什么是感知机?
感知机是二类分类的线性分类模型,其输入为实例的特征向量,输出为实例的类别,取+1和-1二值。感知机对应于输入空间中将实例划分为正负两类的分离超平面,属于判别模型。
感知机的定义?

其图像表示为:
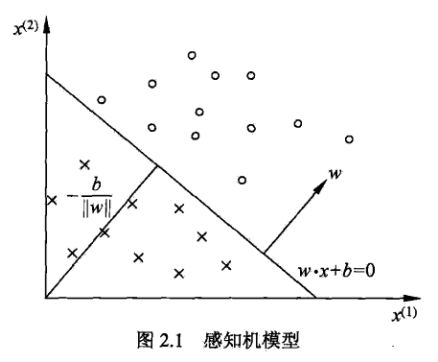
即找到分离超平面将不同类别的数据区分开来。
感知机的线性可分性?

感知机的损失函数?

感知机学习算法的原始形式?

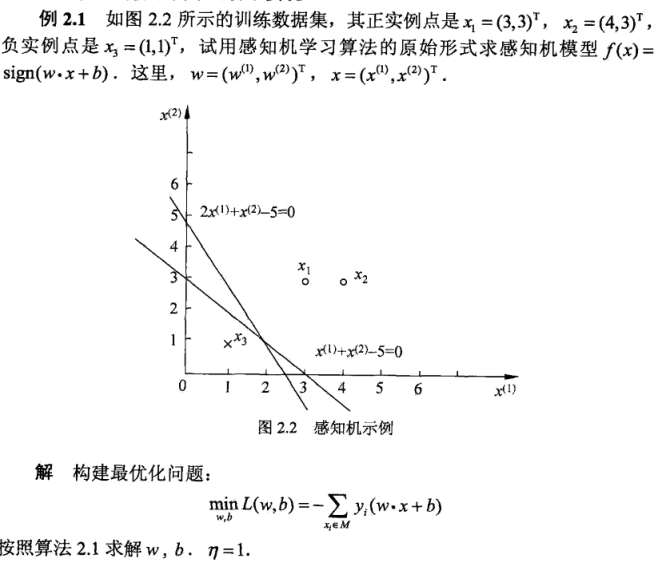
举个例子:



感知机学习的对偶形式?



举个例子:

