大厂算法面试之leetcode精讲21.树
视频讲解(高效学习):点击学习
目录:
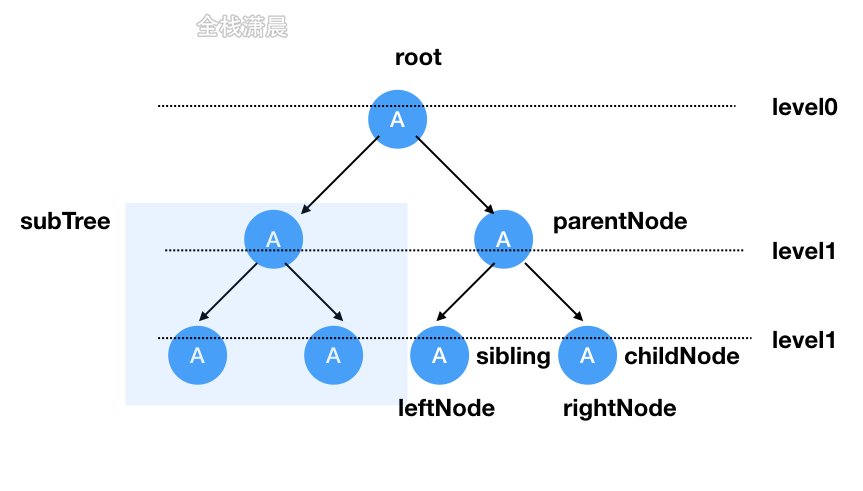
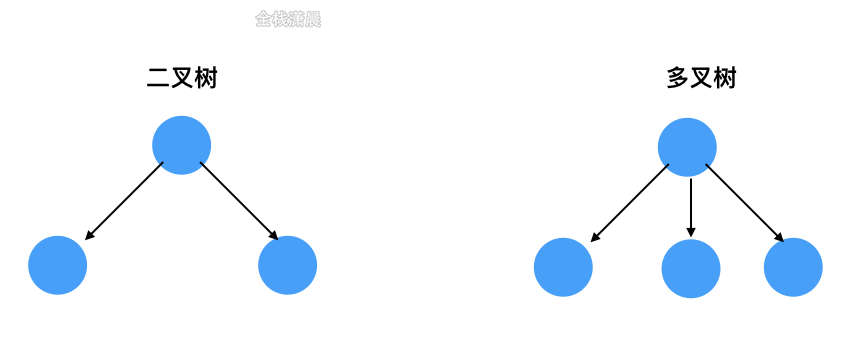
树这种数据结构包括根节点root,左右节点,子树中又有父节点,子节点,兄弟节点,没有子节点的成为叶子节点,树分为二叉树和多叉树
List 就是特殊化的tree,Tree就是特殊化的Graph
二分搜索树
二分搜索树(英语:Binary Search Tree),也称为 有序二叉树或排序二叉树。满足以下几个条件:
- 若它的左子树不为空,左子树上所有节点的值都小于它的根节点。
- 若它的右子树不为空,右子树上所有的节点的值都大于它的根节点。
- 它的左、右子树也都是二分搜索树。
二分搜索树的优势:不仅可以查找数据,还可以高效的插入、删除数据
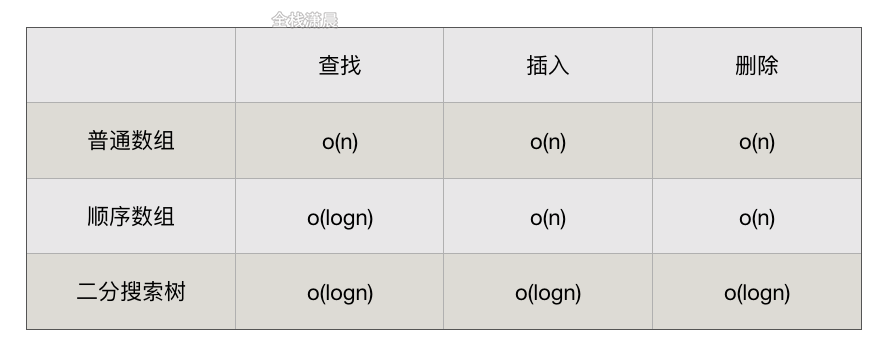
注意二分搜索树不一定是完全二叉树
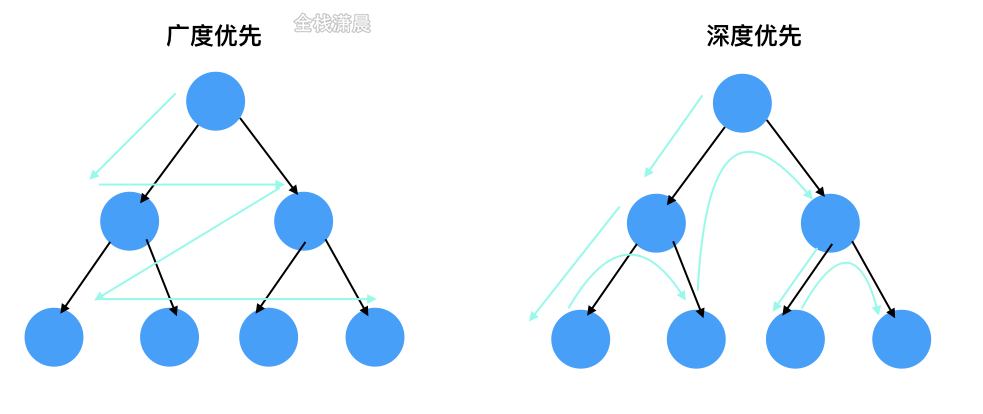
树的遍历
-
深度优先
-
广度优先
- 前序:根-左-右
- 中序:左-根-右
- 后序:左-右-根
144. 二叉树的前序遍历(easy)
94. 二叉树的中序遍历 (easy)
145. 二叉树的后序遍历 (easy)
方法1.递归
js:
//时间复杂度O(n),n为节点个树,空间复杂度O(n),即递归的空间开销(树的高度),最坏的情况下树是链表,所以是O(n),平均空间复杂度O(logn)
//前序遍历:
var preorderTraversal = function(root, res = []) {
if (!root) return res;
res.push(root.val);
preorderTraversal(root.left, res)
preorderTraversal(root.right, res)
return res;
};
//中序遍历:
var inorderTraversal = function(root, res = []) {
if (!root) return res;
inorderTraversal(root.left, res);
res.push(root.val);
inorderTraversal(root.right, res);
return res;
};
//后序遍历:
var postorderTraversal = function(root, res = []) {
if (!root) return res;
postorderTraversal(root.left, res);
postorderTraversal(root.right, res);
res.push(root.val);
return res;
};
Java:
//时间复杂度O(n),n为节点个树,空间复杂度O(n),即递归的空间开销(树的高度),最坏的情况下树是链表,所以是O(n),平均空间复杂度O(logn)
//前序遍历
class Solution {
ArrayList<Integer> preOrderReverse(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer>();
preOrder(root, result);
return result;
}
void preOrder(TreeNode root, ArrayList<Integer> result) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
