HTML5-postMessage实现跨域
对于使用H5实现跨域,很多人都一直处于半懂状态。知道使用postMessage发送消息,使用onMessage接受消息,但是到底哪个方法应该用window调用哪个应该用iframe的contentWindow调用不是很清楚。下面是我做的一个本地实现跨域的小demo,可以在github下载这个示例。为了执行它,首先,你需要找到你电脑的hosts文件,在127.0.0.1 localhost下添加如下代码:
127.0.0.1 localhost 127.0.0.1 main.com 127.0.0.1 A.com 127.0.0.1 B.com
然后,你需要启动一个服务器,如Apache等,把github上下载的三个html文件放到你的服务器上。最后,你只需访问http://main.com:你的端口号 ,就可以进行跨域通信了。
三个html文件的关系如下。
三个域:http://main.com:8090 ; http://a.com:8090 ; http://b.com:8090 。 主页面maindomain.html在main.com,两个iframe (subAdomain.html , subBdomain.html)分别在 a.com , b.com 。在maindomain.html中,向textarea中输入消息,点击send to iframe按钮,可以发送消息到指定iframe (subAdomain.html 或者subBdomain.html),在ifame中也可以发送消息到maindomain.html,同时,有一个收到ifame消息的回执信息。
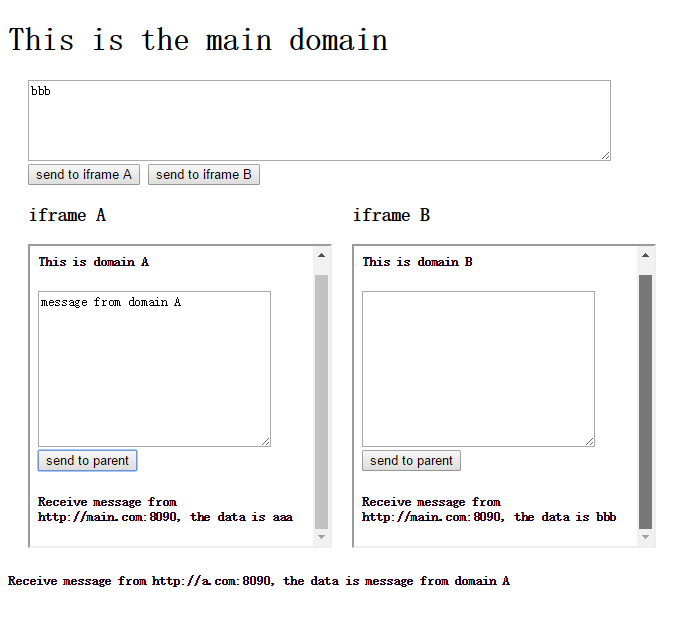
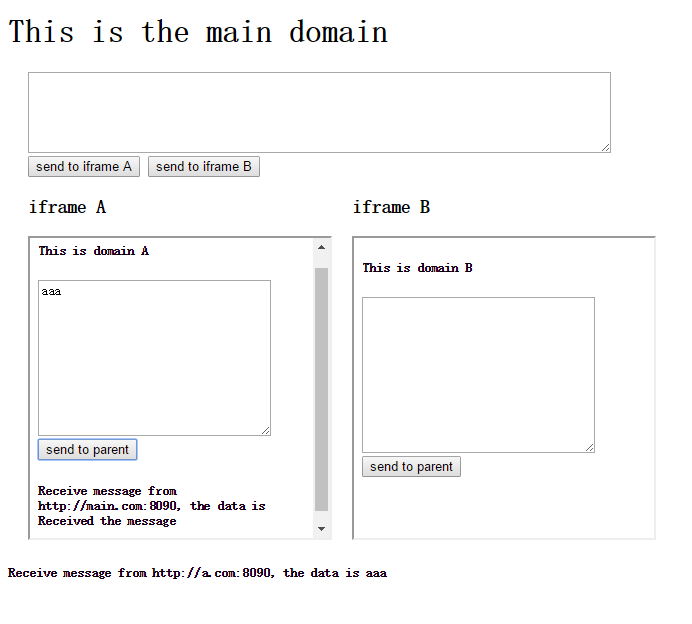
这应该是很常见的场景,把网站公共的资源放到某子域,在其他子域需要访问该子域上的资源。实现的效果如下。
-
不带回执信息:
-
带回执信息:
基本知识
首先介绍onMessage事件中,event的一些属性,理解这些可以使你很容易读懂我的示例。
* data: 传入的数据
* origin: 发送消息的文档所在的域
* source: 发送消息的文档的window对象的代理
如果你想在子域X向子域Y发送消息,你需要,在子域X的html文件,获取Y的window对象(iframe的contentWindow),然后调用postMessage(message, Y所在的域),同时,在子域Y的html文件中,监听window对象message事件(使用onMessage)就好。当然,你可以在onMessage中再次使用postMessage,向子域X发送一个回执信息。 我们时常混乱的是,在哪个域的window对象上调用postMessage。
代码
main.com
<h1>This is the main domain</h1>
<div style="margin:0 20px;">
<textarea name="main" cols="80" rows="5"></textarea><br/>
<input type="button" value="send to iframe A"/>
<input type="button" value="send to iframe B"/>
</div>
<div style="float:left; margin:0 20px;">
<h3>iframe A</h3>
<iframe src="http://a.com:8090/subAdomain.html" frameborder="1" style="300px; height:300px;"></iframe>
</div>
<div style="float:left;">
<h3>iframe B</h3>
<iframe src="http://b.com:8090/subBdomain.html" frameborder="1" style="300px; height:300px;"></iframe>
</div>
<div style="float:left;">
<h5 id="received"></h5>
</div>
<script>
var received = document.querySelector('#received');
var sendToIframeA = document.querySelectorAll('input')[0];
var sendToIframeB = document.querySelectorAll('input')[1];
var iframeA = document.querySelectorAll('iframe')[0];
var iframeB = document.querySelectorAll('iframe')[1];
//receive message
function getMessage(e){
console.log('main received!');
received.innerHTML = 'Receive message from ' + e.origin + ', the data is ' + e.data;
e.source.postMessage('Received the message', e.origin);
}
window.addEventListener('message', getMessage, false);
//post message
sendToIframeA.addEventListener('click', function(){
var content = document.querySelector('textarea').value;
iframeA.contentWindow.postMessage(content, 'http://a.com:8090');
}, false);
sendToIframeB.addEventListener('click', function(){
var content = document.querySelector('textarea').value;
iframeB.contentWindow.postMessage(content, 'http://b.com:8090');
}, false);
</script>
a.com
<h5>This is domain A</h5>
<textarea name="subA" cols="30" rows="10"></textarea>
<input type="button" value="send to parent"/>
<div style="float:left;">
<h5 id="received"></h5>
</div>
<script>
var send = document.querySelector('input');
var text = document.querySelector('textarea');
var received = document.querySelector('#received');
//receive message
function getMessage(e){
console.log('A received!');
received.innerHTML = 'Receive message from ' + e.origin + ', the data is ' + e.data;
//e.source.postMessage('Received the message', e.origin);
}
window.addEventListener('message', getMessage, false);
//post message
send.addEventListener('click', function(){
var content = text.value;
window.parent.postMessage(content, 'http://main.com:8090');
}, false);
</script>
b.com
<h5>This is domain B</h5>
<textarea name="subB" cols="30" rows="10"></textarea>
<input type="button" value="send to parent"/>
<div style="float:left;">
<h5 id="received"></h5>
</div>
<script>
var send = document.querySelector('input');
var text = document.querySelector('textarea');
var received = document.querySelector('#received');
//receive message
function getMessage(e){
console.log('B received!');
received.innerHTML = 'Receive message from ' + e.origin + ', the data is ' + e.data;
//e.source.postMessage('Received the message', e.origin);
}
window.addEventListener('message', getMessage, false);
//post message
send.addEventListener('click', function(){
var content = text.value;
window.parent.postMessage(content, 'http://main.com:8090');
}, false);
</script>
from :https://blog.csdn.net/qiqingjin/article/details/51326060