InitializingBean
记住一点:InitializingBean接口为bean提供了初始化方法的方式,它只包括afterPropertiesSet方法,凡是继承该接口的子类,在初始化bean的时候会执行该方法。
下面看下简单的例子:(环境是用Spring Boot搭建,直接用SpringtestApplication启动即可)
<bean id="myInitializingBean" class="com.paic.phssp.springtest.init.MyInitializingBean" init-method="testInit"></bean>
package com.paic.phssp.springtest.init; import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import javax.annotation.PostConstruct; /** * 继承InitializingBean接口的类,在初始化bean的时候会执行该方法 */ //@Component public class MyInitializingBean implements InitializingBean { public MyInitializingBean() { System.out.println("MyInitializingBean...."); } @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { System.out.println("ceshi MyInitializingBean>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"); } @PostConstruct //功能上近似init-method,但加载时机不同 public void test(){ System.out.println("PostConstruct >>>>>>>>>>>>"); } public void testInit(){ System.out.println("ceshi init-method"); } }
结果:
MyInitializingBean....
PostConstruct >>>>>>>>>>>>
ceshi MyInitializingBean>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
ceshi init-method
说明:
通过上述输出结果,三者的先后顺序也就一目了然了:
Constructor > @PostConstruct > InitializingBean > init-method
(1)通过查看spring的加载bean的源码类(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory)可看出其中奥妙:
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.invokeInitMethods
protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) throws Throwable { boolean isInitializingBean = bean instanceof InitializingBean; if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) { if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) { this.logger.trace("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'"); } if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { try { AccessController.doPrivileged(() -> { ((InitializingBean)bean).afterPropertiesSet(); return null; }, this.getAccessControlContext()); } catch (PrivilegedActionException var6) { throw var6.getException(); } } else { ((InitializingBean)bean).afterPropertiesSet(); } } if (mbd != null && bean.getClass() != NullBean.class) { String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName(); if (StringUtils.hasLength(initMethodName) && (!isInitializingBean || !"afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) && !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) { this.invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd); } } }
说明:
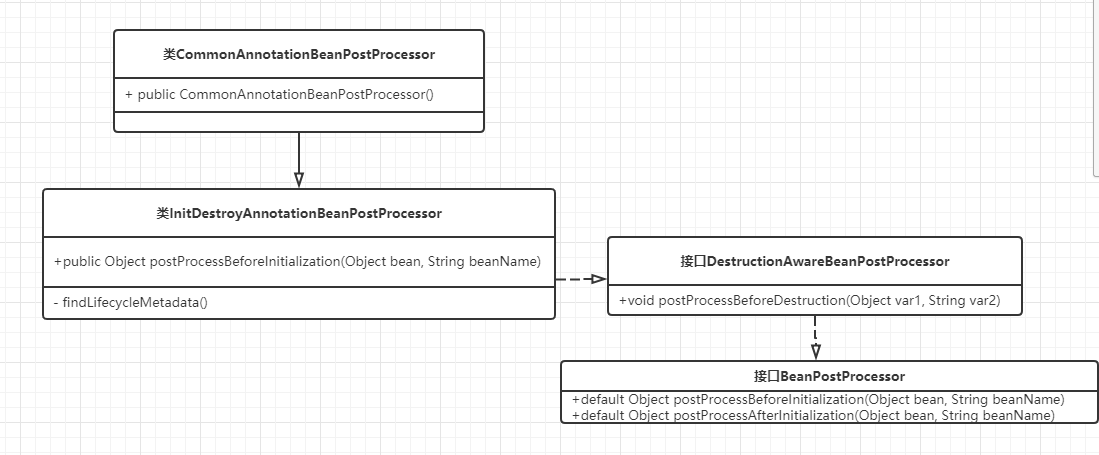
看下源码:InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.LifecycleMetadata metadata = this.findLifecycleMetadata(bean.getClass()); try {
//利用反射,执行注解方法 metadata.invokeInitMethods(bean, beanName); return bean; } catch (InvocationTargetException var5) { throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", var5.getTargetException()); } catch (Throwable var6) { throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Failed to invoke init method", var6); } } private InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.LifecycleMetadata findLifecycleMetadata(Class<?> clazz) { if (this.lifecycleMetadataCache == null) { return this.buildLifecycleMetadata(clazz); } else { InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.LifecycleMetadata metadata = (InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.LifecycleMetadata)this.lifecycleMetadataCache.get(clazz); if (metadata == null) { Map var3 = this.lifecycleMetadataCache; synchronized(this.lifecycleMetadataCache) { metadata = (InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.LifecycleMetadata)this.lifecycleMetadataCache.get(clazz); if (metadata == null) { metadata = this.buildLifecycleMetadata(clazz); this.lifecycleMetadataCache.put(clazz, metadata); } return metadata; } } else { return metadata; } } } private InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.LifecycleMetadata buildLifecycleMetadata(Class<?> clazz) { List<InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.LifecycleElement> initMethods = new ArrayList(); List<InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.LifecycleElement> destroyMethods = new ArrayList(); Class targetClass = clazz; do { List<InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.LifecycleElement> currInitMethods = new ArrayList(); List<InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.LifecycleElement> currDestroyMethods = new ArrayList(); ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, (method) -> {
//判断是否是指定的注解类型 if (this.initAnnotationType != null && method.isAnnotationPresent(this.initAnnotationType)) { InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.LifecycleElement element = new InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.LifecycleElement(method); currInitMethods.add(element); if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) { this.logger.trace("Found init method on class [" + clazz.getName() + "]: " + method); } } if (this.destroyAnnotationType != null && method.isAnnotationPresent(this.destroyAnnotationType)) { currDestroyMethods.add(new InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.LifecycleElement(method)); if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) { this.logger.trace("Found destroy method on class [" + clazz.getName() + "]: " + method); } } }); initMethods.addAll(0, currInitMethods); destroyMethods.addAll(currDestroyMethods); targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass(); } while(targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class); return new InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.LifecycleMetadata(clazz, initMethods, destroyMethods); }
方法:buildLifecycleMetadata(),判断是否是指定的注解类型,而这个属性,在CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class构造方法中被初始化为PostConstruct。
public CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor() { this.setOrder(2147483644); this.setInitAnnotationType(PostConstruct.class); this.setDestroyAnnotationType(PreDestroy.class); this.ignoreResourceType("javax.xml.ws.WebServiceContext"); }
那么问题来了,以上只能说明实现了BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization()方法,不足说明@PostConstruct 先InitializingBean 。
再看AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.class 的initializeBean()方法。
protected Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) { if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { AccessController.doPrivileged(() -> { this.invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); return null; }, this.getAccessControlContext()); } else { this.invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); } Object wrappedBean = bean; if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { wrappedBean = this.applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(bean, beanName); } try { this.invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd); } catch (Throwable var6) { throw new BeanCreationException(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null, beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", var6); } if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { wrappedBean = this.applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); } return wrappedBean; }
这下明显了,下面小结下:
--> 调用BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法 (@PostConstruct在此)
--> 调用bean实例的初始化方法(invokeInitMethods-> InitializingBean->init-method)
--> 调用BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization方法
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/zl834205311/article/details/78802584
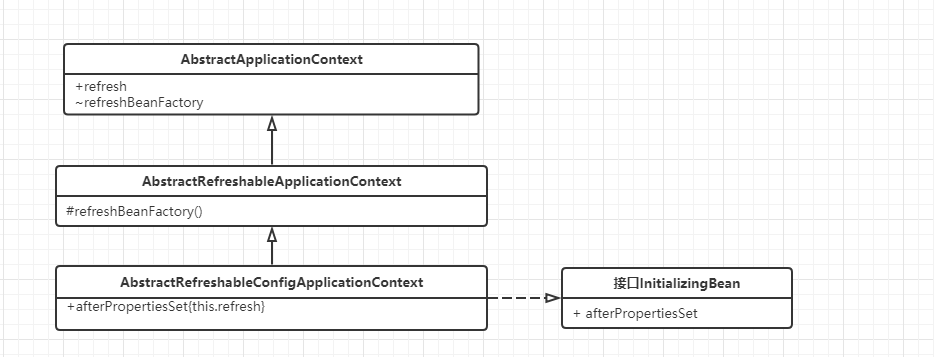
其中AbstractApplicationContext.refresh()
@Override public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. // 为刷新工作做一些当前上下文 context 上的准备工作 prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. // ApplicationContext 实现了 BeanFactory 接口,但是并非直接作为 Bean 容器。 // ApplicationContext 中真正直接作为 Bean 容器的是一个内部Bean工厂 BeanFactory, // 通过其方法 getBeanFactory() 得到,此方法在 AbstractApplicationContext 中 // 被声明为 abstract, 其实现要求由实现子类提供。下面的语句 obtainFreshBeanFactory() // 内部就是通过调用 getBeanFactory() 获得这个内部 Bean 工厂的。 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. // 准备当前上下文使用的Bean容器 BeanFactory,设置其标准上下文特征,比如类加载器等 // 1. BeanFactory 的类加载器设置为当前上下文的类加载器 // 2. BeanFactory 的Bean表达式解析器设置为 new StandardBeanExpressionResolver() // 3. BeanFactory 增加 BeanPostProcessror new ApplicationListenerDetector(this) // 4.三个单例Bean被注册 : environment,systemProperties,systemEnvironment prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. // 在当前上下文使用的Bean容器BeanFactory的标准初始化完成后对其做一些修改。此时 // 所有的Bean definition都已经加载但是还没有 Bean 被创建。 // 当前上下文使用的Bean容器 BeanFactory 的 post process // 1.当前上下文是 EmbeddedWebApplicationContext 时, // 这个步骤中会对 beanFactory 注册一个 BeanPostProcessor : // WebApplicationContextServletContextAwareProcessor // 2.当前上下文是 AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext 时, // 如果设置了 basePackages, // 这里会使用 AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader扫描basePackages; // 如果设置了 annotatedClasses, // 这里会使用 ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner登记annotatedClasses; postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. // 在 beanFactory 上调用 BeanFactoryPostProcessors, // 当前上下文可能会有多个 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 需要应用在 beanFactory 上 // **************************************************************** // 这里需要尤其注意区别 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 和 BeanPostProcessor // BeanFactoryPostProcessor : 作用在 Bean定义 上,用来定制修改 Bean定义 // BeanPostProcessor :作用在 Bean实例 上,用来修改或者包装 Bean实例 // **************************************************************** // 该方法实际上将实现委托出去 : // PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors() invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. // 注册 BeanPostProcessor // 该步骤实际工作委托给工具类 PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate 的静态方法 // void registerBeanPostProcessors( // ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, // AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context. initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context. // 初始化当前上下文ApplicationContext要使用的 事件多播器 // ApplicationEventMulticaster applicationEventMulticaster。 // // 如果容器中已经注册类型为ApplicationEventMulticaster并且名称为 // applicationEventMulticaster 的Bean,则直接使用;否则, // 新建一个SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster实例并注册到 // Bean容器,Bean名称使用 applicationEventMulticaster。 initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. // AbstractApplicationContext 中 onRefresh() 方法实现为空,其目的就是 // 留给实现子类一个机会做一些上下文相关的刷新工作。在一些特殊Bean初始化时,单 // 例 singleton Bean 初始化之前该方法被调用。 // 1. 当前上下文是 EmbeddedWebApplicationContext 时,该步骤会创建一个 // 内置的 Servlet 容器, 具体参考 EmbeddedWebApplicationContext 的 // 方法 void createEmbeddedServletContainer() onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them. // 1. 