1 背景
新购了一个工业微型计算机,无风扇、可7*24h运行的那种,于是打算装个linux,做一下科研工作。本身也是初学linux,以前用虚拟机跑过CentOS,也经过比选,据说稳定,最终操作系统还是选它。考虑要尽快上手,本身对MySQL比较熟悉,但目前来看,MySQL在Oracle下有闭源的可能性,就选了MariaDB。CentOS 7.9 默认MariaDB yum 源版本较低(5.x),故打算从修改 yum 源开始。
操作系统:CentOS 7.9
数据库:MariaDB 10.6.8
2 yum安装MariaDB 10.6.8
2.1 添加MariaDB yum 源
CentOS 7.9 默认yum安装的版本如下。
$ yum info mariadb Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, product-id, search-disabled-repos, subscription-manager This system is not registered with an entitlement server. You can use subscription-manager to register. Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile Available Packages Name : mariadb Arch : x86_64 Epoch : 1 Version : 5.5.68 Release : 1.el7 Size : 8.8 M Repo : base/7/x86_64 Summary : A community developed branch of MySQL URL : http://mariadb.org License : GPLv2 with exceptions and LGPLv2 and BSD Description : MariaDB is a community developed branch of MySQL. : MariaDB is a multi-user, multi-threaded SQL database server. : It is a client/server implementation consisting of a server daemon (mysqld) : and many different client programs and libraries. The base package : contains the standard MariaDB/MySQL client programs and generic MySQL files
因为系统默认从阿里的yum源下载,没有提供较新的版本,此处需要手动添加源。
vim /etc/yum.repos.d/MariaDB.repo [mariadb] name = MariaDB # URL可替换为想用的版本的URL baseurl = http://yum.mariadb.org/10.6.8/centos7-amd64/ gpgkey=https://yum.mariadb.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-MariaDB gpgcheck=1
版本URL可在此处找:http://yum.mariadb.org
重新构建缓存。
yum clean all yum makecache //此步骤是用刚才所编辑 MariaDB.repo 源的关键
2.2 卸载旧版
systemctl stop mariadb // 或者直接ps找出来kill掉 yum remove mariadb-server mariadb mariadb-libs yum clean all
找出并删除残留目录。
$ find / -name mariadb $ find / -name mysql
2.3 安装新版及启动数据库
yum install MariaDB-server
查看状态:
$ systemctl status mariadb ● mariadb.service - MariaDB 10.6.8 database server Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/mariadb.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled) Drop-In: /etc/systemd/system/mariadb.service.d └─migrated-from-my.cnf-settings.conf Active: inactive (dead) Docs: man:mariadbd(8) https://mariadb.com/kb/en/library/systemd/
此时说明已经安装成功,直接启动。
$ systemctl start mariadb
再次查看状态:
$ systemctl status mariadb ● mariadb.service - MariaDB 10.6.8 database server Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/mariadb.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled) Drop-In: /etc/systemd/system/mariadb.service.d └─migrated-from-my.cnf-settings.conf Active: active (running) since Fri 2022-06-10 10:15:34 CST; 3s ago Docs: man:mariadbd(8) https://mariadb.com/kb/en/library/systemd/ Process: 22045 ExecStartPost=/bin/sh -c systemctl unset-environment _WSREP_START_POSITION (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Process: 22019 ExecStartPre=/bin/sh -c [ ! -e /usr/bin/galera_recovery ] && VAR= || VAR=`cd /usr/bin/..; /usr/bin/galera_recovery`; [ $? -eq 0 ] && systemctl set-environment _WSREP_START_POSITION=$VAR || exit 1 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Process: 22017 ExecStartPre=/bin/sh -c systemctl unset-environment _WSREP_START_POSITION (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 22031 (mariadbd) Status: "Taking your SQL requests now..." Tasks: 13 Memory: 56.5M CGroup: /system.slice/mariadb.service └─22031 /usr/sbin/mariadbd
说明启动成功。
2.4 特别说明
MariaDB 10.6.8中(包括之前几个版本,至少是10.4.12之后的版本),user 已经不是 mysql 数据库下的表,而是一个视图,故无法直接修改。如下图所示。
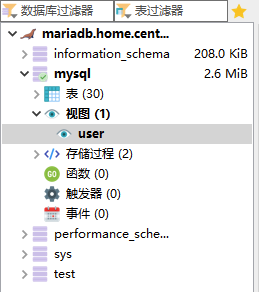
主要mysql中还有两个存储过程,作者表示理解不能。关于user的设置方法参考官网手册:
https://mariadb.com/kb/en/create-user/
https://mariadb.com/kb/en/set-password/
详细设置方法将在下一章介绍。
3 修改MariaDB数据存放路径
3.1 背景
因为所购工控计算机包括一个256GB的SSD,以及一个1TB的2.5英寸机械硬盘,打算将数据默认存放路径设在机械硬盘中。机器上的linux采用LVM(Logical Volume Manager)进行的分区管理,机械硬盘中有500GB挂载至 /opt,具体如下。
[root@192 ~]# lsblk NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT sda 8:0 0 238.5G 0 disk ├─sda1 8:1 0 1G 0 part /boot └─sda2 8:2 0 207.8G 0 part ├─centos-root 253:0 0 150G 0 lvm / ├─centos-swap 253:1 0 7.8G 0 lvm [SWAP] └─centos-var 253:2 0 50G 0 lvm /var sdb 8:16 0 931.5G 0 disk └─sdb1 8:17 0 931.5G 0 part └─centos-opt 253:3 0 500G 0 lvm /opt
考虑以后数据增加,故希望将数据存储位置修改至 /opt 下。
3.2 查看MariaDB数据当前存储位置
[root@192 ~]# mysql Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MariaDB connection id is 3 Server version: 10.6.8-MariaDB MariaDB Server Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. MariaDB [(none)]> select @@datadir;+-----------------+ | @@datadir | +-----------------+ | /var/lib/mysql/ | +-----------------+ 1 row in set (0.000 sec)
(注意,此时执行 mysql 并未要求输入用户名和密码)。通过上述查询结果可知,数据存储位置在 /var/lib/mysql 目录下。
3.3 关闭连接MariaDB的相关程序
这是为了避免正在连接MariaDB的程序因连接中断而报错。
3.4 在期望位置创建数据存放目录(datadir)
mkdir /opt/data mkdir /opt/data/mysql chown -R mysql:mysql /opt/data/mysql
3.5 关闭mariadb服务
systemctl stop mariadb
3.6 复制目录文件至新目录
cp -Rp /var/lib/mysql/* /opt/data/mysql
3.7 修改MariaDB的config文件
默认情况下,mysql的config信息在 /etc/my.cnf 中,为了确认 MariaDB 的config信息未发生变化,先查询该文件。
[root@192 ~]# find / -name my.*
/etc/my.cnf
/etc/my.cnf.d
结果显示相较于mysql还是有变化,下面我们来看 /etc/my.cnf 中的内容。
#
# This group is read both by the client and the server
# use it for options that affect everything
#
[client-server]
#
# include *.cnf from the config directory
#
!includedir /etc/my.cnf.d
此处需添加一部分内容,如下。(此处若不添加,服务器外客户端将无法访问数据库)
# # This group is read both by the client and the server # use it for options that affect everything # [client-server] port=3306
socket = /opt/data/mysql/mysql.sock
# # include *.cnf from the config directory # !includedir /etc/my.cnf.d
另外,最后一行代码
!includedir /etc/my.cnf.d
表示包含 /etc/my.cnf.d 目录下的所有 *.cnf 文件。我们来看下 /etc/my.cnf.d 目录下包括哪些文件。
ls /etc/my.cnf.d/ enable_encryption.preset mysql-clients.cnf server.cnf spider.cnf
其中有三个配置文件:mysql-clients.cnf、server.cnf、spider.cnf,其中 mysql-clients.cnf 用于配置客户端,我们不用管它,spider.cnf 也不相关,此目录下仅需要在 server.cnf 文件中配置:
server.cnf
# # These groups are read by MariaDB server. # Use it for options that only the server (but not clients) should see # # See the examples of server my.cnf files in /usr/share/mysql/ # # this is read by the standalone daemon and embedded servers [server] # this is only for the mysqld standalone daemon [mysqld] datadir =/opt/data/mysql socket = /opt/data/mysql/mysql.sock
......
