前面的话
本文将介绍如何实现和使用链表这种动态的数据结构
数据结构
要存储多个元素,数组(或列表)可能是最常用的数据结构。每种语言都实现了数组。这种数据结构非常方便,提供了一个便利的[]语法来访问它的元素。然而,这种数据结构有一个缺点:(在大多数语言中)数组的大小是固定的,从数组的起点或中间插入或移除项的成本很高,因为需要移动元素
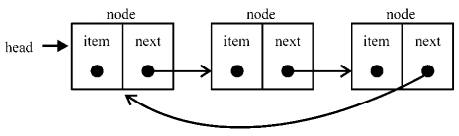
链表存储有序的元素集合,但不同于数组,链表中的元素在内存中并不是连续放置的。每个元素由一个存储元素本身的节点和一个指向下一个元素的引用(也称指针或链接)组成。下图展示了一个链表的结构:
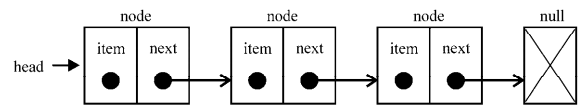
相对于传统的数组,链表的一个好处在于,添加或移除元素的时候不需要移动其他元素。然而,链表需要使用指针,因此实现链表时需要额外注意。数组的另一个细节是可以直接访问任何位置的任何元素,而要想访问链表中间的一个元素,需要从起点(表头)开始迭代列表直到找到所需的元素
现实中也有一些链表的例子。第一个例子就是康加舞队。每个人是一个元素,手就是链向下一个人的指针。可以向队列中增加人——只需要找到想加入的点,断开连接,插入一个人,再重新连接起来
另一个例子是寻宝游戏。你有一条线索,这条线索是指向寻找下一条线索的地点的指针。你顺着这条链接去下一个地点,得到另一条指向再下一处的线索。得到列表中间的线索的唯一办法,就是从起点(第一条线索)顺着列表寻找
还有一个可能是用来说明链表的最流行的例子,那就是火车。一列火车是由一系列车厢(也称车皮)组成的。每节车厢或车皮都相互连接。你很容易分离一节车皮,改变它的位置,添加或移除它。下图演示了一列火车。每节车皮都是列表的元素,车皮间的连接就是指针:

创建链表
理解了链表是什么之后,现在就要开始实现我们的数据结构了。以下是我们的LinkedList 类的骨架:
function LinkedList() { var Node = function(element){ // {1} this.element = element; this.next = null; }; var length = 0; // {2} var head = null; // {3} this.append = function(element){}; this.insert = function(position, element){}; this.removeAt = function(position){}; this.remove = function(element){}; this.indexOf = function(element){}; this.isEmpty = function() {}; this.size = function() {}; this.toString = function(){}; this.print = function(){}; }
LinkedList数据结构还需要一个Node辅助类(行{1})。Node类表示要加入列表的项。它包含一个element属性,即要添加到列表的值,以及一个next属性,即指向列表中下一个节点项的指针
LinkedList类也有存储列表项的数量的length属性(内部/私有变量)(行{2})。另一个重要的点是,我们还需要存储第一个节点的引用。为此,可以把这个引用存储在一个称为head的变量中(行{3})
然后就是LinkedList类的方法。在实现这些方法之前,先来看看它们的职责
append(element):向列表尾部添加一个新的项。 insert(position, element):向列表的特定位置插入一个新的项。 remove(element):从列表中移除一项。 indexOf(element):返回元素在列表中的索引。如果列表中没有该元素则返回-1。 removeAt(position):从列表的特定位置移除一项。 isEmpty():如果链表中不包含任何元素,返回true,如果链表长度大于0则返回false。 size():返回链表包含的元素个数。与数组的length属性类似。 toString() :由 于列表项使 用了 Node 类 ,就 需要重写 继承自 JavaScript对 象默认 的 toString方法,让其只输出元素的值。
【append】
向LinkedList对象尾部添加一个元素时,可能有两种场景:列表为空,添加的是第一个元素,或者列表不为空,向其追加元素
下面是我们实现的append方法:
this.append = function(element){ var node = new Node(element), //{1} current; //{2} if (head === null){ //列表中第一个节点 //{3} head = node; } else { current = head; //{4} //循环列表,直到找到最后一项 while(current.next){ current = current.next; } //找到最后一项,将其next赋为node,建立链接 current.next = node; //{5} } length++; //更新列表的长度 //{6} };
首先需要做的是把element作为值传入,创建Node项(行{1})
先来实现第一个场景:向为空的列表添加一个元素。当我们创建一个LinkedList对象时,head会指向null:
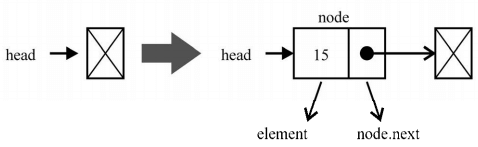
如果head元素为null(列表为空——行{3}),就意味着在向列表添加第一个元素。因此要做的就是让head元素指向node元素。下一个node元素将会自动成为null
第二个场景是向一个不为空的列表尾部添加元素
要向列表的尾部添加一个元素,首先需要找到最后一个元素。记住,我们只有第一个元素的引用(行{4}),因此需要循环访问列表,直到找到最后一项。为此,我们需要一个指向列表中current项的变量(行{2})。循环访问列表时,当current.next元素为null时,我们就知道已经到达列表尾部了。然后要做的就是让当前(也就是最后一个)元素的next指针指向想要添加到列表的节点(行{5})。下图展示了这个行为:
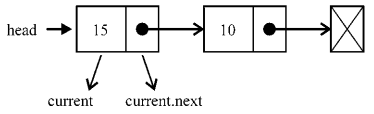
当一个Node元素被创建时,它的next指针总是null。这没问题,因为我们知道它会是列表的最后一项。当然,别忘了递增列表的长度,这样就能控制它,轻松地得到列表的长度(行{6})。 我们可以通过以下代码来使用和测试目前创建的数据结构
var list = new LinkedList(); list.append(15); list.append(10);
【remove】
现在,让我们看看如何从LinkedList对象中移除元素。移除元素也有两种场景:第一种是移除第一个元素,第二种是移除第一个以外的任一元素。我们要实现两种remove方法:第一种是从特定位置移除一个元素,第二种是根据元素的值移除元素(稍后会展示第二种remove方法)
下面是根据给定位置移除一个元素的方法的实现:
this.removeAt = function(position){ //检查越界值 if (position > -1 && position < length){ // {1} var current = head, // {2} previous, // {3} index = 0; // {4} //移除第一项 if (position === 0){ // {5} head = current.next; } else { while (index++ < position){ // {6} previous = current; // {7} current = current.next; // {8} } //将previous与current的下一项链接起来:跳过current,从而移除它 previous.next = current.next; // {9} } length--; // {10} return current.element; } else { return null; // {11} } };
