MySort
要求:
- 模拟实现Linux下
Sort -t : -k 2的功能。 - 要有伪代码,产品代码,测试代码(注意测试用例的设计)
1 import java.util.*;
2
3 public class MySort1 {
4 public static void main(String [] args) {
5 String [] toSort = {"aaa:10:1:1",
6 "ccc:30:3:4",
7 "bbb:50:4:5",
8 "ddd:20:5:3",
9 "eee:40:2:20"};
10
11 System.out.println("Before sort:");
12 for (String str: toSort)
13 System.out.println(str);
14
15 Arrays.sort(toSort);
16
17 System.out.println("After sort:");
18 for( String str : toSort)
19 System.out.println(str);
20 }
21 }
原理:
sort方法:

Sort -t : -k 2的功能:
-t -k n表示输出按第n列的数值进行排序后的字符串
因此sort -t : -k 2表示用:分隔的第二列字符串按照从小到大的顺序重新排列
split方法:

代码:
伪代码:
1、调用`split`方法,将`tosort`数组以`:`为分隔符存入数组`tmp`
2、新建数组`a`,将`tmp`数组的第二列数值给数组`a`
3、调用`sort`方法对数组`a`进行升序排序
4、输出排序后的结果
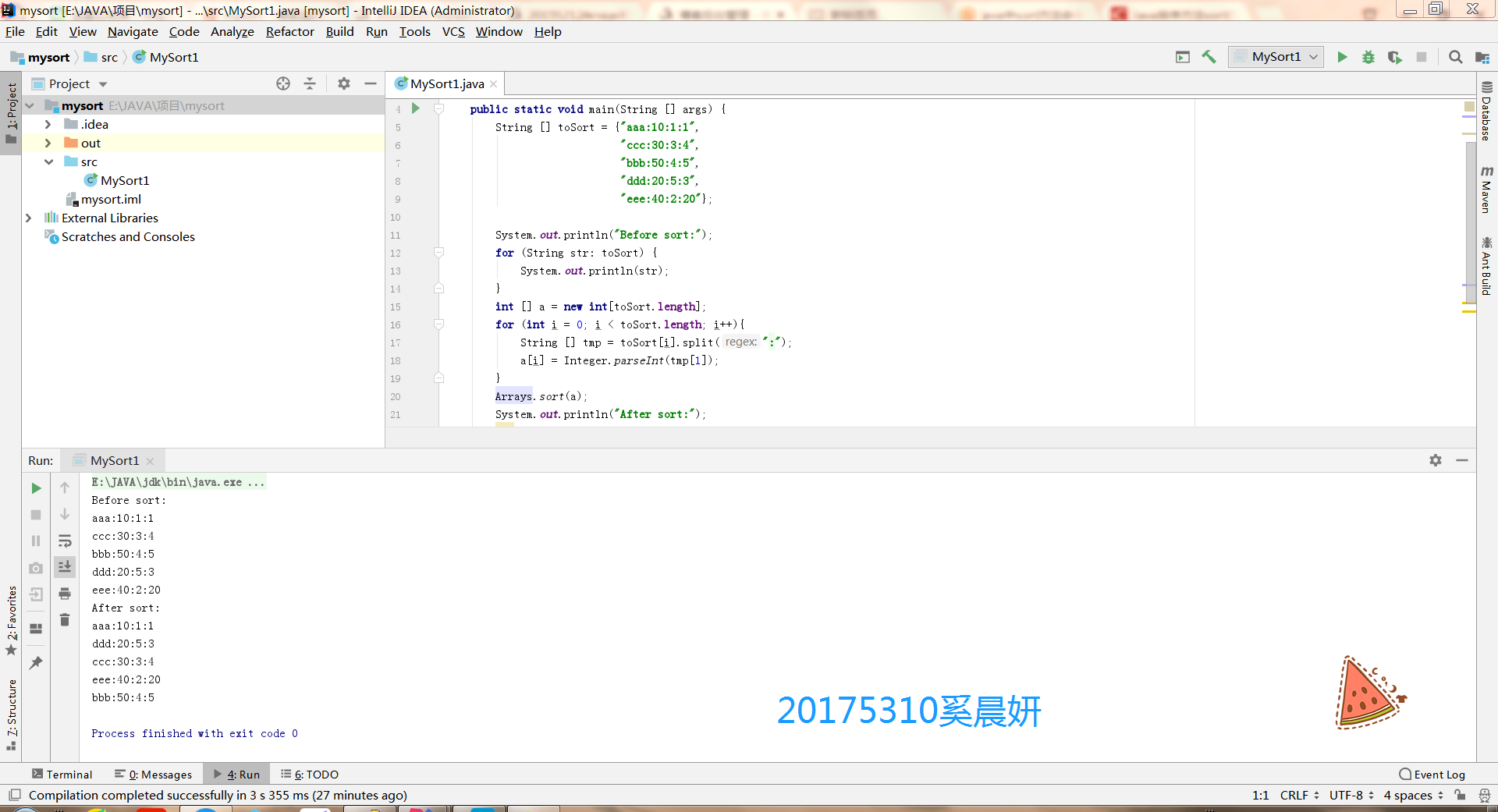
产品代码:
import java.util.*;
public class MySort1 {
public static void main(String [] args) {
String [] toSort = {"aaa:10:1:1",
"ccc:30:3:4",
"bbb:50:4:5",
"ddd:20:5:3",
"eee:40:2:20"};
System.out.println("Before sort:");
for (String str: toSort) {
System.out.println(str);
}
int [] a = new int[toSort.length];
for (int i = 0; i < toSort.length; i++){
String [] tmp = toSort[i].split(":");
a[i] = Integer.parseInt(tmp[1]);
}
Arrays.sort(a);
System.out.println("After sort:");
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < toSort.length; j++) {
if (a[i] == Integer.parseInt((toSort[j].split(":"))[1])) {
System.out.println(toSort[j]);
}
}
}
}
}
运行结果: