第2章 数据和基本类型
1. 整型

2. 习题:左值和右值

3. C++关键字/保留字和操作符替代值

4. 声明,定义, 初始化和赋值是不同的概念。
声明是说明一个变量的存在,不会为变量进行内存空间的分配。
定义是说明一个变量的存在,同时为这个变量分配对应的内存空间。
初始化就是在进行变量定义的时候在所分配的内存空间中同时填入有意义的值。如果不进行初始化的话,变量虽然有对应的内存空间,但是内存空间中对应 的内容却是无意义的。
赋值是为已经存在的变量的改写值,也就是重新擦写变量内存空间的数据,填入新的数据。
C++中因为有类的存在所以,对初始化进行了更细的划分,分为直接初始化和复制初始化。
C++对于变量的初始化规定了一些规则:内置类型和类类型是不一样的,内置类型在函数体外自动初始化为0,函数体内不进行初始化。而类类型的话是调用类的默认构造函数。


5. const变量/对象的初始化


6. 引用声明后就必须初始化,并且一经初始化就不能再改变。

不能使用const变量来初始化非const引用。
7. 定义变量和定义类成员变量是不一样的。

第3章 标准库类型
1.string对象的读写

下面的代码可以从输入不断的读入单词。
string word;
while(cin>>word)
cout<<word<<endl;
}
上面的程序的大致输出是这样的:
如果从标准输入读入的话,产生的结果是这样的:每次按回车键之后才产生输出。主要cin是从缓冲区读取输入的,只有每次按下回车键的时候才将缓冲区进行刷新。
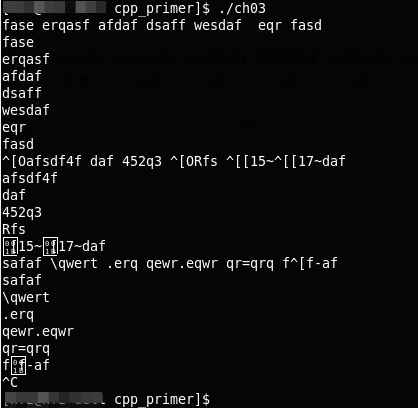
如果是使用管道来进行输入的话,结果是这样的
可以看到单词是通过空白符(空格,回车,制表符)进行划分的。而结束是根据文件结束符进行判断的。


getline的使用方法如下:
string line;
while(getline(cin,line))
cout<<line<<endl;
}

8. bitset类型



第4章 数组和指针
1. 指针与引用

2. 动态数组的初始化

第5章 表达式
1. C++中前置操作符还是后置操作符

2. 动态创建对象时的默认初始化。

3. 删除const对象,使用delete来收回内存

4. C++中的类型转换

第6章 语句
1. 标准库异常

第7章 函数
1. 形参与实参:形参是变量,实参是表达式。

2. const形参
对于C++内置类型,由于采用的是值复制的方式,所以加const与否都是无影响的。

如果形参是引用的形式,采用const和非const的情况就不一样了。
3. const成员函数

4. 构造函数
默认构造函数,构造函数的初始化列表
5. 实参类型的转换
C++支持函数重载,所以就存在函数的匹配问题。在进行函数匹配的过程中,如果没有找到最佳匹配的话,需要进行实参类型的转换来寻找次优的匹配。

6. const参数与重载


7. 习题,枚举类型对象只能用同一枚举类型的另一对象或一个枚举成员进行初始化。

8. const引用形参
下面的函数是错误的
void swap(const int &a,const int &b){
int tmp=a;
a=b;
b=a;
}

const在此处的用法就是防止对传入形参的修改。
下面的函数也是错误的:
void swap(const int *a,const int *b){
int tmp=*a;
*a=*b;
*b=tmp;
}