该方法要得到需要移除的元素的位置,就需要验证这个位置是有效的(行{1})。从0(包括0)到列表的长度(size – 1,因为索引是从零开始的)都是有效的位置。如果不是有效的位置,就返回null(意即没有从列表中移除元素)
下面来为第一种场景编写代码:我们要从列表中移除第一个元素(position === 0——行{5})。下图展示了这个过程:
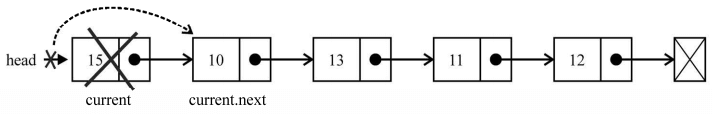
因此,如果想移除第一个元素,要做的就是让head指向列表的第二个元素。我们将用current变量创建一个对列表中第一个元素的引用(行{2})。这样 current 变量就是对列表中第一个元素的引用。如果把 head 赋为current.next,就会移除第一个元素。
现在,假设我们要移除列表的最后一项或者中间某一项。为此,需要依靠一个细节来迭代列表,直到到达目标位置(行{6}——我们会使用一个用于内部控制和递增的index变量):current 变量总是为对所循环列表的当前元素的引用(行{8})。我们还需要一个对当前元素的前一个元 素的引用(行{7});它被命名为previous(行{3})。
因此,要从列表中移除当前元素,要做的就是将previous.next和current.next链接起 来(行{9})。这样,当前元素就会被丢弃在计算机内存中,等着被垃圾回收器清除
下面试着通过一些图表来更好地理解。首先考虑移除最后一个元素:

对于最后一个元素,当我们在行{6}跳出循环时,current变量将是对列表中最后一个元素的引用(要移除的元素)。current.next的值将是null(因为它是最后一个元素)。由于还保留了对previous元素的引用(当前元素的前一个元素),previous.next就指向了current。那么要移除current,要做的就是把previous.next的值改变为current.next
现在来看看,对于列表中间的元素是否可以应用相同的逻辑:
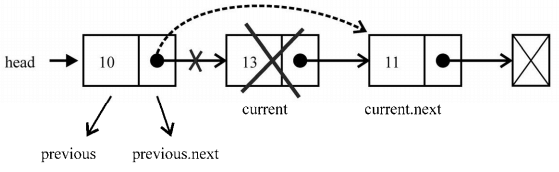
current变量是对要移除元素的引用。previous变量是对要移除元素的前一个元素的引用。 那么要移除current元素,需要做的就是将previous.next与current.next链接起来。因此,我们的逻辑对这两种情况都管用
【insert】
接下来,我们要实现insert方法。使用这个方法可以在任意位置插入一个元素。下面来看一看它的实现
this.insert = function(position, element){ //检查越界值 if (position >= 0 && position <= length){ //{1} var node = new Node(element), current = head, previous, index = 0; if (position === 0){ //在第一个位置添加 node.next = current; //{2} head = node; } else { while (index++ < position){ //{3} previous = current; current = current.next; } node.next = current; //{4} previous.next = node; //{5} } length++; //更新列表的长度 return true; } else { return false; //{6} } };
由于处理的是位置,就需要检查越界值(行{1},跟remove方法类似)。如果越界了, 就返回false值,表示没有添加项到列表中(行{6})
现在要处理不同的场景。第一种场景,需要在列表的起点添加一个元素,也就是第一个位置。下图展示了这种场景
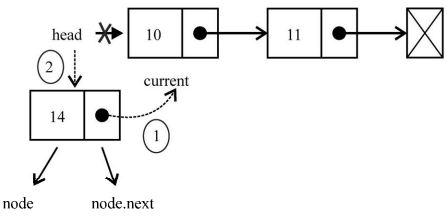
current变量是对列表中第一个元素的引用。我们需要做的是把node.next的值设为current(列表中第一个元素)。现在head和node.next都指向了current。接下来要做的就是把head的引用改为node(行{2}),这样列表中就有了一个新元素
现在来处理第二种场景:在列表中间或尾部添加一个元素。首先,我们需要循环访问列表, 找到目标位置(行{3})。当跳出循环时,current变量将是对想要插入新元素的位置之后一个元素的引用,而previous将是对想要插入新元素的位置之前一个元素的引用。在这种情况下,我们要在previous和current之间添加新项。因此,首先需要把新项(node)和当前项链接起来(行{4}),然后需要改变previous和current之间的链接。我们还需要让previous.next指向node(行{5})
我们通过一张图表来看看代码所做的事:

如果我们试图向最后一个位置添加一个新元素,previous将是对列表最后一项的引用,而current将是null。在这种情况下,node.next将指向current,而previous.next将指向 node,这样列表中就有了一个新的项
现在来看看如何向列表中间添加一个新元素
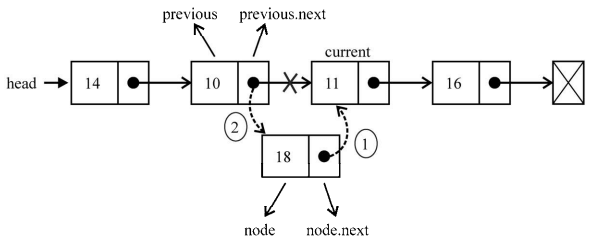
在这种情况下,我们试图将新的项(node)插入到previous和current元素之间。首先, 我们需要把node.next的值指向current。然后把previous.next的值设为node。这样列表中就有了一个新的项
【toString】
toString方法会把LinkedList对象转换成一个字符串。下面是toString方法的实现:
this.toString = function(){ let current = head, //{1} string = ''; //{2} while (current) { //{3} string +=current.element +(current.next ? 'n' : '');//{4} current = current.next; //{5} } return string; //{6} };
首先,要循环访问列表中的所有元素,就需要有一个起点,也就是head。我们会把current 变量当作索引(行{1}),控制循环访问列表。我们还需要初始化用于拼接元素值的变量(行{2})。
接下来就是循环访问列表中的每个元素(行{3})。我们要用current来检查元素是否存在(如果列表为空,或是到达列表中最后一个元素的下一位(null),while循环中的代码就不会执行)。然后我们就得到了元素的内容,将其拼接到字符串中(行{4})。最后,继续迭代下一个元 素(行{5})。最后,返回列表内容的字符串(行{6})
【indexOf】
indexOf是我们下一个要实现的方法。indexOf方法接收一个元素的值,如果在列表中找到它,就返回元素的位置,否则返回-1。下面来看看它的实现:
this.indexOf = function(element){ let current = head, //{1} index = -1; while (current) { //{2} if (element === current.element) { return index; //{3} } index++; //{4} current = current.next; //{5} } return -1; };
我们需要一个变量来帮助循环访问列表,这个变量是current,它的初始值是head(列表的第一个元素——我们还需要一个index变量来计算位置数(行{1}))。然后循环访问元素(行{2}),检查当前元素是否是我们要找的。如果是,就返回它的位置(行{3});如果不是,就继续计数(行{4}),检查列表中下一个节点(行{5})
如果列表为空,或是到达列表的尾部(current = current.next将是null),循环就不会执行。如果没有找到值,就返回-1
【remove】
实现了indexOf方法,我们就可以实现remove等其他的方法:
this.remove = function(element){ var index = this.indexOf(element); return this.removeAt(index); };
