在项目中创建新应用:Login,来实现注册、登录、认证功能。
一、注册接口
1、创建注册路由
首先在工程路由中添加login应用路由:
from django.contrib import admin from django.urls import path, include, re_path from django.views.static import serve from LuffyCity import settings urlpatterns = [ path('admin/', admin.site.urls), path('api/course/', include("Course.urls")), path('api/', include("Login.urls")), # media路径配置 # path('media/(?P<path>.*)', serve, {'document_root': settings.MEDIA_ROOT}), re_path('media/(?P<path>.*)', serve, {'document_root': settings.MEDIA_ROOT}) ]
随后在login应用中添加路由文件./Login/urls.py:
from django.urls import path from .views import RegisterView urlpatterns = [ path('register', RegisterView.as_view()) ]
2、创建注册序列化器
添加新文件:./Login/serializers.py,内容如下所示:
from rest_framework import serializers from Course.models import Account # 账户表 import hashlib # class RegisterSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer): # 注册序列化器 class Meta: model = Account fields = "__all__" def create(self, validated_data): # 重写pwd,用md5加盐 pwd = validated_data["pwd"] pwd_salt = "mao_password" + pwd md5_str = hashlib.md5(pwd_salt.encode()).hexdigest() # hexdigest方法拿到md5的str user_obj = Account.objects.create(username=validated_data["username"], pwd=md5_str) return user_obj
3、配置消息响应
在工程根目录创建utils目录,添加base_response.py文件:
class BaseResponse(object): def __init__(self): self.code = 1000 # 默认码1000 self.data = None self.error = None # 错误信息 @property # 方法变属性 def dict(self): print('222', self.__dict__) return self.__dict__
发送请求,可以看到这里dict函数中会打印如下信息:222 {'code': 1000, 'data': {'id': 33, 'username': 'alex', 'pwd': '7ab71bb07cb065c4f5261ea81159c100'}, 'error': None}
4、编写注册视图
在./Login/views.py中编写注册视图:
from rest_framework.views import APIView from rest_framework.response import Response from django.http import JsonResponse, HttpResponse from .serializers import RegisterSerializer # 引入序列化器 from utils.base_response import BaseResponse # Create your views here. class RegisterView(APIView): def post(self, request): res = BaseResponse() # 实例化response # 用序列化器做校验 ser_obj = RegisterSerializer(data = request.data) if ser_obj.is_valid(): # 检验通过 ser_obj.save() res.data = ser_obj.data else: # 检验失败 res.code = 1020 res.error = ser_obj.errors print('1111', res.data, res.dict) return Response(res.dict)
发送请求会打印如下信息:1111 {'id': 33, 'username': 'alex', 'pwd': '7ab71bb07cb065c4f5261ea81159c100'} {'code': 1000, 'data': {'id': 33, 'username': 'alex', 'pwd': '7ab71bb07cb065c4f5261ea81159c100'}, 'error': None}
5、测试注册请求

二、登录接口
因为HTTP请求是无状态的,要区分用户,需要给用户发一个会话标识。前后端不分离的项目,是用cookie和session来解决这个问题。对于前后端分离的项目,则通常是给用户生成一个唯一标识——token令牌。
1、配置路由和redis连接池
在Login/urls.py中添加登录路由:
from django.urls import path from .views import RegisterView, LoginView, TestView urlpatterns = [ path('register', RegisterView.as_view()), path('login', LoginView.as_view()), ]
创建utils/redis_pool.py,配置redis连接池:
import redis POOL = redis.ConnectionPool(host='127.0.0.1', port=6379, decode_responses=True, max_connections=10) # 最大连接数
2、登录视图
from rest_framework.views import APIView from rest_framework.response import Response from .serializers import RegisterSerializer # 引入序列化器 from utils.base_response import BaseResponse from Course.models import Account from utils.redis_pool import POOL import redis import uuid class LoginView(APIView): def post(self, request): res = BaseResponse() username = request.data.get("username", "") pwd = request.data.get("pwd", "") user_obj = Account.objects.filter(username=username, pwd=pwd).first() # 查询用户表拿到用户对象 if not user_obj: res.code = 1030 res.error = "用户名或密码错误" return Response(res.dict) # 用户登录成功生成一个token写入redis # 写入redis token(唯一): user_id conn = redis.Redis(connection_pool=POOL) try: token = uuid.uuid4() # 生成随机字符串,类型是:<class 'uuid.UUID'> conn.set(str(token), user_obj.id, ex=120) # ex:过期时间120秒 res.data = token except Exception as e: print(e) res.code = 1031 res.error = "创建令牌失败" return Response(res.dict)
注意uuid不能作为redis的key,需要转化为字符串、数字等数据类型。
另外需要注意到conn.set()方法的参数:
class Redis(object): def set(self, name, value, ex=None, px=None, nx=False, xx=False): """ Set the value at key ``name`` to ``value`` ``ex`` sets an expire flag on key ``name`` for ``ex`` seconds. ``px`` sets an expire flag on key ``name`` for ``px`` milliseconds. ``nx`` if set to True, set the value at key ``name`` to ``value`` only if it does not exist. ``xx`` if set to True, set the value at key ``name`` to ``value`` only if it already exists. """
在Redis中设置值,默认,不存在则创建,存在则修改。各个参数的含义:
- ex:过期时间(秒)
- px:过期时间(毫秒)
- nx:如设置为True,则只有name不存在时,当前set操作才执行,值存在,就修改不了,执行没有效果。
- xx:如设置为True,则只有name存在时,当前set操作才执行,值存在才能修改,值不存在,不会设置新值。
3、登录测试
图中data就是生成的token。

三、认证接口
校验请求头中携带的token信息。
1、添加认证测试路由
在/Login/urls.py中添加认证测试路由:
from django.urls import path from .views import RegisterView, LoginView, TestView urlpatterns = [ path('register', RegisterView.as_view()), path('login', LoginView.as_view()), path('test_auth', TestView.as_view()), ]
2、添加自定义登录验证
在utils中添加my_auth.py文件:
from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication from rest_framework.exceptions import AuthenticationFailed from Course.models import Account from .redis_pool import POOL import redis CONN = redis.Redis(connection_pool=POOL) class LoginAuth(BaseAuthentication): def authenticate(self, request): # 从请求头中获取前端带过来的token token = request.META.get("HTTP_AUTHENTICATION", "") # request.META是一个Python字典,包含本次HTTP请求的Header信息 if not token: raise AuthenticationFailed("没有携带token") # 有token,去redis中比对 user_id = CONN.get(str(token)) # 取不到值会报:None if user_id == None: # token不合法 raise AuthenticationFailed("token已经过期") user_obj = Account.objects.filter(id=user_id).first() return user_obj, token
3、添加测试认证视图
from utils.my_auth import LoginAuth class TestView(APIView): authentication_classes = [LoginAuth, ] # 局部认证,该接口必须登录认证 def get(self, request): return Response("认证测试")
4、测试认证
通过POST http://127.0.0.1:8008/api/login,获取到token信息后,执行测试认证如下所示:
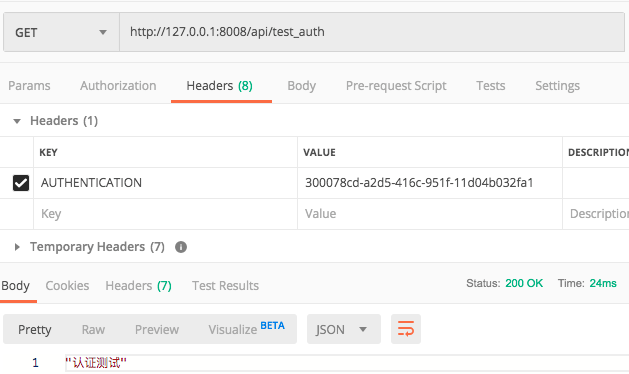
在登录视图中曾设置超时时间120秒,120秒后再次测试认证如下所示:
