Vue项目环境搭建
node 是由c++编写的专门用来运行javascript语言的。
npm(cnpm)~~pip:npm是一个终端应用商城,就像python的pip一样,只不过他服务器也在国外,所以可以换国内源cnpm
vue~~django:vue是用来搭建vue前端项目的。
js是前端的弱语言的脚本编程语言,而node则是一个后端语言
1.安装node
官网下载安装包,傻瓜式安装:https://nodejs.org/zh-cn/
2.换源安装cnpm,后续下载只需要将npm换成cnpm
>: npm install -g cnpm --registry=https://registry.npm.taobao.org
3.安装vue脚手架
>: cnpm install -g @vue/cli
4.如果2,3执行失败了,可以先清空下缓存,再继续执行相应的步骤
npm cache clean --force
Vue项目创建
1.进入到指定的存放目录
>: cd ***
2.创建项目
>: vue create 项目名
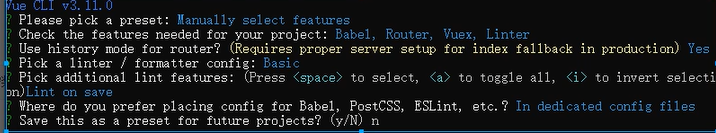
就是默认第一个,有大写选大写就ok
j3) 项目初始化
pcharm配置并启动vue项目
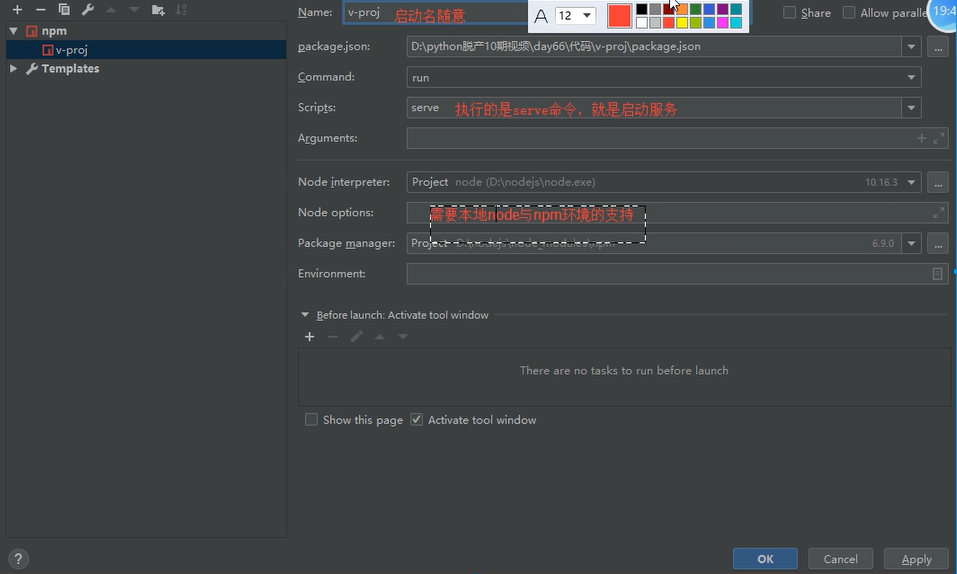
1.用pycharm打开vue项目
2.添加npm配置启动
vue项目目录结构分析
├── v-proj
| ├── node_modules // 这个是整个项目的所有的依赖,因为过于庞大,一般不可以移植给其他电脑环境
| ├── public
| | ├── favicon.ico //标签图标
| | └── index.html // 项目唯一的页面
| ├── src
| | ├── assets // 静态资源(html,css,js)
| | ├── components // 小组件
| | ├── views // 页面组件
| | ├── App.vue // 根组件
| | ├── main.js // 全局组件,入口文件
| | ├── router.js // 路由脚本文件(配置路由url与页面组件的对应)
| | └── store.js // 仓库脚本文件(vuex插件的配置文件,数据仓库)
| ├── README.md
└ └── **配置文件
Vue组件(.vue文件)
template:有且只有一个根标签(这个template是用于标识组件自身的html结构)
script:必须将组件对象导出 export default{}
style:style样式要明确scoped属性,表示该样式只能在组件内部起作用
<template> <div class="test"> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: "Test" } </script> <style scoped> </style>
全局脚本文件main.js(项目入口文件)
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import router from './router'
import store from './store'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
router,
store,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
改写
import Vue from 'vue' // 加载vue环境
import App from './App.vue' // 加载根组件
import router from './router' // 加载路由环境
import store from './store' // 加载数据仓库环境
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
store,
render: function (readFn) {
return readFn(App);
},
});
vue项目启动生命周期以及页面组件的应用(重点)
请求过程
1) 加载mian.js启动项目 i) import Vue from 'vue' 为项目加载vue环境 ii) import App from './App.vue' 加载根组件用于渲染替换挂载点 iii) import router from './router' 加载路由脚本文件,进入路由相关配置 2) 加载router.js文件,为项目提供路由服务,并加载已配置的路由(链接与页面组件的映射关系) 注:不管当前渲染的是什么路由,页面渲染的一定是根组件,链接匹配到的页面组件只是替换根组件中的 <router-view></router-view> 3) 如果请求链接改变(路由改变),就会匹配新链接对应的页面组件,新页面组件会替换渲染router-view标签,替换掉之前的页面标签(就是完成了页面跳转)
参与文件
main.js:该文件内容不变 App.vue <template> <div id="app"> <!-- url路径会加载不同的页面组件 eg:/red => RegPage | /blue => BluePage 来替换router-view标签,完成页面的切换 --> <router-view></router-view> </div> </template>
