第3章 数据结构与算法
1. memmove边界问题

void memmove_(char *pDst,const char* pSrc,size_t size){
assert(pSrc!=NULL&&pDst!=NULL);
const char* p;
char*q;
if(pSrc<pDst&&pSrc+size>pDst){
p=pSrc+size-1;
q=pDst+size-1;
while(size--)
*q--=*p--;
}
else{
p=pSrc;
q=pDst;
while(size--)
*q++=*p++;
}
}
assert(pSrc!=NULL&&pDst!=NULL);
const char* p;
char*q;
if(pSrc<pDst&&pSrc+size>pDst){
p=pSrc+size-1;
q=pDst+size-1;
while(size--)
*q--=*p--;
}
else{
p=pSrc;
q=pDst;
while(size--)
*q++=*p++;
}
}
2. 出错处理方式

3. 字符串算法的实现
(1) strstr函数: 进行了比较好的判断, 主要是便于比较快的结束判断
char* strstr_(const char *str1,const char* str2){
assert(str1!=NULL&&str2!=NULL);
int len1=strlen(str1);
int len2=strlen(str2);
if(len2>len1)//如果str2的长度大于str1的长度, 直接可以返回NULL
return NULL;
while(*str1!='\0'){
const char *p=str1;
const char *q=str2;
while(*q&&*p==*q)
p++,q++;
if(*q=='\0')
return str1;
str1++;
len1--;
if(len1<len2)//如果此时str1剩余的长度小于str2的话,这样就没有再继续查找的必要了
return NULL;
}
}
assert(str1!=NULL&&str2!=NULL);
int len1=strlen(str1);
int len2=strlen(str2);
if(len2>len1)//如果str2的长度大于str1的长度, 直接可以返回NULL
return NULL;
while(*str1!='\0'){
const char *p=str1;
const char *q=str2;
while(*q&&*p==*q)
p++,q++;
if(*q=='\0')
return str1;
str1++;
len1--;
if(len1<len2)//如果此时str1剩余的长度小于str2的话,这样就没有再继续查找的必要了
return NULL;
}
}
(2) strtok函数的实现
char *strtok_(char *str,const char *delim){
char *p;
static char *nexttoken;
char map[32]={0};//map是一个位图,256位,用来记录delim中的字符(分隔符)
do{
map[*delim>>3]|=(1<<(*delim&7));//将分隔符对应的位置设置为1
}while(*delim++);
if(str)
p=str;
else
p=nexttoken;
//如果开始字符为分隔符, 略过
while((map[*p>>3]&(1<<(*p&7)))&&*p)
p++;
str=p;
while(*p){
if(map[*p>>3]&(1<<(*p&7))){//如果*p为分隔符, 那么将这个位置设为’\0’, 这样就完成了一个单词的分割
*p++='\0';
break;
}
p++;
}
nexttoken=p;//用static变量记录下一个分隔开始的起点.
if(str==p)
return NULL;
else
return str;
char *p;
static char *nexttoken;
char map[32]={0};//map是一个位图,256位,用来记录delim中的字符(分隔符)
do{
map[*delim>>3]|=(1<<(*delim&7));//将分隔符对应的位置设置为1
}while(*delim++);
if(str)
p=str;
else
p=nexttoken;
//如果开始字符为分隔符, 略过
while((map[*p>>3]&(1<<(*p&7)))&&*p)
p++;
str=p;
while(*p){
if(map[*p>>3]&(1<<(*p&7))){//如果*p为分隔符, 那么将这个位置设为’\0’, 这样就完成了一个单词的分割
*p++='\0';
break;
}
p++;
}
nexttoken=p;//用static变量记录下一个分隔开始的起点.
if(str==p)
return NULL;
else
return str;
(3) 删除特定的字符数组
这儿同样是使用map位图来记录出现的字符
char *deleteChars(char *str, const char *chr){
assert(str!=NULL);
char map[32]={0};
int i=0,j=0;
while(*chr){
map[*chr>>3]|=(1<<(*chr&7));
chr++;
}
do{
if(!(map[str[j]>>3]&(1<<(str[j]&7))))
str[i++]=str[j];
}
while(str[j++]!='\0');
return str;
}
assert(str!=NULL);
char map[32]={0};
int i=0,j=0;
while(*chr){
map[*chr>>3]|=(1<<(*chr&7));
chr++;
}
do{
if(!(map[str[j]>>3]&(1<<(str[j]&7))))
str[i++]=str[j];
}
while(str[j++]!='\0');
return str;
}
(4) IP地址与无符号整型数的转换
unsigned int str2int(char *str,int n){
unsigned int val=0;
int i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
val=val*10+(str[i]-'0');
}
return val;
}
unsigned int ip2int(char* ip,int* flag){
char *p1=ip;
int len=0;
char pos[3];
int count=0;
unsigned int s1,s2,s3,s4;
while(*p1!='\0'){
if(!(*p1>='0'&&*p1<='9'||*p1=='.')) {
printf("Invalid char:%c\n",*p1);
// exit(-1);
*flag=-1;
return -1;
}
if(*p1=='.')
pos[count++]=len;
p1++;
len++;
}
if(count!=3) {
printf("Not enough \'.\'\n");
*flag=-2;
return -2;
// exit(-2);
}
printf("pos:%d %d %d\n",pos[0],pos[1],pos[2]);
if(pos[0]==0||pos[2]==len-1||pos[1]-pos[0]==1||pos[2]-pos[1]==1) {
printf("Invalid Format:缺少一个IP段\n");
*flag=-3;
return -3;
// exit(-3);
}
if(pos[0]>3||pos[1]-pos[0]>4||pos[2]-pos[1]>4||len-pos[2]>4){
printf("Invalid Format:IP段太长\n");
*flag=-4;
return -4;
// exit(-4);
}
s1=str2int(ip,pos[0]);
s2=str2int(ip+pos[0]+1,pos[1]-pos[0]-1);
s3=str2int(ip+pos[1]+1,pos[2]-pos[1]-1);
s4=str2int(ip+pos[2]+1,len-pos[2]-1);
printf("%x.%x.%x.%x -> ",s1,s2,s3,s4);
if(!(s1>=0&&s1<=255&&
s2>=0&&s2<=255&&
s3>=0&&s3<=255&&
s4>=0&&s4<=255)) {
printf("Invalid Format:IP段超出范围\n");
*flag=-5;
return -5;
// exit(-5);
}
*flag=1;
return s1<<24|s2<<16|s3<<8|s4;
}
void ip_test(){
char *ip[]={"0.0.0.0","211.211.22.33",
".","..","...","......","211...","211.22.0.0",
"211.22..0","211.22.ab.33",".22.33.55"
};
int len=sizeof(ip)/sizeof(ip[0]);
int i;
for(i=0;i<len;i++){
int flag;
unsigned int val;
printf("%s\n",ip[i]);
val=ip2int(ip[i],&flag);
printf("%#x\n",val);
printf("flag=%d\n");
if(flag<0){
printf("Invalid Format\n");
}
printf("==================\n");
}
}
unsigned int val=0;
int i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
val=val*10+(str[i]-'0');
}
return val;
}
unsigned int ip2int(char* ip,int* flag){
char *p1=ip;
int len=0;
char pos[3];
int count=0;
unsigned int s1,s2,s3,s4;
while(*p1!='\0'){
if(!(*p1>='0'&&*p1<='9'||*p1=='.')) {
printf("Invalid char:%c\n",*p1);
// exit(-1);
*flag=-1;
return -1;
}
if(*p1=='.')
pos[count++]=len;
p1++;
len++;
}
if(count!=3) {
printf("Not enough \'.\'\n");
*flag=-2;
return -2;
// exit(-2);
}
printf("pos:%d %d %d\n",pos[0],pos[1],pos[2]);
if(pos[0]==0||pos[2]==len-1||pos[1]-pos[0]==1||pos[2]-pos[1]==1) {
printf("Invalid Format:缺少一个IP段\n");
*flag=-3;
return -3;
// exit(-3);
}
if(pos[0]>3||pos[1]-pos[0]>4||pos[2]-pos[1]>4||len-pos[2]>4){
printf("Invalid Format:IP段太长\n");
*flag=-4;
return -4;
// exit(-4);
}
s1=str2int(ip,pos[0]);
s2=str2int(ip+pos[0]+1,pos[1]-pos[0]-1);
s3=str2int(ip+pos[1]+1,pos[2]-pos[1]-1);
s4=str2int(ip+pos[2]+1,len-pos[2]-1);
printf("%x.%x.%x.%x -> ",s1,s2,s3,s4);
if(!(s1>=0&&s1<=255&&
s2>=0&&s2<=255&&
s3>=0&&s3<=255&&
s4>=0&&s4<=255)) {
printf("Invalid Format:IP段超出范围\n");
*flag=-5;
return -5;
// exit(-5);
}
*flag=1;
return s1<<24|s2<<16|s3<<8|s4;
}
void ip_test(){
char *ip[]={"0.0.0.0","211.211.22.33",
".","..","...","......","211...","211.22.0.0",
"211.22..0","211.22.ab.33",".22.33.55"
};
int len=sizeof(ip)/sizeof(ip[0]);
int i;
for(i=0;i<len;i++){
int flag;
unsigned int val;
printf("%s\n",ip[i]);
val=ip2int(ip[i],&flag);
printf("%#x\n",val);
printf("flag=%d\n");
if(flag<0){
printf("Invalid Format\n");
}
printf("==================\n");
}
}
(5)正则表达式匹配问题

int PatternMatch(const char* pat,const char*str){
const char *s=NULL;
const char *p=NULL;
int star=0,bBreak=0;
do{
bBreak=0;
for(s=str,p=pat;*s;++s,++p){
switch(*p){
case '?':
break;
case '*':
star=1;
str=s;
pat=p;
if(!*++pat)
return 1;
bBreak=1;
break;
default:
if(*s!=*p){
if(!star)
return 0;
str++;
bBreak=1;
}
break;
}
if(bBreak)
break;
}
if(!bBreak){
if(*p=='*')
++p;
return !*p;
}
}while(1);
}
void PatternMatch_test(){
char *pat="hell*world*!";
char *str="hellfasdfdworldfadsf!";
int b=PatternMatch(pat,str);
printf("%d\n",b);
}
const char *s=NULL;
const char *p=NULL;
int star=0,bBreak=0;
do{
bBreak=0;
for(s=str,p=pat;*s;++s,++p){
switch(*p){
case '?':
break;
case '*':
star=1;
str=s;
pat=p;
if(!*++pat)
return 1;
bBreak=1;
break;
default:
if(*s!=*p){
if(!star)
return 0;
str++;
bBreak=1;
}
break;
}
if(bBreak)
break;
}
if(!bBreak){
if(*p=='*')
++p;
return !*p;
}
}while(1);
}
void PatternMatch_test(){
char *pat="hell*world*!";
char *str="hellfasdfdworldfadsf!";
int b=PatternMatch(pat,str);
printf("%d\n",b);
}
4. 判断单向链表中是否存在循环?


