Java基础(四)
输入输出
输出
System.out.println();
printlin是print line的缩写,表示输出并换行,如果不想换行,也可以用print()
格式化输出:printf() 把数据显示成我们期望的格式
常用占位符:
- %d:格式化输出整数
- %x:格式化输出16进制
- %f:格式化输出浮点数
- %e:格式化输出科学计数法表示的浮点数
- %s:格式化输出字符串
由于%表示占位符,所以%%表示一个%字符本身
a = %08x; 表示把一个整数格式化成16进制,并用0补足八位
b = %.2f;表示保留两位小数
输入
通过 java.util.Scanner 创建Scanner对象,传入System.in。Systme.out代表标准输出流,System.in代表标准输入流。System.in可以用来读取用户输入,但是需要更复杂的代码,用Scanner就可以简化后续的代码。
scanner.nextLine():读取用户输入的字符串;
scanner.nextInt():读取用户输入的整数;
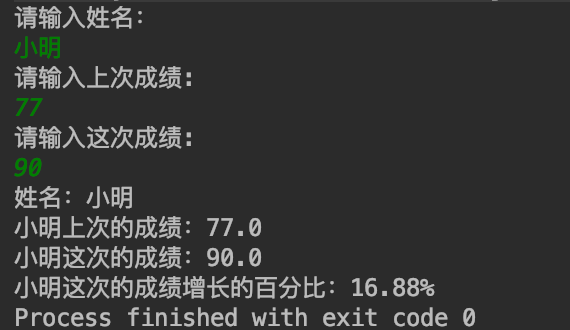
public class Test { public static void main (String[] args){ Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入姓名:"); String name = scanner.nextLine(); System.out.println("请输入上次成绩:"); Double lastScore = scanner.nextDouble(); System.out.println("请输入这次成绩:"); Double nowScore = scanner.nextDouble(); Double addS = (nowScore - lastScore)/lastScore * 100; System.out.println("姓名:"+name); System.out.printf("%s上次的成绩:%.1f ", name,lastScore); System.out.printf("%s这次的成绩:%.1f ",name,nowScore); System.out.printf("%s这次的成绩增长的百分比:%.2f%%",name,addS); } }
if判断
if结构:
if (条件){
.......//条件满足时执行
}else if (条件){
......//条件满足时执行
}else{
.......
}
当if语句只有一行时,可以省略 {},但是不建议使用
串联使用多个if时,要特别注意判断顺序,if语句是按照从上到下的顺序执行的,符合一个条件后,后续的条件不会再被执行。
浮点数在计算机中不能准确表示,所以浮点数判断用==不靠谱,判断浮点数,利用差值小于某个临界值来判断;
eg:
public class Test { public static void main (String[] args){ double x = 1 - 9.0 / 10; if(Math.abs(x - 0.1) < 0.00001){ System.out.println("x is 0.1"); }else { System.out.println("x is NOT 0.1 "); } } }
判断引用类型相等
Java中判断值类型的变量是否相等可以用==运算符,判断引用类型的变量是否相等,==表示"引用是否相等"或者说是否指向同一个对象。
判断引用类型变量的内容是否相等,用equals()
eg:
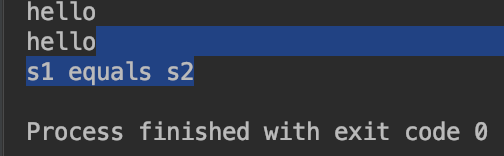
public class Test { public static void main (String[] agrs){ String s1 = "hello"; String s2 = "HELLO".toLowerCase(); System.out.println(s1); System.out.println(s2); if (s1.equals(s2)){ System.out.println("s1 equals s2"); }else { System.out.println("s1 nor equals s2"); } } }
如果变量s1为null,会报错NullPointerException:,为了避免这种报错可以利用短路运算符&&
public class Test { public static void main (String[] agrs){ String s1 = null; String s2 = "HELLO".toLowerCase(); System.out.println(s1); System.out.println(s2); if (s1 != null && s1.equals(s2)){ // if (s1.equals(s2)){ System.out.println("s1 equals s2"); }else { System.out.println("s1 nor equals s2"); } } }
还可以吧一定不是null的对象放前面,eg:if (s2.equals(s1)){......}
if使用时要注意边界条件
练习:
public class Test { public static void main (String[] args){ Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入你的体重(kg):"); Double weight = scanner.nextDouble(); System.out.println("请输入你的身高(m):"); Double height = scanner.nextDouble(); Double bmi = weight / Math.pow(height,2); if (bmi >= 32){ System.out.println("非常肥胖"); }else if (bmi >= 28 && bmi < 32){ System.out.println("肥胖"); }else if (bmi >= 25 && bmi < 28){ System.out.println("过重"); }else if (bmi >=18.5 && bmi <25){ System.out.println("正常"); }else if (bmi < 18.5){ System.out.println("过轻"); } System.out.println("BMI的值为:"+bmi); } }
switch多重选择
switch 结构
switch (表达式){
case 条件1:
......;
break;
case 条件2:
......;
break;
default:
......;
break;
}
case语句具有穿透性,如果漏写了break,则会挨个执行,直到遇上break。
如果有几个case是同一个语句块的,则可以如下方式写:
switch (表达式){
case 条件1:
......;
break;
case 条件2:
case 条件3:
......;
break;
default:
......;
break;
}
switch 语句还可以匹配字符串,字符串匹配时,是比较“内容相等”。
switch表达式
Java12开始switch升级为表达式语句,使用类似模式匹配的方法,保证只有一条路径会被执行,并且不需要break。
eg:
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args){ String fruit = "apple"; int opt = switch (fruit){ case "apple" -> 1; case "pear" ,"mango"->2; default -> 0; }; System.out.println("opt="+opt); } }
yield,返回一个值,作为switch语句的返回值。
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args){ String fruit = "orange"; int opt = switch (fruit) { case "apple" -> 1; case "pear", "mango" -> 2; default -> { int code = 22; yield code; // switch语句返回值 } }; System.out.println("opt = " + opt); } }
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请在:石头、剪刀、布 中选择一个"); String op = scanner.nextLine(); System.out.println("你的出招为:"+op); String[] arr = {"石头","剪刀","布"}; Random rn = new Random(); int n = rn.nextInt(3); String ro = arr[n]; int result = 0; if (op.equals(ro)){ result = 0; }else if ((op.equals("石头") && ro.equals("剪刀") || (op.equals("剪刀") && ro.equals("布")) || (op.equals("布") && (ro.equals("石头")))) ){ result = 1; }else if ((op.equals("石头") && ro.equals("布") || (op.equals("剪刀") && ro.equals("石头")) || (op.equals("布") && (ro.equals("剪刀")))) ){ result = 2; } switch (result){ case 0: System.out.printf("机器人的出招为:%s 平局",ro); break; case 1: System.out.printf("机器人的出招为:%s you win",ro); break; case 2: System.out.printf("机器人的出招为: %s you lose",ro); break; default: System.out.println("请输入指定的操作"); break; }; } }