JPEG编码中的采样过程其实就是一个图像数据转换成若干个8*8数据块的过程,如下图将原始图像分成8*8个小块(block),每个block中有64个像素:
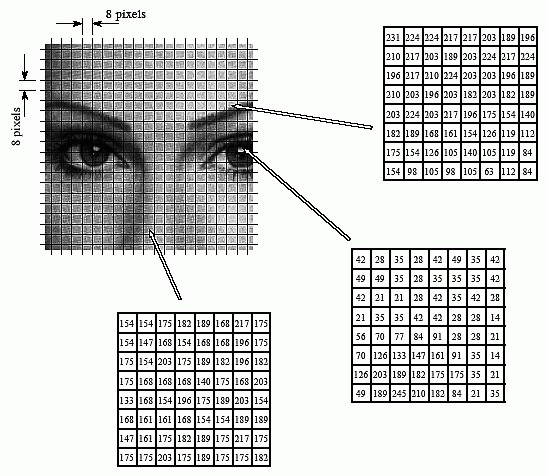
ImageSharp源码中关于采样有有两种选择,一种叫JpegSubsample.Ratio444,一种叫JpegSubsample.Ratio420。这两种选择就是对于JPEG图像的两种采样方法,就是我们常说的YUV采样。
1. 什么是YUV
与我们熟知的RGB类似,YUV也是一种颜色编码方法,主要用于电视系统以及模拟视频领域,它将亮度信息(Y)与色彩信息(UV)分离,没有UV信息一样可以显示完整的图像,只不过是黑白的,下图就是我用ImageSharp源码做的实验,只保留Y通道,UV通道设成0:
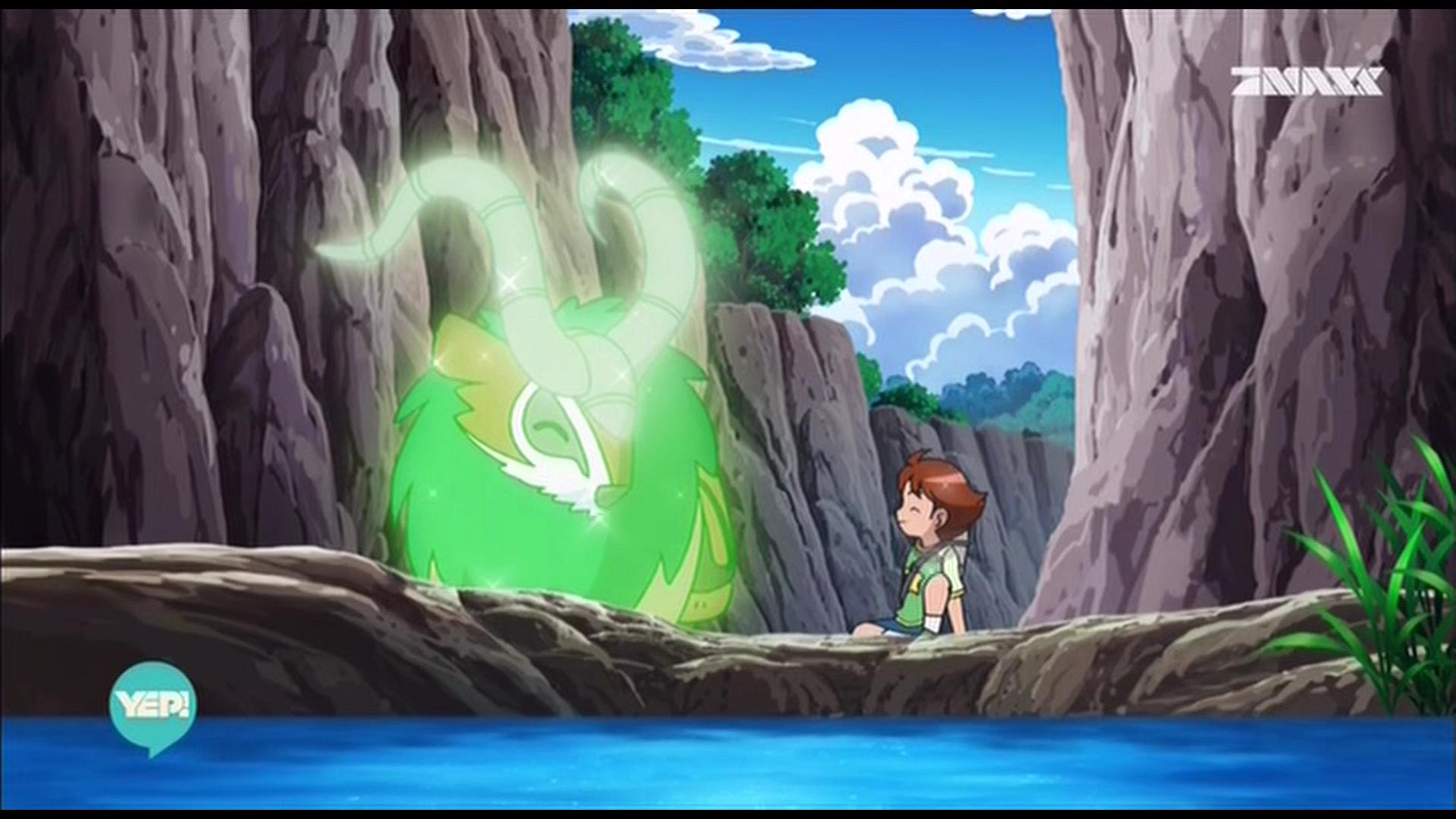
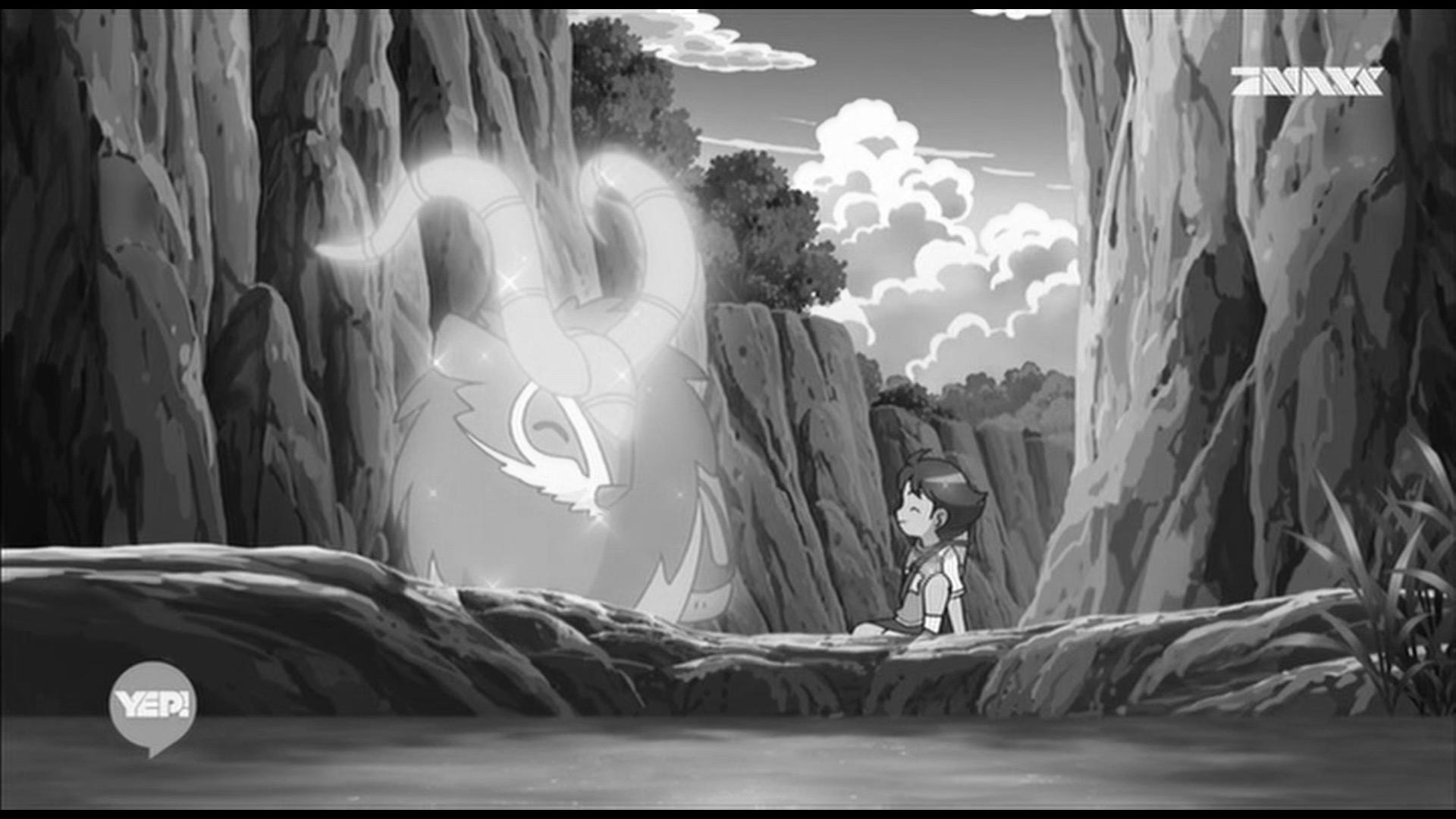


原图 Ratio420只留Y通道,159KB
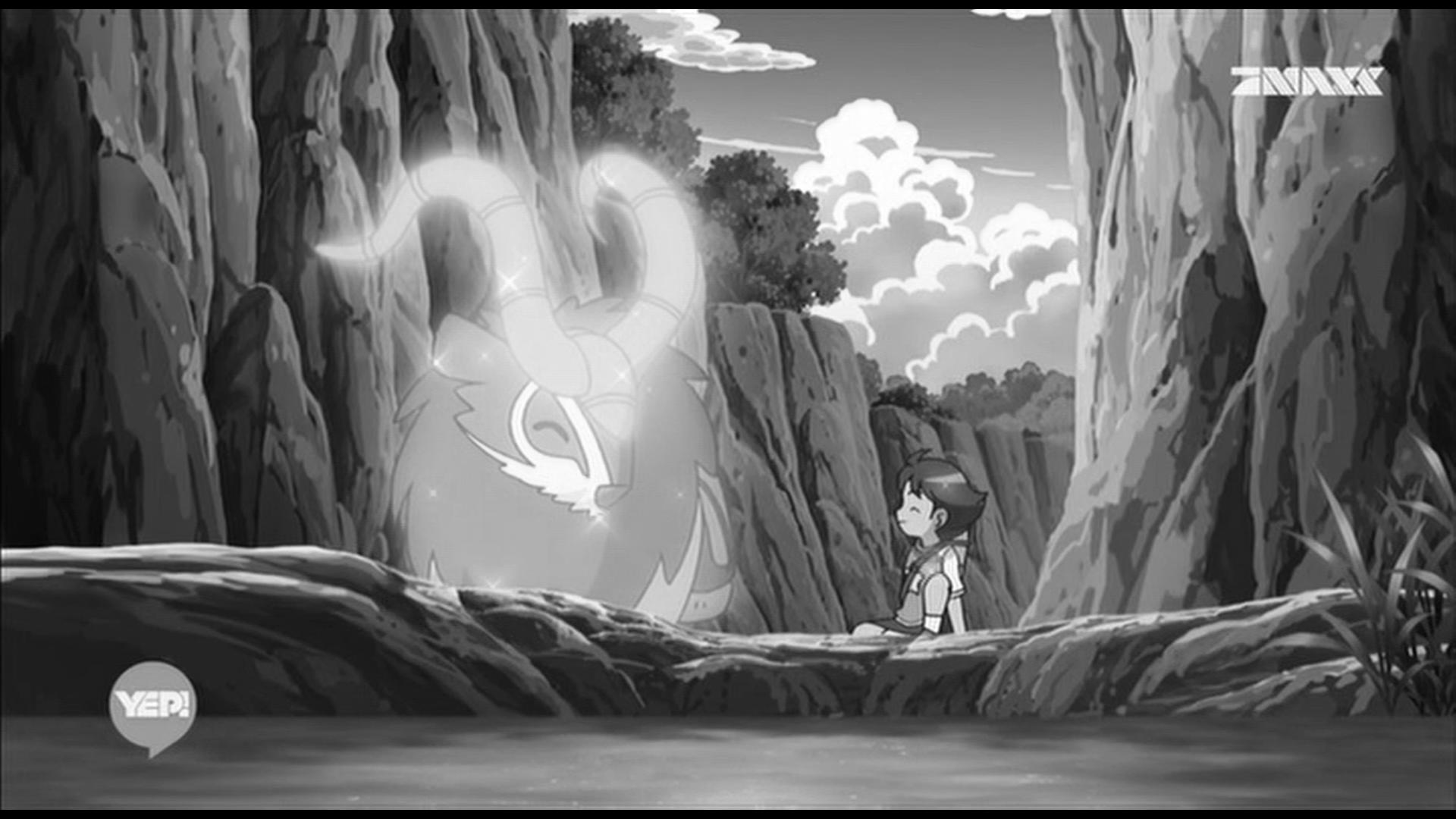

Ratio444只留Y通道,181KB
YUV不像RGB那样要求三个独立的视频信号同时传输,所以用YUV方式传送占用极少的频宽。YUV码流的存储格式其实与其采样的方式密切相关,主流的采样方式有三种,YUV4:4:4,YUV4:2:2,YUV4:2:0。现在的YUV是通常用于计算机领域用来表示使用YCbCr编码的文件。可以粗浅地视YUV为YCbCr,我们后面也换成这种叫法。
一般看到这里,会出现一个概念,叫做MCU。不是单片机更不是漫威,它中文意思是最小的编码单元(Minimum Coded Unit),它是图像中一个正方矩阵像素的数据,对于不同的采样,MCU的像素也不一样:
1.YCbCr 4:4:4(其他资料可能叫1:1:1)
这种是最简单的采样方式,这种方式里面,数据流存放数据顺序就是YCbCr ,每个MCU代表着8*8个像素块。
2.YCbCr 4:2:2
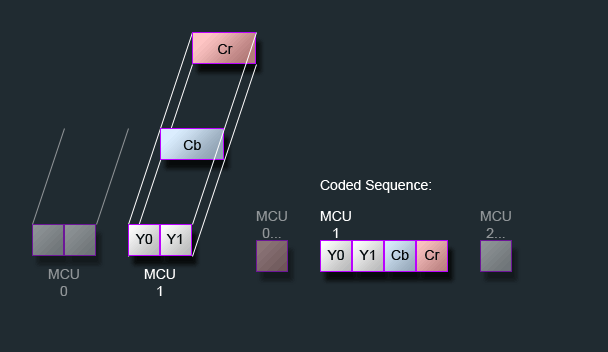
这种方式下数据流存放顺序如图所示,每个MCU代表着16x8个像素,Y0和Y1分别指向两个8*8像素块,这两个像素块共用一个Cb和Cr通道。
3.YCbCr 4:2:0(其他资料可能叫4:1:1)

这种方式下每个MCU代表着16x16个像素,Y0和Y1分别指向4个8*8像素块,这4个像素块共用一个Cb和Cr通道。
2. YUV采样源码分析
回到ImageSharp源码中,我们可以看到两种采样方法,分别是4:4:4和4:2:0,我们看一下他们的方法,先是4:4:4。

1 /// <summary> 2 /// Encodes the image with no subsampling. 3 /// </summary> 4 /// <typeparam name="TPixel">The pixel format.</typeparam> 5 /// <param name="pixels">The pixel accessor providing access to the image pixels.</param> 6 private void Encode444<TPixel>(Image<TPixel> pixels) 7 where TPixel : struct, IPixel<TPixel> 8 { 9 // TODO: Need a JpegScanEncoder<TPixel> class or struct that encapsulates the scan-encoding implementation. (Similar to JpegScanDecoder.) 10 // (Partially done with YCbCrForwardConverter<TPixel>) 11 Block8x8F temp1 = default; 12 Block8x8F temp2 = default; 13 14 Block8x8F onStackLuminanceQuantTable = this.luminanceQuantTable; 15 Block8x8F onStackChrominanceQuantTable = this.chrominanceQuantTable; 16 17 var unzig = ZigZag.CreateUnzigTable(); 18 19 // ReSharper disable once InconsistentNaming 20 int prevDCY = 0, prevDCCb = 0, prevDCCr = 0; 21 22 var pixelConverter = YCbCrForwardConverter<TPixel>.Create(); 23 24 for (int y = 0; y < pixels.Height; y += 8) 25 { 26 for (int x = 0; x < pixels.Width; x += 8) 27 { 28 pixelConverter.Convert(pixels.Frames.RootFrame, x, y); 29 30 prevDCY = this.WriteBlock( 31 QuantIndex.Luminance, 32 prevDCY, 33 &pixelConverter.Y, 34 &temp1, 35 &temp2, 36 &onStackLuminanceQuantTable, 37 unzig.Data); 38 prevDCCb = this.WriteBlock( 39 QuantIndex.Chrominance, 40 prevDCCb, 41 &pixelConverter.Cb, 42 &temp1, 43 &temp2, 44 &onStackChrominanceQuantTable, 45 unzig.Data); 46 prevDCCr = this.WriteBlock( 47 QuantIndex.Chrominance, 48 prevDCCr, 49 &pixelConverter.Cr, 50 &temp1, 51 &temp2, 52 &onStackChrominanceQuantTable, 53 unzig.Data); 54 } 55 } 56 }
首先对图像长宽进行两次for循环,不难看出每次for循环就是一个8*8的行程,然后通过pixelConverter.Convert方法将RGB转换为YCbCr,最后依次写入这8*8个像素的Y,Cb,Cr通道数据。
再看4:2:0的源码:

1 /// <summary> 2 /// Encodes the image with subsampling. The Cb and Cr components are each subsampled 3 /// at a factor of 2 both horizontally and vertically. 4 /// </summary> 5 /// <typeparam name="TPixel">The pixel format.</typeparam> 6 /// <param name="pixels">The pixel accessor providing access to the image pixels.</param> 7 private void Encode420<TPixel>(Image<TPixel> pixels) 8 where TPixel : struct, IPixel<TPixel> 9 { 10 // TODO: Need a JpegScanEncoder<TPixel> class or struct that encapsulates the scan-encoding implementation. (Similar to JpegScanDecoder.) 11 Block8x8F b = default; 12 13 BlockQuad cb = default; 14 BlockQuad cr = default; 15 var cbPtr = (Block8x8F*)cb.Data; 16 var crPtr = (Block8x8F*)cr.Data; 17 18 Block8x8F temp1 = default; 19 Block8x8F temp2 = default; 20 21 Block8x8F onStackLuminanceQuantTable = this.luminanceQuantTable; 22 Block8x8F onStackChrominanceQuantTable = this.chrominanceQuantTable; 23 24 var unzig = ZigZag.CreateUnzigTable(); 25 26 var pixelConverter = YCbCrForwardConverter<TPixel>.Create(); 27 28 // ReSharper disable once InconsistentNaming 29 int prevDCY = 0, prevDCCb = 0, prevDCCr = 0; 30 31 for (int y = 0; y < pixels.Height; y += 16) 32 { 33 for (int x = 0; x < pixels.Width; x += 16) 34 { 35 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) 36 { 37 int xOff = (i & 1) * 8; 38 int yOff = (i & 2) * 4; 39 40 pixelConverter.Convert(pixels.Frames.RootFrame, x + xOff, y + yOff); 41 42 cbPtr[i] = pixelConverter.Cb; 43 crPtr[i] = pixelConverter.Cr; 44 45 prevDCY = this.WriteBlock( 46 QuantIndex.Luminance, 47 prevDCY, 48 &pixelConverter.Y, 49 &temp1, 50 &temp2, 51 &onStackLuminanceQuantTable, 52 unzig.Data); 53 } 54 55 Block8x8F.Scale16X16To8X8(&b, cbPtr); 56 prevDCCb = this.WriteBlock( 57 QuantIndex.Chrominance, 58 prevDCCb, 59 &b, 60 &temp1, 61 &temp2, 62 &onStackChrominanceQuantTable, 63 unzig.Data); 64 65 Block8x8F.Scale16X16To8X8(&b, crPtr); 66 prevDCCr = this.WriteBlock( 67 QuantIndex.Chrominance, 68 prevDCCr, 69 &b, 70 &temp1, 71 &temp2, 72 &onStackChrominanceQuantTable, 73 unzig.Data); 74 } 75 } 76 }
这里先对图像进行16*16行程的遍历,然后在for循环内部,再单独对Y通道进行4*4的遍历,每次遍历都写入依次Y通道的编码,最后再写入Cb和Cr的编码,这样一来,就使得每4个Y通道共用一个Cb和Cr通道,我们根据这个采样规则也不难得出结论:4:2:0采样的图像存储大小肯定比4:4:4的少。我们从上面那个实验也可以证明这个结论。
注意这里的WriteBlock这个方法,这个方法就包含后面要说的DCT变换、量化和熵编码。

1 /// <summary> 2 /// Writes a block of pixel data using the given quantization table, 3 /// returning the post-quantized DC value of the DCT-transformed block. 4 /// The block is in natural (not zig-zag) order. 5 /// </summary> 6 /// <param name="index">The quantization table index.</param> 7 /// <param name="prevDC">The previous DC value.</param> 8 /// <param name="src">Source block</param> 9 /// <param name="tempDest1">Temporal block to be used as FDCT Destination</param> 10 /// <param name="tempDest2">Temporal block 2</param> 11 /// <param name="quant">Quantization table</param> 12 /// <param name="unzigPtr">The 8x8 Unzig block pointer</param> 13 /// <returns> 14 /// The <see cref="int"/> 15 /// </returns> 16 private int WriteBlock( 17 QuantIndex index, 18 int prevDC, 19 Block8x8F* src, 20 Block8x8F* tempDest1, 21 Block8x8F* tempDest2, 22 Block8x8F* quant, 23 byte* unzigPtr) 24 { 25 //1.DCT变换 26 FastFloatingPointDCT.TransformFDCT(ref *src, ref *tempDest1, ref *tempDest2); 27 //2.量化 28 Block8x8F.Quantize(tempDest1, tempDest2, quant, unzigPtr); 29 float* unziggedDestPtr = (float*)tempDest2; 30 //JTEST:如果是色度的话,全部舍去 31 if (index== QuantIndex.Chrominance) 32 { 33 for (int i = 0; i < 64; i++) 34 { 35 unziggedDestPtr[i] = 0; 36 } 37 } 38 int dc = (int)unziggedDestPtr[0]; 39 //3.熵编码写入DC分量 40 // Emit the DC delta. 41 this.EmitHuffRLE((HuffIndex)((2 * (int)index) + 0), 0, dc - prevDC); 42 //4.熵编码写入AC分量 43 // Emit the AC components. 44 var h = (HuffIndex)((2 * (int)index) + 1); 45 int runLength = 0; 46 47 for (int zig = 1; zig < Block8x8F.Size; zig++) 48 { 49 int ac = (int)unziggedDestPtr[zig]; 50 //JTEST:这里将ac分量变成0 zig>0 zig>1 zig>2... zig>64 51 //if (zig>0) 52 //{ 53 // ac = 0; 54 //} 55 if (ac == 0) 56 { 57 runLength++; 58 } 59 else 60 { 61 while (runLength > 15) 62 { 63 this.EmitHuff(h, 0xf0); 64 runLength -= 16; 65 } 66 67 this.EmitHuffRLE(h, runLength, ac); 68 runLength = 0; 69 } 70 } 71 72 if (runLength > 0) 73 { 74 this.EmitHuff(h, 0x00); 75 } 76 77 return dc; 78 }
这个WriteBlock方法将是后面文章分析重点。
3. 采样因子
我们怎么确定一张JPEG图像是用那种采样方式呢,这个信息可以在标记为SOF0中获取到,这个标记中有一个颜色分类信息通常为9个字节,里面就包含了 水平/垂直采样因子 ,我们根据采样因子就能知道是用4:4:4、4:2:2还是4:2:0。
4. 总结
这一章算是JPEG编码解码过程中的头一场戏,请大家记住我们在这个过程中输入的是一张图像数据,输出的是若干个8*8数据块,8*8数据块这个概念将会一直伴随我们JPEG整个编码。后面章节我们将重点分析上文出现的WriteBlock这个方法,这个方法里包含DCT变换、量化和熵编码。
系列目录:
ImageSharp源码详解之JPEG编码原理(1)JPEG介绍
ImageSharp源码详解之JPEG压缩原理(3)DCT变换
ImageSharp源码详解之JPEG压缩原理(4)量化
ImageSharp源码详解之JPEG压缩原理(6)C#源码解析及调试技巧