5. 树的遍历算法
使用两种方式:递归和非递归的方式
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#define print_arr(a,n) for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\
printf("%d ",a[i]);\
printf("\n")
using namespace std;
struct node{
node():left(0),right(0){}
node(int d):data(d),left(0),right(0){}
int data;
node* left;
node* right;
};
//node *tree_create(int *first,int* end){
// if(first!=end){
// node *root=new node;
// root->data=*first++;
// node* p=root;
// while(first!=end){
// node *q1=new node;
// q1->data=*first++;
// p->left=q1;
// if(first!=end){
// node *q2=new node;
// q2->data=*first++;
// p->right=q2;
// }
// }
// }
//}
node *make_tree(node*root,int l,int r){
node* p=new node(l);
root->left=p;
p=new node(r);
root->right=p;
return root;
}
node *make_tree(node*root,int l,bool flag=true){
node* p=new node(l);
if(flag)
root->left=p;
else
root->right=p;
return root;
}
node *free_tree(node *root){
if(root!=0){
free_tree(root->left);
free_tree(root->right);
}
}
//递归的前序遍历
void preorder(node *root){
if(root){
cout<<root->data<<' ';
preorder(root->left);
preorder(root->right);
}
}
//使用栈来实现非递归的前序遍历
void preorder_(node *root){
if(!root)
return;
stack<node*> st;
st.push(root);
node* p;
while(!st.empty()){
p=st.top();
st.pop();
cout<<p->data<<' ';
if(p->right!=0)//将左子树压入栈
st.push(p->right);
if(p->left!=0)//将右子树压入栈
st.push(p->left);
}
}
//递归方式的中序遍历
void inorder(node *root){
if(root){
inorder(root->left);
cout<<root->data<<' ';
inorder(root->right);
}
}
//同样使用栈来实现非递归的中序遍历
void inorder_(node *root){
if(!root)
return;
stack<node*> st;
node *p=root;
do{
//先将左子树不断的入栈
while(p!=0){
st.push(p);
p=p->left;
}
//访问节点的值,然后再转向处理右子树
if(!st.empty()){
p=st.top();
st.pop();
cout<<p->data<<' ';
p=p->right;
}
}while(p!=0||!st.empty());
}
//递归方式的后序遍历
void postorder(node *root){
if(root){
postorder(root->left);
postorder(root->right);
cout<<root->data<<' ';
}
}//这是一种比较好的方式来实现后序遍历的
//使用栈来实现非递归的后序遍历
void postorder_(node *root){
if(!root)
return;
stack<node*> st;
stack<bool> tag;//用来区分左右子树,false表示左子树,true表示右子树
node *p=root;
do{
while(p!=0){
st.push(p);
tag.push(false);
p=p->left;
}
if(!st.empty()){
p=st.top();
if(tag.top()){//如果是右子树就输出节点值
st.pop();
tag.pop();
cout<<p->data<<' ';
p=0;
}
else{//当前是节点的左子树,需要将其右子树进行处理(入栈)
p=p->right;
tag.top()=true;
}
}
}while(p!=0||!st.empty());
}
//分层遍历,很自然的使用队列
void levelorder(node *root){
if(!root)
return;
queue<node*> q;
node *p=root;
q.push(p);
while(!q.empty()){
p=q.front();
q.pop();
cout<<p->data<<' ';
if(p->left!=0)
q.push(p->left);
if(p->right!=0)
q.push(p->right);
}
}
void in_post_pre(int* in,int *post,int *pre,int n){
}
int main(){
node *root=new node(20);
make_tree(root,10,30);
node *p=root->left;
make_tree(p,15,14);
p=p->right;
make_tree(p,28,false);
p=root->right;
make_tree(p,29,41);
// preorder(root); cout<<endl;
// preorder_(root); cout<<endl;
// inorder(root);cout<<endl;
// inorder_(root);cout<<endl;
// postorder(root);cout<<endl;
// postorder_(root);cout<<endl;
levelorder(root);cout<<endl;
free_tree(root);
}
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#define print_arr(a,n) for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\
printf("%d ",a[i]);\
printf("\n")
using namespace std;
struct node{
node():left(0),right(0){}
node(int d):data(d),left(0),right(0){}
int data;
node* left;
node* right;
};
//node *tree_create(int *first,int* end){
// if(first!=end){
// node *root=new node;
// root->data=*first++;
// node* p=root;
// while(first!=end){
// node *q1=new node;
// q1->data=*first++;
// p->left=q1;
// if(first!=end){
// node *q2=new node;
// q2->data=*first++;
// p->right=q2;
// }
// }
// }
//}
node *make_tree(node*root,int l,int r){
node* p=new node(l);
root->left=p;
p=new node(r);
root->right=p;
return root;
}
node *make_tree(node*root,int l,bool flag=true){
node* p=new node(l);
if(flag)
root->left=p;
else
root->right=p;
return root;
}
node *free_tree(node *root){
if(root!=0){
free_tree(root->left);
free_tree(root->right);
}
}
//递归的前序遍历
void preorder(node *root){
if(root){
cout<<root->data<<' ';
preorder(root->left);
preorder(root->right);
}
}
//使用栈来实现非递归的前序遍历
void preorder_(node *root){
if(!root)
return;
stack<node*> st;
st.push(root);
node* p;
while(!st.empty()){
p=st.top();
st.pop();
cout<<p->data<<' ';
if(p->right!=0)//将左子树压入栈
st.push(p->right);
if(p->left!=0)//将右子树压入栈
st.push(p->left);
}
}
//递归方式的中序遍历
void inorder(node *root){
if(root){
inorder(root->left);
cout<<root->data<<' ';
inorder(root->right);
}
}
//同样使用栈来实现非递归的中序遍历
void inorder_(node *root){
if(!root)
return;
stack<node*> st;
node *p=root;
do{
//先将左子树不断的入栈
while(p!=0){
st.push(p);
p=p->left;
}
//访问节点的值,然后再转向处理右子树
if(!st.empty()){
p=st.top();
st.pop();
cout<<p->data<<' ';
p=p->right;
}
}while(p!=0||!st.empty());
}
//递归方式的后序遍历
void postorder(node *root){
if(root){
postorder(root->left);
postorder(root->right);
cout<<root->data<<' ';
}
}//这是一种比较好的方式来实现后序遍历的
void postorder(Node* root){
stack<Node*> st;
Node* p=root,*visited=0;
while(p!=0||!st.empty()){
while(p!=0){
st.push(p);
p=p->left;
}
p=st.top();
if(p->right==0||visited==p->right){
cout<<(int)p->data<<' ';
st.pop();
visited=p;
p=0;
}
else{
p=p->right;
}
}
cout<<endl;
}
stack<Node*> st;
Node* p=root,*visited=0;
while(p!=0||!st.empty()){
while(p!=0){
st.push(p);
p=p->left;
}
p=st.top();
if(p->right==0||visited==p->right){
cout<<(int)p->data<<' ';
st.pop();
visited=p;
p=0;
}
else{
p=p->right;
}
}
cout<<endl;
}
void postorder_(node *root){
if(!root)
return;
stack<node*> st;
stack<bool> tag;//用来区分左右子树,false表示左子树,true表示右子树
node *p=root;
do{
while(p!=0){
st.push(p);
tag.push(false);
p=p->left;
}
if(!st.empty()){
p=st.top();
if(tag.top()){//如果是右子树就输出节点值
st.pop();
tag.pop();
cout<<p->data<<' ';
p=0;
}
else{//当前是节点的左子树,需要将其右子树进行处理(入栈)
p=p->right;
tag.top()=true;
}
}
}while(p!=0||!st.empty());
}
//分层遍历,很自然的使用队列
void levelorder(node *root){
if(!root)
return;
queue<node*> q;
node *p=root;
q.push(p);
while(!q.empty()){
p=q.front();
q.pop();
cout<<p->data<<' ';
if(p->left!=0)
q.push(p->left);
if(p->right!=0)
q.push(p->right);
}
}
void in_post_pre(int* in,int *post,int *pre,int n){
}
int main(){
node *root=new node(20);
make_tree(root,10,30);
node *p=root->left;
make_tree(p,15,14);
p=p->right;
make_tree(p,28,false);
p=root->right;
make_tree(p,29,41);
// preorder(root); cout<<endl;
// preorder_(root); cout<<endl;
// inorder(root);cout<<endl;
// inorder_(root);cout<<endl;
// postorder(root);cout<<endl;
// postorder_(root);cout<<endl;
levelorder(root);cout<<endl;
free_tree(root);
}
6. 平衡二叉排序树

