Crossing clock domains - Flag
A flag to another clock domain
If the signal that needs to cross the clock domains is just a pulse (i.e. it lasts just one clock), we call it a "flag". The previous design usually doesn't work (the flag might be missed, or be seen for too long, depending on the ratio of the clocks used).
We still want to use a synchronizer, but one that works for flags.
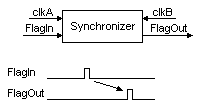
The trick is to transform the flags into level changes, and then use the two flip-flops technique.
module Flag_CrossDomain(
clkA, FlagIn_clkA,
clkB, FlagOut_clkB);
// clkA domain signals
input clkA, FlagIn_clkA;
// clkB domain signals
input clkB;
output FlagOut_clkB;
reg FlagToggle_clkA;
reg [2:0] SyncA_clkB;
// this changes level when a flag is seen
always @(posedge clkA) if(FlagIn_clkA) FlagToggle_clkA <= ~FlagToggle_clkA;
// which can then be synched to clkB
always @(posedge clkB) SyncA_clkB <= {SyncA_clkB[1:0], FlagToggle_clkA};
// and recreate the flag from the level change
assign FlagOut_clkB = (SyncA_clkB[2] ^ SyncA_clkB[1]);
endmodule
Now if you want the clkA domain to receive an acknowledgment (that clkB received the flag), add a busy signal.
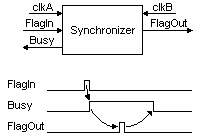
module FlagAck_CrossDomain(
clkA, FlagIn_clkA, Busy_clkA,
clkB, FlagOut_clkB);
// clkA domain signals
input clkA, FlagIn_clkA;
output Busy_clkA;
// clkB domain signals
input clkB;
output FlagOut_clkB;
reg FlagToggle_clkA;
reg [2:0] SyncA_clkB;
reg [1:0] SyncB_clkA;
always @(posedge clkA) if(FlagIn_clkA & ~Busy_clkA) FlagToggle_clkA <= ~FlagToggle_clkA;
always @(posedge clkB) SyncA_clkB <= {SyncA_clkB[1:0], FlagToggle_clkA};
always @(posedge clkA) SyncB_clkA <= {SyncB_clkA[0], SyncA_clkB[1]};
assign FlagOut_clkB = (SyncA_clkB[2] ^ SyncA_clkB[1]);
assign Busy_clkA = FlagToggle_clkA ^ SyncB_clkA[1];
endmodule