result.add(root.val);
preOrder(root.left, result);
preOrder(root.right, result);
}
}
// 中序遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
inorder(root, res);
return res;
}
void inorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
inorder(root.left, list);
list.add(root.val);
inorder(root.right, list);
}
}
// 后序遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
postorder(root, res);
return res;
}
void postorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
postorder(root.left, list);
postorder(root.right, list);
list.add(root.val);
}
}
方法2.迭代
js:
// 时间复杂度O(n),n为节点个树,空间复杂度O(n),显示栈的空间开销
// 前序遍历:中左右
// 压栈顺序:右左中
var preorderTraversal = function(root, res = []) {
const stack = [];
if (root) stack.push(root);
while(stack.length) {
const node = stack.pop();
if(!node) {
res.push(stack.pop().val);
continue;
}
if (node.right) stack.push(node.right); // 右
if (node.left) stack.push(node.left); // 左
stack.push(node); // 中
stack.push(null);
};
return res;
};
// 中序遍历:左中右
// 压栈顺序:右中左
var inorderTraversal = function(root, res = []) {
const stack = [];
if (root) stack.push(root);
while(stack.length) {
const node = stack.pop();
if(!node) {
res.push(stack.pop().val);
continue;
}
if (node.right) stack.push(node.right); // 右
stack.push(node); // 中
stack.push(null);
if (node.left) stack.push(node.left); // 左
};
return res;
};
// 后续遍历:左右中
// 压栈顺序:中右左
var postorderTraversal = function(root, res = []) {
const stack = [];
if (root) stack.push(root);
while(stack.length) {
const node = stack.pop();
if(!node) {
res.push(stack.pop().val);
continue;
}
stack.push(node); // 中
stack.push(null);
if (node.right) stack.push(node.right); // 右
if (node.left) stack.push(node.left); // 左
};
return res;
};
Java:
// 时间复杂度O(n),n为节点个树,空间复杂度O(n),显示栈的空间开销
// 前序遍历顺序:中-左-右,入栈顺序:中-右-左
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new LinkedList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> st = new Stack<>();
if (root != null) st.push(root);
while (!st.empty()) {
TreeNode node = st.peek();
if (node != null) {
st.pop();
if (node.right!=null) st.push(node.right);
if (node.left!=null) st.push(node.left);
st.push(node);
st.push(null);
} else {
st.pop();
node = st.peek();
st.pop();
result.add(node.val);
}
}
return result;
}
}
// 中序遍历顺序: 左-中-右 入栈顺序: 左-右
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new LinkedList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> st = new Stack<>();
if (root != null) st.push(root);
while (!st.empty()) {
TreeNode node = st.peek();
if (node != null) {
st.pop();
if (node.right!=null) st.push(node.right);
st.push(node);
st.push(null);
if (node.left!=null) st.push(node.left);
} else {
st.pop();
node = st.peek();
st.pop();
result.add(node.val);
}
}
return result;
}
}
// 后序遍历顺序 左-右-中 入栈顺序:中-左-右 出栈顺序:中-右-左, 最后翻转结果
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new LinkedList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> st = new Stack<>();
if (root != null) st.push(root);
while (!st.empty()) {
TreeNode node = st.peek();
if (node != null) {
st.pop();
st.push(node);
st.push(null);
if (node.right!=null) st.push(node.right);
if (node.left!=null) st.push(node.left);
} else {
st.pop();
