SOM(自组织映射神经网络)是一种可以根据输入对象的特征自动进行分类(聚类)的神经网络。向该网络输入任意维度的向量都会得到一个二维图像, 不同特征的输入会被映射到二维图像的不同地方(所以SOM也可以用来降维)。它有两种学习规则:Winner-Take-All和Kohonen学习算法,后者在前者的基础上改进得到。
Som类最主要的三个方法:
- initialize方法,用于设定输出层节点数、输入向量维度
- mapping方法,方便用户应用模型做预测
- train方法,用来训练模型
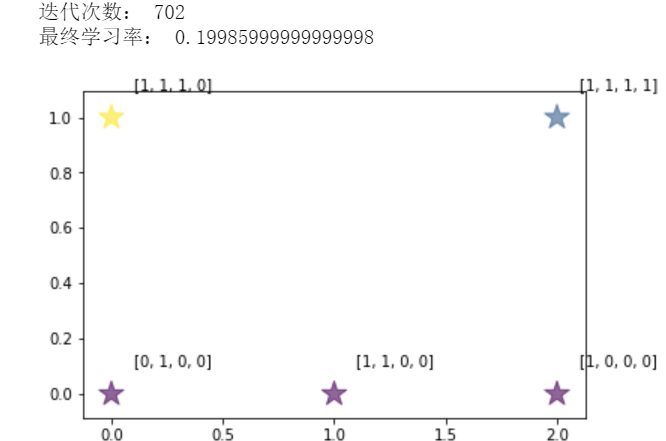
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import math import csv # 向量归一化,转化为对应单位向量,这样计算欧几里得距离就 # 可以转化为计算向量的点积(二维平面中,单位向量点积就是 # cos theta),点积越大距离越近 def normalize(vector): return vector / np.linalg.norm(vector) class Som: def initialize(self, model, dimension): self.nodes = [] # 初始化节点 for i in range(model[0]): temp = [] for j in range(model[1]): vector = np.random.randn(dimension) # 每个节点都包含一个维度和输入向量维度相同的向量 vector = normalize(vector) # 归一化 temp.append(vector) self.nodes.append(temp) self.model = model # 便于遍历节点 def best_matching_unit(self, vector): result = [0, 0] # 返回优胜节点坐标 max = -10000 for i in range(self.model[0]): for j in range(self.model[1]): temp = self.nodes[i][j].dot(vector) if temp > max: max = temp result[0], result[1] = i, j return result def get_r_p(self, N): # 根据距离优胜节点的距离变化的值 return 1.0 / math.exp(N) def neighbor(self, pos, table): result = [] x = pos[0] y = pos[1] if x - 1 >= 0: if not table[x - 1][y]: result.append([x - 1, y]) table[x - 1][y] = True if x + 1 < self.model[0]: if not table[x + 1][y]: result.append([x + 1, y]) table[x + 1][y] = True if y - 1 >= 0: if not table[x][y - 1]: result.append([x, y - 1]) table[x][y - 1] = True if y + 1 < self.model[1]: if not table[x][y + 1]: result.append([x, y + 1]) table[x][y + 1] = True return result def get_neighbor(self, BMU, r): # 获取邻居节点,返回值为[[距离为1坐标集合..], [距离为2坐标集合..], [...], ...] result = [] if r > 0: table = [] # 记录已经存入的结点 for i in range(self.model[0]): table.append([False] * self.model[1]) table[BMU[0]][BMU[1]] = True # print("table=", table) neighbors = self.neighbor(BMU, table); # 距离为1的节点 result.append(neighbors) for i in range(r - 1): temp = [] for x in neighbors: temp += self.neighbor(x, table) neighbors = temp # 距离为2+i的结点 result.append(neighbors) return result def update_nodes(self, BMU, example, r, eta): # 参数:优胜节点坐标,输入向量,优胜领域半径,学习率 # print("r, eta=", r, eta) # print("before update=", self.nodes) w = self.nodes[BMU[0]][BMU[1]] w += eta * self.get_r_p(0) * (example - w) # 更新优胜节点 self.nodes[BMU[0]][BMU[1]] = normalize(w) neighbors = self.get_neighbor(BMU, r); # print("neighbors=", neighbors) for i in range(len(neighbors)): for pos in neighbors[i]: # 更新距离为i+1的节点 w = self.nodes[pos[0]][pos[1]] w += eta * self.get_r_p(i + 1) * (example - w) self.nodes[pos[0]][pos[1]] = normalize(w) # print("after update=", self.nodes) def eta(self, t): # 参数:当前迭代次数,隐含参数:最大迭代次数,学习率初始值 if t <= self.MAX_ITERATION / 10: # 前1/10次迭代学习率线性下降到1/20 return self.init_eta - t * self.k1 else: # 后9/10次迭代学习率线性下降到0 return self.init_eta / 20 - (t - self.MAX_ITERATION / 10) * self.k2 def get_r(self, t): # 优胜邻域随着迭代次数变小 return int(self.init_r * (1 - t / self.MAX_ITERATION)) # 向下取整 def train(self, get_batch, MAX_ITERATION, init_eta, MIN_ETA, init_r): # 参数:获取每次迭代所需样本的函数,最大迭代次数,学习率初始值,最小学习率,优胜领域初始值 self.MAX_ITERATION = MAX_ITERATION self.init_eta = init_eta # 学习率初始值 self.k1 = (19/20 * self.init_eta) / (1/10 * self.MAX_ITERATION) # 学习率线性下降斜率1 self.k2 = (1/20 * self.init_eta) / (9/10 * self.MAX_ITERATION) # 学习率线性下降斜率2 self.init_r = init_r count = 0 while count < MAX_ITERATION and self.eta(count) > MIN_ETA: batch = get_batch() # print(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>count=", count) # print("batch=", batch) for example in batch: # print("example=", example) BMU = self.best_matching_unit(example) # print("BMU=",BMU) self.update_nodes(BMU, example, self.get_r(count), self.eta(count)) count = count + 1 print("迭代次数:", count) print("最终学习率:", self.eta(count)) def mapping(self, vector): vector = normalize(vector) return self.best_matching_unit(vector) # 返回优胜节点坐标 data = [[1, 0, 0, 0], [1, 1, 0, 0], [1, 1, 1, 0], [0, 1, 0, 0], [1, 1, 1, 1]] features = np.array(list(map(normalize, data))) # 归一化 def full_batch(): return features som = Som() som.initialize([3, 2], 4) def testModel(): result = list(map(som.mapping, features)) count_pos = {} for pos in result: if result.count(pos) >= 1: count_pos[str(pos[0]) + ',' + str(pos[1])] = result.count(pos) x = np.array(list(map(lambda x: x[0], result))); y = np.array(list(map(lambda x: x[1], result))); size = np.array(list(map(lambda x: count_pos[str(x[0]) + ',' + str(x[1])], result))); color = np.arctan2(y, x) plt.scatter(x, y, s=size * 300, c=color,alpha=0.6, marker='*') for i in range(len(x)): # 打上标签 plt.annotate(str(data[i]), xy = (x[i], y[i]), xytext = (x[i]+0.1, y[i]+0.1)) plt.show() som.train(full_batch, 10000, 0.6, 0.2, 3) testModel()