前端周刊发表每周前端技术相关的大事件、文章教程、一些框架的版本更新、以及代码和工具。每周定期发表,欢迎大家关注、转载。
欢迎关注公众号「前端每周看」
工具
vscode
vscode 可以说是前端最流行的编辑器,其有丰富的插件系统。不同开发人员对编辑器设置不同,比如缩进是用空格还是 tab,缩进几个等等。如果多人开发同一个项目,必然会引起文件冲突,所以一个团队最好能统一编辑器。 参考:https://editorconfig.org,在项目根目录新建.editconfig文件
root = true
[*]
charset = utf-8
indent_style = space
indent_size = 2
end_of_line = lf
insert_final_newline = true
trim_trailing_whitespace = true
[*.md]
insert_final_newline = false
trim_trailing_whitespace = false
prettier
代码格式化工具,vscode 有很多格式化插件,像 formate、vetur 等,我们选择 prettier 作为团队格式化工具。 1、安装 prettier
yarn add prettier --save-dev
在项目根目录新建.prettierrc.js
module.exports = {
// 强制使用单引号
singleQuote: true,
// 字符串使用单引号
singleQuote: true,
// 大括号内的首尾需要空格
bracketSpacing: true,
// 末尾不需要逗号
trailingComma: 'none',
// 箭头函数参数括号
arrowParens: 'avoid',
// 在jsx中把'>' 是否单独放一行
jsxBracketSameLine: true,
// 使用默认的折行标准
proseWrap: 'preserve',
// 根据显示样式决定 html 要不要折行
htmlWhitespaceSensitivity: 'css',
// 换行符使用 crlf/lf/auto
endOfLine: 'auto'
};
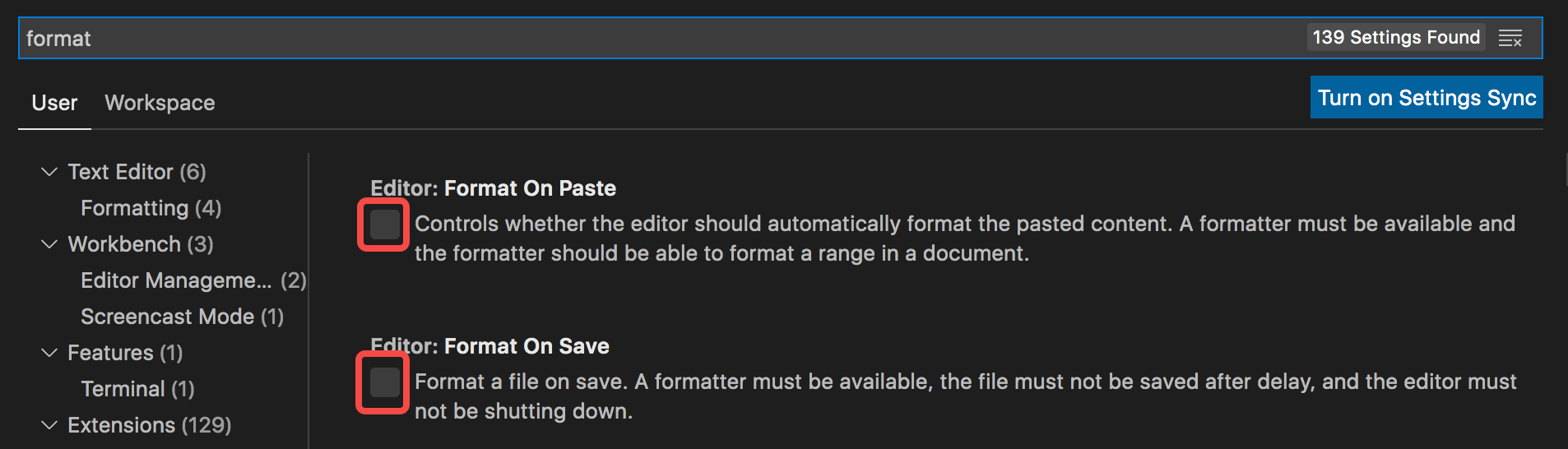
2、配置 vscode 保存自动格式化, 第一步,打开 vscode 设置,搜索 format,勾选 OnPaste、OnSave,如下图
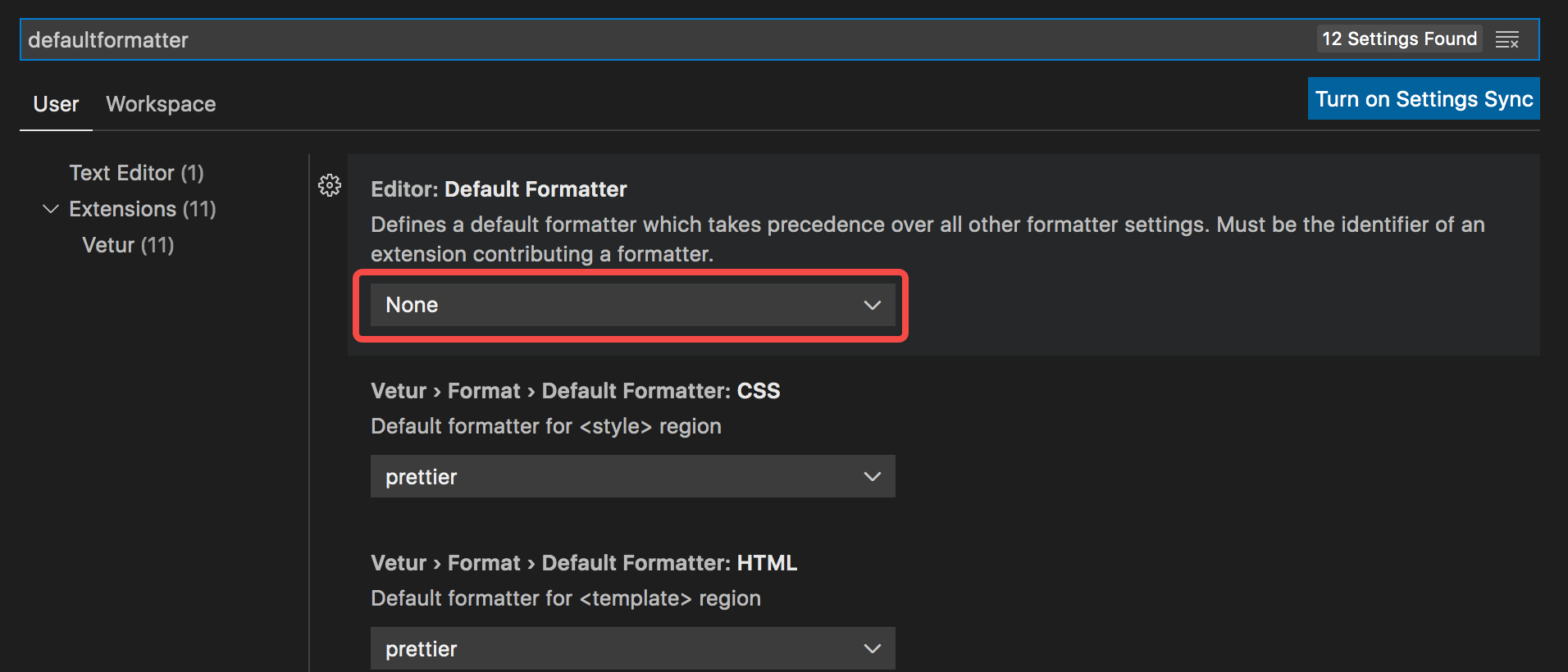
第二步,搜索,defaultformatter,设置默认格式化工具,选择 Prettier
3、可以在项目 package.json 里配置 format 脚本,
"format": "prettier --write --parser typescript \"(src|test)/**/*.ts\""
eslint
eslint 作为代码检测工具,支持 ts、tsx
1、安装 eslint
yarn add eslint --save-dev
2、安装 ts 解析器以及 ts 规则补充
yarn add @typescript-eslint/parser --save-dev
yarn add @typescript-eslint/eslint-plugin --save-dev
eslint 默认使用 Espree 进行解析,无法识别 ts 的一些语法,所以需要安装一个 ts 的解析器 @typescript-eslint/parser,用它来代替默认的解析器@typescript-eslint/eslint-plugin 作为 eslint 默认规则的补充,提供了一些额外的适用于 ts 语法的规则。
3、支持 tsx
yarn add eslint-plugin-react --save-dev
由于是 react 项目,所以还需要插件 eslint-plugin-react 来支持 .tsx
4、在项目根目录创建 .eslintrc.js 当运行 ESLint 的时候检查一个文件的时候,它会首先尝试读取该文件的目录下的配置文件,然后再一级一级往上查找,将所找到的配置合并起来,作为当前被检查文件的配置。
module.exports = {
parser: '@typescript-eslint/parser',
plugins: [
'react',
'react-hooks',
'@typescript-eslint/eslint-plugin',
'prettier'
],
settings: {
react: {
version: 'detect'
}
},
rules: {
'prettier/prettier': 'error',
'no-debugger': 'error',
// 取消函数参数需要重新赋值给另一个变量才能使用
'no-param-reassign': [0],
// 取消 { a, b, c } 多个变量需要换行
'object-curly-newline': [0],
// 禁用var,用let和const代替
'no-var': 2,
// 开启强制单引号
quotes: [2, 'single'],
// 强制全等( === 和 !==)
eqeqeq: 2,
// 语句强制分号结尾
semi: [2, 'always'],
// 禁止出现未使用的变量
'@typescript-eslint/no-unused-vars': [2],
// 箭头函数参数括号,一个参数时可省略括号
'arrow-parens': [2, 'as-needed'],
// 箭头函数,箭头前后空格
'arrow-spacing': [2, { before: true, after: true }],
// 禁止对象最后一项逗号
'comma-dangle': [2, 'never'],
// 单行代码/字符串最大长度
'max-len': [2, { code: 120 }],
// jsx缩进2个空格
'react/jsx-indent': [2, 2],
// 文件末尾强制换行
'eol-last': 2,
// react配置
// 强制组件方法顺序
'react/sort-comp': [2],
// 结束标签,组件省略闭合标签,html不省略闭合标签
'react/self-closing-comp': [2, { component: true, html: false }],
// 检查 Hook 的规则,不允许在if for里面使用
'react-hooks/rules-of-hooks': [2],
// 检查 effect 的依赖
'react-hooks/exhaustive-deps': [2]
}
};
git-commit-message
验证 git 提交规则,创建 verify-commit-msg.js 文件
const chalk = require('chalk')
const msgPath = process.env.GIT_PARAMS
const msg = require('fs').readFileSync(msgPath, 'utf-8').trim()
const commitRE =
/^(revert: )?(wip|release|feat|fix|polish|docs|style|refactor|perf|test|workflow|ci|chore|types|build)(\(.+\))?: .{1,50}/
if (!commitRE.test(msg)) {
console.log()
console.error(
` ${chalk.bgRed.white(' ERROR ')} ${chalk.red(
`invalid commit message format.`
)}\n\n` +
chalk.red(
` Proper commit message format is required for automated changelog generation. Examples:\n\n`
) +
` ${chalk.green(`feat(compiler): add 'comments' option`)}\n` +
` ${chalk.green(
`fix(v-model): handle events on blur (close #28)`
)}\n\n` +
chalk.red(` See .github/COMMIT_CONVENTION.md for more details.\n`)
)
process.exit(1)
}
代码提交规则
feat: 新功能
fix: 修复
docs: 文档变更
style: 代码格式(不影响代码运行的变动)
refactor: 重构(既不是增加feature,也不是修复bug)
perf: 性能优化
test: 增加测试
chore: 构建过程或辅助工具的变动
revert: 回退
build: 打包
代码
整个团队是用 umi 封装的脚手架,所有项目都是 React.js+Mobx+TypeScript,下面列出了基本规范。
React.js
命名
React 组件文件名使用 PascalCase 命名规则,并且以.tsx 后缀名。例如:AnotherComponent.tsx
如果 React 组件是一个单文件,以组件名作为文件名;如果是将 React 组件放在一个目录里,以组件名作为目录名,并且组件所在文件以 index.jsx 命名
src
|-- components
| |-- BadNamedComponent
| |-- BadNamedComponent.jsx
| |-- BadNamedComponent.css
| |-- GoodNamedComponent
| |-- ChildComponent.jsx
| |-- ChildComponent.css
| |-- index.jsx
| |-- index.css
| |-- AnotherComponent.jsx
| |-- AnotherComponent.csssha
// ❌
import BadNamedComponent from '@/components/BadNamedComponent/BadNamedComponent';
// ❌
import GoodNamedComponent from '@/components/GoodNamedComponent/index';
// ✅
