1.缓冲输入文件
-
FileReader
-
BufferedReader
FileReader可以直接对文件进行读操作。但是简化编程,加快读取速度,我们加入了缓冲机制,使用了BufferedReader。BufferedReader内置了一个char[]数组(大小为8192)作为缓冲区,每次调用fill()函数将该缓冲区尽可能填满。而我们自己的程序在调用BufferedReader提供的方法时,实质上是从该缓冲区读取的。
BufferedReader中的fill()方法
1 private void fill() throws IOException { 2 int dst; 3 if (markedChar <= UNMARKED) { 4 /* No mark */ 5 dst = 0; 6 } else { 7 /* Marked */ 8 int delta = nextChar - markedChar; 9 if (delta >= readAheadLimit) { 10 /* Gone past read-ahead limit: Invalidate mark */ 11 markedChar = INVALIDATED; 12 readAheadLimit = 0; 13 dst = 0; 14 } else { 15 if (readAheadLimit <= cb.length) { 16 /* Shuffle in the current buffer */ 17 System.arraycopy(cb, markedChar, cb, 0, delta); 18 markedChar = 0; 19 dst = delta; 20 } else { 21 /* Reallocate buffer to accommodate read-ahead limit */ 22 char ncb[] = new char[readAheadLimit]; 23 System.arraycopy(cb, markedChar, ncb, 0, delta); 24 cb = ncb; 25 markedChar = 0; 26 dst = delta; 27 } 28 nextChar = nChars = delta; 29 } 30 } 31 32 int n; 33 do { 34 n = in.read(cb, dst, cb.length - dst);//该方法调用了read方法 35 } while (n == 0); 36 if (n > 0) { 37 nChars = dst + n; 38 nextChar = dst; 39 } 40 }
BufferedReader中的read()方法
1 public int read() throws IOException { 2 synchronized (lock) { 3 ensureOpen(); 4 for (;;) { 5 if (nextChar >= nChars) { 6 fill(); //调用内置的fill()方法 7 if (nextChar >= nChars) 8 return -1; 9 } 10 if (skipLF) { 11 skipLF = false; 12 if (cb[nextChar] == ' ') { 13 nextChar++; 14 continue; 15 } 16 } 17 return cb[nextChar++]; //返回给用户的是个缓冲区 18 } 19 } 20 }
从上面的代码中可以看出BufferedReader对我们普通的Reader进行了包装,通过缓冲区机制提高了用户读写的速度。
使用方式:
1 package com.dy.xidian; 2 3 import java.io.BufferedReader; 4 import java.io.FileReader; 5 6 public class BufferedInputFile { 7 public static String read(String filename) throws Exception { 8 BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filename)); 9 String s; 10 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); 11 while ((s = in.readLine()) != null) { 12 sb.append(s); 13 } 14 in.close(); 15 return sb.toString(); 16 } 17 18 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 19 if (args.length != 1) { 20 System.out.println("Usage: BufferedInputFile filepath!"); 21 } 22 String s = read(args[0]); 23 System.out.println(s); 24 } 25 }
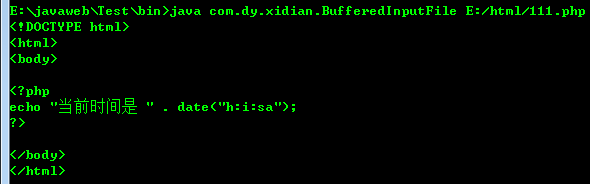
注意readline()的使用:
- 读入的数据要注意有/r或/n或/r/n
- 没有数据时会阻塞,在数据流异常或断开时才会返回null
- 使用socket之类的数据流时,要避免使用readLine(),以免为了等待一个换行/回车符而一直阻塞
2.从内存输入
StringReader的输入是一个String对象,所以StringReader是从内存读取数据的。上一个例子输出的是个String对象,我们恰好可以利用一下。
1 public class MemoryInput { 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 3 String filename = "E:/html/111.php"; 4 StringReader sr = new StringReader(BufferedInputFile.read(filename)); 5 int c; 6 while ((c = sr.read()) != -1) 7 System.out.print((char) c); 8 } 9 }
3.格式化的内存输入
要读取格式化数据,可以使用DataInputStream,它是一个面向字节的I/O类。
