摘自:https://www.cnblogs.com/javaadu/p/11748415.html
Spring Boot项目中使用Mockito
本文首发于个人网站:Spring Boot项目中使用Mockito
Spring Boot可以和大部分流行的测试框架协同工作:通过Spring JUnit创建单元测试;生成测试数据初始化数据库用于测试;Spring Boot可以跟BDD(Behavier Driven Development)工具、Cucumber和Spock协同工作,对应用程序进行测试。
进行软件开发的时候,我们会写很多代码,不过,再过六个月(甚至一年以上)你知道自己的代码怎么运作么?通过测试(单元测试、集成测试、接口测试)可以保证系统的可维护性,当我们修改了某些代码时,通过回归测试可以检查是否引入了新的bug。总得来说,测试让系统不再是一个黑盒子,让开发人员确认系统可用。
在web应用程序中,对Controller层的测试一般有两种方法:(1)发送http请求;(2)模拟http请求对象。第一种方法需要配置回归环境,通过修改代码统计的策略来计算覆盖率;第二种方法是比较正规的思路,但是在我目前经历过的项目中用得不多,今天总结下如何用Mock对象测试Controller层的代码。
在之前的几篇文章中,我们都使用bookpub这个应用程序作为例子,今天也不例外,准备测试它提供的RESTful接口是否能返回正确的响应数据。这种测试不同于单元测试,需要为之初始化完整的应用程序上下文、所有的spring bean都织入以及数据库中需要有测试数据,一般来说这种测试称之为集成测试或者接口测试。
实战
通过spirng.io新建的Spring Boot项目提供了一个空的测试文件——BookPubApplicationTest.java,内容是:
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@SpringApplicationConfiguration(classes = BookPubApplication.class)
public class BookPubApplicationTests {
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
}
}- 在pom文件中增加spring-boot-starter-test依赖,添加jsonPath依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.jayway.jsonpath</groupId>
<artifactId>json-path</artifactId>
</dependency>- 在BookPubApplicationTest中添加测试用例
package com.test.bookpub;
import com.test.bookpub.domain.Book;
import com.test.bookpub.repository.BookRepository;
import org.junit.Before;import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.test.SpringApplicationConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.test.TestRestTemplate;
import org.springframework.boot.test.WebIntegrationTest;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.setup.MockMvcBuilders;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertNotNull;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.containsString;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.get;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.content;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.status;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@SpringApplicationConfiguration(classes = BookPubApplication.class)
@WebIntegrationTest("server.port:0")
public class BookPubApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private WebApplicationContext context;
@Autowired
private BookRepository bookRepository;
@Value("${local.server.port}")
private int port;
private MockMvc mockMvc;
private RestTemplate restTemplate = new TestRestTemplate();
@Before
public void setupMockMvc() {
mockMvc = MockMvcBuilders.webAppContextSetup(context).build();
}
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
assertEquals(1, bookRepository.count());
}
@Test
public void webappBookIsbnApi() {
Book book = restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:" + port +"/books/9876-5432-1111", Book.class);
assertNotNull(book);
assertEquals("中文测试", book.getPublisher().getName());
}
@Test
public void webappPublisherApi() throws Exception {
//MockHttpServletRequestBuilder.accept方法是设置客户端可识别的内容类型
//MockHttpServletRequestBuilder.contentType,设置请求头中的Content-Type字段,表示请求体的内容类型
mockMvc.perform(get("/publishers/1")
.accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().string(containsString("中文测试")))
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.name").value("中文测试"));
