第2章、Programming in Objective-C
// main.m
// prog1
//
// Created by Steve Kochan on 1/30/11.
// Copyright 2011 ClassroomM, Inc.. All rights reserved.
//
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
int main (int argc, const char * argv[])
{
NSAutoreleasePool * pool = [[NSAutoreleasePool alloc] init];
NSLog (@"Programming is fun!");
[pool drain];
return 0;
}
NSAutoreleasePool * pool = [[NSAutoreleasePool alloc] init]; 申请一块内存用于自动释放池,Xcode 自动生成
@"Programming is fun!" : NSString 对象常量
[pool drain];退出前调用,用于释放分配的内存池;Xcode 自动生成
第3章、Classes, Objects, and Methods
调用类或对象的方法:
[ ClassOrInstance method ]
调用一个类或对象的方法:向这个对象或类发送消息;
消息的接受者也叫做receiver,因此上面的表达方式可以等同于:
[ receiver message ] ;
例如:yourCar = [Car new]; get a new car
你发送一个new消息给Car这个类,让它给你生成一个新的car对象,对象的结果存储在变量 yourCar中;
这里的new是一个类方法或工厂方法,下面的方法是对象方法:
[yourCar prep]; get it ready for first-time use
[yourCar drive]; drive your car
[yourCar wash]; wash your car
[yourCar getGas]; put gas in your car if you need it
[yourCar service]; service your car
[yourCar topDown]; if it's a convertible
[yourCar topUp];
一个Objective-C的类分为3部分:
1、 @interface section
2、@implementation section
3、program section
接口部分的格式:
@interface NewClassName: ParentClassName
{
memberDeclarations;
}
methodDeclarations;
@end
例如:
//---- @interface section ----
@interface Fraction: NSObject
{
int numerator;
int denominator;
}
-(void) print;
-(void) setNumerator: (int) n;
-(void) setDenominator: (int) d;
@end
按惯例,类名以大写字母开头;
变量的命名规则:
以字母或下划线开头,后面可以跟随任何字符的组合;
以下是不合法的命名:
1、sum$value $—is not a valid character.
2、piece flag—Embedded spaces are not permitted.
3、3Spencer —Names can’t start with a number
4、int —This is a reserved word.
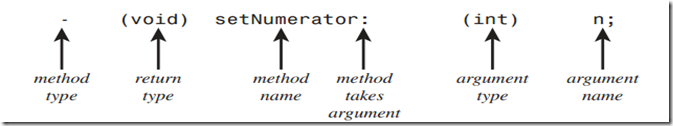
成员方法的定义:
–(void) setNumerator: (int) n;
“-”表示类实例的方法;方法名后的“:”表示后面是方法的参数;参数前的括号内是参数的类型;最后以“;”结束
实现部分的格式:
@implementation NewClassName
methodDefinitions;
@end
例如:
@implementation Fraction
–(void) print
{
NSLog (@"%i/%i", numerator, denominator);
}
–(void) setNumerator: (int) n
{
numerator = n;
}
–(void) setDenominator: (int) d
{
denominator = d;
}
@end
program部分:
例如:
//---- program section ----
int main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
NSAutoreleasePool * pool = [[NSAutoreleasePool alloc] init];
Fraction *myFraction;
// Create an instance of a Fraction and initialize it
myFraction = [Fraction alloc];
myFraction = [myFraction init];
// Set fraction to 1/3
[myFraction setNumerator: 1];
[myFraction setDenominator: 3];
// Display the fraction using the print method
NSLog (@"The value of myFraction is:");
[myFraction print];
[myFraction release];
[pool drain];
return 0;
}
这里:
1、Fraction *myFaction : 定义一个Faction变量;确切的说是一个Faction的引用,存的是对象的内存地址;(就是C中指针的概念)
2、myFaction = [Fraction alloc]:调用Faction类的alloc方法,并将放回的Faction实例保存在myFaction变量中(或者说是发送一个alloc消息给类Faction);
3、myFaction = [myFaction init]:调用myFaction实例的init方法进行初始化;2、3常常可以写成:
Fraction *myFraction = [[Fraction alloc] init];
4、[myFraction setNumerator: 1];调用myFaction实例的setNumerator方法,将值1设给成员变量numerator ;setDenominator也是类似;
5、[myFraction print];调用myFaction实例的print方法,打印内容;
6、[myFraction release];调用release方法,释放之前alloc分配的内存;虽然Apple运行时系统提供了一套自动垃圾回收机制,但是养成好的内存管理的习惯更加重要;
第4章 Data Types and Expressions
int
数据类型的大小取决于机器,
在 Mac OS X中,你可以通过编译开关来决编译成32-bit 还是64-bit的应用程序. 前者,一个int变量占32bits空间;后者一个int变量占64bits空间。
float
显示一个float值,NSLog 通过转换符 %f 或 %g进行转换;
char
以单引号的形式表示,例如:‘a’,‘;’‘\n’
不要混淆:
char : ‘a’
C string : “a”
NSString:@“a”
限定符: long, long long, short, unsigned , and signed
长整型:long int factorial;
长长整型:long long int
长浮点:long double
无符号:unsigned int counter;
id类型
id类型的变量可以存储任何类型的对象,从某种意义上讲,它是一种通用类型;
|
Type |
Constant Examples |
NSLog chars |
|
char |
'a', '\n' |
%c |
|
short int |
- |
%hi, %hx, %ho |
|
unsigned short int |
- |
%hu, %hx, %ho |
|
int |
12, -97, 0xFFE0, 0177 |
%i, %x, %o |
|
unsigned int |
12u, 100U, 0XFFu |
%u, %x, %o |
|
long int |
12L, -2001, 0xffffL |
%li, %lx, %lo |
|
unsigned long int |
12UL, 100ul, 0xffeeUL |
%lu, %lx, %lo |
|
long long int |
0xe5e5e5e5LL, 500ll |
%lli, %llx, &llo |
|
unsigned long long int |
12ull, 0xffeeULL |
%llu, %llx, %llo |
|
float |
12.34f, 3.1e-5f, 0x1.5p10, 0x1P-1 |
%f, %e, %g, %a |
|
double |
12.34, 3.1e-5, 0x.1p3 |
%f, %e, %g, %a |
|
long double |
12.34L, 3.1e-5l |
%Lf, $Le, %Lg |
|
id |
nil |
%p |
整型和浮点型的转换
整型和浮点型的计算差别:
运行结果:
第5章 Program Looping
for 循环的例子:
for循环的初始化可以有多个变量:
for ( i = 0, j = 100; i < 10; ++i, j -= 10 )
...
也可以没有初始化部分(适用于变量在之前已经定义和初始化的情况):
for ( ; j != 100; ++j )
...
第7章 More on Classes
getter\setter方法:用过@property和@@synthesize
interface部分:@property int numerator, denominator;
implementation部分:@synthesize numerator, denominator;
属性的访问可以这么写:
[myFraction numerator] 或 myFraction.numerator
属性的设置:instance.property = value <=> [instance setProperty: value ]
多参数方法:
interface部分:
-(void) setTo: (int) n over: (int) d;
implemerntation部分:
-(void) setTo: (int) n over: (int) d
{
numerator = n;
denominator = d;
}
调用:
[aFraction setTo: 1 over: 3];