node = st.peek();
st.pop();
result.add(node.val);
}
}
return result;
}
}
98. 验证二叉搜索树 (medium)
方法1.递归
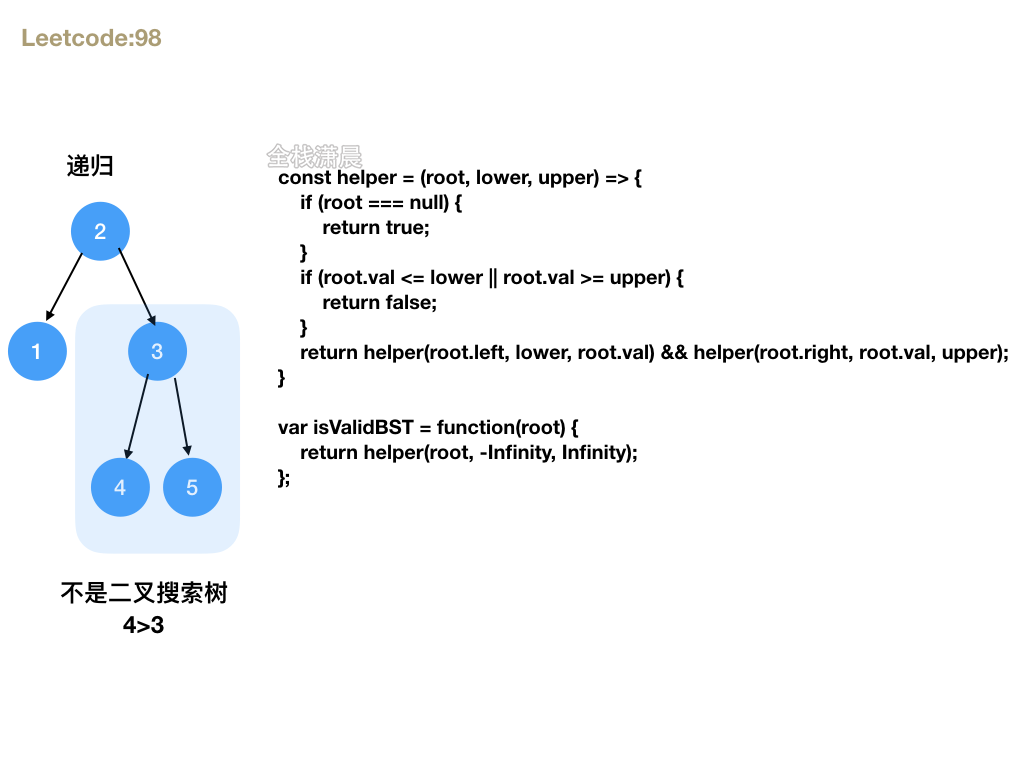
- 思路:利用二叉搜索树的性质,每个节点都大于它左子树所有节点,小于右子树上所有节点,并且每个节点左右子树不为空,那它的左右子树也是二叉搜索树。我们可以递归验证每个节点的左右子树。
- 复杂度分析:时间复杂度 :
O(n),n是二叉树节点的个树。空间复杂度 :O(n),n是递归的层数,最差的情况下二叉树是一条链,树高n,也就是总共n层
Js:
const helper = (root, lower, upper) => {
if (root === null) {
return true;
}
if (root.val <= lower || root.val >= upper) {//终止条件 不满足二叉搜索树的性质
return false;
}
//递归左右子树
return helper(root.left, lower, root.val) && helper(root.right, root.val, upper);
}
var isValidBST = function(root) {
//定义low=-Infinity,让所有值都大于low
//定义upper=Infinity,让所有值都小于upper
return helper(root, -Infinity, Infinity);
};
Java:
class Solution {
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
return helper(root, Long.MIN_VALUE, Long.MAX_VALUE);
}
public boolean helper(TreeNode root, long lower, long upper) {
if (root == null) {
return true;
}
if (root.val <= lower || root.val >= upper) {
return false;
}
return helper(root.left, lower, root.val) && helper(root.right, root.val, upper);
}
}
方法2:中序遍历
- 思路:从二叉搜素树的性质可知,中序遍历二叉搜索树,得到的就是升序的数组
- 复杂度分析:时间复杂度 :
O(n),每个元素被访问一次。空间复杂度 :O(n),中序遍历用栈存储元素,需要额外的O(n)空间
Js:
//非递归版中序遍历
var isValidBST = function(root) {
let stack = [];
let inorder = -Infinity;
while (stack.length || root !== null) {
while (root !== null) {
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
if (root.val <= inorder) {
return false;
}
inorder = root.val;
root = root.right;
}
return true;
};
//递归版中序遍历
var isValidBST = function (root) {
let arr = [];
const buildArr = (root) => {
if (root) {
buildArr(root.left);
arr.push(root.val);
buildArr(root.right);
}
}
buildArr(root);
for (let i = 1; i < arr.length; ++i) {
if (arr[i] <= arr[i - 1])
return false;
}
return true;
};
Java:
class Solution {
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
double inorder = -Double.MAX_VALUE;
while (!stack.isEmpty() || root != null) {
while (root != null) {
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
if (root.val <= inorder) {
return false;
}
inorder = root.val;
root = root.right;
}
return true;
}
}
236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先 (medium)
方法1.递归
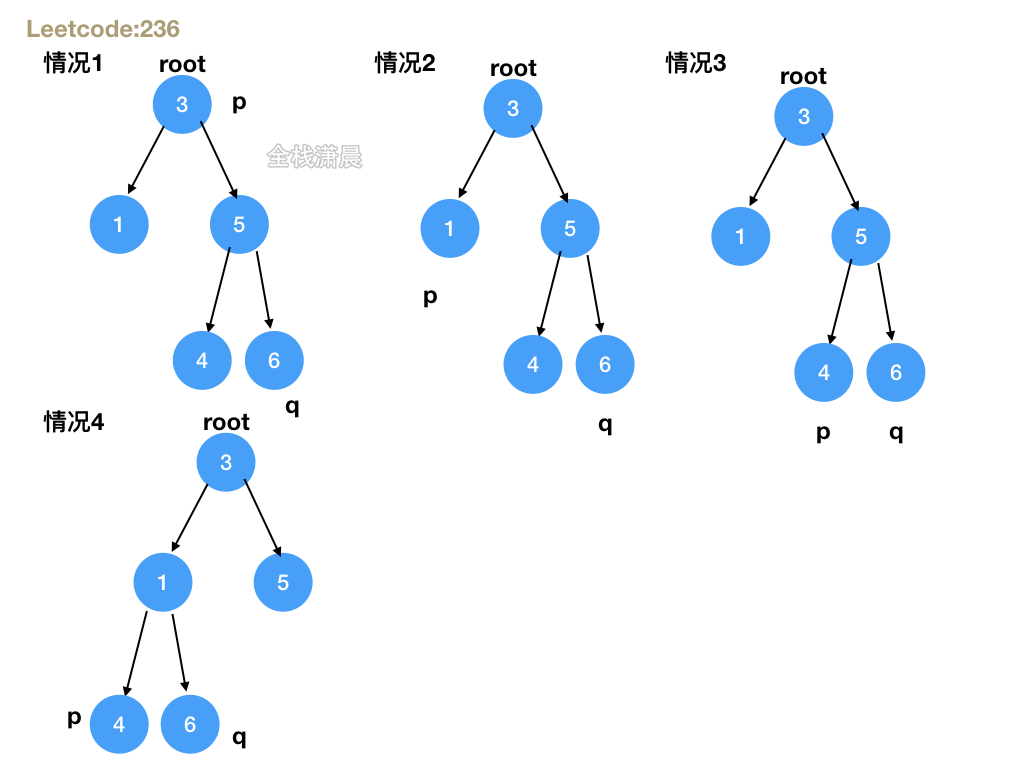
- 思路:分四种情况,1.root是null或者root等于p或q,说明root是p,q的公共祖先,2.递归左右子树,如果左右子树递归函数返回的都不为空,则root就是p,q的公共祖先,3.左子树递归函数返回的值为空,则p,q都在右子树,4.右子树递归函数返回的值为空,则p,q都在左子树
- 复杂度分析:时间复杂度 :
O(n),n是二叉树节点的个树,空间复杂度 :O(n),n是递归的层
Js:
var lowestCommonAncestor = function(root, p, q) {
// 1. 确定递归的函数
const travelTree = function(root,p,q) {
// 2. 确定递归终止条件
if(root === null || root === p||root === q) {
return root;
}
// 3. 确定递归单层逻辑
let left = travelTree(root.left,p,q);
let right = travelTree(root.right,p,q);
//如果在某一个节点的左右子树都能找到p和q说明这个节点就是公共祖先
if(left !== null&&right !== null) {
return root;
}
if(left ===null) {//如果左子树没找到就说明p,q都在右子树
return right;
}
return left;//如果右子树没找到就说明p,q都在左子树
}
return travelTree(root,p,q);//递归开始
};
Java:
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
return travelTree(root, p, q);
}
public TreeNode travelTree(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (root == null || root == p || root == q) {
return root;
}
TreeNode left = travelTree(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode right = travelTree(root.right, p, q);
if (left != null && right != null) {// 左右子树分别找到了,说明此时的root就是要求的结果
return root;
}
if (left == null) {
return right;
}
return left;
}
}
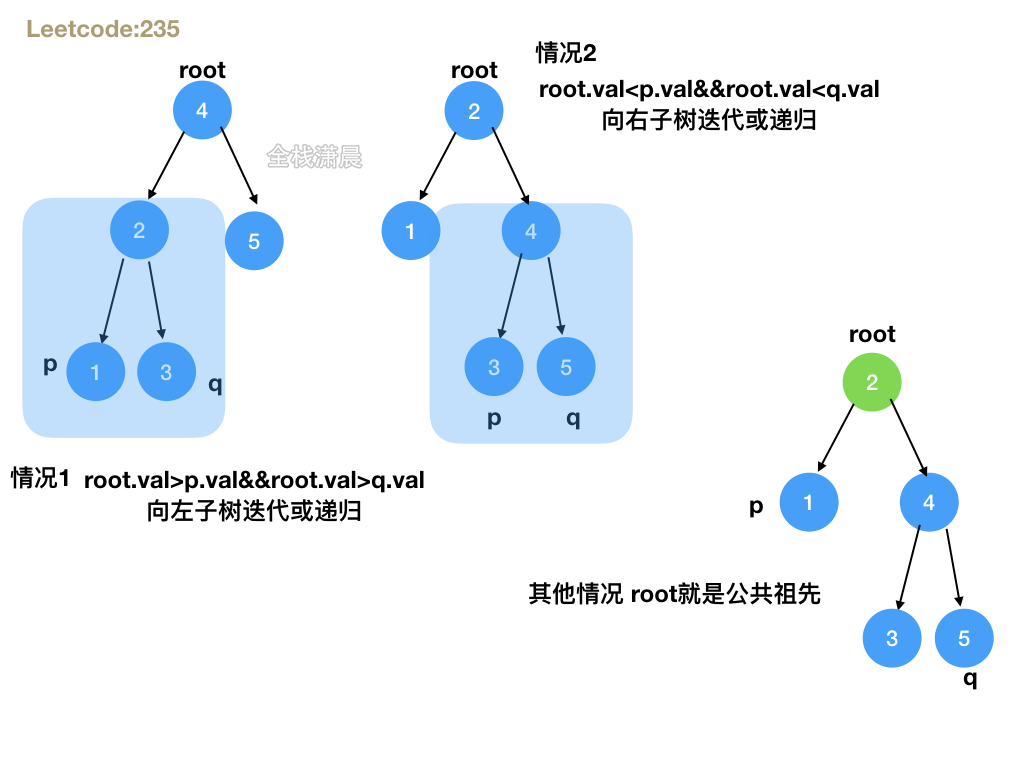
235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先 (easy)
方法1:从二叉搜索树中不断向左右子树寻找p或q的路径,最后寻找两个路径的第一个相同的节点,时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(n)
方法2:递归
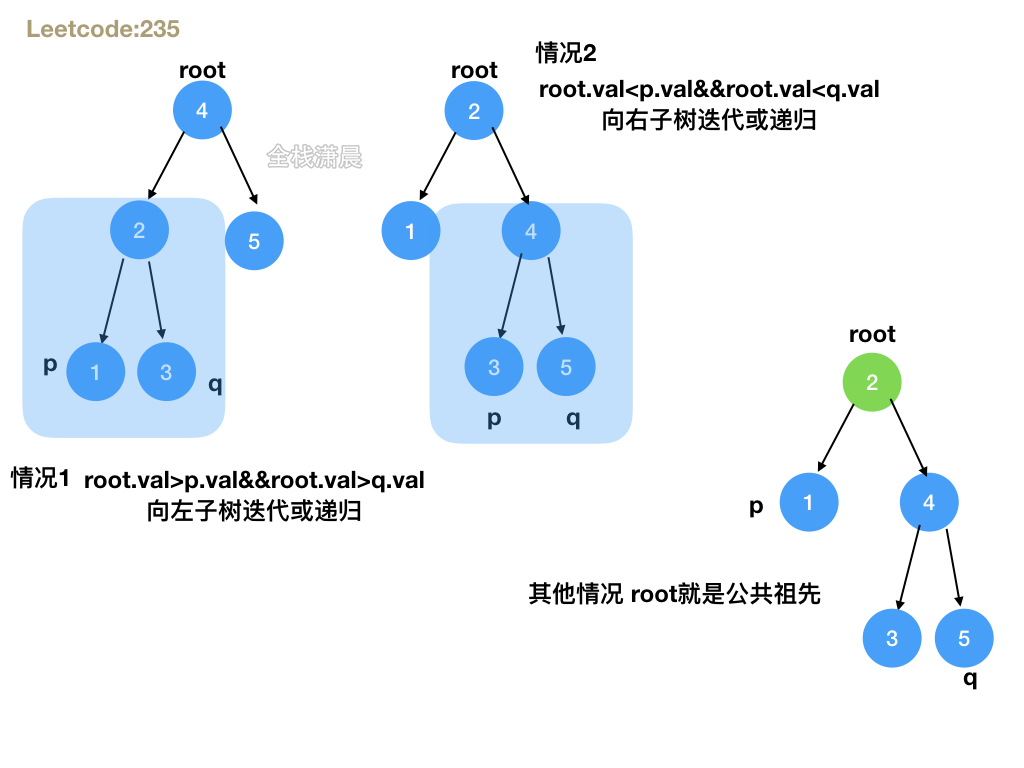
- 思路:分为三种情况,1.root节点大于p并且大于q,说明p和q都在root的左子树, 2.root节点小于p并且小于q,说明p和q都在root的右子树,3.其他情况比如root等于p或q,说明root就是公共祖先,前两种情况直接递归左右子树,第3种情况直接返回root
- 复杂度分析:时间复杂度 :
O(n),n是二叉树节点的个树,空间复杂度 :O(n),n是递归的层数,最坏情况和n相等,此时的树是一个链表
Js:
var lowestCommonAncestor = function(root, p, q) {
if(root === null) {//递归终止条件
return root;
}
//如果root节点大于p并且大于q,说明p和q都在root的左子树
if(root.val>p.val&&root.val>q.val) {
let left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
return left !== null&&left;
}
//如果root节点小于p并且小于q,说明p和q都在root的右子树
if(root.val<p.val&&root.val<q.val) {
let right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
return right !== null&&right;
}
return root;//如果上述条件都不满足说明root就是公共祖先
};
Java:
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val) return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
if (root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val) return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
return root;
}
}
方法3:迭代
- 思路:和递归的情况一样,只不过用root变量不断迭代左右子树
- 复杂度分析:时间复杂度 :
O(n),空间复杂度 :O(1),n是二叉树节点的个树
js:
var lowestCommonAncestor = function(root, p, q) {
while(root) {
