,// 生成的html的文件名
template: 'index.html',// 依据的模板
inject: true,// 注入的js文件会被放在Body标签中,当值为'head'的时候,将被放在head标签中
// 压缩配置
minify: {
removeComments: true,// 删除html中的注释代码
collapseWhitespace: true,// 删除html中的空白符
removeAttributeQuotes: true// 删除html元素中属性的引号
// more options:
// https://github.com/kangax/html-minifier#options-quick-reference
},
// necessary to consistently work with multiple chunks via CommonsChunkPlugin
chunksSortMode: 'dependency'//按dependency的顺序引入
}),
// keep module.id stable when vendor modules does not change
new webpack.HashedModuleIdsPlugin(),
// enable scope hoisting
new webpack.optimize.ModuleConcatenationPlugin(),
// 分离公共js到vendor中
new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({
name: 'vendor',// 文件名
minChunks (module) {
// 声明公告的模块来自 node_modules文件夹
return (
module.resource &&
/.js$/.test(module.resource) &&
module.resource.indexOf(
path.join(__dirname, '../node_modules')
) === 0
)
}
}),
//将运行时代码提取到单独的manifest文件中,防止影响vendor.js
new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({
name: 'manifest',
minChunks: Infinity
}),
// This instance extracts shared chunks from code splitted chunks and bundles them
// in a separate chunk, similar to the vendor chunk
// see: https://webpack.js.org/plugins/commons-chunk-plugin/#extra-async-commons-chunk
new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({
name: 'app',
async: 'vendor-async',
children: true,
minChunks: 3
}),
// 复制静态资源,将static文件内的内容复制到指定文件夹
new CopyWebpackPlugin([
{
from: path.resolve(__dirname, '../static'),
to: config.build.assetsSubDirectory,
ignore: ['.*']//忽视.*文件
}
])
]
3.3.5 webpack.prod.conf.js——额外配置
// 配置文件开启gzip压缩
if (config.build.productionGzip) {
// 引入压缩文件的组件,该插件会对生成的文件进行压缩,生成一个.gz文件
const CompressionWebpackPlugin = require('compression-webpack-plugin')
webpackConfig.plugins.push(
new CompressionWebpackPlugin({
asset: '[path].gz[query]',//目标文件名
algorithm: 'gzip',//使用gzip压缩
// 满足正则表达式的文件会被压缩
test: new RegExp(
'\.(' +
config.build.productionGzipExtensions.join('|') +
')$'
),
threshold: 10240,//资源文件大于10kb的时候会被压缩
minRatio: 0.8//最小压缩比达到0.8的时候会被压缩
})
)
}
//打包体积优化
if (config.build.bundleAnalyzerReport) {
const BundleAnalyzerPlugin = require('webpack-bundle-analyzer').BundleAnalyzerPlugin
webpackConfig.plugins.push(new BundleAnalyzerPlugin())
}