全文摘自http://www.cnblogs.com/g1mist/p/3227290.html,很好的一个实例。
反射提供了封装程序集、模块和类型的对象。您可以使用反射动态地创建类型的实例,将类型绑定到现有对象,或从现有对象中获取类型。然后,可以调用类型的方法或访问其字段和属性。
1.先建立实体类
用户实体类:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
public class User { public int id { get; set; } public string UserName { get; set; } public string Password { get; set; } public int Age { get; set; } public string PhoneNumber { get; set; } public string Address { get; set; } } |
书籍实体类:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
public class Book { public int id { set; get; } public string BookName { get; set; } public string ISBN { set; get; } public string Author { set; get; } public double Price { set; get; } } |
2.通过反射技术来生成Insert语句(举个例子而已,只生成Insert语句)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
/// <summary> /// 泛型方法,反射生成SQLInsert语句/// </summary> /// <typeparam name="T">实体类型</typeparam> /// <param name="entity">实体对象</param> /// <returns></returns> public string CreateInsertSQL<T>(T entity) { //1.先获取实体的类型描述 Type type = entity.GetType(); //2.获得实体的属性集合 PropertyInfo[] props = type.GetProperties(); //实例化一个StringBuilder做字符串的拼接 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.Append("insert into " + type.Name + " ("); //3.遍历实体的属性集合 foreach (PropertyInfo prop in props) { //4.将属性的名字加入到字符串中 sb.Append(prop.Name + ","); } //**去掉最后一个逗号 sb.Remove(sb.Length - 1, 1); sb.Append(" ) values("); //5.再次遍历,形成参数列表"(@xx,@xx@xx)"的形式 foreach (PropertyInfo prop in props) { sb.Append("@" + prop.Name + ","); } //**去掉最后一个逗号 sb.Remove(sb.Length - 1, 1); sb.Append(")"); return sb.ToString(); } |
3.测试
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //调用ReflationCreateSQL类中的CreateInsertSQL方法 string sql = new ReflationCreateSQL().CreateInsertSQL(new User()); string sql1 = new ReflationCreateSQL().CreateInsertSQL(new Book()); Console.WriteLine(sql.ToString()); Console.WriteLine(sql1.ToString()); Console.WriteLine("Press any key to continue . . ."); Console.ReadLine(); } } |
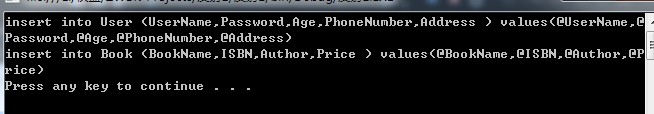
结果:

但是,我们发现id是主键,假设id是自增长的,我们生成的SQL(Insert)语句中就不应该有id,在这里我用自定义Attribute的方法来解决这个问题。
4.先新建一个类,继承Attribute类
|
1
2
3
4
|
public class KEYAttribute : Attribute{} |
这个类仅此而已就够了。
5.在实体类中的id这个字段上加上[KEY]标记
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
public class Book { [KEY] public int id { set; get; } public string BookName { get; set; } public string ISBN { set; get; } public string Author { set; get; } public double Price { set; get; } } |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
public class User { [KEY] public int id { get; set; } public string UserName { get; set; } public string Password { get; set; } public int Age { get; set; } public string PhoneNumber { get; set; } public string Address { get; set; } } |
6.加好标记之后,我们只需要这CreateInsertSQL<T>(T entity)这个方法中的两个foreach循环体中加一些判断即可
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
foreach (PropertyInfo prop in props) { //获取用户自定义标记集合 object[] attrs = prop.GetCustomAttributes(typeof(KEYAttribute), true); //如果属性上有自定义标记KEYAttribute,退出本次循环 if (attrs.Length > 0) { continue; } //将属性的名字加入到字符串中 sb.Append(prop.Name + ","); } |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
foreach (PropertyInfo prop in props) { object[] attrs = prop.GetCustomAttributes(typeof(KEYAttribute), true); if (attrs.Length > 0) { continue; } sb.Append("@" + prop.Name + ","); } |
7.测试