7. 常用的查找方法
主要包括折半查找,二叉排序树查找和Hash表查找.
(1). 折半查找复杂度是O(logn), 需要满足两个条件: 元素必须是连续存储并且是有序的.
(2). 二叉排序树查找.

(3) hash表查找

问题1: 查找兄弟单词

问题2: 查找字符串中第一个不重复的字符

问题3: 统计最热门的10个查询串

8. 树中某些节点的公共祖先问题

问题1: 求出从根节点到给定节点的路径.

代码如下:
void find_path(node*root,node* p){
node* stk[100],*s;
int tag[100],i,top=-1;
s=root;
do{
while(s!=0){//不断的将左子树进行压栈
top++;
stk[top]=s;
tag[top]=0;
s=s->left;
}
if(top>-1){
s=stk[top];
if(tag[top]==1){//右子树遍历完毕,开始遍历根节点
if(s==p) {
for(i=0;i<=top;i++){
printf("%d ",stk[i]->data);
}
break;
}
else
top--;
}
else{//还没有遍历右子树,开始遍历右子树
s=s->right;
tag[top]=1;
}
}
}while(s!=0||top>-1);
}
node* stk[100],*s;
int tag[100],i,top=-1;
s=root;
do{
while(s!=0){//不断的将左子树进行压栈
top++;
stk[top]=s;
tag[top]=0;
s=s->left;
}
if(top>-1){
s=stk[top];
if(tag[top]==1){//右子树遍历完毕,开始遍历根节点
if(s==p) {
for(i=0;i<=top;i++){
printf("%d ",stk[i]->data);
}
break;
}
else
top--;
}
else{//还没有遍历右子树,开始遍历右子树
s=s->right;
tag[top]=1;
}
}
}while(s!=0||top>-1);
}
问题2: 查找两个节点的公共祖先

利用上面的查找到根节点路径的方法就可以了.
问题3: 找出二叉搜索树上两个节点的公共祖先.

公共祖先节点的值肯定位于这两个值之间.

10. 字典树(trie树)

字典树可以解决下面一些问题:
问题1: 纠错问题
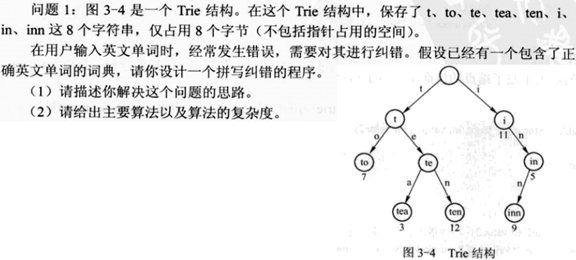

问题2: 查找公共的url

11. 递归在树中的应用

代码如下:
int like(node* root1,node* root2){
if(root1==0&&root2==0)
return 1;
else if(root1==0||root2==0)
return 0;
else
return like(root1->left,root2->left)&&
like(root1->right,root2->right);
}
if(root1==0&&root2==0)
return 1;
else if(root1==0||root2==0)
return 0;
else
return like(root1->left,root2->left)&&
like(root1->right,root2->right);
}

node* copy_tree(node*root){
node*root2;
if(root!=0){
root2=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
root2->data=root->data;
root2->left=copy_tree(root->left);
root2->right=copy_tree(root->right);
return root2;
}
else
return 0;
}
node*root2;
if(root!=0){
root2=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
root2->data=root->data;
root2->left=copy_tree(root->left);
root2->right=copy_tree(root->right);
return root2;
}
else
return 0;
}

void maxminleaf(node*root,int *m,int *n){
int m1,m2,n1,n2;
if(root=0){
*m=0;
*n=0;
}
else{
maxminleaf(root->left,&m1,&n1);
maxminleaf(root->right,&m2,&n2);
m=max(*m1,*m2)+1;
n=min(*n1,*n2)+1;
}
}
int m1,m2,n1,n2;
if(root=0){
*m=0;
*n=0;
}
else{
maxminleaf(root->left,&m1,&n1);
maxminleaf(root->right,&m2,&n2);
m=max(*m1,*m2)+1;
n=min(*n1,*n2)+1;
}
}

node* swap_tree(node*root){
if(root=0)
return 0;
else{
node* root2=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
root2->data=root->data;
root2->left=swap_tree(root->right);
root2->right=swap_tree(root->left);
return root2;
}
}
if(root=0)
return 0;
else{
node* root2=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
root2->data=root->data;
root2->left=swap_tree(root->right);
root2->right=swap_tree(root->left);
return root2;
}
}

int leaf_cnt(node* root){
if(root=0)
return 0;
if(root->left==0&&root->right==0)
return 1;
return leaf_cnt(root->left)+leaf_cnt(root->right);
}
if(root=0)
return 0;
if(root->left==0&&root->right==0)
return 1;
return leaf_cnt(root->left)+leaf_cnt(root->right);
}