我们已经有一个移除给定位置的一个元素的removeAt方法了。现在有了indexOf方法,如果传入元素的值,就能找到它的位置,然后调用removeAt方法并传入找到的位置。这样非常简单,如果需要更改removeAt方法的代码,这样也更容易——两个方法都会被更改(这就是重用代码的妙处)。这样,我们就不需要维护两个从列表中移除一项的方法,只需要一个!同时, removeAt方法将会检查边界约束
【isEmpty】
this.isEmpty = function() { return length === 0; };
【size】
this.size = function() { return length; };
【getHead】
head变量是LinkedList类的私有变量(这意味着它不能在LinkedList实例外部被访问和更改,只有通过LinkedList实例才可以)。但是,如果我们需要在类的实现外部循环访问列表,就需要提供一种获取类的第一个元素的方法
this.getHead = function(){ return head; };
【完整代码】
链表的完整代码如下
function LinkedList() { let Node = function(element){ this.element = element; this.next = null; }; let length = 0; let head = null; this.append = function(element){ let node = new Node(element), current; if (head === null){ //first node on list head = node; } else { current = head; //loop the list until find last item while(current.next){ current = current.next; } //get last item and assign next to added item to make the link current.next = node; } length++; //update size of list }; this.insert = function(position, element){ //check for out-of-bounds values if (position >= 0 && position <= length){ let node = new Node(element), current = head, previous, index = 0; if (position === 0){ //add on first position node.next = current; head = node; } else { while (index++ < position){ previous = current; current = current.next; } node.next = current; previous.next = node; } length++; //update size of list return true; } else { return false; } }; this.removeAt = function(position){ //check for out-of-bounds values if (position > -1 && position < length){ let current = head, previous, index = 0; //removing first item if (position === 0){ head = current.next; } else { while (index++ < position){ previous = current; current = current.next; } //link previous with current's next - skip it to remove previous.next = current.next; } length--; return current.element; } else { return null; } }; this.remove = function(element){ let index = this.indexOf(element); return this.removeAt(index); }; this.indexOf = function(element){ let current = head, index = 0; while (current) { if (element === current.element) { return index; } index++; current = current.next; } return -1; }; this.isEmpty = function() { return length === 0; }; this.size = function() { return length; }; this.getHead = function(){ return head; }; this.toString = function(){ let current = head, string = ''; while (current) { string += current.element + (current.next ? ', ' : ''); current = current.next; } return string; }; this.print = function(){ console.log(this.toString()); }; }
【ES6】
ES6版本的代码如下
let LinkedList2 = (function () { class Node { constructor(element){ this.element = element; this.next = null; } } const length = new WeakMap(); const head = new WeakMap(); class LinkedList2 { constructor () { length.set(this, 0); head.set(this, null); } append(element) { let node = new Node(element), current; if (this.getHead() === null) { //first node on list head.set(this, node); } else { current = this.getHead(); //loop the list until find last item while (current.next) { current = current.next; } //get last item and assign next to added item to make the link current.next = node; } //update size of list let l = this.size(); l++; length.set(this, l); } insert(position, element) { //check for out-of-bounds values if (position >= 0 && position <= this.size()) { let node = new Node(element), current = this.getHead(), previous, index = 0; if (position === 0) { //add on first position node.next = current; head.set(this, node); } else { while (index++ < position) { previous = current; current = current.next; } node.next = current; previous.next = node; } //update size of list let l = this.size(); l++; length.set(this, l); return true; } else { return false; } } removeAt(position) { //check for out-of-bounds values if (position > -1 && position < this.size()) { let current = this.getHead(), previous, index = 0; //removing first item if (position === 0) { head.set(this, current.next); } else { while (index++ < position) { previous = current; current = current.next; } //link previous with current's next - skip it to remove previous.next = current.next; } let l = this.size(); l--; length.set(this, l); return current.element; } else { return null; } } remove(element) { let index = this.indexOf(element); return this.removeAt(index); } indexOf(element) { let current = this.getHead(), index = 0; while (current) { if (element === current.element) { return index; } index++; current = current.next; } return -1; } isEmpty() { return this.size() === 0; } size() { return length.get(this); } getHead() { return head.get(this); } toString() { let current = this.getHead(), string = ''; while (current) { string += current.element + (current.next ? ', ' : ''); current = current.next; } return string; } print() { console.log(this.toString()); } } return LinkedList2; })();
双向链表
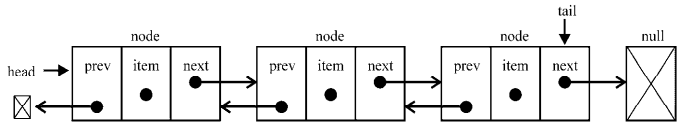
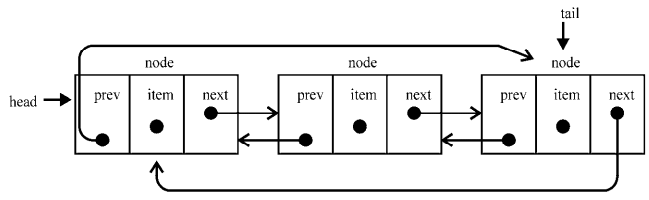
链表有多种不同的类型,下面将介绍双向链表。双向链表和普通链表的区别在于,在链表中,一个节点只有链向下一个节点的链接,而在双向链表中,链接是双向的:一个链向下一个元素, 另一个链向前一个元素,如下图所示:
先从实现DoublyLinkedList类所需的变动开始:
function DoublyLinkedList() { let Node = function(element){ this.element = element; this.next = null; this.prev = null; //新增的 }; let length = 0; let head = null; let tail = null; //新增的 //这里是方法 }
在代码中可以看到,LinkedList类和DoublyLinkedList类之间的区别标为新增的。在Node类里有prev属性(一个新指针),在DoublyLinkedList类里也有用来保存对列表最后一项的引用的tail属性
双向链表提供了两种迭代列表的方法:从头到尾,或者反过来。我们也可以访问一个特定节点的下一个或前一个元素。在单向链表中,如果迭代列表时错过了要找的元素,就需要回到列表起点,重新开始迭代。这是双向链表的一个优点
【insert】
向双向链表中插入一个新项跟(单向)链表非常类似。区别在于,链表只要控制一个next指针,而双向链表则要同时控制next和prev(previous,前一个)这两个指针
这是向任意位置插入一个新元素的算法
this.insert = function(position, element){ //检查越界值 if (position >= 0 && position <= length){ let node = new Node(element), current = head, previous, index = 0; if (position === 0){ //在第一个位置添加 if (!head){ //新增的 {1} head = node; tail = node; } else { node.next = current; current.prev = node; //新增的 {2} head = node; } } else if (position === length) { //最后一项 //新增的 current = tail; // {3} current.next = node; node.prev = current; tail = node; } else { while (index++ < position){ //{4} previous = current; current = current.next; } node.next = current; //{5} previous.next = node; current.prev = node; //新增的 node.prev = previous; //新增的 } length++; //更新列表的长度 return true; } else { return false; } };
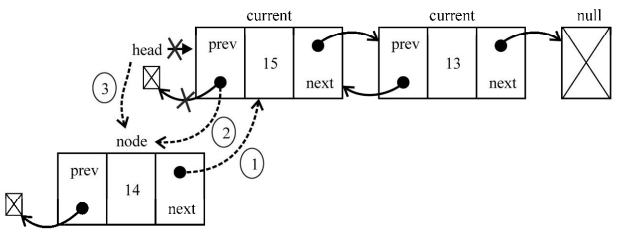
我们来分析第一种场景:在列表的第一个位置(列表的起点)插入一个新元素。如果列表为空(行{1}),只需要把head和tail都指向这个新节点。如果不为空,current变量将是对列表中第一个元素的引用。就像我们在链表中所做的,把node.next设为current,而head将指向node(它将成为列表中的第一个元素)。不同之处在于,我们还需要为指向上一个元素的指针设一个值。current.prev指针将由指向null变为指向新元素(node——行{2})。node.prev指针已经是null,因此不需要再更新任何东西
下图演示了这个过程:
现在来分析一下,假如我们要在列表最后添加一个新元素。这是一个特殊情况,因为我们还控制着指向最后一个元素的指针(tail)。current变量将引用最后一个元素(行{3})。然后开始建立第一个链接:node.prev将引用current。current.next指针(指向null)将指向node(由于构造函数,node.next已经指向了null)。然后只剩一件事了,就是更新tail,它将由指向current变为指向node。下图展示了这些行为
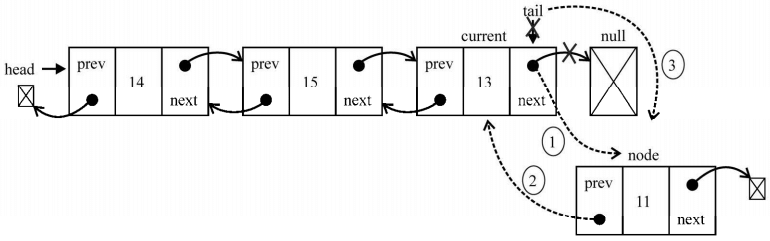
然后还有第三种场景:在列表中间插入一个新元素。就像我们在之前的方法中所做的迭代列表,直到到达要找的位置(行{4})。我们将在current和previous元素之间插入新元素。首先,node.next将指向current(行{5}),而previous.next将指向node,这样就不会丢失节点之间的链接。然后需要处理所有的链接:current.prev将指向node,而node.prev将指向 previous。下图展示了这一过程:
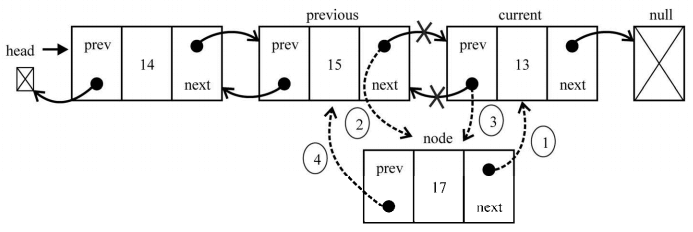