package com.dy.xidian; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream; import java.io.DataInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.IOException; class BufferedInputFile { BufferedReader br; public BufferedInputFile(String path) throws FileNotFoundException { br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(path)); } public String read() throws IOException { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); String s; while ((s = br.readLine()) != null) sb.append(s); return sb.toString(); } } public class FormattedMemoryInput { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String path = "E:/html/utf-8.php"; DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream( path.getBytes())); while (in.available() != 0) System.out.print((char) in.readByte()); } }
4.基本的文件输出
FileWriter对象可以向文件中写入数据。首先创建一个与指定文件连接的FileWriter。然后我们对其进行装饰。为了提高写的效率,加入缓冲机制,使用BufferedWriter类对其进行包装。为了能够格式化输出,使用PrintWriter类包装。
package com.dy.xidian; import java.io.BufferedWriter; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PrintWriter; public class BasicFileOutput { static String File = "E:/html/utf-8.php"; public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { PrintWriter os = new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter( new FileWriter(File))); String s1 = "hello world!"; String s2 = "世界 你好"; os.println(s1); os.print(s2); os.close(); } }
更为简单的方式:利用PrintWriter提供的辅助构造器
1 public PrintWriter(String fileName) throws FileNotFoundException { 2 this(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(fileName))), 3 false); 4 } 5 6 /* Private constructor */ 7 private PrintWriter(Charset charset, File file) 8 throws FileNotFoundException 9 { 10 this(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(file), charset)), 11 false); 12 }
package com.dy.xidian; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PrintWriter; public class BasicFileOutput { static String File = "E:/html/utf-8.php"; public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { PrintWriter os = new PrintWriter(File); String s1 = "hello world!"; String s2 = "世界 你好"; os.println(s1); os.print(s2); os.close(); } }
5.储存和恢复数据
DataInputStream和DataOutputStream一般用来对对象的成员属性读取和输出操作。这两个类都是面向字节流的。
package com.dy.xidian; import java.io.BufferedInputStream; import java.io.BufferedOutputStream; import java.io.DataInputStream; import java.io.DataOutputStream; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class StoringAndRecoveringData { public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException { String path = "E:/html/utf-8.php"; FileOutputStream fs = new FileOutputStream(path); DataOutputStream os = new DataOutputStream(new BufferedOutputStream(fs)); os.writeDouble(3141.5); os.writeUTF("这是Pi1"); //使用UTF-8编码 os.close(); DataInputStream is = new DataInputStream(new BufferedInputStream( new FileInputStream(path))); System.out.println(is.readDouble()); //先读double System.out.println(is.readUTF()); //在读字符串 is.close(); } }
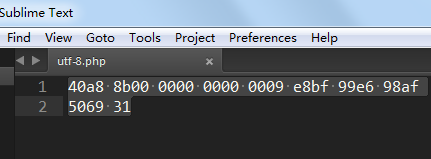
从输出文件的内容我们可以发现是DataOutputStream输出的是一大堆编码,这些编码只适合DataInputStream来读取。这种方式可以用来进行对象的序列化存储。并且读取的顺序要与存储的顺序保持一致。
6.随机访问文件
RandomAccessFile提供了随机访问的文件的方法,它可以看成是DataInputStream和DataOutputStream的组合。RandomAccessFile也是面向字节流的,所以我们想修改文件某处的值时,需要计算出该值的偏移量(单位为字节),通过seek方法,将文件指针指向该处,才可以修改成功。