const的作用就是说明指针指向的地方是只读的,不允许修改。
9.C++中函数指针的不同写法

函数重载存在时,必须对函数指针进行精确的匹配

第8章 标准IO库
1. IO流类的继承关系以及所在的头文件

2. IO对象不可复制或赋值

3. C++中的IO流的最大的特点就是有流的状态,可以通过判断流的状态
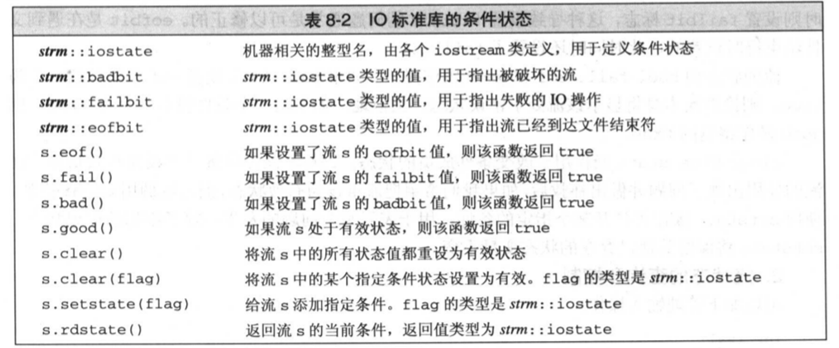
4. 文件流对象的使用



第9章 顺序容器
1. 顺序容器中定义的类型

2. swap操作节省删除元素的成本

3. vector容器的自增长

5. string中的substr,append和replace操作

6. string类型的操作操作,这个其实挺重要的,可以借助这个类find操作完成很多工作。
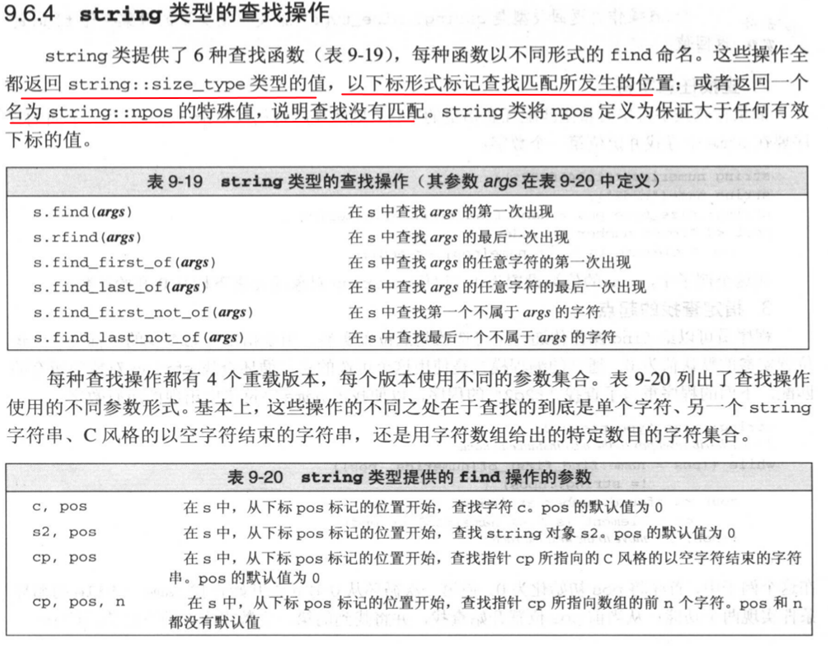






下面是string几个查找函数的例子:
 View Code
View Code
string::size_type pos=0;
string numerics("0123456789");
string name("r2d2");
while((pos=name.find_first_of(numerics,pos))
!=string::npos){
cout<<"found number at index:"<<pos
<<" element is "<<name[pos]<<endl;
++pos;
}
cout<<"=================================="<<endl;
string dept("03714p3d232ewq");
pos=0;
while((pos=dept.find_first_not_of(numerics,pos))
!=string::npos){
cout<<"found not number at index:"<<pos
<<" element is "<<dept[pos]<<endl;
++pos;
}
cout<<"=================================="<<endl;
string river("Mississippi");
string pat("is");
pos=0;
string::size_type len=pat.size();
string::size_type pos2;
while((pos2=river.find(pat,pos))
!=string::npos){
cout<<"found \"is\" at index:"<<pos2
<<" element is "<<river.substr(pos2,len)<<endl;
pos=pos2+1;
}
cout<<"=================================="<<endl;
pos=river.size()-1;
while((pos2=river.rfind(pat,pos))
!=string::npos){
cout<<"found \"is\" at index:"<<pos2
<<" element is "<<river.substr(pos2,len)<<endl;
pos=pos2-1;
if(pos<0)
break;
}
}