}
}- spring boot项目的代码覆盖率
使用cobertura,参考项目的github地址:spring boot template
# To create test coverage reports (in target/site/cobertura)
mvn clean cobertura:cobertura test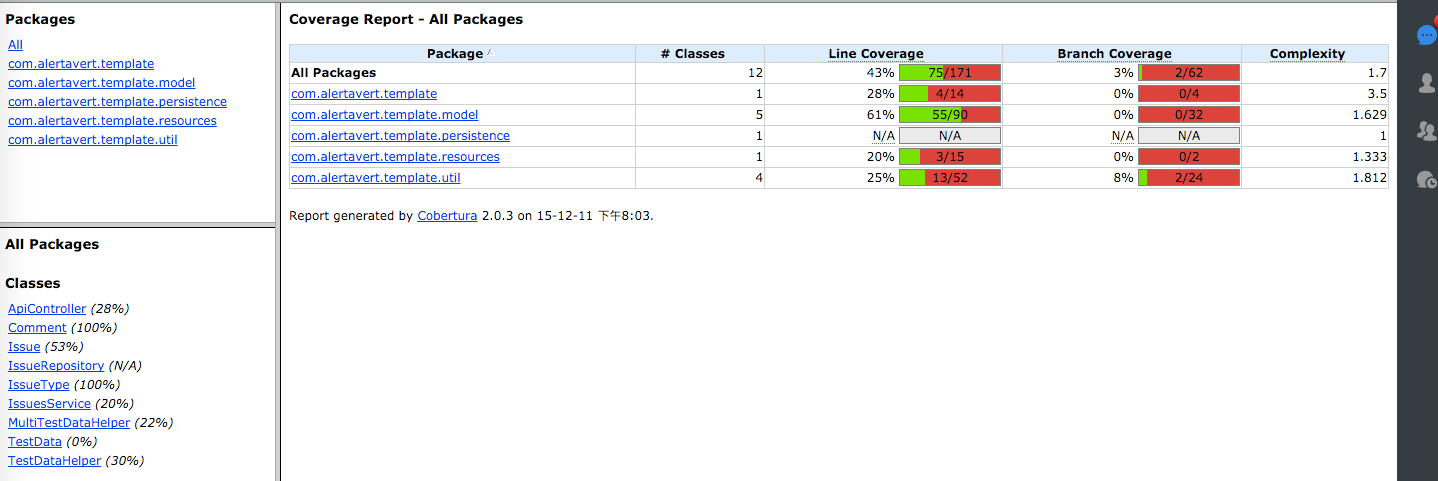
分析
首先分析在BookPubApplicationTests类中用到的注解:
- @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class),这是JUnit的注解,通过这个注解让SpringJUnit4ClassRunner这个类提供Spring测试上下文。
- @SpringApplicationConfiguration(classes = BookPubApplication.class),这是Spring Boot注解,为了进行集成测试,需要通过这个注解加载和配置Spring应用上下文。这是一个元注解(meta-annoation),它包含了@ContextConfiguration( loader = SpringApplicationContextLoader.class)这个注解,测试框架通过这个注解使用Spring Boot框架的SpringApplicationContextLoader加载器创建应用上下文。
- @WebIntegrationTest("server.port:0"),这个注解表示当前的测试是集成测试(integration test),因此需要初始化完整的上下文并启动应用程序。这个注解一般和@SpringApplicationConfiguration一起出现。server.port:0指的是让Spring Boot在随机端口上启动Tomcat服务,随后在测试中程序通过@Value("${local.server.port}")获得这个端口号,并赋值给port变量。当在Jenkins或其他持续集成服务器上运行测试程序时,这种随机获取端口的能力可以提供测试程序的并行性。
了解完测试类的注解,再看看测试类的内部。由于这是Spring Boot的测试,因此我们可通过@Autowired注解织入任何由Spring管理的对象,或者是通过@Value设置指定的环境变量的值。在现在这个测试类中,我们定义了WebApplicationContext和BookRepository对象。
每个测试用例用@Test注解修饰。在第一个测试用例——contextLoads()方法中,我仅仅需要确认BookRepository连接已经建立,并且数据库中已经包含了对应的测试数据。
第二个测试用例用来测试我们提供的RESTful URL——通过ISBN查询一本书,即“/books/{isbn}”。在这个测试用例中我们使用TestRestTemplate对象发起RESTful请求。
第三个测试用例中展示了如何通过MockMvc对象实现跟第二个测试类似的功能。Spring测试框架提供MockMvc对象,可以在不需要客户端-服务端请求的情况下进行MVC测试,完全在服务端这边就可以执行Controller的请求,跟启动了测试服务器一样。
测试开始之前需要建立测试环境,setup方法被@Before修饰。通过MockMvcBuilders工具,使用WebApplicationContext对象作为参数,创建一个MockMvc对象。
MockMvc对象提供一组工具函数用来执行assert判断,都是针对web请求的判断。这组工具的使用方式是函数的链式调用,允许程序员将多个测试用例链接在一起,并进行多个判断。在这个例子中我们用到下面的一些工具函数:
- perform(get(...))建立web请求。在我们的第三个用例中,通过MockMvcRequestBuilder执行GET请求。
- andExpect(...)可以在perform(...)函数调用后多次调用,表示对多个条件的判断,这个函数的参数类型是ResultMatcher接口,在MockMvcResultMatchers这这个类中提供了很多返回ResultMatcher接口的工具函数。这个函数使得可以检测同一个web请求的多个方面,包括HTTP响应状态码(response status),响应的内容类型(content type),会话中存放的值,检验重定向、model或者header的内容等等。这里需要通过第三方库json-path检测JSON格式的响应数据:检查json数据包含正确的元素类型和对应的值,例如jsonPath("$.name").value("中文测试")用于检查在根目录下有一个名为name的节点,并且该节点对应的值是“中文测试”。
一个字符乱码问题
-
问题描述:通过spring-boot-starter-data-rest建立的repository,取出的汉字是乱码。
-
分析:使用postman和httpie验证都没问题,说明是Mockmvc的测试用例写得不对,应该主动设置客户端如何解析HTTP响应,用get.accept方法设置客户端可识别的内容类型,修改后的测试用例如下:
@Test
public void webappPublisherApi() throws Exception {
//MockHttpServletRequestBuilder.accept方法是设置客户端可识别的内容类型
//MockHttpServletRequestBuilder.contentType,设置请求头中的Content-Type字段,表示请求体的内容类型
mockMvc.perform(get("/publishers/1")
.accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().string(containsString("中文测试")))
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.name").value("中文测试"));
}参考资料
- 基于Spring-WS的Restful API的集成测试
- J2EE要懂的小事—图解HTTP协议
- Integration Testing a Spring Boot Application
- spring boot project template
Spring Boot 1.x系列
- Spring Boot的自动配置、Command-line-Runner
- 了解Spring Boot的自动配置
- Spring Boot的@PropertySource注解在整合Redis中的使用
- Spring Boot项目中如何定制HTTP消息转换器
- Spring Boot整合Mongodb提供Restful接口
- Spring中bean的scope
- Spring Boot项目中使用事件派发器模式
- Spring Boot提供RESTful接口时的错误处理实践
- Spring Boot实战之定制自己的starter
- Spring Boot项目如何同时支持HTTP和HTTPS协议
- 自定义的Spring Boot starter如何设置自动配置注解
本号专注于后端技术、JVM问题排查和优化、Java面试题、个人成长和自我管理等主题,为读者提供一线开发者的工作和成长经验,期待你能在这里有所收获。