package com.dy.xidian; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.RandomAccessFile; public class UsingRandomAccessFile { static String file = "E:/html/utf-8.php"; static void display() throws IOException { RandomAccessFile rf = new RandomAccessFile(file, "r"); for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) System.out.println("Value " + i + ": " + rf.readDouble()); System.out.println(rf.readUTF()); rf.close(); } public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { RandomAccessFile rf = new RandomAccessFile(file, "rw"); for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) rf.writeDouble(i * 1.414); rf.writeUTF("文件末尾"); rf.close(); display(); rf = new RandomAccessFile(file, "rw"); rf.seek(5 * 8); rf.writeDouble(47.0001); rf.close(); display(); } }
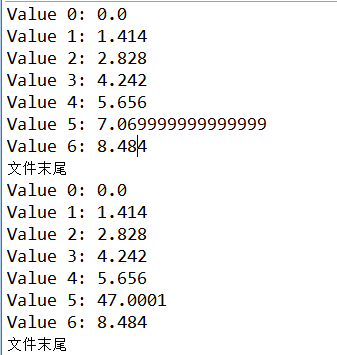
我们想修改第六个Double值。首先算出偏移量,每个double类型8个字节,所以第六个double起始位置的偏移量为40=5*8,所以应该调用seek(5*8)将文件指针指向该处,在调用write方法来修改该值。
7.读写文件工具类

1 package com.dy.xidian; 2 3 import java.io.BufferedReader; 4 import java.io.File; 5 import java.io.FileInputStream; 6 import java.io.IOException; 7 import java.io.InputStreamReader; 8 import java.io.PrintWriter; 9 import java.util.ArrayList; 10 import java.util.Arrays; 11 import java.util.TreeSet; 12 13 public class TextFile extends ArrayList<String> { 14 15 /** 16 * 17 */ 18 private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; 19 20 /** 21 * 22 * @param 文件名 23 * @param 字符集编码 24 * @return 文件内容 25 */ 26 public static String read(String fileName, String Charset) { 27 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); 28 try { 29 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader( 30 new FileInputStream(fileName), Charset)); 31 try { 32 String s; 33 while ((s = br.readLine()) != null) { 34 sb.append(s); 35 sb.append(" "); 36 } 37 } finally { 38 br.close(); 39 } 40 } catch (IOException e) { 41 throw new RuntimeException(e); 42 } 43 return sb.toString(); 44 } 45 46 /** 47 * 48 * @param 文件名 49 * @param 文本内容 50 */ 51 public static void write(String fileName, String text) { 52 try { 53 PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter( 54 new File(fileName).getAbsoluteFile()); 55 try { 56 out.print(text); 57 } finally { 58 out.close(); 59 } 60 } catch (IOException e) { 61 throw new RuntimeException(); 62 } 63 } 64 65 public TextFile(String fileName, String splitter) { 66 super(Arrays.asList(read(fileName, "utf-8").split(splitter))); 67 // split()会留一个空字符串在开始的位置 68 if (get(0).equals("")) 69 remove(0); 70 } 71 72 public TextFile(String fileName) { 73 this(fileName, " "); 74 } 75 76 public void write(String fileName) { 77 try { 78 PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter( 79 new File(fileName).getAbsoluteFile()); 80 try { 81 for (String item : this) { 82 out.print(item); 83 } 84 } finally { 85 out.close(); 86 } 87 } catch (IOException e) { 88 throw new RuntimeException(); 89 } 90 } 91 92 public static void main(String[] args) { 93 String file = TextFile.read("com/dy/xidian/TextFile.java", "utf-8"); 94 TextFile.write("test.txt", file); 95 TextFile text = new TextFile("test.txt"); 96 text.write("test2.txt"); 97 TreeSet<String> words = new TreeSet<String>(new TextFile( 98 "com/dy/xidian/TextFile.java", "\W+")); 99 for (String string : words) { 100 System.out.println(string); 101 } 102 System.out.println(words.headSet("a")); 103 } 104 }

