Spring MVC
SpringMVC中扮演关键角色的DispatcherServlet类。
1 DispatcherServlet
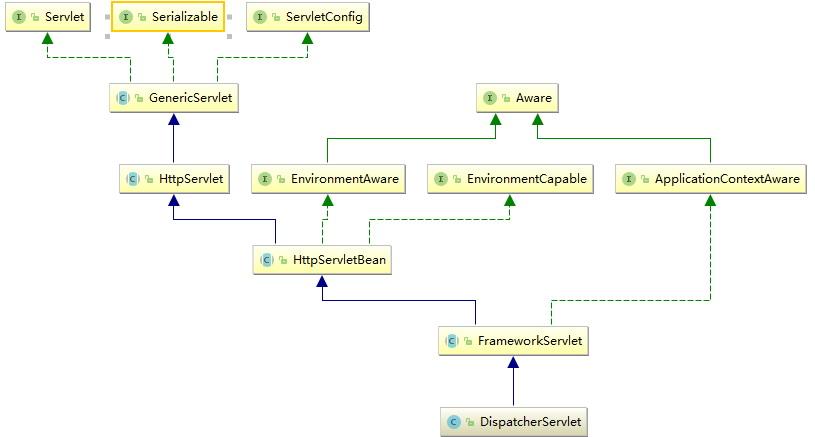
1.1DispatcherServlet 类图
1.2 初始准备阶段
1.2.1 init()
HttpServletBean类中init()方法

public final void init() throws ServletException { if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) { this.logger.debug("Initializing servlet '" + this.getServletName() + "'"); } try { PropertyValues pvs = new HttpServletBean.ServletConfigPropertyValues(this.getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties); BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this); ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(this.getServletContext()); bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, this.getEnvironment())); this.initBeanWrapper(bw); bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true); } catch (BeansException var4) { this.logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + this.getServletName() + "'", var4); throw var4; } this.initServletBean(); if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) { this.logger.debug("Servlet '" + this.getServletName() + "' configured successfully"); } }
DispatcherServlet的初始化过程主要是通过当前的servlet类型实例转换为BeanWrapper类型实例,
以便使用Spring中提供的注入功能进行对应属性的注入。如ContextAttribute、contextClass、 namespace
contextConfigLocation等,都可以在web.xml文件中以初始化参数的方式配置在servlet的声明中。
1.2.2 initServletBean()
FrameworkServlet的initServletBean()

this.webApplicationContext = this.initWebApplicationContext(); this.initFrameworkServlet();

this.webApplicationContext = this.initWebApplicationContext(); this.initFrameworkServlet(); protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() { //从ServletContext中获得根容器 WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(this.getServletContext()); WebApplicationContext wac = null; if (this.webApplicationContext != null) { wac = this.webApplicationContext; if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) { ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)wac; if (!cwac.isActive()) { if (cwac.getParent() == null) { cwac.setParent(rootContext); } this.configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac); } } } if (wac == null) { wac = this.findWebApplicationContext(); } if (wac == null) { wac = this.createWebApplicationContext(rootContext); } if (!this.refreshEventReceived) { this.onRefresh(wac); } if (this.publishContext) { String attrName = this.getServletContextAttributeName(); this.getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac); if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) { this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + this.getServletName() + "' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]"); } } return wac; }
createWebApplicationContext ()以根容器为父容器创建新的容器,所以在新创建的容器中找不到的bean可以在根容器中找到。
1.2.3 onRefresh()

protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) { this.initStrategies(context); } protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) { this.initMultipartResolver(context); this.initLocaleResolver(context); this.initThemeResolver(context); this.initHandlerMappings(context); this.initHandlerMappings(context); this.initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context); this.initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context); this.initViewResolvers(context); this.initFlashMapManager(context); }
这里就是DispatherServlet初始化的地方。其中我们重点关注initHandlerMappings()、 initHandlerMappings();
以initHandlerMappings()为例,主要是从容器中获得类类型为HandlerMapping.class的bean并存储在list中。如果找不到则获取DispatchServlet.properties文件中默认的两个HandMapping.

# Default implementation classes for DispatcherServlet's strategy interfaces. # Used as fallback when no matching beans are found in the DispatcherServlet context. # Not meant to be customized by application developers. org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver org.springframework.web.servlet.ThemeResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.theme.FixedThemeResolver org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping=org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping, org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter, org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter, org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver, org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.ResponseStatusExceptionResolver, org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver org.springframework.web.servlet.RequestToViewNameTranslator=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver org.springframework.web.servlet.FlashMapManager=org.springframework.web.servlet.support.SessionFlashMapManager
static { try { ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource("DispatcherServlet.properties", DispatcherServlet.class); defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); } catch (IOException var1) { throw new IllegalStateException("Could not load 'DispatcherServlet.properties': " + var1.getMessage()); } }

private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) { this.handlerMappings = null; if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) { Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false); if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) { this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList(matchingBeans.values()); AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings); } } else { try { HandlerMapping hm = (HandlerMapping)context.getBean("handlerMapping", HandlerMapping.class); this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm); } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException var3) { ; } } if (this.handlerMappings == null) { this.handlerMappings = this.getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class); if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) { this.logger.debug("No HandlerMappings found in servlet '" + this.getServletName() + "': using default"); } } }
1.3功能实现
一句话概括流程:根据request对象获得对应的handler,然后得到对应view,最后对view进行渲染。
DispatcherServlet中doService()、doDispatch().
1.3.1 doDispatch()

protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null; boolean multipartRequestParsed = false; WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); try { ModelAndView mv = null; Exception dispatchException = null; try { processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request); // Determine handler for the current request. mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) { noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); return; } // Determine handler adapter for the current request. HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); // Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler. String method = request.getMethod(); boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method); if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) { long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified); } if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) { return; } } if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { return; } // Actually invoke the handler. mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return; } applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv); mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv); } catch (Exception ex) { dispatchException = ex; } catch (Throwable err) { // As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well, // making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios. dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err); } processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); } catch (Exception ex) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex); } catch (Throwable err) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err)); } finally { if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion if (mappedHandler != null) { mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response); } } else { // Clean up any resources used by a multipart request. if (multipartRequestParsed) { cleanupMultipart(processedRequest); } } } }
1.3.1.1 getHandler()
完成URL与Handlerd的映射关系。

protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { for (HandlerMapping hm : this.handlerMappings) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace( "Testing handler map [" + hm + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'"); } HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request); if (handler != null) { return handler; } } return null; }
简单理解从request中获得url,使用HandlerMapping获得HandlerExecutionChain,注意,这个执行链中包括了HandlerInterceptor和handler。
HandlerInterceptor接口
如同拦截器一般,依次执行上述方法。
1.3.1.2 getHandlerAdapter

protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException { for (HandlerAdapter ha : this.handlerAdapters) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Testing handler adapter [" + ha + "]"); } if (ha.supports(handler)) { return ha; } } throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler + "]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler"); }
getHandlerAdapter方法,如同名字一样,获得handler的适配器,handler的实现多种多样,但是我们要定义一个统一的接口来使用handler,
ex:

public class HttpRequestHandlerAdapter implements HandlerAdapter { @Override public boolean supports(Object handler) { return (handler instanceof HttpRequestHandler); } @Override public ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { ((HttpRequestHandler) handler).handleRequest(request, response); return null; } @Override public long getLastModified(HttpServletRequest request, Object handler) { if (handler instanceof LastModified) { return ((LastModified) handler).getLastModified(request); } return -1L; } } public class SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter implements HandlerAdapter { @Override public boolean supports(Object handler) { return (handler instanceof Controller); } @Override public ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { return ((Controller) handler).handleRequest(request, response); } @Override public long getLastModified(HttpServletRequest request, Object handler) { if (handler instanceof LastModified) { return ((LastModified) handler).getLastModified(request); } return -1L; } } public class SimpleServletHandlerAdapter implements HandlerAdapter { @Override public boolean supports(Object handler) { return (handler instanceof Servlet); } @Override public ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { ((Servlet) handler).service(request, response); return null; } @Override public long getLastModified(HttpServletRequest request, Object handler) { return -1; } }
参考资料:
《SPRING技术内幕:深入解析SPRING架构与设计原理》
《Spring源码深度解析》
《深入分析Java Web技术内幕》
