前面几篇学习了Spring的依赖注入,这篇开始学习另一个核心功能——面向切面编程AOP。
通过本文,你可以了解到:
1 Spring xml规范
2 通过配置文件实现面向切面编程
3 对比与传统AOP编程
Spring的xml文件
Spring的xml一般起名叫做bean.xml或者xxxapplication.xml这种,然后放在src下通过ClassPathXmlApplicationContext进行加载。文件的内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.0.xsd"> <bean id="audience"class="com.spring.test.aop.Audience"/> <aop:config> </aop:config> </beans>
最上面的是xml的编码,这个就不解释了。
下面的<beans>是Spring的配置标签,beans里面几个重要的属性:
xmlns:
是默认的xml文档解析格式,即spring的beans。地址是http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans。
通过设置这个属性,所有在beans里面声明的属性,可以直接通过<>来使用,比如<bean>等等。
xmlns:xsi:
是xml需要遵守的规范,通过URL可以看到,是w3的统一规范,后面通过xsi:schemaLocation来定位所有的解析文件。
xmlns:aop:
这个是重点,是我们这里需要使用到的一些语义规范,与面向切面AOP相关。
xmlns:tx:
Spring中与事务相关的配置内容。
一个XML文件,只能声明一个默认的语义解析的规范。
例如上面的xml中就只有beans一个是默认的,其他的都需要通过特定的标签来使用,比如aop,它自己有很多的属性,如果要使用,前面就必须加上aop:xxx才可以。比如上面的aop:config。
类似的,如果默认的xmlns配置的是aop相关的语义解析规范,那么在xml中就可以直接写config这种标签了。
基于配置的AOP编程过程
首先,如果要在工程中使用AOP需要几个jar包:
1 Aop的核心包,即org.springframework.aop-xxx.jar
2 Spring的联盟包:aopalliance-1.0.jar
3 aspectJ相关的jar包:aspectjrt.jar aspectjweaver.jar
4 如果使用了动态代理,还需要添加cglib相关的jar包:cglib.zip
首先需要一个AOP的切面类,用于定义各种响应事件
package com.spring.test.aop; public class Audience { public void takeSeats(){ System.out.println("The audience is taking their seats."); } public void turnOffCellPhones(){ System.out.println("The audience is turning off their cellphones"); } public void applaud(){ System.out.println("CLAP CLAP CLAP"); } public void demandRefund(){ System.out.println("Boo! We want money back"); } }
然后在bean.xml中编写aop:config的相关内容:
...省略beans的定义内容 <bean id="audience" class="com.spring.test.aop.Audience"/> <bean id="sax" class="com.spring.test.setter.Saxophone"/> <bean id="kenny" class="com.spring.test.setter.Instrumentalist"> <property name="song" value="Jingle Bells" /> <property name="age" value="25" /> <property name="instrument" ref="sax"/> </bean> <aop:config proxy-target-class="true"> <aop:aspect ref="audience"> <aop:pointcut id="performance" expression="execution(* com.spring.test.action1.Performer.perform(..))"/> <aop:before pointcut-ref="performance" method="takeSeats"/> <aop:before pointcut-ref="performance" method="turnOffCellPhones"/> <aop:after-returning pointcut-ref="performance" method="applaud"/> <aop:after-throwing pointcut-ref="performance" method="demandRefund"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config> </beans>
这里面的aop:pointcut 就是使用AspectJ来定位的。意思是:当执行com.spring.test.action1.Performer的perform方法时,就会触发该切面的事件响应。
而Performer以及Instrumentalist等等的代码,就在下面简单的都罗列出来了:
配置文件:bean.xml

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.0.xsd"> <bean id="audience" class="com.spring.test.aop.Audience"/> <bean id="sax" class="com.spring.test.setter.Saxophone"/> <bean id="kenny" class="com.spring.test.setter.Instrumentalist"> <property name="song" value="Jingle Bells" /> <property name="age" value="25" /> <property name="instrument" ref="sax"/> </bean> <aop:config proxy-target-class="true"> <aop:aspect ref="audience"> <aop:pointcut id="performance" expression="execution(* com.spring.test.action1.Performer.perform(..))"/> <aop:before pointcut-ref="performance" method="takeSeats"/> <aop:before pointcut-ref="performance" method="turnOffCellPhones"/> <aop:after-returning pointcut-ref="performance" method="applaud"/> <aop:after-throwing pointcut-ref="performance" method="demandRefund"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config> </beans>
表演者接口:Performer.java

package com.spring.test.action1; public interface Performer { void perform() throws PerformanceException; }
表演者实现类:Instrumentalist.java

package com.spring.test.setter; import com.spring.test.action1.PerformanceException; import com.spring.test.action1.Performer; public class Instrumentalist implements Performer{ private String song; private int age; private Instrument instrument; public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public String getSong() { return song; } public void setSong(String song) { this.song = song; } public Instrument getInstrument() { return instrument; } public void setInstrument(Instrument instrument) { this.instrument = instrument; } public Instrumentalist(){} public Instrumentalist(String song,int age,Instrument instrument){ this.song = song; this.age = age; this.instrument = instrument; } public void perform() throws PerformanceException { System.out.println("Instrumentalist age:"+age); System.out.print("Playing "+song+":"); instrument.play(); } }
内部bean接口:Instrument.java

package com.spring.test.setter; public interface Instrument { public void play(); }
内部bean实现类:Saxophone.java

package com.spring.test.setter; public class Saxophone implements Instrument { public Saxophone(){} public void play() { System.out.println("TOOT TOOT TOOT"); } }
测试主函数:main

package com.spring.test.setter; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.spring.test.action1.PerformanceException; public class test { public static void main(String[] args) throws PerformanceException { ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml"); Instrumentalist performer = (Instrumentalist)ctx.getBean("kenny"); performer.perform(); } }
运行结果:
The audience is taking their seats. The audience is turning off their cellphones Instrumentalist age:25 Playing Jingle Bells:TOOT TOOT TOOT CLAP CLAP CLAP
通过这种声明方式,可以 快速的实现切点与切面的整合,成为下面这种格式的新代码:
class{ try{ audience.takeSeats(); audience.turnOffCellphones(); performance.perform(); audience.applaud(); }catch(Exception){ audience.demandRefund(); } }
面向切面的好处,要在实际工作中多加领会才可以,常用的场景就是日志的记录了。
与传统的AOP编程相比
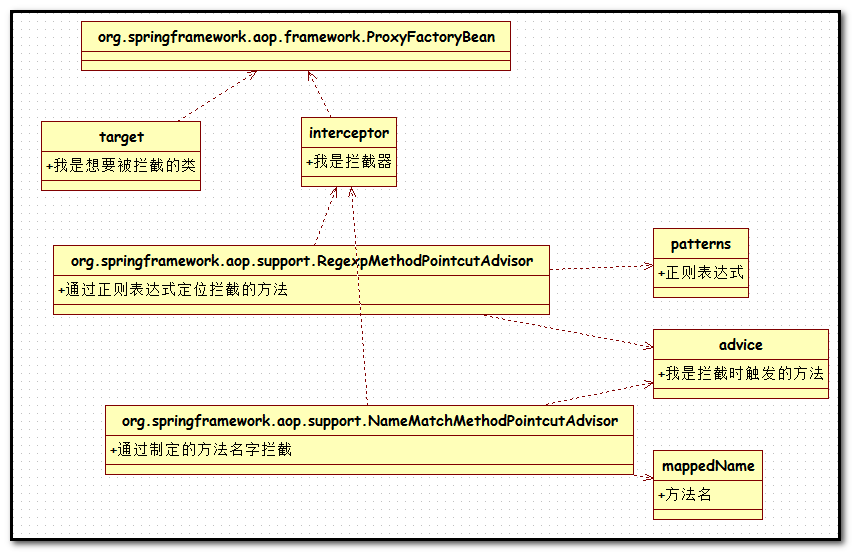
前面也做过一个传统的spring aop的实现方法:http://www.cnblogs.com/xing901022/p/4143696.html
不得不说,通过ProxyFactoryBean达到的面向切面的编程,过于复杂,光是那几个功能就要好好理解一番。
而基于配置的AOP使用就要简单的多,只需要一个切面的程序,然后通过配置文件就可以完全解耦的融入到切点中。