import GoodNamedComponent from '@/components/GoodNamedComponent';
// ✅
import AnotherComponent from '@/components/AnotherComponent';
+ React 组件使用 PascalCase 方式命名,React 组件实例使用 camelCase 方式命名
// ❌
import someComponent from './SomeComponent';
// ✅
import SomeComponent from './SomeComponent';
// ❌
const AnotherComponent = <AnotherComponent />;
// ✅
const anotherComponent = <AnotherComponent />;
不推荐 使用高阶组件。如果必需使用,以 with 前缀命名高阶组件
// ❌
export default function wrapForm(WrappedComponent) {
return function FormWrapper(props) {
return <WrappedComponent {...props} {...somePropsFromWrapper} />;
}
}
// ✅
export default function withForm(WrappedComponent) {
return function WithForm(props) {
return <WrappedComponent {...props} {...somePropsFromWrapper} />;
}
}
高阶组件需要添加 displayName 属性方便调试, displayName 属性的格式为:装饰器函数名称加上圆括号 () 包裹的 WrappedComponent 的 displayName 或者 name 属性,如下所示
// ❌
export default function withForm(WrappedComponent) {
function WithForm(props) {
return <WrappedComponent {...props} {...somePropsFromWrapper} />;
}
return WithForm;
}
// ✅
export default function withForm(WrappedComponent) {
function WithForm(props) {
return <WrappedComponent {...props} {...somePropsFromWrapper} />;
}
const wrappedComponentName = WrappedComponent.displayName
|| WrappedComponent.name
|| 'Component';
WithForm.displayName = `withForm(${wrappedComponentName})`;
return WithForm;
}
props 使用 camelCase 方式命名
// ❌
<SomeComponent
SomeProp="value1"
other_prop="value2"
/>
// ✅
<SomeComponent
someProp="value1"
otherProp="value2"
/>
不要使用下划线作为变量名的前缀
function SomeComponent() {
// ❌
const \_handleSubmit = useCallback((params) => {
submitWith(params);
}, []);
// ✅
const handleSubmit = useCallback((params) => {
submitWith(params);
}, []);
return (
<Form onSubmit={_handleSubmit} onSubmit2={handleSubmit} />
);
}
括号
当 JSX 标签跨多行时,必须使用圆括号 () 包裹
// ❌
function ParentComponent() {
return <div>
<ChildComponent />
</div>;
}
// ✅
function ParentComponent() {
return (
<div>
<ChildComponent />
</div>
);
}
标签
没有 children 时必须使用自闭合标签
// ❌
<SomeComponent prop="value"></SomeComponent>
// ✅
<SomeComponent prop="value" />
2.7.5 对齐
+ 多行属性的折行和对齐方式
// ❌
<SomeComponent superLongParam="bar"
anotherSuperLongParam="baz" />
// ✅
<SomeComponent
superLongParam="bar"
anotherSuperLongParam="baz"
/>
// ✅
<ParentComponent
superLongParam="bar"
anotherSuperLongParam="baz"
> <ChildComponent />
> </ParentComponent>
条件渲染语句对齐方式
// ❌
{
someCondition
? <ComponentA />
: <ComponentB />
}
// ✅
{someCondition ? (
<ComponentA />
) : (
<ComponentB />
)}
引号
JSX 上的字符串字面量属性使用双引号,其它地方全部使用单引号
function SomeComponent() {
// ❌
const wrongString = "double quotes is wrong";
// ✅
const rightString = 'single quotes is right';
}
// ❌
<SomeComponent someProp='value1' />
// ✅
<SomeComponent someProp="value1" />
// ❌
<SomeComponent style={{ fontSize: "12px" }} />
// ✅
<SomeComponent style={{ fontSize: '12px' }} />
空格
自闭合标签在标签闭合处留一个空格,变量属性的花括号 {} 和变量之间不能出现空格,非折行对象属性与花括号之间留一个空格
// ❌
<SomeComponent/>
// ❌
<SomeComponent />
// ✅
<SomeComponent />
// ❌
<SomeComponent someProp={ someValue } />
// ✅
<SomeComponent someProp={someValue} />
// ❌
<SomeComponent someObjectProp={{prop: value}} />
// ✅
<SomeComponent someObjectProp={{ prop: value }} />
样式
不推荐 使用内联 style 样式,建议统一写在单独的 css 文件里或者使用类似 @material-ui/styles 的样式管理方案。如果有必要使用内联样式,建议将 styles 定义为变量统一管理,在 JSX 中通过变量引入使用
// ❌
<SomeComponent style={{
marginTop: '10px',
fontSize: '12px',
color: '#f00',
}} />
// ✅
const styles = {
someComponent: {
marginTop: '10px',
fontSize: '12px',
color: '#f00',
},
};
<SomeComponent style={styles.someComponent} />
样式使用 styled-components 插件包裹
import styled from 'styled-components';
const Wrapper = styled.div`
100%;
`;
const FC: React.FC = () => {
return <Wrapper></Wrapper>;
};
export default FC;
props
值为 true 的 prop 属性只写属性名
// ❌
<SomeComponent visible={true} />
// ✅
<SomeComponent visible />
在使用 <img>标签时,如果不是装饰性 (Decorative Image) 图片必须有 alt 属性,如果是装饰性图片则应该设置 alt="" 或者 role="presentation" 属性
// ❌
<img src="logo.png" />
// ✅
<img src="logo.png" alt="wedoctor" />
// ✅
<img src="some-presentational-image.png" alt="" />
// ✅
<img src="some-presentational-image.png" role="presentation" />
不要使用数组下标 index 作为 key ,从数组项上摘取一个唯一标识该项的属性作为 key,如果没有,先手动给数组里的每一项添加一个唯一标识
// ❌
{someList.map((item, index) => (
<Item key={index} {...item} />
))}
// ✅
{someList.map(item => (
<Item key={item.id} {...item} />
))}
为非必传 (non-required) prop 配置默认属性 defaultProps
// ❌
function SomeComponent({ requiredProp, nonRequiredProp }) {
return (
<div>{requiredProp}{nonRequiredProp}</div>
);
}
SomeComponent.propTypes = {
requiredProp: PropTypes.number.isRequired,
nonRequiredProp: PropTypes.string,
};
// ✅
function SomeComponent({ requiredProp, nonRequiredProp }) {
return (
<div>{requiredProp}{nonRequiredProp}</div>
);
}
SomeComponent.propTypes = {
requiredProp: PropTypes.number.isRequired,
nonRequiredProp: PropTypes.string,
};
SomeComponent.defaultProps = {
nonRequiredProp: '',
};
慎重使用展开语法 (Spread syntax) 给子组件传 props 。中间过渡组件(比如 HOC )可以直接使用 {...this.props} 给内部子组件传 props,其它类型组件必须摘出和内部子组件相关的 props 再使用展开语法 {...relevantProps}
// ❌
function SomeRegularComponent(props) {
return (
<ChildComponent {...props} />
);
}
// ✅
function HOC(WrappedComponent) {
return function WrapperComponent(props) {
const propFromWrapper = 'value';
return (
<WrappedComponent {...props} propFromWrapper={propFromWrapper} />
);
};
}
// ✅
function SomeRegularComponent(props) {
const { irrelevantProp1, irrelevantProp2, ...relevantProps } = props;
return (
<ChildComponent {...relevantProps} />
);
}
props 的书写顺序建议为:字符串字面量 prop > 非字符串的字面量 prop > 变量 prop > 事件处理函数 Event handlers
// ✅
<ChildComponent
literalStringProp="some string prop"
literalNumberProp={1}
literalBooleanProp={false}
variableProp={someVariable}
onChange={handleChange}
/>
Hooks
文档:https://ahooks.js.org/zh-CN/hooks/use-request/index
只允许在组件函数的最外层调用 Hooks 函数,而不能在循环、if 判断以及嵌套函数内调用
function ParentComponent() {
// ❌
if (someCondition) {
useEffect(() => {
doSomeSideEffects();
}, []);
}
// ✅
useEffect(() => {
if (someCondition) {
doSomeSideEffects();
}
}, []);
return (
<ChildComponent onChange={handleChange} />
);
}
只允许在 React 函数组件和自定义 Hooks 函数内部调用 Hooks 函数
// ❌
function someRegularFunction() {
const [state, setState] = useState(1);
}
// ✅
function ParentComponent() {
const [state, setState] = useState(1);
return (
<ChildComponent someProp={state} />
);
}
// ✅
function useSomeCustomHooks() {
const [state, setState] = useState(1);
return state;
}
组件内部定义的函数类型 props 必须使用 useCallback 包裹
// ❌
function ParentComponent() {
const handleChange = () => {
// handle change
};
return (
<ChildComponent onChange={handleChange} />
);
}
// ✅
function ParentComponent() {
const handleChange = useCallback(() => {
// handle change
}, []);
return (
<ChildComponent onChange={handleChange} />
);
}
所有组件必须使用 React.memo 包裹
function ChildComponent() {
return (
<div>
<span>child component</span>
</div>
);
}
// ❌
export default ChildComponent;
// ✅
export default React.memo(ChildComponent);
不要在 JSX 中出现 Hooks 函数
// ❌
function ParentComponent() {
return (
<ChildComponent
onChange={useCallback(() => {
// handle change
}, [])}
someMemoProp={useMemo(() => (
computeWith(dep)
), [dep])}
/>
);
}
// ✅
function ParentComponent() {
const handleChange = useCallback(() => {
// handle change
}, []);
const someMemoProp = useMemo(() => (
computeWith(dep)
), [dep]);
return (
<ChildComponent onChange={handleChange} someMemoProp={someMemoProp} />
);
}
注:后期需求调整过程中,Hooks 函数所在的 JSX 块可能会出现 if 之类的条件渲染逻辑,此时就需要将该 Hooks 函数迁移到组件函数的最外层很不方便,为了后期维护起见,应该统一在组件函数的最外层调用 Hooks 函数
大计算量的计算属性推荐使用 useMemo 包裹
function ParentComponent() {
// ❌
const someComplexComputedValue1 = () => doSomeComplexComputeWith(...deps);
// ✅
const someComplexComputedValue2 = useMemo(() => (
doSomeComplexComputeWith(...deps)
), [...deps]);
return (
<ChildComponent
someComplexComputedValue1={someComplexComputedValue1}
someComplexComputedValue2={someComplexComputedValue2}
/>
);
}
传递给子组件的引用类型的计算属性建议使用 useMemo 包裹
function ParentComponent({ someProp }) {
const [state, setState] = useState(1);
// ❌
const someComputedProp1 = doSomeComputeWith(state, someProp);
// ✅
const someComputedProp2 = useMemo(() => (
doSomeComputeWith(state, someProp)
), [state, someProp]);
return (
<ChildComponent
someComputedProp1={someComputedProp1}
someComputedProp2={someComputedProp2}
/>
);
}
useMemo 只能作为性能优化手段,而不能作为回调函数执行与否的依据
// ❌
export default function usePrevious(value) {
const previousValueRef = useRef(value);
return useMemo(() => {
const previousValue = previousValueRef.current;
previousValueRef.current = value;
return previousValue;
}, [value]);
}
// ✅
function usePrevious(value) {
const previousValueRef = useRef(value);
const currentValueRef = useRef(value);
useEffect(() => {
previousValueRef.current = currentValueRef.current;
currentValueRef.current = value;
}, [value]);
return currentValueRef.current === value
? previousValueRef.current
: currentValueRef.current;
}
参考:https://zh-hans.reactjs.org/docs/hooks-reference.html#usememo
使用 useRef 缓存数据,以移除 useCallback 的 deps 数组里不必要的依赖项,减少因 handler 变化引起的子组件重新渲染
function ParentComponent() {
const [state, setState] = useState(1);
// ❌
const handleSubmit1 = useCallback(() => {
submitWith(state);
}, [state]);
// ✅
const stateRef = useRef(state);
stateRef.current = state;
const handleSubmit2 = useCallback(() => (
submitWith(stateRef.current);
), []);
return (
<ChildComponent
onSubmit1={handleSubmit1}
onSubmit2={handleSubmit2}
/>
);
}
对于需要监听参数组件使用 observe,不需要监听的使用 React.FC
// 需要监听参数变化
export const component = observer((props: any) => {
})
// 不需要监听参数变化
const FC: React.FC = () => {
return <Wrapper></Wrapper>;
};
export default FC;
Hooks 调用位置和顺序建议: useSelector useContext useState useReducer useDispatch 统一在代码最顶层依次调用,其次是 useCallback useMemo ,然后是 useLayoutEffect useEffect , useRef 的位置可以依据被使用到的位置灵活放置, useImperativeHandle 一般和 useRef 一起使用,建议跟随在与其相关的 useRef 之后。其它一些局部变量按需要灵活放置
Mobx
version > 6
import { makeAutoObservable } from 'mobx';
class Store {
constructor() {
makeAutoObservable(this);
}
fontSize = 80;
updateFontSize(fontSize) {
this.fontSize = fontSize;
}
}
export default new Store();
TypeScript
环境
基本遵循 JavaScript Style Guide 与 ES-Next Style Guide
1、工程配置 TypeScript 文件使用 .ts 扩展名。含 JSX 语法的 TypeScript 文件使用 .tsx 扩展名。 tsconfig.json 配置文件应开启 strict、noImplicitReturns、noUnusedLocals 选项。 tsconfig.json 配置文件应开启 allowSyntheticDefaultImports 选项。 示例:
// ✅
import React, { PureComponent } from 'react';
// ❌
import \* as React from 'react';
使用 VS Code 编写 TypeScript。 2、 文件 在文件结尾处,保留一个空行。 3、 命名 接口 使用 Pascal 命名法。 接口名 不使用 I 作为前缀。 示例:
// ✅
interface ButtonProps {
// ...
}
// ❌
interface IButtonProps {
// ...
}
类型别名 使用 Pascal 命名法。 示例:
// ✅
interface HeaderStateProps {
// ...
}
interface HeaderDispatchProps {
// ...
}
type HeaderProps = HeaderStateProps & HeaderDispatchProps;
语言特性
1、 变量 使用 const 声明 枚举 。 示例:
// ✅
const enum Directions {
UP,
DOWM,
LEFT,
RIGHT,
}
// ❌
enum Directions {
UP,
DOWN,
LEFT,
RIGHT,
}
2、 类型 不应显式声明可以自动推导的类型。 示例:
// ✅
let shouldUpdate = false;
// ❌
let shouldUpdate: boolean = false;
使用 string / number / boolean 声明基本类型,不使用 String / Number / Boolean。 示例:
// ✅
let str: string;
// ❌
let str: String;
不使用 Object / Function 声明类型。
数组元素为简单类型(非匿名且不含泛型)时,使用 T[] 声明类型,否则应使用 Array
// ✅
let files: string[];
let tokens: Array<string | number>;
let buffer: Buffer[];
let responses: Array<Promise<number>>;
// ❌
let files: Array<string>;
let tokens: (string | number)[];
let buffer: Array<Buffer>;
let responses: Promise<number>[];
不使用 ! 声明对象属性非空。 示例:
// ✅
if (foo.bar && foo.bar.baz) {
// ...
}
// ❌
if (foo!.bar!.baz) {
// ...
}
不使用 any 声明类型。 示例:
// ✅
const identity = <T>(x: T) => x;
// ❌
const identity = (x: any) => x;
使用 as 进行类型声明转换,不使用 <> 。 示例:
// ✅
const root = document.getElementById('root') as HTMLDivElement;
// ❌
const root = <HTMLDivElement>document.getElementById('root');
接口不应为空。 接口中同一函数重载的类型声明需相邻。 示例:
// ✅
interface AnyInterface {
foo();
foo(x: string);
bar();
bar(x: number);
}
// ❌
interface AnyInterface {
foo();
bar();
foo(x: string);
bar(x: number);
}
3、 条件 使用 === 或 !== 判断相等性,不使用 == 或 !=。 示例:
// ✅
if (foo !== null && foo !== undefined) {
// ...
}
// ❌
if (foo != null) {
// ...
}
4、 循环 使用 Object.keys / Object.values / Object.entries / Object.getOwnPropertyNames 遍历对象,不使用 for .. in 。 示例:
// ✅
Object.keys(obj).forEach(key => /_ ... _/);
// ❌
for (const key in obj) {
if (obj.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
// ...
}
}
索引仅用于获取数组当前被迭代的项时,使用 for .. of 遍历数组,不使用 for 。 示例:
// ✅
for (const item of items) {
// ...
}
// ❌
for (let i = 0; i < items.length; i++) {
const item = items[i];
// ...
}
5、 数组 使用 ... 进行数组浅拷贝,不使用 Array.from / Array.prototype.slice 。 示例:
// ✅
const copies = [...items];
// ❌
const copies = items.slice();
// worst
let copies = [];
for (let i = 0; i < items.length; i++) {
copies.push(items[i]);
}
使用 ... 将类数组对象转化为数组,不使用 Array.from / Array.prototype.slice 。 示例:
// ✅
const elements = [...document.querySelectorAll('.foo')];
// ❌
const element = Array.from(document.querySelectorAll('.foo'));
// worst
const element = Array.prototype.slice.call(document.querySelectorAll('.foo'));
6、 对象 使用 ... 进行对象浅拷贝,不使用 Object.assign 。 示例:
// ✅
this.setState(state => ({...state, clicked: true}));
// ❌
this.setState(state => Object.assign({}, state, {clicked: true}));
7、 函数 避免 return undefined ,应直接 return。 示例:
// ✅
function foo(bar: boolean) {
if (!bar) {
return;
}
}
// ❌
function foo(bar: boolean) {
if (!bar) {
return undefined;
}
}
8、 类 每个文件中最多声明一个类。 类成员的可访问性为 public 时,不应显式声明。 构造函数可忽略时,应忽略。 类成员之间使用空行隔开。 示例:
// ✅
class Button extends PureComponent<ButtonProps, ButtonState> {
readonly state: ButtonState = {
clicked: false,
};
render() {
// ...
}
}
// ❌
class Button extends PureComponent<ButtonProps, ButtonState> {
public state: ButtonState = {
clicked: false,
};
constructor(props: ButtonProps) {
super(props);
}
public render() {
// ...
}
}
构造函数初始化实例属性时,应尽量使用参数属性。 构造函数的参数中,作为属性的参数应排列于其他参数前。 示例:
// ✅
class AppComponent {
constructor(private readonly heroService: HeroService) {}
}
// ❌
class AppComponent {
private readonly heroService: HeroService;
constructor(heroService: HeroService) {
this.heroService = heroService;
}
}
9、 模块 使用 ECMAScript 2015 标准的模块系统。 除类型声明文件外,不使用 module / namespace 关键字。 不使用 /// <reference path= > 。 示例:
// ✅
import foo from 'foo';
// ❌
import foo = require('foo');
对于同一个模块路径,仅 import 一次。 示例:
// ✅
import React, {PureComponent} from 'react';
// ❌
import React from 'react';
import {PureComponent} from 'react';
对于使用 webpack 等构建工具的项目,在模块中引入其他资源(如样式、图片等)时,为资源编写类型声明文件,或使用合适的 loader 生成类型声明文件。 示例:
// ✅
// Button.scss.d.ts
export clicked: string;
// logo.png.d.ts
declare const logo: string;
export default logo;
// Button.tsx
import styles from './Button.scss';
import logo from './logo.png';
// ❌
const styles = require<any>('./Button.scss');
const logo = require<string>('./logo.png');