16、树
操作给定的二叉树,将其变换为源二叉树的镜像。
# class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.left = None # self.right = None class Solution: # 返回镜像树的根节点 def Mirror(self, root): # write code here if root == None: return None if root.left != None or root.right != None: root.left,root.right = root.right,root.left self.Mirror(root.left) self.Mirror(root.right)
17、数组
输入一个矩阵,按照从外向里以顺时针的顺序依次打印出每一个数字,例如,如果输入如下4 X 4矩阵: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 则依次打印出数字1,2,3,4,8,12,16,15,14,13,9,5,6,7,11,10.
方法一:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- class Solution: # matrix类型为二维列表,需要返回列表 def printMatrix(self, matrix): # write code here res=[] i,j=0,0 d=0 vis=[[0 for _ in range(len(matrix[0]))] for _ in range(len(matrix))] tmp=[[0,1],[1,0],[0,-1],[-1,0]] while i>=0 and i<len(matrix) and j>=0 and j<len(matrix[0]) and vis[i][j]==0: res.append(matrix[i][j]) vis[i][j]=1 while i+tmp[d][0]>=0 and i+tmp[d][0]<len(matrix) and j+tmp[d][1]>=0 and j+tmp[d][1]<len(matrix[0]) and vis[i+tmp[d][0]][j+tmp[d][1]]==0: i+=tmp[d][0] j+=tmp[d][1] res.append(matrix[i][j]) vis[i][j]=1 d=(d+1)%4 i+=tmp[d][0] j+=tmp[d][1] return res
方法二:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- class Solution: # matrix类型为二维列表,需要返回列表 def printMatrix(self, matrix): # write code here if not matrix: return matrix rows = len(matrix) cols = len(matrix[0]) result = [] start = 0 # 判断是否继续往里走一圈 while cols > start * 2 and rows > start * 2: # 走一圈的代码 end_x = cols - 1 - start end_y = rows - 1 - start # 打印第一行 for i in range(start, end_x+1): result.append(matrix[start][i]) # 打印最后一列 if start < end_y: for i in range(start+1, end_y+1): result.append(matrix[i][end_x]) # 打印最后一行 if start < end_x and start < end_y: for i in range(end_x-1, start-1, -1): result.append(matrix[end_y][i]) # 打印第一列 if start < end_x and start < end_y - 1: for i in range(end_y-1, start, -1): result.append(matrix[i][start]) start += 1 return result
方法三:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- class Solution: # matrix类型为二维列表,需要返回列表 def printMatrix(self, matrix): if not matrix: return matrix result = [] while len(matrix) > 0: result.extend(matrix[0]) matrix = zip(*matrix[1:])[::-1] return result
18、栈
定义栈的数据结构,请在该类型中实现一个能够得到栈中所含最小元素的min函数(时间复杂度应为O(1))
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- class Solution: def __init__(self): self.s1=[] self.s2=[] def push(self, node): # write code here self.s1.append(node) if len(self.s2)==0: self.s2.append(node) else: if node>self.s2[-1]: self.s2.append(self.s2[-1]) else: self.s2.append(node) def pop(self): # write code here if len(self.s1)==0: return None del self.s2[-1] res=self.s1[-1] del self.s1[-1] return res def top(self): # write code here if len(self.s1)==0: return None else: return self.s1[-1] def min(self): # write code here if len(self.s1)==0: return None else: return self.s2[-1]
较好的思路:开一个新栈,此栈与数值栈一一对应,在元素入栈时,就记录处于每一个位置时的当前最小值,这样不论什么情况,不论之前如何出栈入栈,都能立即获取到最小值。
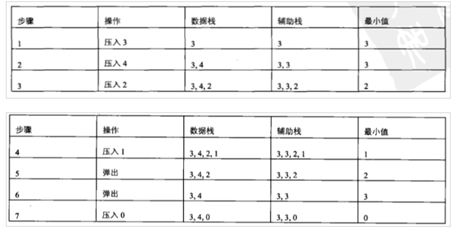
19、栈
输入两个整数序列,第一个序列表示栈的压入顺序,请判断第二个序列是否可能为该栈的弹出顺序。假设压入栈的所有数字均不相等。例如序列1,2,3,4,5是某栈的压入顺序,序列4,5,3,2,1是该压栈序列对应的一个弹出序列,但4,3,5,1,2就不可能是该压栈序列的弹出序列。(注意:这两个序列的长度是相等的)
class Solution: def IsPopOrder(self, pushV, popV): # write code here stack = [] cur = 0 for pop in popV: while len(stack)==0 or pop != stack[-1] and cur < len(pushV): stack.append(pushV[cur]) cur +=1 if cur == len(pushV) and stack[-1] != pop: return False else: stack.pop() return True
解题思路:例如对于压入顺序 12345和弹出顺序45312,首先读到4,则从压入序列里依次压入1234,然后弹出4;读到5,则压入5,弹出5;读到3,栈顶恰好为3,弹出3;读到1,栈顶为2,应当继续压入直到压入1,但压入序列已经读完,没找到1,所以错误。
20、树
从上往下打印出二叉树的每个节点,同层节点从左至右打印。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.left = None # self.right = None class Solution: # 返回从上到下每个节点值列表,例:[1,2,3] def PrintFromTopToBottom(self, root): # write code here if not root: return [] stack=[root] res=[] while stack: for i in range(len(stack)): t=stack.pop(0) res.append(t.val) if t.left: stack.append(t.left) if t.right: stack.append(t.right) return res
解题思路:树的层次遍历,注意的是当root为空时要返回[],而不是None。