<template> <div class="red-page"> <Nav></Nav> </div> </template> <script> import Nav from '@/components/Nav' export default { name: "RedPage", components: { Nav }, } </script> <style scoped> .red-page { width: 100vw; height: 100vh; background-color: red; } </style>
<template> <div class="blue-page"> <Nav></Nav> </div> </template> <script> import Nav from '@/components/Nav' export default { name: "BluePage", components: { Nav } } </script> <style scoped> .blue-page { width: 100vw; height: 100vh; background-color: blue; } </style>
router.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Router from 'vue-router'
import Home from './views/Home.vue'
import RedPage from "./views/RedPage";
import BluePage from "./views/BluePage";
Vue.use(Router);
export default new Router({
mode: 'history',
base: process.env.BASE_URL,
routes: [
{
path: '/',
name: 'home',
component: Home
},
{
path: '/red',
name: 'red',
component: RedPage
},
{
path: '/blue',
name: 'blue',
component: BluePage
}
]
})
全局样式文件配置
assets/css/global.css
html, body, h1, h2, ul, p {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
ul {
list-style: none;
}
a {
color: black;
text-decoration: none;
}
main.js中新增
// 配置全局样式
import '@/assets/css/global.css'
封装小组件-Nav导航栏组件
components/Nav.vue <template> <div class="nav"> <!--采用vue-router完成页面跳转,不能采用a标签(会发生页面刷新,本质就是重新加载了一次项目界面)--> <ul> <li> <!--<a href="/">主页</a>--> <router-link to="/">主页</router-link> </li> <li> <router-link to="/red">红页</router-link> </li> <li> <router-link to="/blue">蓝页</router-link> </li> </ul> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: "Nav", } </script> <style scoped> .nav { width: 100%; height: 60px; background-color: orange; } .nav li { float: left; font: normal 20px/60px '微软雅黑'; padding: 0 30px; } .nav li:hover { cursor: pointer; background-color: aquamarine; } .nav li.active { cursor: pointer; background-color: aquamarine; } </style>
<template> <div class="home"> <!-- 3)使用Nav组件 --> <Nav></Nav> </div> </template> <script> // 1)导入Nav组件 import Nav from '@/components/Nav' export default { // 2)注册Nav组件 components: { Nav, } } </script>
新增页面三步骤
1) 在views文件夹中创建视图组件
2) 在router.js文件中配置路由
3) 设置路由跳转,在指定路由下渲染该页面组件(替换根组件中的router-view标签)
<template> <div class="tan-page"> <Nav></Nav> </div> </template> <script> import Nav from '@/components/Nav' export default { name: "TanPage", components: { Nav } } </script> <style scoped> .tan-page { width: 100vw; height: 100vh; background-color: tan; } </style>
router.js
// ...
import TanPage from "./views/TanPage";
export default new Router({
mode: 'history',
base: process.env.BASE_URL,
routes: [
// ...
{
path: '/tan',
name: 'tan',
component: TanPage
}
]
})
<li> <router-link to="/tan">土页</router-link> </li>
组件生命周期钩子(官方API)
# 1)一个组件从创建到销毁的整个过程,就称之为组件的生命周期
# 2)在组件创建到销毁的过程中,会出现众多关键的时间节点,如 组件要创建了、组件创建完毕了、组件数据渲染完毕了、组件要被销毁了、组件销毁完毕了 等等时间节点,每一个时间节点,vue都为其提供了一个回调函数(在该组件到达该时间节点时,就会触发对应的回调函数,在函数中就可以完成该节点需要完成的业务逻辑)
# 3)生命周期钩子函数就是 vue实例 成员
export default {
// ...
beforeCreate() {
console.log('组件创建了,但数据和方法还未提供');
// console.log(this.$data);
// console.log(this.$options.methods);
console.log(this.title);
console.log(this.alterTitle);
},
// 该钩子需要掌握,一般该组件请求后台的数据,都是在该钩子中完成
// 1)请求来的数据可以给页面变量进行赋值
// 2)该节点还只停留在虚拟DOM范畴,如果数据还需要做二次修改再渲染到页面,
// 可以在beforeMount、mounted钩子中添加逻辑处理
created() {
console.log('组件创建了,数据和方法已提供');
// console.log(this.$data);
// console.log(this.$options.methods);
console.log(this.title);
console.log(this.alterTitle);
console.log(this.$options.name);
},
destroyed() {
console.log('组件销毁完毕')
}
}
"""
1) router-link会被解析为a标签,用to完成指定路径跳转,但是不能添加系统事件(因为是组件标签)
2) 在js方法中可以用 this.$router.push('路径') 完成逻辑跳转
3) 在js方法中可以用 this.$route.path 拿到当前请求的页面路由
"""
<template> <div class="nav"> <!--采用vue-router完成页面跳转,不能采用a标签(会发生页面刷新,本质就是重新加载了一次项目界面)--> <ul> <li @click="changePage('/')" :class="{active: currentPage === '/'}"> <!--<a href="/">主页</a>--> <!--<router-link to="/">主页</router-link>--> 主页 </li> <li @click="changePage('/red')" :class="{active: currentPage === '/red'}"> <!--<router-link to="/red">红页</router-link>--> 红页 </li> <li @click="changePage('/blue')" :class="{active: currentPage === '/blue'}"> <!--<router-link to="/blue">蓝页</router-link>--> 蓝页 </li> <li @click="changePage('/tan')" :class="{active: currentPage === '/tan'}"> <!--<router-link to="/tan">土页</router-link>--> 土页 </li> </ul> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: "Nav", data() { return { // 没渲染一个页面,都会出现加载Nav组件,currentPage就会被重置, // 1)在点击跳转事件中,将跳转的页面用 数据库 保存,在钩子函数中对currentPage进行数据更新 // currentPage: localStorage.currentPage ? localStorage.currentPage: '' // 2)直接在created钩子函数中,获取当前的url路径,根据路径更新currentPage currentPage: '' } }, methods: { changePage(page) { // console.log(page); // 当Nav出现渲染,该语句就无意义,因为在data中将currentPage重置为空 // this.currentPage = page; // 有bug,用户不通过点击,直接修改请求路径完成页面跳转,数据库就不会更新数据 // localStorage.currentPage = page; // 任何一个标签的事件中,都可以通过router完成逻辑条件 // console.log(this.$route); // 管理路由数据 // console.log(this.$router); // 管理路由跳转 this.$router.push(page); // 路由的逻辑跳转 } }, // 当前组件加载成功,要根据当前实际所在的路径,判断单选激活标签 created() { // console.log(this.$route.path); this.currentPage = this.$route.path; } } </script> <style scoped> .nav { width: 100%; height: 60px; background-color: orange; } .nav li { float: left; font: normal 20px/60px '微软雅黑'; padding: 0 30px; } .nav li:hover { cursor: pointer; background-color: aquamarine; } .nav li.active { cursor: pointer; background-color: aquamarine; } </style>