【removeAt】
从双向链表中移除元素跟链表非常类似。唯一的区别就是还需要设置前一个位置的指针。下面来看一下它的实现:
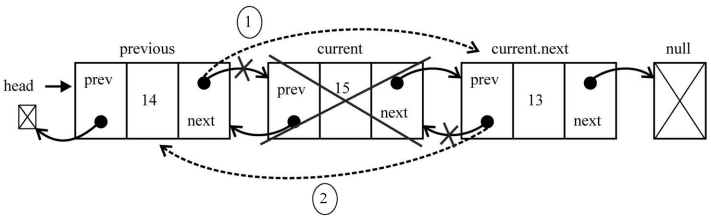
this.removeAt = function(position){ //检查越界值 if (position > -1 && position < length){ let current = head, previous, index = 0; //移除第一项 if (position === 0){ head = current.next; // {1} //如果只有一项,更新tail //新增的 if (length === 1){ // {2} tail = null; } else { head.prev = null; // {3} } } else if (position === length-1){ //最后一项 //新增的 current = tail; // {4} tail = current.prev; tail.next = null; } else { while (index++ < position){ // {5} previous = current; current = current.next; } //将previous与current的下一项链接起来——跳过current previous.next = current.next; // {6} current.next.prev = previous; //新增的 } length--; return current.element; } else { return null; } };
我们需要处理三种场景:从头部、从中间和从尾部移除一个元素。 下面来看看如何移除第一个元素。current变量是对列表中第一个元素的引用,也就是我们想移除的元素。需要做的就是改变 head 的引用,将其从current 改为下一个元素(current.next——行{1})。但我们还需要更新current.next指向上一个元素的指针(因为第一个元素的prev指针是null)。因此,把head.prev的引用改为null(行{3}——因为head也指向列表中新的第一个元素,或者也可以用current.next.prev)。由于还需要控制tail的引用,我们可以检查要移除的元素是否是第一个元素,如果是,只需要把tail也设为null
下图勾画了从双向链表移除第一个元素的过程:
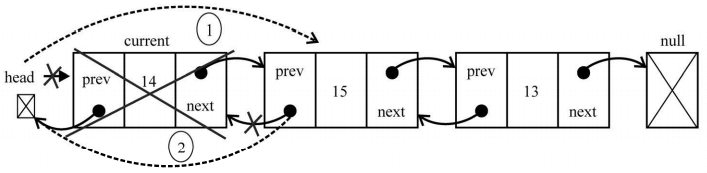
下一种场景是从最后一个位置移除元素。既然已经有了对最后一个元素的引用(tail),我们就不需要为找到它而迭代列表。这样我们也就可以把tail的引用赋给current变量(行{4})。接下来,需要把tail的引用更新为列表中倒数第二个元素(current.prev,或者tail.prev 也可以)。既然tail指向了倒数第二个元素,我们就只需要把next指针更新为null(tail.next=null)。下图演示了这一行为:

第三种也是最后一种场景:从列表中间移除一个元素。首先需要迭代列表,直到到达要找的位置(行{5})。current变量所引用的就是要移除的元素。那么要移除它,我们可以通过更新previous.next和current.next.prev的引用,在列表中跳过它。因此,previous.next将指向current.next,而current.next.prev将指向previous,如下图所示:
【完整代码】
双向链表的完整代码如下所示
function DoublyLinkedList() { let Node = function(element){ this.element = element; this.next = null; this.prev = null; //NEW }; let length = 0; let head = null; let tail = null; //NEW this.append = function(element){ let node = new Node(element), current; if (head === null){ //first node on list head = node; tail = node; //NEW } else { //attach to the tail node //NEW tail.next = node; node.prev = tail; tail = node; } length++; //update size of list }; this.insert = function(position, element){ //check for out-of-bounds values if (position >= 0 && position <= length){ let node = new Node(element), current = head, previous, index = 0; if (position === 0){ //add on first position if (!head){ //NEW head = node; tail = node; } else { node.next = current; current.prev = node; //NEW {1} head = node; } } else if (position === length) { //last item //NEW current = tail; // {2} current.next = node; node.prev = current; tail = node; } else { while (index++ < position){ //{3} previous = current; current = current.next; } node.next = current; previous.next = node; current.prev = node; //NEW node.prev = previous; //NEW } length++; //update size of list return true; } else { return false; } }; this.removeAt = function(position){ //check for out-of-bounds values if (position > -1 && position < length){ let current = head, previous, index = 0; //removing first item if (position === 0){ head = current.next; // {1} //if there is only one item, then we update tail as well //NEW if (length === 1){ // {2} tail = null; } else { head.prev = null; // {3} } } else if (position === length-1){ //last item //NEW current = tail; // {4} tail = current.prev; tail.next = null; } else { while (index++ < position){ // {5} previous = current; current = current.next; } //link previous with current's next - skip it to remove previous.next = current.next; // {6} current.next.prev = previous; //NEW } length--; return current.element; } else { return null; } }; this.remove = function(element){ let index = this.indexOf(element); return this.removeAt(index); }; this.indexOf = function(element){ let current = head, index = -1; //check first item if (element == current.element){ return 0; } index++; //check in the middle of the list while(current.next){ if (element == current.element){ return index; } current = current.next; index++; } //check last item if (element == current.element){ return index; } return -1; }; this.isEmpty = function() { return length === 0; }; this. size = function() { return length; }; this.toString = function(){ let current = head, s = current ? current.element : ''; while(current && current.next){ current = current.next; s += ', ' + current.element; } return s; }; this.inverseToString = function() { let current = tail, s = current ? current.element : ''; while(current && current.prev){ current = current.prev; s += ', ' + current.element; } return s; }; this.print = function(){ console.log(this.toString()); }; this.printInverse = function(){ console.log(this.inverseToString()); }; this.getHead = function(){ return head; }; this.getTail = function(){ return tail; } }
【ES6】
ES6版本的代码如下所示
let DoublyLinkedList2 = (function () { class Node { constructor(element) { this.element = element; this.next = null; this.prev = null; //NEW } } const length = new WeakMap(); const head = new WeakMap(); const tail = new WeakMap(); //NEW class DoublyLinkedList2 { constructor () { length.set(this, 0); head.set(this, null); tail.set(this, null); } append(element) { let node = new Node(element), current, _tail; if (this.getHead() === null) { //first node on list head.set(this, node); tail.set(this, node); //NEW } else { //attach to the tail node //NEW _tail = this.getTail(); _tail.next = node; node.prev = _tail; tail.set(this, node); } //update size of list let l = this.size(); l++; length.set(this, l); } insert(position, element) { //check for out-of-bounds values if (position >= 0 && position <= this.size()) { let node = new Node(element), current = this.getHead(), previous, index = 0; if (position === 0) { //add on first position if (!this.getHead()) { //NEW head.set(this, node); tail.set(this, node); } else { node.next = current; current.prev = node; //NEW {1} head.set(this, node); } } else if (position === this.size()) { //last item //NEW current = tail; // {2} current.next = node; node.prev = current; tail.set(this, node); } else { while (index++ < position) { //{3} previous = current; current = current.next; } node.next = current; previous.next = node; current.prev = node; //NEW node.prev = previous; //NEW } //update size of list let l = this.size(); l++; length.set(this, l); return true; } else { return false; } } removeAt(position) { //check for out-of-bounds values if (position > -1 && position < this.size()) { let _head = this.getHead(), _tail = this.getTail(), current = _head, previous, index = 0; //removing first item if (position === 0) { _head = current.next; // {1} //if there is only one item, then we update tail as well //NEW if (this.size() === 1) { // {2} _tail = null; } else { _head.prev = null; // {3} } } else if (position === this.size() - 1) { //last item //NEW current = _tail; // {4} _tail = current.prev; _tail.next = null; } else { while (index++ < position) { // {5} previous = current; current = current.next; } //link previous with current's next - skip it to remove previous.next = current.next; // {6} current.next.prev = previous; //NEW } head.set(this,_head); tail.set(this,_tail); //update size of list let l = this.size(); l--; length.set(this, l); return current.element; } else { return null; } } remove(element) { let index = this.indexOf(element); return this.removeAt(index); } indexOf(element) { let current = this.getHead(), index = -1; //check first item if (element == current.element) { return 0; } index++; //check in the middle of the list while (current.next) { if (element == current.element) { return index; } current = current.next; index++; } //check last item if (element == current.element) { return index; } return -1; } isEmpty() { return this.size() === 0; } size() { return length.get(this); } toString() { let current = this.getHead(), s = current ? current.element : ''; while (current && current.next) { current = current.next; s += ', ' + current.element; } return s; } inverseToString() { let current = this.getTail(), s = current ? current.element : ''; while (current && current.prev) { current = current.prev; s += ', ' + current.element; } return s; } print() { console.log(this.toString()); } printInverse() { console.log(this.inverseToString()); } getHead() { return head.get(this); } getTail() { return tail.get(this); } } return DoublyLinkedList2; })();
循环链表
循环链表可以像链表一样只有单向引用,也可以像双向链表一样有双向引用。循环链表和链表之间唯一的区别在于,最后一个元素指向下一个元素的指针(tail.next)不是引用null,而是指向第一个元素(head),如下图所示
双向循环链表有指向head元素的tail.next,和指向tail元素的head.prev
【完整代码】
循环链表的代码如下所示
function CircularLinkedList() { let Node = function(element){ this.element = element; this.next = null; }; let length = 0; let head = null; this.append = function(element){ let node = new Node(element), current; if (head === null){ //first node on list head = node; } else { current = head; //loop the list until find last item while(current.next !== head){ //last element will be head instead of NULL current = current.next; } //get last item and assign next to added item to make the link current.next = node; } //set node.next to head - to have circular list node.next = head; length++; //update size of list }; this.insert = function(position, element){ //check for out-of-bounds values if (position >= 0 && position <= length){ let node = new Node(element), current = head, previous, index = 0; if (position === 0){ //add on first position if(!head){ // if no node in list head = node; node.next = head; }else{ node.next = current; //update last element while(current.next !== head){ //last element will be head instead of NULL current = current.next; } head = node; current.next = head; } } else { while (index++ < position){ previous = current; current = current.next; } node.next = current; previous.next = node; } length++; //update size of list return true; } else { return false; } }; this.removeAt = function(position){ //check for out-of-bounds values if (position > -1 && position < length){ let current = head, previous, index = 0; //removing first item if (position === 0){ while(current.next !== head){ //needs to update last element first current = current.next; } head = head.next; current.next = head; } else { //no need to update last element for circular list while (index++ < position){ previous = current; current = current.next; } //link previous with current's next - skip it to remove previous.next = current.next; } length--; return current.element; } else { return null; } }; this.remove = function(element){ let index = this.indexOf(element); return this.removeAt(index); }; this.indexOf = function(element){ let current = head, index = -1; //check first item if (element == current.element){ return 0; } index++; //check in the middle of the list while(current.next !== head){ if (element == current.element){ return index; } current = current.next; index++; } //check last item if (element == current.element){ return index; } return -1; }; this.isEmpty = function() { return length === 0; }; this.size = function() { return length; }; this.getHead = function(){ return head; }; this.toString = function(){ let current = head, s = current.element; while(current.next !== head){ current = current.next; s += ', ' + current.element; } return s.toString(); }; this.print = function(){ console.log(this.toString()); }; }
【ES6】
ES6版本的代码如下所示
let CircularLinkedList2 = (function () { class Node { constructor(element) { this.element = element; this.next = null; } } const length = new WeakMap(); const head = new WeakMap(); class CircularLinkedList2 { constructor () { length.set(this, 0); head.set(this, null); } append(element) { let node = new Node(element), current; if (this.getHead() === null) { //first node on list head.set(this, node); } else { current = this.getHead(); //loop the list until find last item while (current.next !== this.getHead()) { //last element will be head instead of NULL current = current.next; } //get last item and assign next to added item to make the link current.next = node; } //set node.next to head - to have circular list node.next = this.getHead(); //update size of list let l = this.size(); l++; length.set(this, l); } insert(position, element) { //check for out-of-bounds values if (position >= 0 && position <= this.size()) { let node = new Node(element), current = this.getHead(), previous, index = 0; if (position === 0) { //add on first position if(!this.getHead()) { // if no node in list head.set(this, node); node.next = this.getHead(); } else { node.next = current; //update last element while(current.next !== this.getHead()) { //last element will be head instead of NULL current = current.next; } head.set(this, node); current.next = this.getHead(); } } else { while (index++ < position) { previous = current; current = current.next; } node.next = current; previous.next = node; } //update size of list let l = this.size(); l++; length.set(this, l); return true; } else { return false; } } removeAt(position) { //check for out-of-bounds values if (position > -1 && position < this.size()) { let current = this.getHead(), previous, index = 0; //removing first item if (position === 0) { while (current.next !== this.getHead()) { //needs to update last element first current = current.next; } head.set(this, this.getHead().next); current.next = this.getHead(); } else { //no need to update last element for circular list while (index++ < position) { previous = current; current = current.next; } //link previous with current's next - skip it to remove previous.next = current.next; } let l = this.size(); l--; length.set(this, l); return current.element; } else { return null; } } remove(element) { let index = this.indexOf(element); return this.removeAt(index); } indexOf(element) { let current = this.getHead(), index = -1; //check first item if (element == current.element) { return 0; } index++; //check in the middle of the list while (current.next !== this.getHead()) { if (element == current.element) { return index; } current = current.next; index++; } //check last item if (element == current.element) { return index; } return -1; } isEmpty() { return this.size() === 0; } size() { return length.get(this); } getHead() { return head.get(this); } toString() { let current = this.getHead(), s = current.element; while (current.next !== this.getHead()) { current = current.next; s += ', ' + current.element; } return s.toString(); } print() { console.log(this.toString()); } } return CircularLinkedList2; })();