3.8 开启数据库服务
systemctl start mariadb
3.9 验证
MariaDB [(none)]> select @@datadir; +------------------+ | @@datadir | +------------------+ | /opt/data/mysql/ | +------------------+ 1 row in set (0.000 sec)
修改成功。
4 MariaDB设置用户及密码(解决无密码即登录问题)
前文所述 MariaDB v10.6.8 安装好之后不输入用户名和密码就能进入数据库查询,本章将示范如何完善密码设置。
4.1 查看当前认证状态并修改
select user, host, plugin from mysql.user;
若 root 显示为 unix_socket (系统认出是root直接认证)就需要修改模式,按照官网说明(https://mariadb.com/kb/en/authentication-plugin-unix-socket/)即可。
alter user root@localhost identified via mysql_native_password;
修改后再查询,状态如下。
MariaDB [mysql]> SELECT USER, host, PLUGIN FROM user; +-------------+-----------+-----------------------+ | User | Host | plugin | +-------------+-----------+-----------------------+ | mariadb.sys | localhost | mysql_native_password | | root | localhost | mysql_native_password | | mysql | localhost | mysql_native_password | +-------------+-----------+-----------------------+ 3 rows in set (0.003 sec)
修改成功后发现还是可以通过 mysql 或 mysql -u root 命令直接进入。此时需要重新设置密码。即使从 mysql_native_password 模式变为 mysql_native_passoword 模式,也需要设置。
4.2 重设密码
ALTER USER `root`@`localhost` IDENTIFIED BY 'yourpassword';
此时再尝试,如下图,则说明密码设置成功。
[root@192 ~]# mysql -u root ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' (using password: NO)
5 外部访问数据库
若此时从外部通过客户端工具访问数据库,会出现连不上的情况。
Error “cannot connect to mysql server (10060)”
可能有多个原因(Error “cannot connect to mysql server (10060)” – Here’s how to fix it),笔者遇到的是其中两个原因:1)未在mysql.user视图中添加`root`@`%`用户域;2)未将3306端口列入服务器防火墙白名单。
5.1 在mysql.user视图中添加`root`@`%`用户域
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO `root`@`%` IDENTIFIED BY 'yourpassword' WITH GRANT OPTION;
MariaDB [mysql]> SELECT USER, host, PLUGIN FROM user; +-------------+-----------+-----------------------+ | User | Host | plugin | +-------------+-----------+-----------------------+ | mariadb.sys | localhost | mysql_native_password | | root | localhost | mysql_native_password | | mysql | localhost | mysql_native_password | | root | % | mysql_native_password | +-------------+-----------+-----------------------+ 4 rows in set (0.003 sec)
5.2 将3306端口列入服务器防火墙白名单
首先查看防火墙状态,如下图,表示开启。
systemctl status firewalld.service ● firewalld.service - firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Fri ...... CST; 23h ago Docs: man:firewalld(1) Main PID: 809 (firewalld) CGroup: /system.slice/firewalld.service └─809 /usr/bin/python2 -Es /usr/sbin/firewalld --nofork --nopid
# 查看白名单列表
firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-ports
#此处无3306/tcp
# 添加白名单端口
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=3306/tcp --permanent
# 重启防火墙
firewall-cmd --reload
# 查看白名单列表
firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-ports
#表示3306端口已加入白名单
3306/tcp
关于防火墙的其它命令:
# 查看防火墙状态,是否是running firewall-cmd --state # 重新载入配置,比如添加规则之后,需要执行此命令 firewall-cmd --reload # 列出支持的zone firewall-cmd --get-zones # 列出支持的服务,在列表中的服务是放行的 firewall-cmd --get-services # 查看已开放的端口 firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-ports # 永久添加80端口 firewall-cmd --add-port=3306/tcp --permanent # 永久添加80端口 firewall-cmd --remove-port=3306/tcp --permanent
命令说明:
# 作用域 --zone # 添加端口 --add-port=3306/tcp # 永久生效,没有此参数重启后失效 --permanent
参考文献:
[2] CentOS7下更改、移动mysql数据存储的位置(mariaDB适用)
[3] 解决MariaDB无密码可登录
[4] Error “cannot connect to mysql server (10060)” – Here’s how to fix it
[5] CentOS 7 端口白名单设置