将外部指定到当前上下文的 ApplicationListener 实例关联到上下文多播器 // Q : 什么时候外部给当前上下文指定 ApplicationListener ? // A : 举例说明,Springboot 应用 SpringApplication 的情况下,是在 // prepareContext()结尾时SpringApplicationRunListeners的 // contextLoaded() 调用中发生的,此时正在广播事件 // ApplicationPreparedEvent // 2. 将实现了 ApplicationListener 接口的所有 Bean 关联到上下文多播器 // 3. 如果上下文属性earlyApplicationEvents中有要通知的事件,广播出去 registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. // 完成 BeanFactory 的初始化工作 // 1.BeanFactory冻结所有的Bean定义:不再可以修改或者做post process操作 // 2.确保所有的non-lazy-init单例Bean被初始化,也包括FactoryBean // 3.如果所初始化的单例Bean实现了接口SmartInitializingSingleton,调用 // 其方法 afterSingletonsInstantiated() finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event. // 1. 初始化生命周期处理器 LifecycleProcessor, 使用已经存在的Bean或者 // 一个新的DefaultLifecycleProcessor实例; // 2. 生命周期处理器 LifecycleProcessor 上传播 refresh 事件 // 3. 发布事件 ContextRefreshedEvent // 4. 如果存在 LiveBeansView MBean 的话,关联到当前上下文 // 当前上下文是EmbeddedWebApplicationContext的情况下,还会: // 5. 启动EmbeddedServletContainer,比如启动内置 tomcat容器 // 6. 发布事件 EmbeddedServletContainerInitializedEvent finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); } // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag. cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller. throw ex; } finally { // Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... resetCommonCaches(); } } }
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#refresh的这一行代码
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() { refreshBeanFactory(); ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory); } return beanFactory; }
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext#refreshBeanFactory
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException { if (this.hasBeanFactory()) { this.destroyBeans(); this.closeBeanFactory(); } try { DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.createBeanFactory(); beanFactory.setSerializationId(this.getId()); this.customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory); this.loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory); Object var2 = this.beanFactoryMonitor; synchronized(this.beanFactoryMonitor) { this.beanFactory = beanFactory; } } catch (IOException var5) { throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + this.getDisplayName(), var5); } }
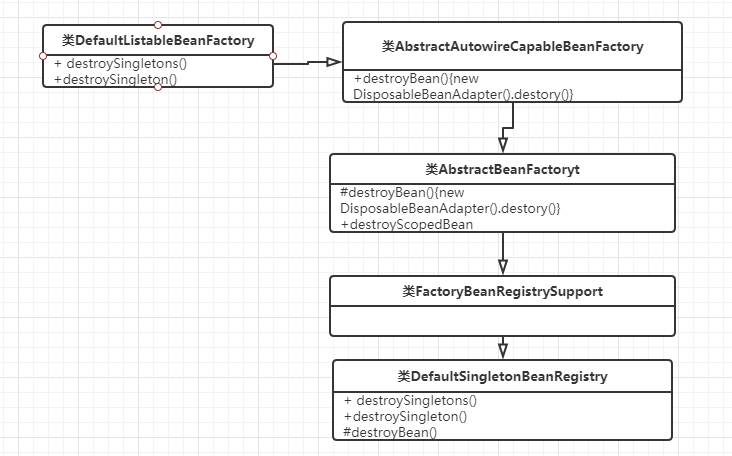
进入到这个方法org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#destroyBeans
protected void destroyBeans() { this.getBeanFactory().destroySingletons(); }
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory#destroySingletons
@Override public void destroySingletons() { super.destroySingletons(); // 清除记录的单例beanName的缓存 this.manualSingletonNames.clear(); clearByTypeCache(); }
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry#destroySingletons

@Override public void destroySingletons() { super.destroySingletons(); // 清空beanFactory缓存 this.factoryBeanObjectCache.clear(); } public void destroySingletons() { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Destroying singletons in " + this); } // 这里使用ConcurrentHashMap本地缓存单例的bean实例,访问次数比较多,提搞并发量 synchronized (this.singletonObjects) { this.singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction = true; } String[] disposableBeanNames; // 这里是用LinkedHashMap本地缓存销毁的bean实例 synchronized (this.disposableBeans) { disposableBeanNames = StringUtils.toStringArray(this.disposableBeans.keySet()); } for (int i = disposableBeanNames.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { // 销毁单例的bean destroySingleton(disposableBeanNames[i]); } this.containedBeanMap.clear(); this.dependentBeanMap.clear(); this.dependenciesForBeanMap.clear(); // 同步清空缓存 synchronized (this.singletonObjects) { this.singletonObjects.clear(); this.singletonFactories.clear(); this.earlySingletonObjects.clear(); this.registeredSingletons.clear(); this.singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction = false; } } public void destroySingleton(String beanName) { // Remove a registered singleton of the given name, if any.删除单例的bean,从本地缓存中删除 removeSingleton(beanName); // Destroy the corresponding DisposableBean instance. DisposableBean disposableBean; synchronized (this.disposableBeans) { // 从本地缓存中删除 disposableBean = (DisposableBean) this.disposableBeans.remove(beanName); } // bean销毁的逻辑 destroyBean(beanName, disposableBean); } protected void destroyBean(String beanName, @Nullable DisposableBean bean) { // Trigger destruction of dependent beans first... 先触发依赖的bean销毁,从本地缓存中删除 Set<String> dependencies = this.dependentBeanMap.remove(beanName); if (dependencies != null) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Retrieved dependent beans for bean '" + beanName + "': " + dependencies); } for (String dependentBeanName : dependencies) { // 这里用了一个递归删除单例bean,当这个bean没有依赖的bean要删除的时候,递归结束 destroySingleton(dependentBeanName); } } // Actually destroy the bean now... 这里开始删除单例bean if (bean != null) { try { // bean可以实现DisposableBean这个接口,重写父类的bean destory的方法 bean.destroy(); } catch (Throwable ex) { logger.error("Destroy method on bean with name '" + beanName + "' threw an exception", ex); } } // Trigger destruction of contained beans...从本地缓存中销毁内部bean Set<String> containedBeans = this.containedBeanMap.remove(beanName); if (containedBeans != null) { for (String containedBeanName : containedBeans) { // 这个地方还是递归调用,删除单例bean,当这个bean没有内部bean时递归结束 destroySingleton(containedBeanName); } } // Remove destroyed bean from other beans' dependencies. 从其他bean依赖中删除销毁的bean synchronized (this.dependentBeanMap) { for (Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Set<String>>> it = this.dependentBeanMap.entrySet().iterator(); it.hasNext();) { Map.Entry<String, Set<String>> entry = it.next(); Set<String> dependenciesToClean = entry.getValue(); dependenciesToClean.remove(beanName); if (dependenciesToClean.isEmpty()) { it.remove(); } } } // Remove destroyed bean's prepared dependency information.删除销毁的bean准备的依赖信息 this.dependenciesForBeanMap.remove(beanName); }
bean可以实现DisposableBean这个接口,重写父类的bean destory的方法

@Override public void destroy() { // 执行beanPostProcessors,beanPostProcessors用对对bean的过程进行处理的抽象 if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.beanPostProcessors)) { for (DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor processor : this.beanPostProcessors) { // 在bean销毁之前进行一些处理 processor.postProcessBeforeDestruction(this.bean, this.beanName); } } if (this.invokeDisposableBean) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Invoking destroy() on bean with name '" + this.beanName + "'"); } try { if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>) () -> { ((DisposableBean) bean).destroy(); return null; }, acc); } else { // bean实现DisposableBean接口的方式,注解调用子类destroy方法 ((DisposableBean) bean).destroy(); } } catch (Throwable ex) { String msg = "Invocation of destroy method failed on bean with name '" + this.beanName + "'"; if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.warn(msg, ex); } else { logger.warn(msg + ": " + ex); } } } if (this.destroyMethod != null) { // 执行bean定义中指定的bean销毁方法 invokeCustomDestroyMethod(this.destroyMethod); } else if (this.destroyMethodName != null) { Method methodToCall = determineDestroyMethod(this.destroyMethodName); if (methodToCall != null) { invokeCustomDestroyMethod(methodToCall); } } }
具体结构如下: