一、注解开发CRUD(比较简单,实用)
创建一个接口:IUserDao,负责用注解开发来实现获取数据
FindAll();查找所有用户:
//查询所有用户
@Select("select * from user")
List<User> findAll();
构建测试类,来输出一下对应的数据
/*
查找所有用户的信息
*/
@Test
public void testFindAll() throws IOException {
//5.使用代理对象执行方法
List<User> users=userDao.findAll();
for(User user:users){
System.out.println(user);
}
}
Insert:插入数据
@Insert("insert into user(username,birthday,sex,address) values(#{username},#{birthday},#{sex},#{address})")
void saveUser(User user);
利用测试类,创建方法来测试
/*
查找所有用户的信息
*/
@Test
public void testSaveUser() throws IOException {
//5.使用代理对象执行方法
User user=new User();
user.setUsername("小峰仔");
user.setSex("男");
userDao.saveUser(user);
}
Update:更新用户,设置参数是#{},通过id找到该用户并进行更新
/**
* 更新用户
*/
@Update("update user set username=#{username},birthday=#{birthday},sex=#{sex},address=#{address} where id=#{id}")
void updateUser(User user);
测试类进行测试
/*
更新操作
*/
@Test
public void testUpdateUser() throws IOException{
User user=new User();
user.setUsername("蛮吉");
user.setSex("男");
user.setBirthday(new Date());
user.setAddress("神兽国有维族窝窝乡独行族妖侠");
user.setId(95);
userDao.updateUser(user);
}
Delete:删除用户,根据id进行删除,如果参数是int,注解开发的参数随意
/**
* 删除用户
*/
@Delete("delete from user where id=#{uid}")
void deleteUser(int id);
测试类构造方法进行测试
/*
删除操作
*/
@Test
public void testDeleteUser() throws IOException{
userDao.deleteUser(90);
}
Select:查找单个用户,根据id查询
/**
* 查找单个用户
*/
@Select("select * from user where id=#{uid}")
User findById(int id);
测试类构造方法
/*
查找单个用户的信息
*/
@Test
public void testFindById() throws IOException {
//5.使用代理对象执行方法
User user=userDao.findById(95);
System.out.println(user);
}
Select:根据姓名模糊查询,这里用没有%出现,因此我们参数里要加上%
/**
* 根据用户名称模糊查询
*/
@Select("select * from user where username like #{name}")
List<User> findByName(String username);
测试类构造方法
/*
查找单个用户的信息
*/
@Test
public void testFindByName() throws IOException {
//5.使用代理对象执行方法
String name="%王%";
List<User> users=userDao.findByName(name);
for(User user:users)
System.out.println(user);
}
Select:汇总人员总数
@Select("select count(*) from user")
int findTotalUser();
测试类构造方法
@Test
public void testTotalUser() throws IOException{
int total=userDao.findTotalUser();
System.out.println(total);
}
二、注解开发,一对一,一对多(User,Account)
一对一开发:
构建Account类,和接口类IAccountDao,
每个account账户对应一个用户,根据建表的规则,uid是引用来自user表的id主键,根据他可以找到对应的用户信息
由于是查询一个,加载方式为eager:立即加载
@Select("select * from account")
@Results(id="accountMap",value = {
@Result(id=true,column = "id",property = "id"),
@Result(column = "uid",property = "uid"),
@Result(column = "money",property = "money"),
@Result(column = "uid",property = "user",one=@One(select = "com.itheima.dao.IUserDao.findById",fetchType = FetchType.EAGER)),
})
List<Account> findAll();
@Select("select * from account where uid=#{userId}")
List<Account> findAccountByUid(Integer userId);
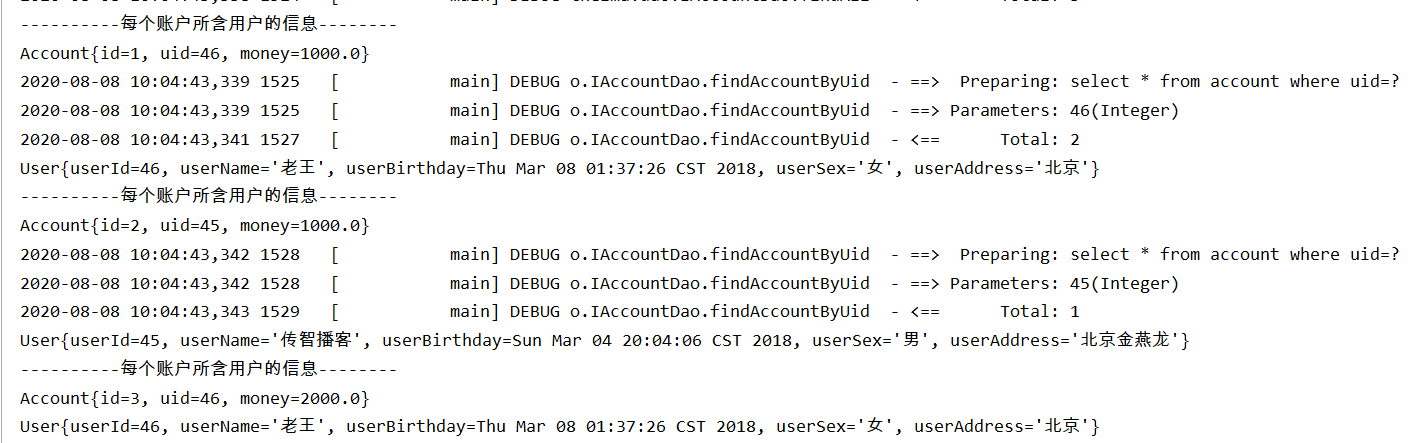
测试类输出一下:
/*
查找账户对应的用户的信息
*/
@Test
public void testFindAll() throws IOException {
//5.使用代理对象执行方法
List<Account> accounts=accountDao.findAll();
for(Account account:accounts){
System.out.println("----------每个账户所含用户的信息--------");
System.out.println(account);
System.out.println(account.getUser());
}
}
输出:
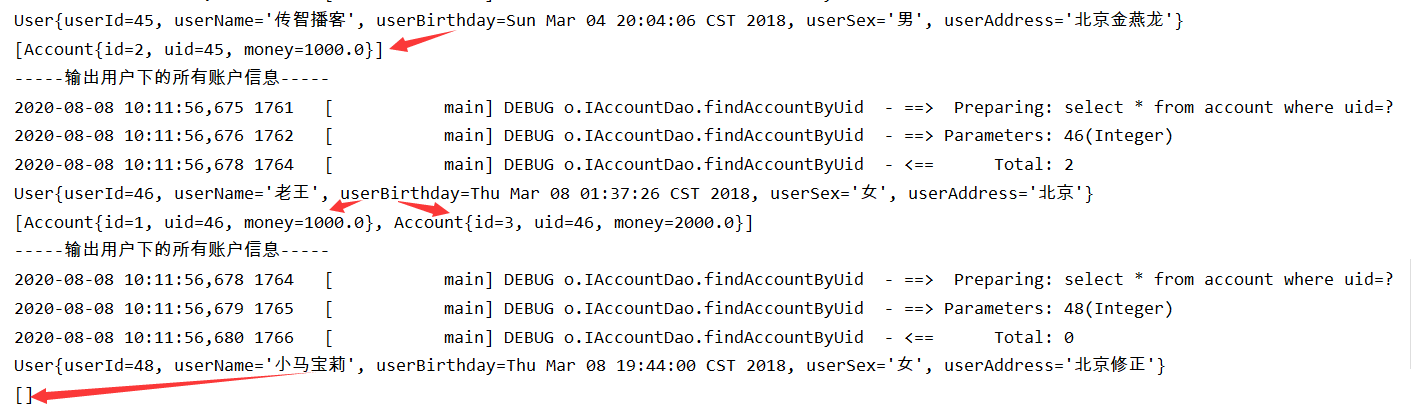
一对多:一个用户可以有多个账户
当表里的字段与用户类里的字段不一致时,我们就需要使用@Results来对他进行命名
在这里是一对多,因此用@Many,同时挑选合适的根据id查找账户的方法名,这里是多个账户的查询,采取了缓存加载lazy
//查询所有用户
@Select("select * from user")
@Results(id="userMap",value={
@Result(id=true,column = "id" ,property = "userId"),
@Result(column = "username" ,property = "userName"),
@Result(column = "sex" ,property = "userSex"),
@Result(column = "birthday" ,property = "userBirthday"),
@Result(column = "address" ,property = "userAddress"),
@Result(property = "accounts",column = "id",many=@Many(select = "com.itheima.dao.IAccountDao.findAccountByUid",fetchType = FetchType.LAZY))
})
List<User> findAll();
构建测试类:
/*
查找用户下所有账户信息
*/
@Test
public void testFindAll() throws IOException {
//5.使用代理对象执行方法
List<User> users=userDao.findAll();
for(User user:users){
System.out.println("-----输出用户下的所有账户信息-----");
System.out.println(user);
System.out.println(user.getAccounts());
}
}
输出: