You are given an array a consisting of n integers, and additionally an integer m. You have to choose some sequence of indices b1, b2, ..., bk (1 ≤ b1 < b2 < ... < bk ≤ n) in such a way that the value of 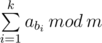 is maximized. Chosen sequence can be empty.
is maximized. Chosen sequence can be empty.
Print the maximum possible value of 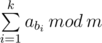 .
.
The first line contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n ≤ 35, 1 ≤ m ≤ 109).
The second line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109).
Print the maximum possible value of 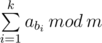 .
.
4 4
5 2 4 1
3
3 20
199 41 299
19
In the first example you can choose a sequence b = {1, 2}, so the sum 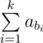 is equal to 7 (and that's 3 after taking it modulo 4).
is equal to 7 (and that's 3 after taking it modulo 4).
In the second example you can choose a sequence b = {3}.
有一串数列 可以从中任取k个数字 令k个数字相加除摸m 求最大的值。
n<=35 如果直接dfs的话 是2^35看到会爆掉,所以可以分两次 这样最大也就是2^18 才二十多万看到能过了。
先求出前半部分的,在求出后半部分的。然后在其中一个里找某个数 使的更接近m就行,这样就要用到二分了
总的复杂度是2^(n/2)*log(n/2) 足够算出这个题目了。
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 #define ll long long 3 using namespace std; 4 const int N = 1<<18; 5 ll a[40], b[40], c[N], d[N], k, ans, sum, n, m; 6 void dfs(int x) { 7 if(x == ans + 1) { 8 c[++k] = sum%m; 9 return ; 10 } 11 sum += b[x]; dfs(x + 1); 12 sum -= b[x]; dfs(x + 1); 13 } 14 int main() { 15 cin >> n >> m; 16 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) cin >> a[i], a[i] %= m, b[i] = a[i]; 17 ans = n/2; 18 dfs(1); 19 ll n1 = k; 20 for(int i = 1; i <= k; i ++) d[i] = c[i]; 21 memset(c, 0, sizeof(c)); 22 ans = n; k = 0; 23 dfs(n/2+1); 24 ll MAX = -1; 25 sort(d+1,d+n1+1); 26 for(int i = 1; i <= k; i ++) { 27 int t = lower_bound(d+1,d+n1,m-c[i]-1)-d; 28 while(c[i]+d[t]>=m)t--; 29 MAX=max(MAX,c[i] + d[t]); 30 } 31 printf("%lld ",MAX); 32 return 0; 33 }