一、JSR107
JSR107核心接口
Java Caching(JSR-107)定义了5个核心接口,分别是CachingProvider, CacheManager, Cache, Entry和 Expiry。
- CachingProvider:创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个CacheManager。
- CacheManager:创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个唯一命名的Cache,Cache存在于CacheManager的上下文中。一个CacheManager仅对应一个CachingProvider。
- Cache:是由CacheManager管理的,CacheManager管理Cache的生命周期,Cache存在于CacheManager的上下文中,是一个类似map的数据结构,并临时存储以key为索引的值。一个Cache仅被一个CacheManager所拥有。
- Entry:是一个存储在Cache中的key-value对。
- Expiry:每一个存储在Cache中的条目都有一个定义的有效期。一旦超过这个时间,条目就自动过期,过期后,条目将不可以访问、更新和删除操作。缓存有效期可以通过ExpiryPolicy设置。
JSR107图示

二、Spring的缓存抽象
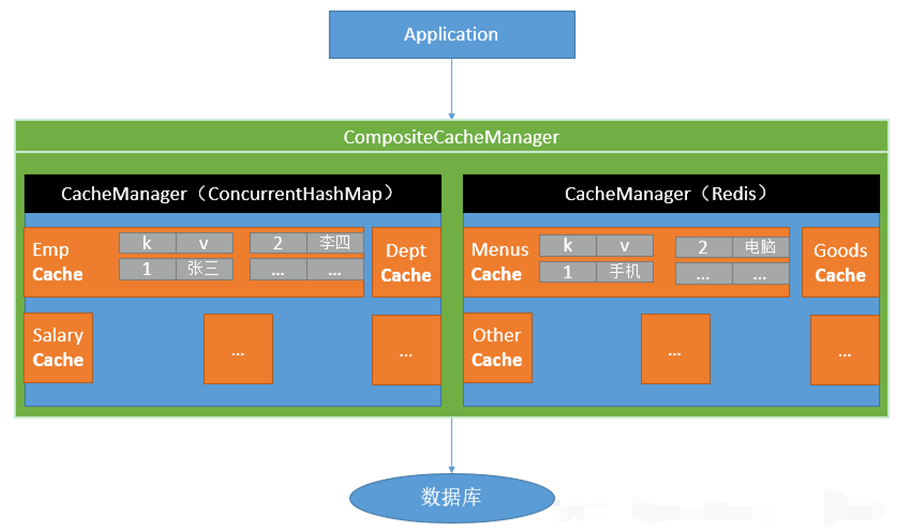
Spring从3.1开始定义了org.springframework.cache.Cache和org.springframework.cache.CacheManager接口来统一不同的缓存技术,并支持使用JCache(JSR-107)注解简化开发。
- Cache接口为缓存的组件规范定义,包含缓存的各种操作集合;
- Cache接口下Spring提供了各种xxxCache的实现,如
RedisCache,EhCacheCache,ConcurrentMapCache等,每次调用需要缓存功能的方法时,Spring会检查检查指定参数的指定的目标方法是否已经被调用过,如果有就直接从缓存中获取方法调用后的结果,如果没有就调用方法并缓存结果返回给用户,下次直接从缓存中获取。
使用Spring缓存抽象时我们需要关注以下两点:
- 确定方法需要被缓存以及他们的缓存策略;
- 从缓存中读取之前缓存存储的数据,如下图所示:
在本文中我们主要讲述Redis缓存的内容。说到缓存,先普及命中、失效、更新等几个内容:
- 命中:指的是应用程序从Cache中获取数据,取到后返回;
- 失效: 缓存是有时间限制的,时间到了,就失效了;
- 更新:应用程序把数据存到数据库中,再放回缓存当中去。
三、Spring中缓存注解的使用


重要注解简介
- @Cacheable:针对方法配置,能够根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存
- @CacheEvict:清空缓存
- @CachePut:既调用方法,又更新缓存数据
- @EnableCaching:开启基于注解的缓存
- @Caching:定义复杂的缓存规则
环境准备
本博客以尚硅谷视频例子进行改写,用这个比较经典的例子进行说明
环境准备:
- maven环境
- IntelliJ IDEA
新建两张表:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `employee`;
CREATE TABLE `employee` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`lastName` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`email` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`gender` int(2) DEFAULT NULL,
`d_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
)
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `department`;
CREATE TABLE `department` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`departmentName` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
引入spring-boot-starter-cache模块
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
实现
在主程序中开启缓存注解
这里用到@EnableCaching注解开启缓存:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching
public class SellApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SellApplication.class, args);
}
}
@Cacheable注解的使用
@Cacheable注解的作用,前面也简介了,主要是针对方法配置,能够根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存,介绍一下注解的主要属性:
- cacheNames/value:指定缓存组件的名字,数组形式
- key:缓存数据使用的key,确定缓存可以用唯一key进行指定;eg:编写SpEL; #id,参数id的值 ,,#a0(第一个参数), #p0(和a0的一样的意义) ,#root.args[0]
- keyGenerator:key的生成器;可以自己指定key的生成器的组件id(注意: key/keyGenerator:二选一使用;不能同时使用)
- cacheManager:指定缓存管理器;或者cacheResolver指定获取解析器
- condition:指定符合条件的情况下才缓存;使用SpEl表达式,eg:condition = "#a0>1":第一个参数的值>1的时候才进行缓存
- unless:否定缓存;当unless指定的条件为true,方法的返回值就不会被缓存;eg:unless = "#a0!=2":如果第一个参数的值不是2,结果不缓存;
- sync:是否使用异步模式
@Cacheable(value = {"emp"}, /*keyGenerator = "myKeyGenerator",*/key = "#id",condition = "#a0>=1",unless = "#a0!=2")
public Employee getEmp(Integer id) {
Employee employee = this.employeeMapper.getEmpById(id);
LOG.info("查询{}号员工数据",id);
return employee;
}
这里也可以使用自定义的keyGenerator,使用属性keyGenerator = "myKeyGenerator"
定义一个@Bean类,将KeyGenerator添加到Spring容器:
@Configuration
public class CacheConfig {
@Bean(value = {"myKeyGenerator"})
public KeyGenerator keyGenerator(){
return new KeyGenerator() {
@Override
public Object generate(Object target, Method method, Object... params) {
return method.getName()+"["+ Arrays.asList(params).toString()+"]";
}
};
}
}
@CachePut注解的使用
@CachePut注解也是一个用来缓存的注解,不过缓存和@Cacheable有明显的区别是既调用方法,又更新缓存数据,也就是执行方法操作之后再来同步更新缓存,所以这个主键常用于更新操作,也可以用于查询,主键属性和@Cacheable有很多类似的。
/**
* @CachePut:既调用方法,又更新缓存数据;同步更新缓存
* 修改了数据,同时更新缓存
*/
@CachePut(value = {"emp"}, key = "#result.id")
public Employee updateEmp(Employee employee){
employeeMapper.updateEmp(employee);
log.info("更新{}号员工数据",employee.getId());
return employee;
}
@CacheEvic注解的使用
主要属性:
- key:指定要清除的数据
- allEntries = true:指定清除这个缓存中所有的数据
- beforeInvocation = false:默认代表缓存清除操作是在方法执行之后执行
- beforeInvocation = true:代表清除缓存操作是在方法运行之前执行
@CacheEvict(value = {"emp"}, beforeInvocation = true,key="#id")
public void deleteEmp(Integer id){
employeeMapper.deleteEmpById(id);
//int i = 10/0;
}
@Caching注解的使用
@Caching用于定义复杂的缓存规则,可以集成@Cacheable和 @CachePut。
// @Caching 定义复杂的缓存规则
@Caching(
cacheable = {
@Cacheable(/*value={"emp"},*/key = "#lastName")
},
put = {
@CachePut(/*value={"emp"},*/key = "#result.id"),
@CachePut(/*value={"emp"},*/key = "#result.email")
}
)
public Employee getEmpByLastName(String lastName){
return employeeMapper.getEmpByLastName(lastName);
}
@CacheConfig注解的使用
@CacheConfig注解可以用于抽取缓存的公共配置,然后在类加上就可以。如:
@CacheConfig(cacheNames = {"emp"},cacheManager = "employeeCacheManager")
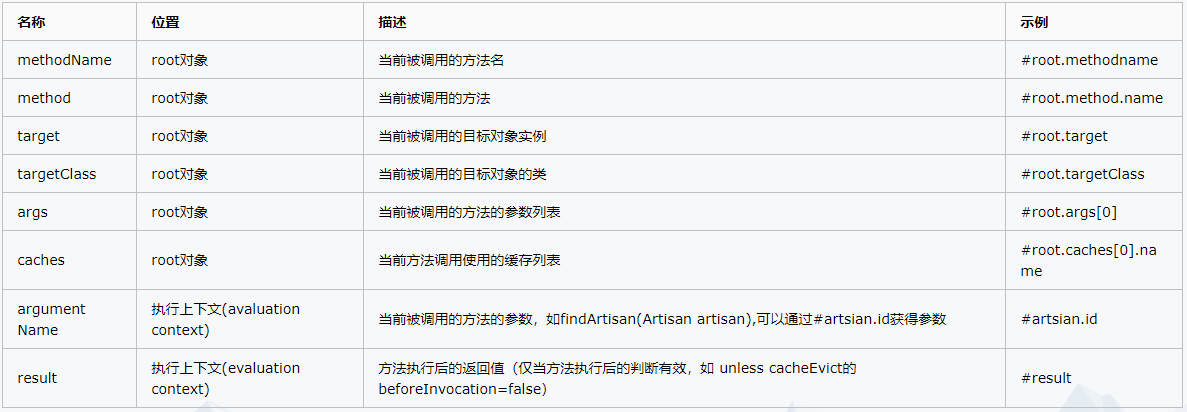
附录拓展:SpEL表达式用法
Cache SpEL available metadata
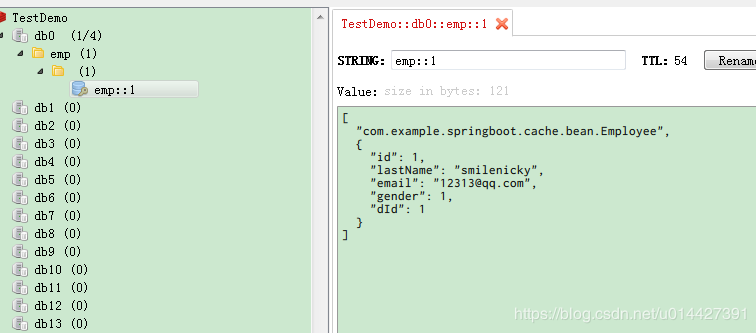
四、集成Redis缓存
环境准备
基于前面的Spring缓存环境,集成redis要引入相关依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
</dependency>
切换缓存方式为Redis:spring.cache.type=redis

Redis配置类实现
RedisTemplate配置
@Resource
private LettuceConnectionFactory lettuceConnectionFactory;
@Bean
@Primary
public RedisTemplate<Object,Object> redisTemplate(){
RedisTemplate<Object,Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<Object, Object>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(lettuceConnectionFactory);
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object> jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = this.initJacksonSerializer();
// 设置value的序列化规则和 key的序列化规则
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.afterPropertiesSet();
return redisTemplate;
}
RestTemplate相关操作
使用RestTemplate操作redis:
1、redisTemplate.opsForValue();//操作字符串
2、redisTemplate.opsForHash();//操作hash
3、redisTemplate.opsForList();//操作list
4、redisTemplate.opsForSet();//操作set
5、redisTemplate.opsForZSet();//操作有序set
缓存业务测试
@Autowired
DepartmentMapper departmentMapper;
@Qualifier("redisCacheManager")
@Autowired
RedisCacheManager redisCacheManager;
// 使用缓存管理器得到缓存,进行api调用
public Department getDeptById(Integer id){
log.info("查询id为{}的员工信息",id);
//获取某个缓存
Cache deptCache = redisCacheManager.getCache("dept");
Department department = null;
if(deptCache.get(id)==null){
department = departmentMapper.getDeptById(id);
deptCache.put(id,department);
}else{
SimpleValueWrapper valueWrapper = (SimpleValueWrapper) deptCache.get(id);
department = (Department)valueWrapper.get();
}
return department;
}