1.直接使用String存储
可以直接将要存储的对象转换成json字符串,代码如下:
//存储 public static void setJsonString(String key, Object obj) { Jedis jedis = RedisConnection.getJedis(); jedis.set(key, JSON.toJSONString(obj)); jedis.close(); } //获取 public static String getJsonString(String key) { Jedis jedis = RedisConnection.getJedis(); String value = jedis.get(key); jedis.close(); return value; }
弊端:
这里是使用fastjson的相关函数toJSONString将对象转换为字符串进行存储。获取的时候直接返回json字符串给前端就可以了。使用这种方式可能只能存储简单的json字符串,对于复杂格式的可能会解析错误。
2.使用对象序列化方式存储
先将对象以字节序列化存储,然后再反序列化得到对象:
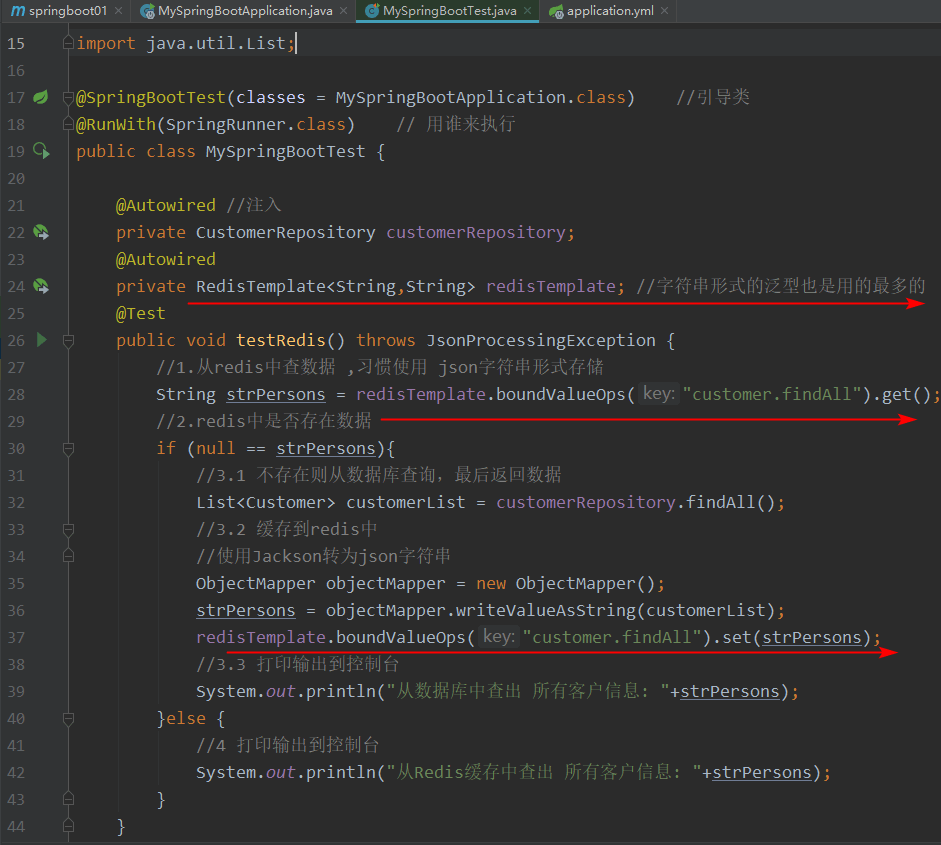
3. 使用hash存储
形如:
{
"cd": [{"Condition": {...}, segs:[1,2,3]}, { }, ...]
"rs": {"way": "休宁路", "road":[{},{},..], "segList": [{object}, {}, ...] }
}
Jedis jedis = RedisConnection.getJedis(); JSONObject res = new JSONObject(); //最终结果 //如果redis中存在,则直接从redis中取,否则计算并存储至redis if(jedis.exists(lm)) { String rs_value = jedis.hget(lm, "rs"); String cd_value = jedis.hget(lm, "cd"); res.put("cd", JSONArray.parseArray(cd_value)); res.put("rs", JSONObject.parseObject(rs_value)); System.out.println("redis get success"); } else { res = computeRes(lm); //更新redis jedis.hset(lm, "cd", res.getJSONArray("cd").toJSONString()); jedis.hset(lm, "rs", JSON.toJSONString(res.getJSONObject("rs"))); System.out.println("redis set success"); } jedis.close(); //候选结果集转json字符串 String jsonStr = JSON.toJSONString(res, SerializerFeature.DisableCircularReferenceDetect); //返回给前端 System.out.println("json string: " + jsonStr); response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8"); //解决前端中文乱码 PrintWriter out = response.getWriter(); out.print(jsonStr);