1.静态成员和非静态成员的区别?
2.const 和 static readonly 区别?
3.extern 是什么意思?
4.abstract 是什么意思?
5.internal 修饰符起什么作用?
6.sealed 修饰符是干什么的?
7.override 和 overload 的区别?
8.什么是索引指示器?
9.new 修饰符是起什么作用?
10.this 关键字的含义?
11.可以使用抽象函数重写基类中的虚函数吗?
12.密封类可以有虚函数吗?
13.什么是属性访问器?
14.abstract 可以和 virtual 一起使用吗?可以和 override 一起使用吗?
15.接口可以包含哪些成员?
16.类和结构的区别?
17.接口的多继承会带来哪些问题?
18.抽象类和接口的区别?
19.别名指示符是什么?
20.如何手工释放资源?
21.P/Invoke是什么?
22.StringBuilder 和 String 的区别?
23.explicit 和 implicit 的含义?
24.params 有什么用?
25.什么是反射?
以下是我做的一份参考答案(C# 语言范畴之内),如果有不准确、不全面的,欢迎各位朋友指正!
1.静态成员和非静态成员的区别?
答:
静态变量使用 static 修饰符进行声明,在类被实例化时创建,通过类进行访问
不带有 static 修饰符声明的变量称做非静态变量,在对象被实例化时创建,通过对象进行访问
一个类的所有实例的同一静态变量都是同一个值,同一个类的不同实例的同一非静态变量可以是不同的值
静态函数的实现里不能使用非静态成员,如非静态变量、非静态函数等
示例:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
namespace Example01
{
class Program
{
class Class1
{
public static String staticStr = "Class";
public String notstaticStr = "Obj";
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//静态变量通过类进行访问,该类所有实例的同一静态变量都是同一个值
Console.WriteLine("Class1's staticStr: {0}", Class1.staticStr);
Class1 tmpObj1 = new Class1();
tmpObj1.notstaticStr = "tmpObj1";
Class1 tmpObj2 = new Class1();
tmpObj2.notstaticStr = "tmpObj2";
//非静态变量通过对象进行访问,不同对象的同一非静态变量可以有不同的值
Console.WriteLine("tmpObj1's notstaticStr: {0}", tmpObj1.notstaticStr);
Console.WriteLine("tmpObj2's notstaticStr: {0}", tmpObj2.notstaticStr);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
结果:
Class1's staticStr: Class
tmpObj1's notstaticStr: tmpObj1
tmpObj2's notstaticStr: tmpObj2
2.const 和 static readonly 区别?
答:
const
用 const 修饰符声明的成员叫常量,是在编译期初始化并嵌入到客户端程序
static readonly
用 static readonly 修饰符声明的成员依然是变量,只不过具有和常量类似的使用方法:通过类进行访问、初始化后不可以修改。但与常量不同的是这种变量是在运行期初始化
示例:
测试类:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
namespace Example02Lib
{
public class Class1
{
public const String strConst = "Const";
public static readonly String strStaticReadonly = "StaticReadonly";
//public const String strConst = "Const Changed";
//public static readonly String strStaticReadonly = "StaticReadonly Changed";
}
}
客户端代码:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using Example02Lib;
namespace Example02
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//修改Example02中Class1的strConst初始值后,只编译Example02Lib项目
//然后到资源管理器里把新编译的Example02Lib.dll拷贝Example02.exe所在的目录,执行Example02.exe
//切不可在IDE里直接调试运行因为这会重新编译整个解决方案!!
//可以看到strConst的输出没有改变,而strStaticReadonly的输出已经改变
//表明Const变量是在编译期初始化并嵌入到客户端程序,而StaticReadonly是在运行时初始化的
Console.WriteLine("strConst : {0}", Class1.strConst);
Console.WriteLine("strStaticReadonly : {0}", Class1.strStaticReadonly);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
结果:
strConst : Const
strStaticReadonly : StaticReadonly
修改后的示例:
测试类:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
namespace Example02Lib
{
public class Class1
{
//public const String strConst = "Const";
//public static readonly String strStaticReadonly = "StaticReadonly";
public const String strConst = "Const Changed";
public static readonly String strStaticReadonly = "StaticReadonly Changed";
}
}
结果
strConst : Const
strStaticReadonly : StaticReadonly Changed
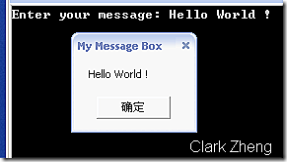
3.extern 是什么意思?