 View Code
View Code
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string numerics("0123456789");
string letters("abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ");
string::size_type pos=0;
string str("ab2c3d7R4E6");
while((pos=str.find_first_of(numerics,pos))
!=string::npos){
cout<<"found number at index: "<<pos
<<" element is "<<str[pos]<<endl;
++pos;
}
pos=0;
while((pos=str.find_first_of(letters,pos))
!=string::npos){
cout<<"found letter at index: "<<pos
<<" element is "<<str[pos]<<endl;
++pos;
}
}

下面的程序不严格的事这个习题的程序,该程序只是找到一个个的单词。
 View Code
View Code
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string line;
string word;
string sep(" :;,.\t\v\r\n\f[]{}()<>+-=*&^%$#@!~`\'\"|\\/?");
vector<string> words;
int count=0;
while(getline(cin,line)){
string::size_type pos=0,pos2=0;
while((pos2=line.find_first_not_of(sep,pos))
!=string::npos){
++count;
pos=line.find_first_of(sep,pos2);
if(pos!=string::npos){
word=line.substr(pos2,pos-pos2);
}
else{
word=line.substr(pos2);
}
cout<<word<<endl;
words.push_back(word);
}
}
}
第10章 关联容器
1.STL中的关联容器
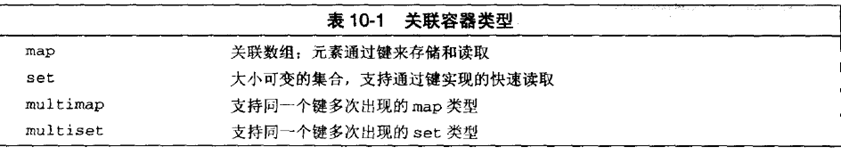
在C++11中添加了unordered_map,unordered_set,unordered_multimap,unordered_multiset. 这四个容器其实就是常见的hash_map,hash_set, hash_multimap, hash_multiset
2. pair类型

3. map容器定义的类型

对map迭代器进行解引用得到的是pair类型
4. map下标访问的特殊之处

5. map的insert操作

统计单词数目的一个简单程序:
 View Code
View Code
#include <string>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string word;
map<string,int> wordlist;
while(cin>>word){
pair<map<string,int>::iterator,bool> ret=
wordlist.insert(make_pair(word,1));
if(!ret.second)
++ret.first->second;
}
cout<<"word\t\t"<<" times"<<endl;
for(map<string,int>::iterator iter=wordlist.begin();
iter!=wordlist.end();++iter)
cout<<iter->first<<"\t\t"
<<iter->second<<endl;
}
6. map中的查找操作:count和find函数


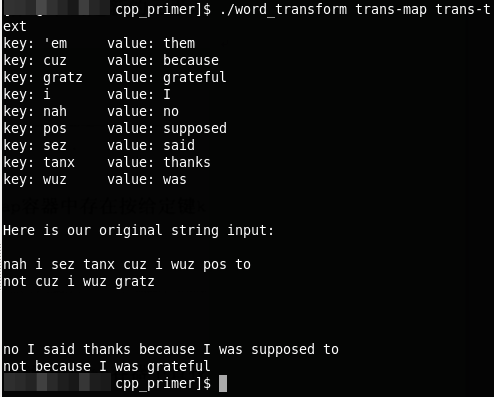
7. 一个简单的单词转换程序
 View Code
View Code
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <sstream>
using std::map;
using std::string;
using std::vector;
using std::ifstream;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::getline;
using std::make_pair;
using std::runtime_error;
using std::istringstream;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
map<string, string> trans_map;
string key, value;
if (argc != 3)
throw runtime_error("wrong number of arguments");
ifstream map_file(argv[1]);
if (!map_file)
throw runtime_error("no transformation file");
while (map_file >> key >> value)
trans_map.insert(make_pair(key, value));
{
map<string, string>::iterator map_it = trans_map.begin();
while (map_it != trans_map.end()) {
cout << "key: " << map_it->first;
if (map_it->first.size() == 1)
cout << " ";
if (map_it->first.size() == 3)
cout << " ";
else if (map_it->first.size() == 4)
cout << " ";
else if (map_it->first.size() == 5)
cout << " ";
cout << "value: " << map_it->second << endl;
++map_it;
}
cout << "\n\n";
{
cout << "Here is our original string input:\n\n";
ifstream input(argv[2]);
if (!input)
throw runtime_error("no input file");
string word;
while (getline(input, word))
cout << word << endl;
cout << "\n\n\n";
input.close(); input.clear();
}
}
ifstream input(argv[2]);
if (!input)
throw runtime_error("no input file");
string line;
while (getline(input, line)) {
istringstream stream(line);
string word;
bool firstword = true;
while (stream >> word) {
map<string, string>::const_iterator map_it =
trans_map.find(word);
if (map_it != trans_map.end())
word = map_it->second;
if (firstword)
firstword = false;
else
cout << " ";
cout << word;
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
运行结果如下:
8. map,set,list差异

9. set的定义与使用

10. 利用set来排除一些常见的单词,这样在统计的时候就避开了常见的单词
 View Code
View Code
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
void restricted_wc(ifstream &remove_file,
map<string, int> &word_count)
{
set<string> excluded;
string remove_word;
while (remove_file >> remove_word)
excluded.insert(remove_word);
for (set<string>::iterator set_it = excluded.begin();
set_it != excluded.end();
++set_it)
cout << *set_it << endl;
string word;
while (cin >> word)
if (!excluded.count(word))
++word_count[word];
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
ifstream remove_file(argv[1]);
map<string, int> word_count;
restricted_wc(remove_file, word_count);
map<string, int>::iterator map_it = word_count.begin();
while (map_it != word_count.end()) {
cout << map_it->first << " occurs "
<< map_it->second << " times" << endl;
++map_it;
}
return 0;
}
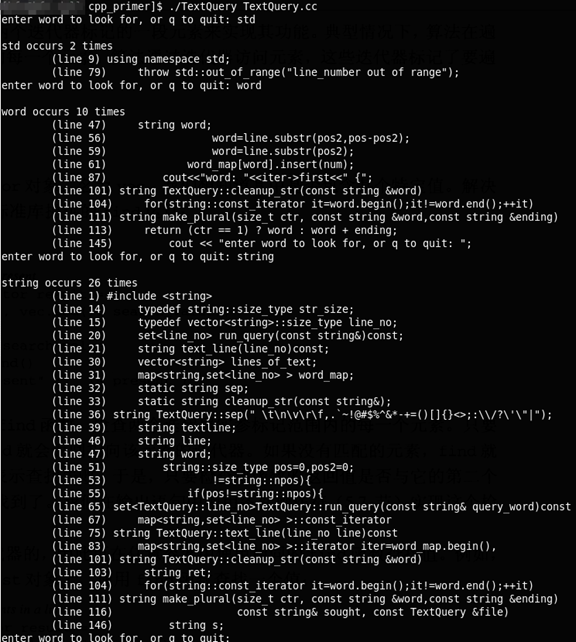
11. 容器的综合应用:文本查询程序
 View Code
View Code
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <stdexcept>
using namespace std;
class TextQuery
{
public:
typedef string::size_type str_size;
typedef vector<string>::size_type line_no;
void read_file(ifstream&is) {
store_file(is);
build_map();
}
set<line_no> run_query(const string&)const;
string text_line(line_no)const;
void display_map();
str_size size()const {
return lines_of_text.size();
}
private:
void store_file(ifstream&);
void build_map();
private:
vector<string> lines_of_text;
map<string,set<line_no> > word_map;
static string sep;
static string cleanup_str(const string&);
};
string TextQuery::sep(" \t\n\v\r\f,.`~!@#$%^&*-+=()[]{}<>;:\\/?\'\"|");
void TextQuery::store_file(ifstream& is)
{
string textline;
while(getline(is,textline))
lines_of_text.push_back(textline);
}
void TextQuery::build_map()
{
string line;
string word;
for(line_no num=0;num!=lines_of_text.size();++num)
{
line=lines_of_text[num];
string::size_type pos=0,pos2=0;
while((pos2=line.find_first_not_of(sep,pos))
!=string::npos){
pos=line.find_first_of(sep,pos2);
if(pos!=string::npos){
word=line.substr(pos2,pos-pos2);
}
else{
word=line.substr(pos2);
}
word_map[word].insert(num);
}
}
}
set<TextQuery::line_no>TextQuery::run_query(const string& query_word)const
{
map<string,set<line_no> >::const_iterator
loc=word_map.find(query_word);
if(loc==word_map.end())
return set<line_no>();
else
return loc->second;
}
string TextQuery::text_line(line_no line)const
{
if(line<lines_of_text.size())
return lines_of_text[line];
throw std::out_of_range("line_number out of range");
}
void TextQuery::display_map()
{
map<string,set<line_no> >::iterator iter=word_map.begin(),
iter_end=word_map.end();
for(;iter!=iter_end;++iter)
{
cout<<"word: "<<iter->first<<" {";
const set<line_no>&text_locs=iter->second;
set<line_no>::const_iterator loc_iter=text_locs.begin(),
loc_iter_end=text_locs.end();
while(loc_iter!=loc_iter_end)
{
cout<<*loc_iter;
if(++loc_iter!=loc_iter_end)
cout<<", ";
}
cout<<"}\n";
}
cout<<endl;
}
string TextQuery::cleanup_str(const string &word)
{
string ret;
for(string::const_iterator it=word.begin();it!=word.end();++it)
{
if(!ispunct(*it))
ret+=tolower(*it);
}
return ret;
}
string make_plural(size_t ctr, const string &word,const string &ending)
{
return (ctr == 1) ? word : word + ending;
}
void print_results(const set<TextQuery::line_no>& locs,
const string& sought, const TextQuery &file)
{
typedef set<TextQuery::line_no> line_nums;
line_nums::size_type size = locs.size();
cout << "\n" << sought << " occurs "
<< size << " "
<< make_plural(size, "time", "s") << endl;
line_nums::const_iterator it = locs.begin();
for ( ; it != locs.end(); ++it) {
cout << "\t(line "
<< (*it) + 1 << ") "
<< file.text_line(*it) << endl;
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
ifstream infile;
if (argc < 2) {
cerr << "No input file!" << endl;
return -1;
}
infile.open(argv[1]);
TextQuery tq;
tq.read_file(infile);
while (true) {
cout << "enter word to look for, or q to quit: ";
string s;
cin >> s;
if (!cin || s == "q") break;
set<TextQuery::line_no> locs = tq.run_query(s);
print_results(locs, s, tq);
}
infile.close();
return 0;
}
以该程序源文件为输入的话,有下面的输出:
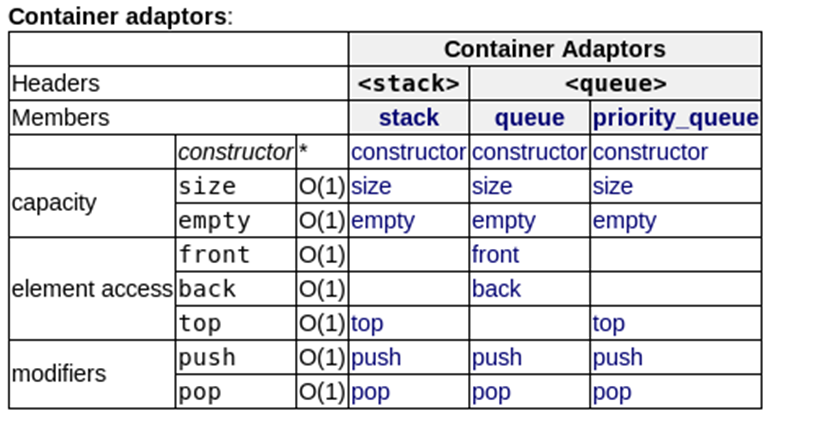
12. 常见常用容器总结

第11章 泛型算法
1. 插入迭代器

2. iostream迭代器






3. 使用copy算法将文件写入到输出:

 View Code
View Code
#include <iterator>
#include <algorithm>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string filename;
cin>>filename;
ifstream ifile(filename.c_str());
if(!ifile){
cout<<"Can't open file: "<<filename<<endl;
return -1;
}
ostream_iterator<string> out(cout," ");
istream_iterator<string> in(ifile),eof;
copy(in,eof,out);
ifile.close();
}
4. 三种迭代器

5. 迭代器分类





