数据库:

什么是数据库?
是存放数据的电子仓库。以某种方式存储百万条,上亿条数据,供多个用户访问共享。
每个数据库有一个或多个api用于创建,访问,管理,和复制所保存的数据;
系统中很多动态的数据都存储在数据库中,需要通过访问数据库才能显示;

api就是接口,


数据库类型分类:
一、关系型数据库
关系型数据库:数据库中表与表之间存在某种关系,数据存储在不同的表中
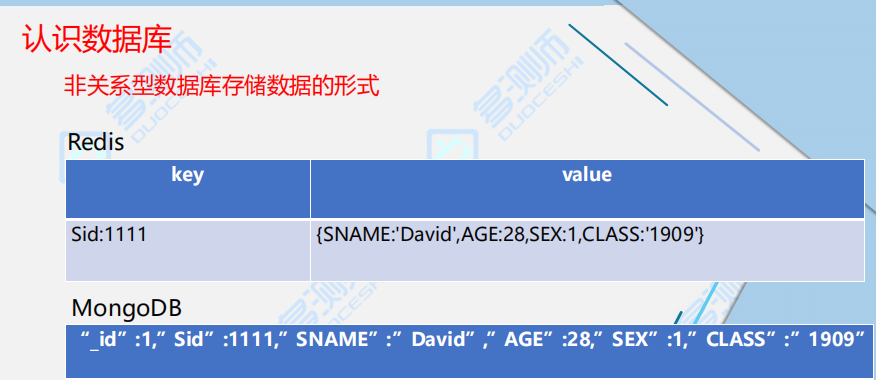
非关系型数据库:通常数据以对象的实行存储在数据库中
例如:存储列数据,键值对的方式存储

常用的数据库软件有哪些?
常见的关系型数据库软件:
1.db2 IBM公司
2.oracle 甲骨文公司
3.mysql oracle 公司(我们学的是mysql )
4、sql server
常见的非关系型数据库软件:
1.hbase(列模型)
2.redis(键值对模型) #电商类的系统用的特别多 ,缓存方式
3.mongodb(文档类模型)
mysql
mysql是指mysql数据库管理系统
属于 关系型数据库
瑞典公司mysql db 开发的,oracle收购,
mysql 是一种关联数据库将数据保存在不同的表中,而不是讲所有的数据放在一个大仓库中,增加了速度和灵活性
MySQL数据在目前web应用领域使用最广泛,也是B/S 架构常用的数据库

mysql数据库的特点:
1.体积小,安装简单,维护成本低
2.开源,免费
3.使用C++编写
4.支持多系统
5、与其他工具组合可以搭建免费的网站系统
常见:
LAMP=linux+apache+mysql+php 多有米
LNMP=linu+nginx+mysql+php 论坛
都用到mysql ,mysql免费,
6、myql支持多种编程语言,提供了api包括:c,c++,Python,java,php 等
7、支持多种存储引擎
mysql版本 5.0以后才支持存储引擎
现在学的是5.1版本
应用架构:
单点数据库, 适用于小规模应用
复制,适用于中小规模应用
集群,适合大规模应用(大多数)
比如:三主三从 ,mgr集群 ,一主三从 ,ks8集群
我们可以理解为:数据库一个excel表格,由多个表格组成的一个数据库
数据库
数据表
列
行
冗余 (重复:如一个电商项目,下单 ,退货, 都用有用户名,用户账号)
主键
外键
索引
视图
存储
临时表
单表
多表




冗余:
多余的重复或啰嗦内容(包括信息、语言、代码、结构、服务、软件、硬件等等)均称为冗余。冗余有两层含义,第一层含义是指多余的不需要的部分,第二层含义是指人为增加重复部分,其目的是用来对原本的单一部分进行备份,以达到增强其安全性的目的,这在信息通信系统当中有着较为广泛的应用。
linux中mysql
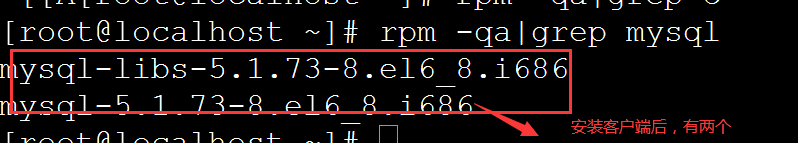
rpm -qa|grep mysql 查询linux中的数据库
yum remove mysql * 删除linux中数据库
yum erase +数据库包 删除linux中数据
rpm -e --nodeps 查询出的数据库 删除linux中数据

![]()
yum install mysql 安装mysql客户端 查看有两个包名
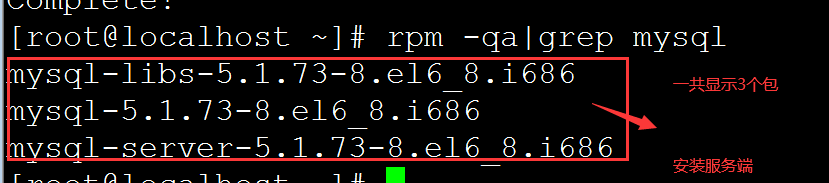
yum install mysql-server 安装mysql服务端 查看以后有单个包
ps -ef|grep msyql 查看数据库服务是否启动
开启数据库中:注意mysql加上d
service mysqld start 数据库开启服务
service mysqld stop 数据库关闭服务
service mysqld restart 数据库重启服务
service mysqld status 数据库查看状态
![]()
![]()
![]()

service iptables stop 防火墙的关闭 (因为我们要连接navicat)
mysqladmin -uroot password 密码 设置秘密(linux界面)

mysql -u root -p 进入mysql操作界面

![]()
show databases ;显示所有的数据库
注意点:加了s 表示所有的数据库

create database 数据库名 #创建数据库

drop database 数据库 # 删除数据库

show tables 查询指定库中的所有表

use 数据库名
![]()
ctrl+z ctrl+c q exit quit 退出
grant all privileges on *.* to root@'%' identified by '123456'; 设置权限
flush privileges ,刷新权限
grant 授权
all privileges :所有权限
on
*.* 第一个*代表所有数据库, 第二个* 代表所有的表
to
root @ :针对root用户
% :表示所有的远程主机
identified by :设置密码

![]()
mysql存储引擎
1 MyISAM存储引擎(默认的存储引擎)
Mysql5.0之前默认的存储引擎,有较高的插入,查询速度,但不支持事务,支持数据压缩,表级锁定,支持索引。
2 InnoDB存储引擎
事务型数据库首选引擎,(外键)Mysql5.5之后默认的存储引擎,支持行级锁定,支持索引
show tables ;查看指定库里的表
navicat连接
注意事项:
1、防火墙 (service iptables stop)
2、mysql服务器是否开启 (service mysqld status)
3、权限设置成功,并刷新
(grant all privileges on *.* to root@'%' identified by '123456'; 设置权限 ,
flush privileges ,刷新权限)
4、ip地址是否输入有误,
5、密码不正确
常报错:1045,2003,1064,1130,2002

知识点:
一个汉字占多少 长度和编码有关
(utf8和gbk 都是字符集格式,如:在我们禅道中导入用例的格式也用到了gbk)
utf-8:一个汉字=3个字节
gbk: 一个汉字=2个字节
常用
数值格式:
int 整数 2^-3----2^31 节:4
bigint 超大的整数 字节:8
float 浮点型数据 字节:4
字符格式:
char 固定长度的字符串 最大字符255
varchar 具有最大限制的可变长度 最大65535字符
时间格式:
date yyyy-mm-dd 格式的日期 字节:3
time hh:mm:ss 格式的时间 字节:3
datetime 日期+时间 字节:8
year , 年 :字节1
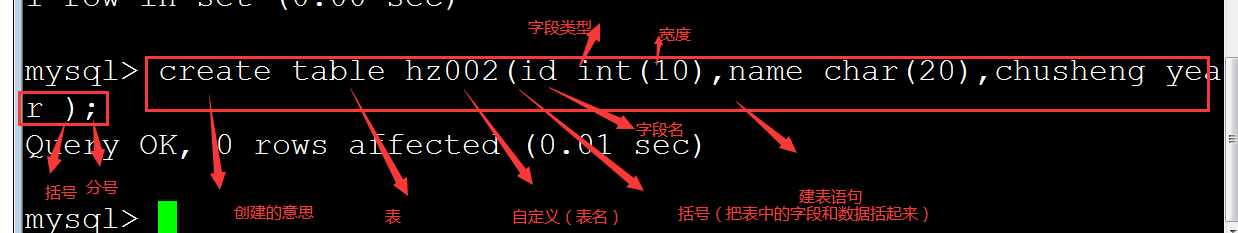
例如:
create table hz002(id int(10),name char(20),chusheng year );
注意:时间直接在字段名后面接上时间类型;不需要宽度;
create table +表名
(
字段1名称,数据类型, 约束 ,备注,
字段2名称,数据类型,约束,备注,
字段3名称,数据类型,约束,备注,
)
约束:
定义实际上就是表中的限制条件
作用:表在设计的时候加入约束的目的是为了保证表中的记录完整和有效
约束的种类:
1、非空约束:(not null)非空 用于保证字段的值不能为空;
2、唯一约束:(unique) 保证字段值最具有唯一性(不能重复),并且为空
3、主键约束:(primary key)主键,用于保证字段值具有唯一性,并且非空
4、外键约束:(foreign key)
5、默认: default
6、自增长:auto_increment
(1)与主键 约束一起使用 ,针对id
(2)每插入一条数据,指定的字段值+1
添加约束的的时机:
1、建表
2、修改表
主键约束和唯一约束的区别:
主键 不允许为空,最多一个, 允许组合
唯一 允许为空 ,可以由多个, 允许组合
外键:
1、要求有主表和从表
2、建立外键是在从表设置外键,
3、主表和从表的字符类型要一致
4、主表的关联列是以key
5、插入 数据:先插入主表,在插入从表
6、删除数据,先删除从表,在删除主表

----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
表结构语句:
建表:
desc 表名;查看表结构


select * from 表名 查看表中所有的数据 * 表示所有
创建表格式:
create table 表名 (字段名1 字符类型1(字符宽度1) 约束 ,字段名2 字符类型2(字符宽度2));
#create table gz16 (id int(10)primary key,name VARCHAR(20));
default charset=utf8
SELECT * from hz0001;
删除表:格式:drop table 表名
#drop table gz16;
目前我都在liunx中操作,我们也可以在navicat 上操作,


弹出一个会话框,在会话框中输入语句
表添加字段:alter table 表名 add 字段名 字符类型(字符宽度)
举例:alter table hz001 add sex VARCHAR(10);
表修改字段: alter table 表名 change 旧字段名 新字段名(字符累类型(字符宽度))
举例:alter table hz001 change chinese math int(10);
删除字段: alter table 表名 dorp 字段名
举例:ALTER table hz001 drop math ;
修改表名:alter table 表名 rename 新表名
举例:alter table hz001 rename hz01;
表字段调换:
第一种情况:字段都存在的顺序调换
modify after 在....... 后面
alter table 表名 MODIFY 已存在字段名 字符类型(字符宽度) after 字段名 ;
alter table bb MODIFY age int(10) after id ;
第二种情况: 添加字段到第一位
first 字段放在第一位(添加字段到表的第一位)
格式:alter table 表名 add 字段名 字符类型(字符宽度) first;
举例:alter table bb add sex char(10) first;
第三种情况:添加新字段到指定字段的后面
格式:alter table 表名 add 字段名 字符类型(字符宽度) AFTER 字段名;
举例:alter table bb add chinese int(10) AFTER id;
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
增:
方法一:
insert into 表名 (字段1, 字段2 ,字段3) values (1,'xiao' ,"nan","86" )
举例:
情况1:所有的字段数据都插入:
INSERT into hz01(id,name,sex) VALUES (1,'hwy','女'),(2,'junlei','男'),(3,'ruifeng','男');
情况2:
部分的字段数据都插入:
INSERT into hz0001(id) VALUES (4);
方法二:
insert into 表名 values (1,"wang ","nv","76"),(3,"wang ","nv","76"),(4,"wang ","nv","76")
举例:注意:要求所有的字段都有值,
INSERT into hz0001 VALUES (6,'hwy','女'),(7,'junlei','男'),(8,'ruifeng','男');
不常用:alter table 表名 default charset=utf8 ; #修改默认的编码格式
举例“”#alter table hz01 DEFAULT charset=utf8 ;
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
查询语句
对表的数据进行查询,修改,删除,添加
#从一个表中查询所有的数据
格式:select * from 表名;
举例:select * from bb ;
![]()
#查询表中指定字段的数据; 注意多个字段需要用(,逗号隔开)
格式:select 字段名1,字段名2 ,字段3 from 表名 ;
举例1:select id,name ,age from student2 ;
举例2:select id,name from hz0001 ;
![]()
#给表字段取别名 AS ,注意点:as也可以省略不写
格式:select 字段名 1 "别名1",字段名2 " 别名2" from 表名 ;
举例 1:select id "编号",name as "姓名" ,age as"年龄" from baoan003 ;
举例2:select id "编号",name " 姓名"from hz0001 ; 注意点:as也可以省略不写

#指定条件查询内容 用where+条件
格式:select * from 表名 where 字段名 =字段值 ;
select * from baoan003 where age=23 ;
where 条件使用注意:
where +条件 条件中有(=,>,<,>=,<=,!= ,<>) 比较运算符
如:select * from baoan003 where age!=23 ;
举例:
select * from hz0001 where id=1;
select * from hz0001 where id>4;
select * from hz0001 where id<4;
select * from hz0001 where id!=4;
select * from hz0001 where id<>4;
select * from hz0001 where id>=4;
select * from hz0001 where id<=4;
and 与 同是满足所有条件,比如 :条件1和条件2 都要同时满足
举例1:select * from baoan003 where age!=23 and math=98;
举例2:select * from hz0001 where id=1 and name="hwy";
or 或 条件1和条件2 至少满足一个,满足其中一个就可以显示;
举例1:select * from hz0001 where id=1 or id=2;
between and 在什么范围之间 (注意:between的值包含了本身)
举例1:select * from baoan003 where math between 81 AND 98;
举例2:select * from hz0001 where id BETWEEN 2 and 6 ;
in 在一组指定数据中选(或匹配其中的数据)
举例1:select * from hz0001 where id in(1,2,9);
is null 为空
举例1:select * from baoan003 where class is null;
举例2:select * from hz0001 where name is null ;
is not null 非空
举例1:select * from baoan003 where class is not null;
举例2:select * from hz0001 where name is not null ;
多行注释:ctrl+/ 多行取消注释:ctrl+shift+/
单行注释:shift +#
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
排序:
# 对表中的数据进行排序 order by ,asc 升序 ,desc 降序
降序:select * from 表名 order by 字段名 desc;
举例:select * from baoan003 order by id desc;
升序:
格式:select * from 表名 order by 字段名 asc ;
举例:select * from baoan003 order by chinese asc;
注意点:升序asc可以省略不写
#二次排序(理解为:第一个字段排序一样,在排第二个字段)
select * from 表名 order by 字段名1 desc ,字段名2 desc;
select * from baoan003 order by math ASC, chinese desc ;
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#模糊匹配查询 like
% :匹配0个字符或者多个字符
_:表示一个字符
select * from baoan003 where english like "7%";#表示匹配 7开头的分数
select * from baoan003 where english like "%7";#表示匹配7结尾的分数
select * from baoan003 where english like "%7%";#表示含有7的分数
select * from baoan003 where english like "7__";表示匹配具体的位数的数据
限制 limit m,n 后面接两个值
#m 表示下标 ,n 表示步长(可以理解为取多少个数)

格式1: select * from 表名 limit (下标值, 行数) ;
select * from baoan003 limit 2,4 ;
![]()
格式2: select * from 表名 limit 行数 ; (默认从下标值0开始取值)
举例:select * from student2 limit 3 ;
#group by 分组 having
select sum(age),sex from baoan003 group by sex ;
select sum(age) from student2 group by sex ;
groupby 一般不会单独使用,通常都是和聚合函数组合使用 ,
group by 后 查询出来的结果,在需要根据条件查询用having
select max(age) s,sex from baoan003 group by sex having s>23 ;
select max(age) ,sex from baoan003 group by sex having max(age) >23 ;
having +条件 和where +条件 用法一样,但是场景不一样,一般group
by 的后面 接having
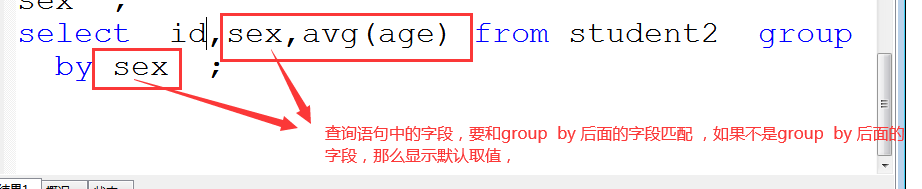
举例1:select sex,avg(age) from student2 group by sex HAVING avg(age) >22 ;
举例2:select sex,avg(age) s from student2 group by sex HAVING s >22 ;
举例3:select sex,max(math+chinese+english) from student2 group by sex ;
取别名:把avg(sage)当成一个字段来来判断;
注意:分组 使用函数 ,在select 和from 接的字段 ,只能是函数, 和指定分组的字段 才能匹配;

sql函数
max 最大值
min 最小值
avg 平均值
count 统计总数
sum 求和
distinct 去重
select sum(age) from baoan003 ; #求年龄综合
select min(age) from baoan003 ;#求最小年龄
select max(age) from baoan003 ; #求最大年龄
select count(age) from baoan003 ; #统计个数
select avg(age) from baoan003 ; #求平均值
select distinct(age) from baoan003 ; #去重复的数据
#SELECT 查
#insert into 增
#update ..... set 改
# delete 删
#update ..... set 改
update 表名. set 修改的字段=字段新值 where 条件
update xiaodao set name="国龙" where id=2 ;
update xiaodao set name="国龙" where id=4 or id=1;
# delete 删
delete from 表名 清空表数据
#truncate 快速删除表内大量数据
truncate baoan003
#drop
drop>truncate>delete
注意:1、drop 是删除表和表数据
2、truncate 删除无法恢复
3、delete 删除可恢复
#如:
1、delete from xiaodao ;
2、delete from xiaodao where id=1;
3 truncate student2 ;
delete from 表名 where 条件
如:delete from xiaodao ; 删除表内所有数据
如:delete from xiaodao where id =6; 指定条件删除
表可以取别名:
select * from baoan003 as s ; as可以省略 s可以自定义,代表表的别名
备份表结构
create table 新表名 like 备份的原表 ;
create table nn like mm ;
备份数据:
INSERT into 新表有表结构 select * from 备份的原表;
INSERT into nn select * from mm;

注意:备份表中的某些表字段的数据:
步骤先备份表,在备份数据
INSERT into 新表 (字段名1,字段名2) select 字段名1 ,段名2 from 备份原表;
INSERT into jj (id,name) select id ,name from mm;
备份表结构和表数据:
create table 新表名 as(select * from 备份的原表);
如:create table ss as(select * from baoan003);
![]()
linux中备份:
> 备份数据库
mysqldump -u root -p baoan > baoan00
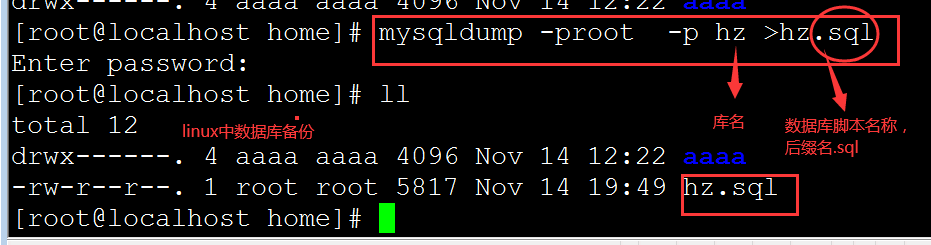
< 还原数据库
先建一个库名,
mysql -u root -p 新库 < 脚本.sql