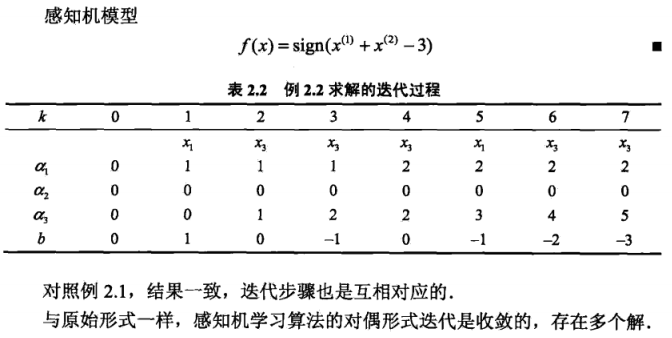
上述解释摘自《统计学习方法》 。
下面是代码实现:代码来源:https://github.com/eriklindernoren/ML-From-Scratch
from __future__ import print_function, division import math import numpy as np # Import helper functions from mlfromscratch.utils import train_test_split, to_categorical, normalize, accuracy_score from mlfromscratch.deep_learning.activation_functions import Sigmoid, ReLU, SoftPlus, LeakyReLU, TanH, ELU from mlfromscratch.deep_learning.loss_functions import CrossEntropy, SquareLoss from mlfromscratch.utils import Plot from mlfromscratch.utils.misc import bar_widgets import progressbar class Perceptron(): """The Perceptron. One layer neural network classifier. Parameters: ----------- n_iterations: float The number of training iterations the algorithm will tune the weights for. activation_function: class The activation that shall be used for each neuron. Possible choices: Sigmoid, ExpLU, ReLU, LeakyReLU, SoftPlus, TanH loss: class The loss function used to assess the model's performance. Possible choices: SquareLoss, CrossEntropy learning_rate: float The step length that will be used when updating the weights. """ def __init__(self, n_iterations=20000, activation_function=Sigmoid, loss=SquareLoss, learning_rate=0.01): self.n_iterations = n_iterations self.learning_rate = learning_rate self.loss = loss() self.activation_func = activation_function() self.progressbar = progressbar.ProgressBar(widgets=bar_widgets) def fit(self, X, y): n_samples, n_features = np.shape(X) _, n_outputs = np.shape(y) # Initialize weights between [-1/sqrt(N), 1/sqrt(N)] limit = 1 / math.sqrt(n_features) self.W = np.random.uniform(-limit, limit, (n_features, n_outputs)) self.w0 = np.zeros((1, n_outputs)) for i in self.progressbar(range(self.n_iterations)): # Calculate outputs linear_output = X.dot(self.W) + self.w0 y_pred = self.activation_func(linear_output) # Calculate the loss gradient w.r.t the input of the activation function error_gradient = self.loss.gradient(y, y_pred) * self.activation_func.gradient(linear_output) # Calculate the gradient of the loss with respect to each weight grad_wrt_w = X.T.dot(error_gradient) grad_wrt_w0 = np.sum(error_gradient, axis=0, keepdims=True) # Update weights self.W -= self.learning_rate * grad_wrt_w self.w0 -= self.learning_rate * grad_wrt_w0 # Use the trained model to predict labels of X def predict(self, X): y_pred = self.activation_func(X.dot(self.W) + self.w0) return y_pred
运行主代码:
from __future__ import print_function from sklearn import datasets import numpy as np # Import helper functions import sys sys.path.append("/content/drive/My Drive/learn/ML-From-Scratch/") from mlfromscratch.utils import train_test_split, normalize, to_categorical, accuracy_score from mlfromscratch.deep_learning.activation_functions import Sigmoid from mlfromscratch.deep_learning.loss_functions import CrossEntropy from mlfromscratch.utils import Plot from mlfromscratch.supervised_learning import Perceptron def main(): data = datasets.load_digits() X = normalize(data.data) y = data.target # One-hot encoding of nominal y-values y = to_categorical(y) X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.33, seed=1) # Perceptron clf = Perceptron(n_iterations=5000, learning_rate=0.001, loss=CrossEntropy, activation_function=Sigmoid) clf.fit(X_train, y_train) y_pred = np.argmax(clf.predict(X_test), axis=1) y_test = np.argmax(y_test, axis=1) accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred) print ("Accuracy:", accuracy) # Reduce dimension to two using PCA and plot the results Plot().plot_in_2d(X_test, y_pred, title="Perceptron", accuracy=accuracy, legend_labels=np.unique(y)) if __name__ == "__main__": main()
其中相关函数如下:
def normalize(X, axis=-1, order=2): """ Normalize the dataset X """ l2 = np.atleast_1d(np.linalg.norm(X, order, axis)) l2[l2 == 0] = 1 return X / np.expand_dims(l2, axis)
def train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.5, shuffle=True, seed=None): """ Split the data into train and test sets """ if shuffle: X, y = shuffle_data(X, y, seed) # Split the training data from test data in the ratio specified in # test_size split_i = len(y) - int(len(y) // (1 / test_size)) X_train, X_test = X[:split_i], X[split_i:] y_train, y_test = y[:split_i], y[split_i:] return X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test
def shuffle_data(X, y, seed=None): """ Random shuffle of the samples in X and y """ if seed: np.random.seed(seed) idx = np.arange(X.shape[0]) np.random.shuffle(idx) return X[idx], y[idx]
class Sigmoid(): def __call__(self, x): return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x)) def gradient(self, x): return self.__call__(x) * (1 - self.__call__(x))
class CrossEntropy(Loss): def __init__(self): pass def loss(self, y, p): # Avoid division by zero p = np.clip(p, 1e-15, 1 - 1e-15) return - y * np.log(p) - (1 - y) * np.log(1 - p) def acc(self, y, p): return accuracy_score(np.argmax(y, axis=1), np.argmax(p, axis=1)) def gradient(self, y, p): # Avoid division by zero p = np.clip(p, 1e-15, 1 - 1e-15) return - (y / p) + (1 - y) / (1 - p)
运行结果:
Training: 100% [------------------------------------------------] Time: 0:00:09 Accuracy: 0.9527824620573356