答:
extern 修饰符用于声明由程序集外部实现的成员函数
经常用于系统API函数的调用(通过 DllImport )。注意,和DllImport一起使用时要加上 static 修饰符
也可以用于对于同一程序集不同版本组件的调用(用 extern 声明别名)
不能与 abstract 修饰符同时使用
示例:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace Example03
{
class Program
{
//注意DllImport是一个Attribute Property,在System.Runtime.InteropServices命名空间中定义
//extern与DllImport一起使用时必须再加上一个static修饰符
[DllImport("User32.dll")]
public static extern int MessageBox(int Handle, string Message, string Caption, int Type);
static int Main()
{
string myString;
Console.Write("Enter your message: ");
myString = Console.ReadLine();
return MessageBox(0, myString, "My Message Box", 0);
}
}
}
4.abstract 是什么意思?
答:
abstract 修饰符可以用于类、方法、属性、事件和索引指示器(indexer),表示其为抽象成员
abstract 不可以和 static 、virtual 一起使用
声明为 abstract 成员可以不包括实现代码,但只要类中还有未实现的抽象成员(即抽象类),那么它的对象就不能被实例化,通常用于强制继承类必须实现某一成员
示例:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
namespace Example04
{
#region 基类,抽象类
public abstract class BaseClass
{
//抽象属性,同时具有get和set访问器表示继承类必须将该属性实现为可读写
public abstract String Attribute
{
get;
set;
}
//抽象方法,传入一个字符串参数无返回值
public abstract void Function(String value);
//抽象事件,类型为系统预定义的代理(delegate):EventHandler
public abstract event EventHandler Event;
//抽象索引指示器,只具有get访问器表示继承类必须将该索引指示器实现为只读
public abstract Char this[int Index]
{
get;
}
}
#endregion
#region 继承类
public class DeriveClass : BaseClass
{
private String attribute;
public override String Attribute
{
get
{
return attribute;
}
set
{
attribute = value;
}
}
public override void Function(String value)
{
attribute = value;
if (Event != null)
{
Event(this, new EventArgs());
}
}
public override event EventHandler Event;
public override Char this[int Index]
{
get
{
return attribute[Index];
}
}
}
#endregion
class Program
{
static void OnFunction(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
for (int i = 0; i < ((DeriveClass)sender).Attribute.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(((DeriveClass)sender)[i]);
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
DeriveClass tmpObj = new DeriveClass();
tmpObj.Attribute = "1234567";
Console.WriteLine(tmpObj.Attribute);
//将静态函数OnFunction与tmpObj对象的Event事件进行关联
tmpObj.Event += new EventHandler(OnFunction);
tmpObj.Function("7654321");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
结果:
1234567
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
5.internal 修饰符起什么作用?
答:
internal 修饰符可以用于类型或成员,使用该修饰符声明的类型或成员只能在同一程集内访问
接口的成员不能使用 internal 修饰符
值得注意的是,如果为 internal 成员加上了 protected 修饰符,这时的访问级别为 internal 或 protected。只是看字面意思容易弄错,许多人认为 internal protected 应该是“只有同一个程序集中的子类可以访问”,但其实它表示“同一个程序集中的所有类,以及所有程序集中的子类都可以访问”
示例
Example05Lib 项目的 Class1
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
namespace Example05Lib
{
public class Class1
{
internal String strInternal = null;
public String strPublic;
internal protected String strInternalProtected = null;
}
}
结果
Example05Lib 项目的 Class2 类可以访问到 Class1 的 strInternal 成员,当然也可以访问到 strInternalProtected 成员,因为他们在同一个程序集里
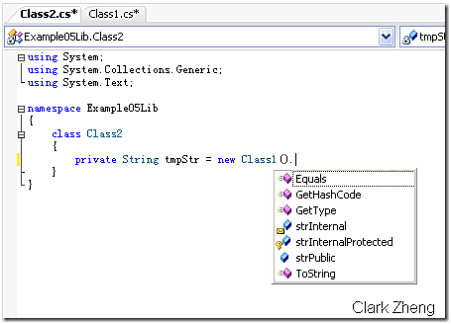
Example05 项目里的 Class3 类无法访问到 Class1 的 strInternal 成员,因为它们不在同一个程序集里。但却可以访问到 strInternalProtected 成员,因为 Class3 是 Class1 的继承类
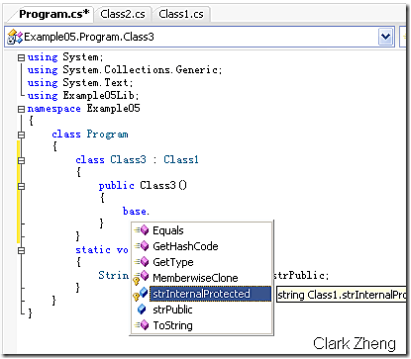
Example05 项目的 Program 类既无法访问到 Class1 的 strInternal 成员,也无法访问到 strInternalProtected 成员,因为它们既不在同一个程序集里也不存在继承关系