KAZE系列笔记:
1. OpenCV学习笔记(27)KAZE 算法原理与源码分析(一)非线性扩散滤波
2. OpenCV学习笔记(28)KAZE 算法原理与源码分析(二)非线性尺度空间构建
3. OpenCV学习笔记(29)KAZE 算法原理与源码分析(三)特征检测与描述
4. OpenCV学习笔记(30)KAZE 算法原理与源码分析(四)KAZE特征的性能分析与比较
KAZE算法资源:
1. 论文: http://www.robesafe.com/personal/pablo.alcantarilla/papers/Alcantarilla12eccv.pdf
2. 项目主页:http://www.robesafe.com/personal/pablo.alcantarilla/kaze.html
3. 作者代码:http://www.robesafe.com/personal/pablo.alcantarilla/code/kaze_features_1_4.tar
(需要boost库,另外其计时函数的使用比较复杂,可以用OpenCV的cv::getTickCount代替)
4. Computer Vision Talks的评测:http://computer-vision-talks.com/2013/03/porting-kaze-features-to-opencv/
5. Computer Vision Talks 博主Ievgen Khvedchenia将KAZE集成到OpenCV的cv::Feature2D类,但需要重新编译OpenCV,并且没有实现算法参数调整和按Mask过滤特征点的功能:https://github.com/BloodAxe/opencv/tree/kaze-features
6. 我在Ievgen的项目库中提取出KAZE,封装成继承cv::Feature2D的类,无需重新编译OpenCV,实现了参数调整和Mask过滤的功能: https://github.com/yuhuazou/kaze_opencv
7. Matlab 版的接口程序,封装了1.0版的KAZE代码:https://github.com/vlfeat/vlbenchmarks/blob/unstable/%2BlocalFeatures/Kaze.m
2.3 与其他特征算法的比较
2.3.1 与OpenCV API的融合
KAZE算法作者在其项目主页提供了源码,其中包括KAZE的核心算法库以及KAZE特征的提取、匹配和比较等例程,是基于OpenCV实现的。Computer Vision Talks的博主Ievgen Khvedchenia不久前将KAZE代码融合到OpenCV的cv::Feature2D API中,不过他是OpenCV项目的维护者之一,他的目标是在未来的OpenCV版本中加入KAZE。使用他的KAZE类需要重新编译OpenCV,并且目前只是简单地嵌入、还不能调整KAZE类的参数,也不支持Mask过滤。
因为想尽快测试和比较KAZE算法的性能,又不想重新编译OpenCV,我在Ievgen的项目库中将KAZE相关的代码抽离出来,改造为一个相对独立的cv::KAZE类,继承于cv::Feature2D类。这样就可以方便地在OpenCV中使用,并能够通过一致的接口与其它特征算法进行比较。cv::KAZE类包括如下文件:
|--KAZE | kaze_features.cpp // Class that warps KAZE to cv::Feature2D | kaze_features.h | kaze.cpp // Implementation of KAZE | kaze.h | kaze_config.cpp // Configuration variables and options | kaze_config.h | kaze_ipoint.cpp // Class that defines a point of interest | kaze_ipoint.h | kaze_nldiffusion_functions.cpp // Functions for non-linear diffusion applications | kaze_nldiffusion_functions.h | kaze_utils.cpp // Some useful functions | kaze_utils.h
其中kaze_feature.h和kaze_feature.cpp是继承cv::Feature2D的cv::KAZE类,通过这个类将KAZE核心算法库与OpenCV的Feature2D类关联起来。其具体代码如下:
#ifndef _KAZE_FEATURES_H_
#define _KAZE_FEATURES_H_
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Extract from ..\opencv\modules\features2d\src\precomp.hpp
//
#ifdef HAVE_CVCONFIG_H
#include "cvconfig.h"
#endif
#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc_c.h"
#include "opencv2/core/internal.hpp"
#include <algorithm>
#ifdef HAVE_TEGRA_OPTIMIZATION
#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d_tegra.hpp"
#endif
//
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#include "kaze_config.h"
/*!
KAZE features implementation.
!! Note that it has NOT been warped to cv::Algorithm in oder to avoid rebuilding OpenCV
So most functions of cv::Algorithm can not be used in cv::KAZE
http://www.robesafe.com/personal/pablo.alcantarilla/papers/Alcantarilla12eccv.pdf
*/
namespace cv
{
class CV_EXPORTS_W KAZE : public Feature2D
{
public:
CV_WRAP explicit KAZE();
KAZE(toptions &_options);
// returns the descriptor size in bytes
int descriptorSize() const;
// returns the descriptor type
int descriptorType() const;
// Compute the KAZE features and descriptors on an image
void operator()( InputArray image, InputArray mask, vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints,
OutputArray descriptors, bool useProvidedKeypoints=false ) const;
// Compute the KAZE features with mask
void operator()(InputArray image, InputArray mask, vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints) const;
// Compute the KAZE features and descriptors on an image WITHOUT mask
void operator()(InputArray image, vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints, OutputArray descriptors) const;
//AlgorithmInfo* info() const;
protected:
void detectImpl( const Mat& image, vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints, const Mat& mask=Mat() ) const;
// !! NOT recommend to use because KAZE descriptors ONLY work with KAZE features
void computeImpl( const Mat& image, vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints, Mat& descriptors ) const;
CV_PROP_RW int nfeatures;
private:
toptions options;
};
typedef KAZE KazeFeatureDetector;
//typedef KAZE KazeDescriptorExtractor; // NOT available because KAZE descriptors ONLY work with KAZE features
}
#endif
/*********************************************************************
* Software License Agreement (BSD License)
*
* Copyright (c) 2009, Willow Garage, Inc.
* All rights reserved.
*
* Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
* modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions
* are met:
*
* * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
* * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above
* copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following
* disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided
* with the distribution.
* * Neither the name of the Willow Garage nor the names of its
* contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived
* from this software without specific prior written permission.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
* "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
* LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS
* FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
* COPYRIGHT OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT,
* INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING,
* BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES;
* LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER
* CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT
* LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN
* ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE
* POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
*********************************************************************/
/** Authors: Ievgen Khvedchenia */
/** Modified: Yuhua Zou, 2013-03-20 */
#include <iterator>
#include "kaze_features.h"
#include "kaze.h"
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#define DEGREE_TO_RADIAN(x) ((x) * CV_PI / 180.0)
#define RADIAN_TO_DEGREE(x) ((x) * 180.0 / CV_PI)
namespace cv
{
/***
* Convertions between cv::Keypoint and KAZE::Ipoint
*/
static inline void convertPoint(const cv::KeyPoint& kp, Ipoint& aux)
{
aux.xf = kp.pt.x;
aux.yf = kp.pt.y;
aux.x = fRound(aux.xf);
aux.y = fRound(aux.yf);
//cout << "SURF size: " << kpts_surf1_[i].size*.5 << endl;
aux.octave = kp.octave;
// Get the radius for visualization
aux.scale = kp.size*.5/2.5;
aux.angle = DEGREE_TO_RADIAN(kp.angle);
//aux.descriptor_size = 64;
}
static inline void convertPoint(const Ipoint& src, cv::KeyPoint& kp)
{
kp.pt.x = src.xf;
kp.pt.y = src.yf;
kp.angle = RADIAN_TO_DEGREE(src.angle);
kp.response = src.dresponse;
kp.octave = src.octave;
kp.size = src.scale;
}
/***
* runByPixelsMask() for KAZE Ipoint
*/
class MaskPredicate
{
public:
MaskPredicate( const Mat& _mask ) : mask(_mask) {}
bool operator() (const Ipoint& key_pt) const
{
return mask.at<uchar>( (int)(key_pt.yf + 0.5f), (int)(key_pt.xf + 0.5f) ) == 0;
}
private:
const Mat mask;
MaskPredicate& operator=(const MaskPredicate&);
};
void runByPixelsMask( std::vector<Ipoint>& keypoints, const Mat& mask )
{
if( mask.empty() )
return;
keypoints.erase(std::remove_if(keypoints.begin(), keypoints.end(), MaskPredicate(mask)), keypoints.end());
}
/***
* Implementation of cv::KAZE
*/
KAZE::KAZE()
{
}
KAZE::KAZE(toptions &_options)
{
options = _options;
}
int KAZE::descriptorSize() const
{
return options.extended ? 128 : 64;
}
int KAZE::descriptorType() const
{
return CV_32F;
}
void KAZE::operator()(InputArray _image, InputArray _mask, vector<KeyPoint>& _keypoints,
OutputArray _descriptors, bool useProvidedKeypoints) const
{
bool do_keypoints = !useProvidedKeypoints;
bool do_descriptors = _descriptors.needed();
if( (!do_keypoints && !do_descriptors) || _image.empty() )
return;
cv::Mat img1_8, img1_32;
// Convert to gray scale iamge and float image
if (_image.getMat().channels() == 3)
cv::cvtColor(_image, img1_8, CV_RGB2GRAY);
else
_image.getMat().copyTo(img1_8);
img1_8.convertTo(img1_32, CV_32F, 1.0/255.0,0);
// Construct KAZE
toptions opt = options;
opt.img_width = img1_32.cols;
opt.img_height = img1_32.rows;
::KAZE kazeEvolution(opt);
// Create nonlinear scale space
kazeEvolution.Create_Nonlinear_Scale_Space(img1_32);
// Feature detection
std::vector<Ipoint> kazePoints;
if (do_keypoints)
{
kazeEvolution.Feature_Detection(kazePoints);
if (!_mask.empty())
{
runByPixelsMask(kazePoints, _mask.getMat());
}
}
else
{
kazePoints.resize(_keypoints.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < kazePoints.size(); i++)
{
convertPoint(_keypoints[i], kazePoints[i]);
}
}
// Descriptor generation
if (do_descriptors)
{
kazeEvolution.Feature_Description(kazePoints);
cv::Mat& descriptors = _descriptors.getMatRef();
descriptors.create(kazePoints.size(), descriptorSize(), descriptorType());
for (size_t i = 0; i < kazePoints.size(); i++)
{
std::copy(kazePoints[i].descriptor.begin(), kazePoints[i].descriptor.end(), (float*)descriptors.row(i).data);
}
}
// Transfer from KAZE::Ipoint to cv::KeyPoint
if (do_keypoints)
{
_keypoints.resize(kazePoints.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < kazePoints.size(); i++)
{
convertPoint(kazePoints[i], _keypoints[i]);
}
}
}
void KAZE::operator()(InputArray image, InputArray mask, vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints ) const
{
(*this)(image, mask, keypoints, noArray(), false);
}
void KAZE::operator()(InputArray image, vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints, OutputArray descriptors) const
{
(*this)(image, noArray(), keypoints, descriptors, false);
}
void KAZE::detectImpl( const Mat& image, vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints, const Mat& mask) const
{
(*this)(image, mask, keypoints, noArray(), false);
}
void KAZE::computeImpl( const Mat& image, vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints, Mat& descriptors) const
{
(*this)(image, Mat(), keypoints, descriptors, false); // Regenerate keypoints no matter keypoints is empty or not
}
}
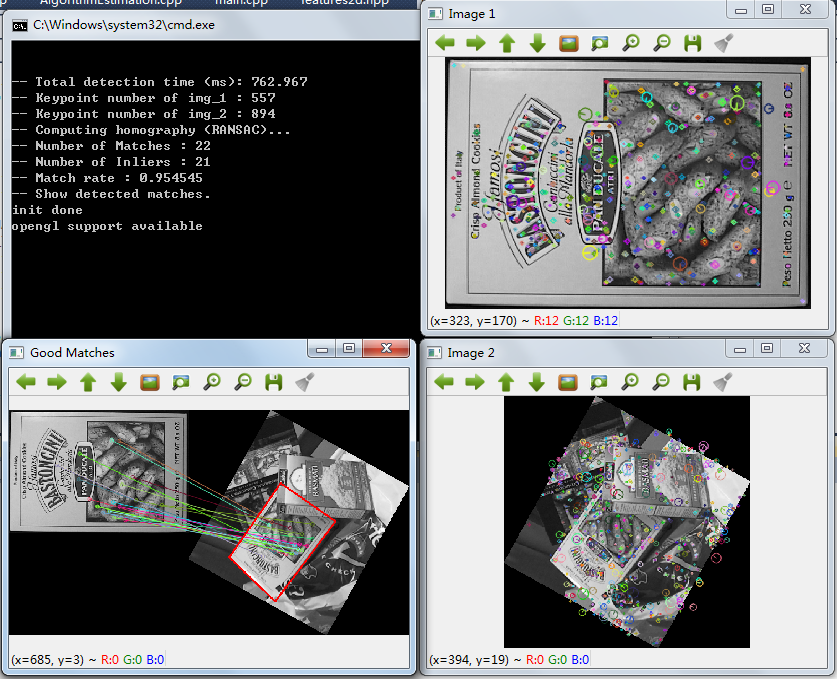
下面是基于cv::KAZE类的特征提取与图像匹配例程及结果图:
// KazeOpenCV.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "predep.h"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp"
#include "KAZE/kaze_features.h"
#pragma comment( lib, cvLIB("core") )
#pragma comment( lib, cvLIB("imgproc") )
#pragma comment( lib, cvLIB("highgui") )
#pragma comment( lib, cvLIB("flann") )
#pragma comment( lib, cvLIB("features2d") )
#pragma comment( lib, cvLIB("calib3d") )
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main(int argc, char** argv[])
{
Mat img_1 = imread("box.png");
Mat img_2 = imread("box_in_scene.png");
std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2;
Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;
toptions opt;
opt.extended = true; // 1 - 128-bit vector, 0 - 64-bit vector, default: 0
opt.verbosity = true; // 1 - show detail information while caculating KAZE, 0 - unshow, default: 0
KAZE detector_1(opt);
KAZE detector_2(opt);
double t2 = 0.0, t1 = 0.0, tkaze = 0.0;
int64 start_t1 = cv::getTickCount();
//-- Detect keypoints and calculate descriptors
detector_1(img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1);
detector_2(img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2);
t2 = cv::getTickCount();
tkaze = 1000.0 * (t2 - start_t1) / cv::getTickFrequency();
cout << "\n\n-- Total detection time (ms): " << tkaze << endl;
printf("-- Keypoint number of img_1 : %d \n", keypoints_1.size() );
printf("-- Keypoint number of img_2 : %d \n", keypoints_2.size() );
//-- Matching descriptor vectors using FLANN matcher
FlannBasedMatcher matcher;
vector< DMatch > matches;
matcher.match( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, matches );
double max_dist = 0; double min_dist = 100;
//-- Quick calculation of max and min distances between keypoints
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
double dist = matches[i].distance;
if( dist < min_dist ) min_dist = dist;
if( dist > max_dist ) max_dist = dist;
}
//-- Find initial good matches (i.e. whose distance is less than 2*min_dist )
vector< DMatch > good_matches, inliers;
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
if( matches[i].distance < 2*min_dist )
{
good_matches.push_back( matches[i]);
}
}
cout << "-- Computing homography (RANSAC)..." << endl;
//-- Get the keypoints from the good matches
vector<Point2f> points1( good_matches.size() );
vector<Point2f> points2( good_matches.size() );
for( size_t i = 0; i < good_matches.size(); i++ )
{
points1[i] = keypoints_1[ good_matches[i].queryIdx ].pt;
points2[i] = keypoints_2[ good_matches[i].trainIdx ].pt;
}
//-- Computing homography (RANSAC) and find inliers
vector<uchar> flags(points1.size(), 0);
Mat H = findHomography( points1, points2, CV_RANSAC, 3.0, flags );
//cout << H << endl << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < good_matches.size(); i++)
{
if (flags[i])
{
inliers.push_back( good_matches[i] );
}
}
//-- Draw Keypoints
Mat img_1k, img_2k;
drawKeypoints(img_1, keypoints_1, img_1k, Scalar::all(-1), DrawMatchesFlags::DRAW_RICH_KEYPOINTS);
drawKeypoints(img_2, keypoints_2, img_2k, Scalar::all(-1), DrawMatchesFlags::DRAW_RICH_KEYPOINTS);
//-- Draw inliers
Mat img_matches;
drawMatches( img_1, keypoints_1, img_2, keypoints_2,
inliers, img_matches, Scalar::all(-1), Scalar::all(-1),
vector<char>(), DrawMatchesFlags::NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS );
printf("-- Number of Matches : %d \n", good_matches.size() );
printf("-- Number of Inliers : %d \n", inliers.size() );
printf("-- Match rate : %f \n", inliers.size() / (float)good_matches.size() );
//-- Localize the object
//-- Get the corners from the image_1 ( the object to be "detected" )
vector<Point2f> obj_corners;
obj_corners.push_back( Point2f(0,0) );
obj_corners.push_back( Point2f(img_1.cols,0) );
obj_corners.push_back( Point2f(img_1.cols,img_1.rows) );
obj_corners.push_back( Point2f(0,img_1.rows) );
if (!H.empty())
{
vector<Point2f> scene_corners;
perspectiveTransform(obj_corners, scene_corners, H);
//-- Draw lines between the corners (the mapped object in the scene - image_2 )
int npts = scene_corners.size();
for (int i=0; i<npts; i++)
line( img_matches, scene_corners[i] + Point2f( img_1.cols, 0),
scene_corners[(i+1)%npts] + Point2f( img_1.cols, 0), Scalar(0,0,255), 2 );
}
//-- Show detected matches
cout << "-- Show detected matches." << endl;
namedWindow("Image 1",CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
namedWindow("Image 2",CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
namedWindow("Good Matches",CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow( "Image 1", img_1k );
imshow( "Image 2", img_2k );
imshow( "Good Matches", img_matches );
waitKey(0);
destroyAllWindows();
return 0;
}
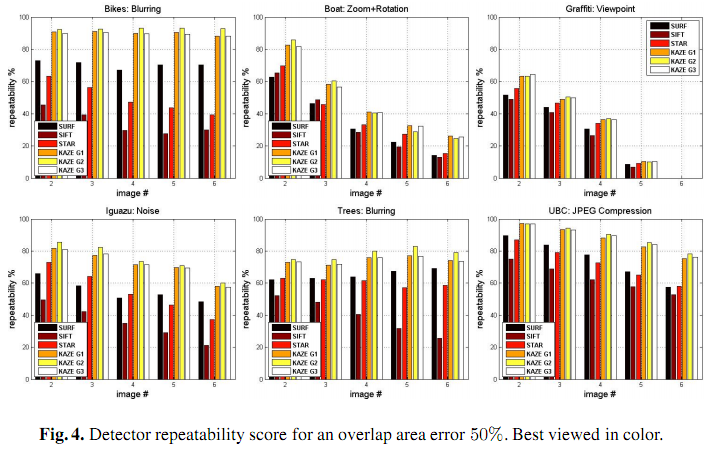
2.3.2 KAZE特征的性能测试与比较
KAZE论文中给出了若干实验图表数据,与SURF、SIFT和STAR相比,KAZE有更好的尺度和旋转不变性,并且稳定、可重复检测。主要的实验包括:
(1) 重复检测试验
这里主要从旋转缩放、视角变换、噪声干扰、模糊图像、压缩图像等方面进行了测试,可以看出KAZE的可重复性明显优于其它特征。
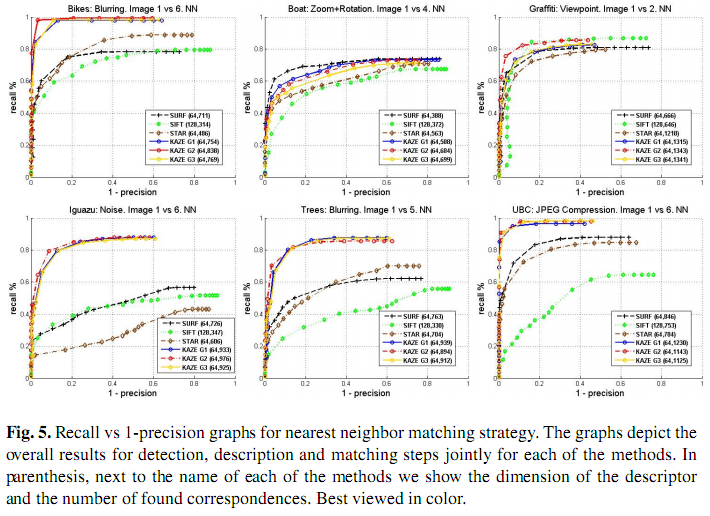
(2) 特征检测与匹配试验
这里也是从旋转缩放、视角变换、噪声干扰、模糊图像、压缩图像等方面进行了测试,给出了特征匹配的Precision-Recall图。使用的匹配算法是最近邻匹配。这里可以看出,在图像模糊、噪声干扰和压缩重构等造成的信息丢失的情况下,KAZE特征的鲁棒性明显优于其它特征。
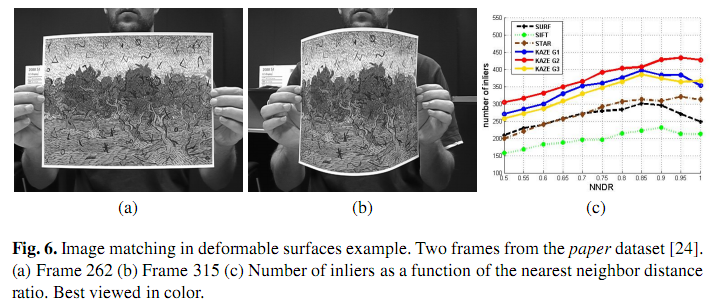
(3) 表面形变目标的特征匹配
这里可以看出基于g2传导函数的KAZE特征性能最好。
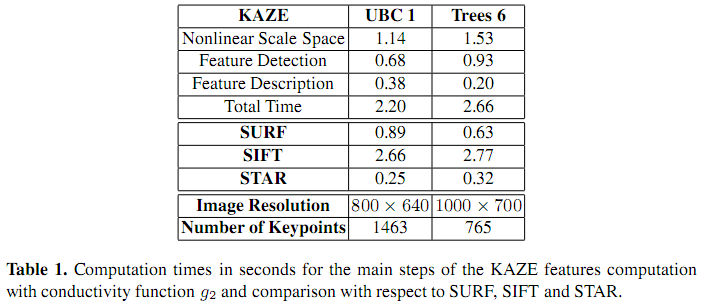
(4) 检测效率测试
这里可以看出KAZE的特征检测时间高于SURF和STAR,但与SIFT相近。这里比较花时间的是非线性尺度空间的构建。
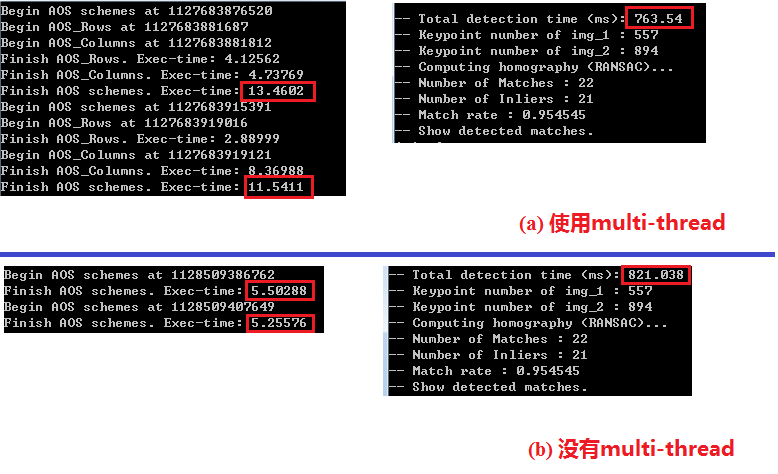
作者提出通过多线程并行计算进行AOS求解的方法来加快运行速度,在实现代码中,他们用boost/thread库进行AOS求解和寻找局部极大值点。不过我通过测试发现这并没有明显提高运行速度,可能是因为他们的代码中,分发的多个线程最后要用thread.join()等待所有计算线程结束,然后才能继续后续运算。这个join的使用反而可能会降低运行速度。
Computer Vision Talks博客不久前对KAZE算法进行了评测,并与其它特征进行了性能比较。这里我根据Ievgen在github上的OpenCV-Features-Comparison代码进行了更深入的测试,进一步显示了KAZE特征在尺度缩放、旋转变换、亮度变化和高斯模糊等情况下的优良性能。
(1) Percent of correct matches
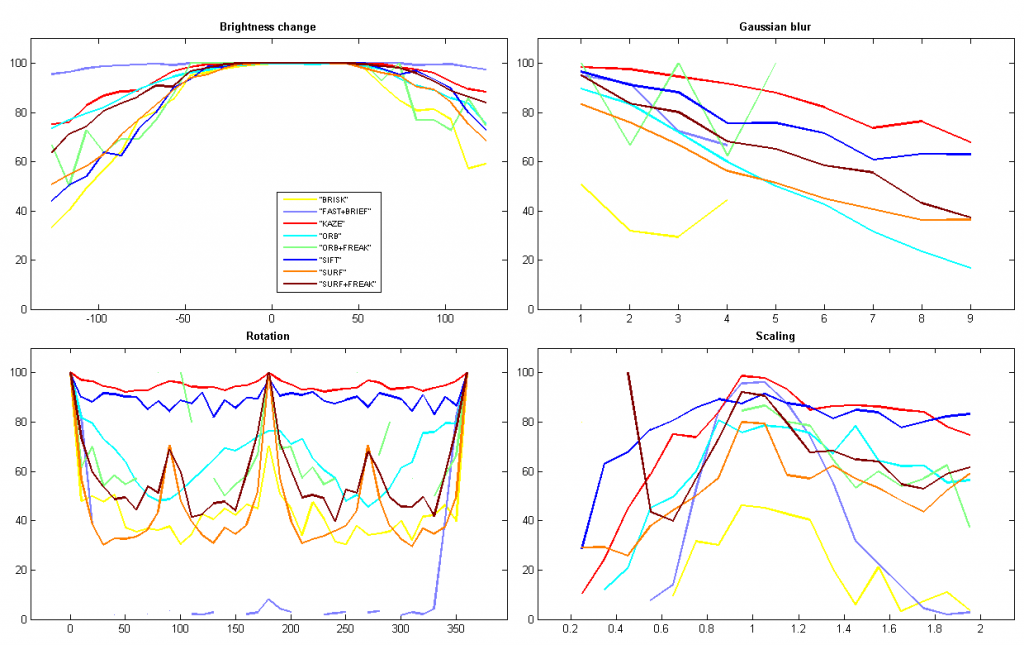
(2) Percent of matches
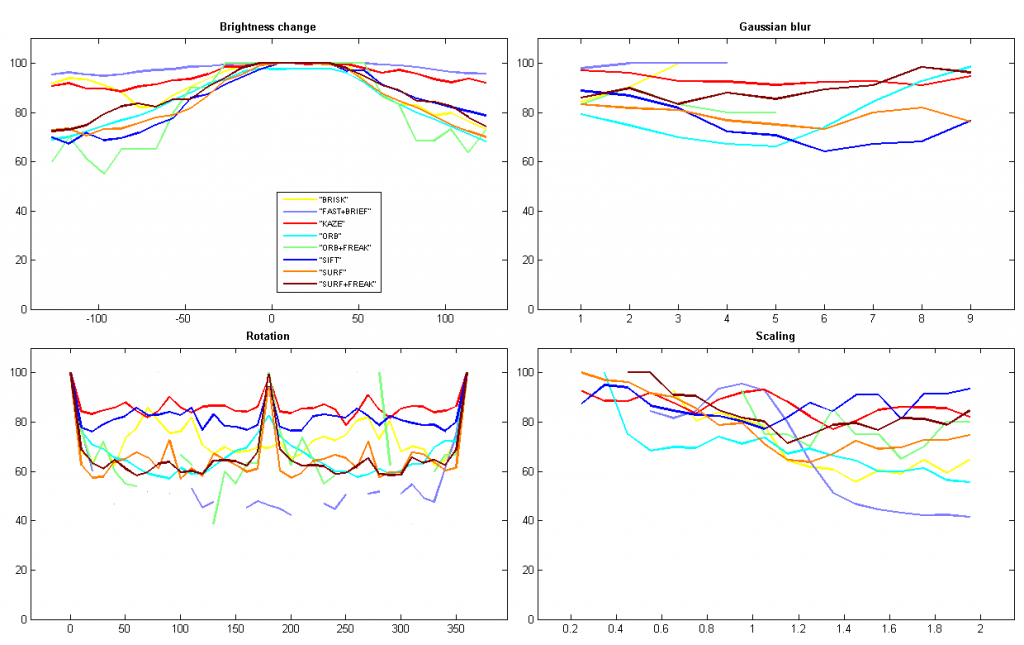
(3) Match ratio
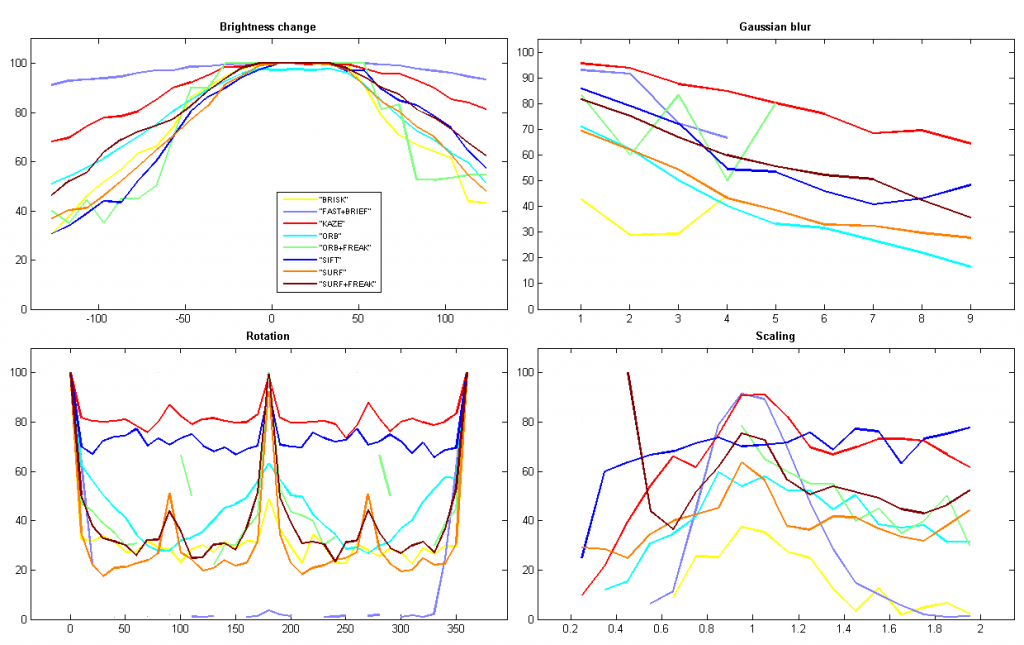
(4) Mean distance
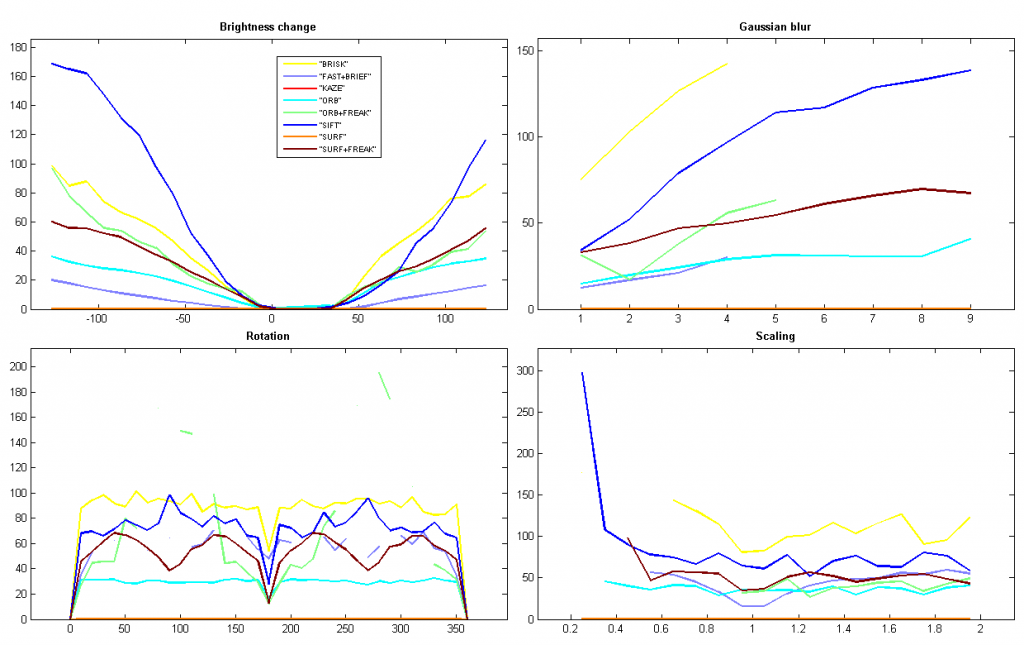
(5) Homography error
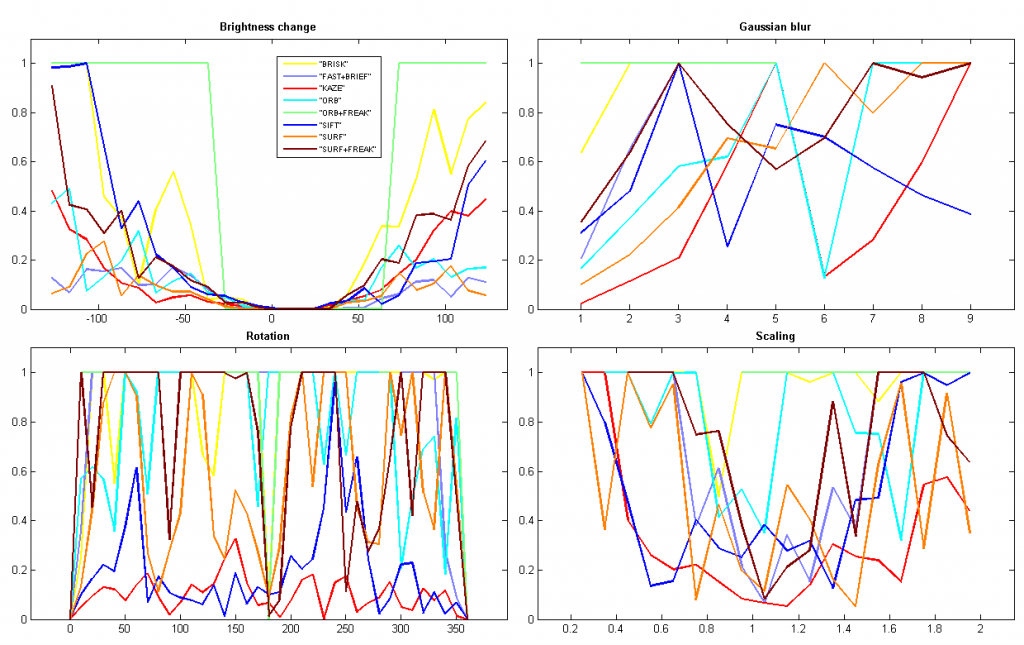
不过KAZE在运行时间上的短板的确很明显,远高于其他特征。特别是,论文的实验显示KAZE和SIFT的检测速度相差并不大。但在我的实验中,KAZE的检测时间是SIFT的10倍,而且SIFT比SURF还快一倍!这可能是OpenCV的实现代码中对SIFT做了较大的优化。具体还需要再研究下OpenCV的代码。
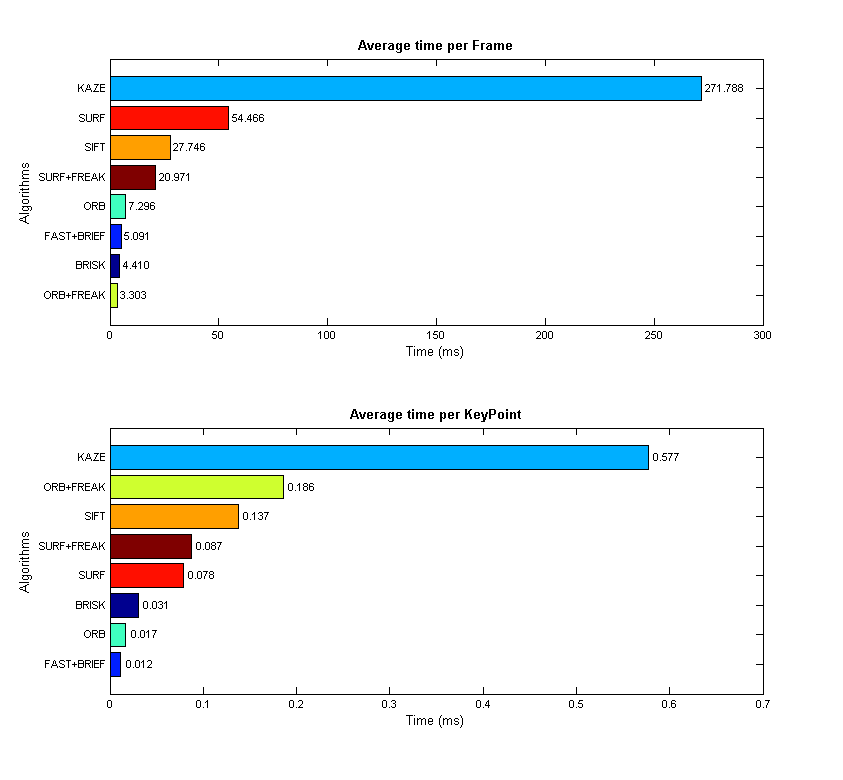
最后分享一下上述图表的Matlab代码:
%%
% MATLAB script for the visualization of the results of OpenCV-Features-Comparison
% Copyright (c) by Yuhua Zou.
% Email: yuhuazou AT gmail DOT com OR chenyusiyuan AT 126 DOT com
%
close all;
clear all;
clc;
% cmap: table of line color
% generated in this way:
% >> cmap = colormap(jet(8))
cmap = [
1.0000 1.0000 0;
0.5000 0.5000 1.0000;
1.0000 0 0;
0 1.0000 1.0000;
0.5000 1.0000 0.5000;
0 0 1.0000;
1.0000 0.5000 0;
0.5000 0 0 ];
% workroot: directory which contains files as follows:
% HomographyError.txt
% MatchingRatio.txt
% MeanDistance.txt
% PercentOfCorrectMatches.txt
% PercentOfMatches.txt
% Performance.txt
%
workroot='.\4\';
files=dir([workroot,'*.txt']);
% use the file name as the figure name, stored in a cell 'nameFigure'
nameFigure = cell(1,length(files));
for i=1:length(files),
% get file name and create a correspoinding figure
filename = files(i,1).name;
nameFigure{i} = filename(1:end-4);
figure('Name',nameFigure{i},'Position',[20 40 1240 780]);
% initialize 2 cells to store title name and legends of each plot
nameTitle{1} = '';
nameLegend{1} = '';
% open file
file = fullfile(workroot,filename);
fid = fopen(file,'r');
% process 'Performance.txt' individually
if strcmp(nameFigure{i},'Performance') ,
nl = 0;
data = 0;
%% analyze each line
tline = fgetl(fid);
while ischar(tline),
nl = nl + 1;
tline(tline == '"') = '';
if nl == 1,
nameTitle{ 1 } = tline;
elseif nl == 2,
args = regexp(tline,'\t','split');
nameLegend = args(2:end);
elseif ~isempty(tline),
args = regexp(tline,'\t','split');
cols = length(args) - 1;
tick = args{1};
nameTick{nl-2} = tick;
for n = 1:cols, data(nl-2,n) = str2num( args{n+1} ); end
end
tline = fgetl(fid);
end
% plotting
for k=1:2,
subplot(2,1,k);
[data_sorted,idx] = sort(data(:,k),'ascend');
h = barh( data_sorted ); % get the handle to change bar color
xlabel('Time (ms)'); ylabel('Algorithms');
title(nameLegend{ k }, 'FontWeight', 'bold');
set(gca, 'yticklabel', nameTick(idx), 'FontSize', 7);
% set(gca,'yticklabel','','FontSize',7); % unshow y-axis ticks
%% attach the value to the right side of each bar
x = get(h, 'XData');
y = get(h, 'YData');
horiGap = 0.5*min(y);
for c=1:length(x),
text( y(c) + horiGap, x(c), num2str(y(c), '%0.3f'),...
'HorizontalAlignment','left','VerticalAlignment','middle',...
'FontSize',7);
end
%% Change the color of each bar
ch = get(h,'Children'); % get children of the bar group
fvd = get(ch,'Faces'); % get faces data
fvcd = get(ch,'FaceVertexCData'); % get face vertex cdata
% [zs, izs] = sortrows(datak,1); % sort the rows ascending by first columns
for c = 1:length(data_sorted)
fvcd(fvd(c,:)) = idx(c); % adjust the face vertex cdata to be that of the row
end
set(ch,'FaceVertexCData',fvcd) % set to new face vertex cdata
% you can search 'FaceVertexCData' in MATLAB Help for more info.
end
else
%% process other documents
nDataRow = 0; % rows of numerical data in each plot
nPlot = 0; % number of plots
data{1} = 0; % all numerical data in current document
%% analyze each line
tline = fgetl(fid);
while ischar(tline) && ~strcmp(tline, -1),
% split the line into strings by '\t'
args = regexp(tline,'\t','split');
if strcmp(args{end},''), args = args(1:end-1); end; % remove the last empty one
% the line which contains only one string
% is recognized as the beginning of a new plot
% the string is stored as plot title
% which represents the transformation type
if length(args) == 1,
nDataRow = 0;
nPlot = nPlot + 1;
tline(tline == '"') = '';
nameTitle{ nPlot } = tline;
else
% the line with several '"'s under the 'plot title' line
% stores legends of the plot
% which represent feature methods
if ~isempty( find( tline=='"', 1 ) ),
tline(tline == '"') = '';
nameLegend{ nPlot } = args(2:end);
else
% the line without '""'s contains numerical data
% which represent experiment data
nDataRow = nDataRow + 1;
for n = 1:length(args),
data{ nPlot }(nDataRow,n) = str2double( args{n} );
end
end
end
tline = fgetl(fid);
end
%% plotting
for p = 1:nPlot,
subplot( ceil(nPlot/2), 2, p);
xdata = data{p}(:,1);
ydata = data{p}(:,2:end);
for r=1:size(ydata,2)
plot(xdata, ydata(:,r), 'Color', cmap(r,:), 'LineWidth',2); hold on; % draw each line with different color
end
title(nameTitle{p},'FontWeight','bold');
if p == 1, legend(nameLegend{p},'Location','Best','FontSize',7); end
xlim([min(xdata(:)-0.1*max(xdata(:))), 1.1*max(xdata(:))]);
ylim([0, 1.1*max(ydata(:))]);
end
end
fclose(fid);
end
其中bar的颜色设置参考自:http://www.mathworks.cn/support/solutions/en/data/1-4LDEEP/index.html?solution=1-4LDEEP
KAZE特征分析的系列笔记到此暂告一段落了,我觉得如果能够在非线性尺度空间的构建和特征检测方面对算法做出优化和改进、提高其实时性,KAZE 将大有用武之地。笔记仓促写完,还有很多不足和问题,欢迎大家指正和讨论,谢谢!