if(root.val>p.val&&root.val>q.val) {
root = root.left;
}else if(root.val<p.val&&root.val<q.val) {
root = root.right;
}else {
return root;
}
}
return null;
};
java:
//java
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
while (true) {
if (root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val) {
root = root.left;
} else if (root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val) {
root = root.right;
} else {
break;
}
}
return root;
}
}
102. 二叉树的层序遍历 (medium)
方法1.广度优先遍历
- 思路:准备一个队列,将根节点加入队列,当队列不为空的时候循环队列,每次循环拿到当前队列的大小,在循环当前层的每个元素,然后加入输出数组ret中,如果这个元素存在左右节点则将左右节点加入队列
- 复杂度分析:时间复杂度
O(n),每个点进队出队各一次,故渐进时间复杂度为O(n)。空间复杂度O(n),队列中元素的个数不超过 n 个
Js:
var levelOrder = function(root) {
const ret = [];
if (!root) {
return ret;
}
const q = [];
q.push(root);//初始队列
while (q.length !== 0) {
const currentLevelSize = q.length;//当前层节点的数量
ret.push([]);//新的层推入数组
for (let i = 1; i <= currentLevelSize; ++i) {//循环当前层的节点
const node = q.shift();
ret[ret.length - 1].push(node.val);//推入当前层的数组
if (node.left) q.push(node.left);//检查左节点,存在左节点就继续加入队列
if (node.right) q.push(node.right);//检查左右节点,存在右节点就继续加入队列
}
}
return ret;
};
Java:
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
if (root == null) {
return ret;
}
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
q.offer(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> level = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int currentLevelSize = q.size();
for (int i = 1; i <= currentLevelSize; ++i) {
TreeNode node = q.poll();
level.add(node.val);
if (node.left != null) {
q.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
q.offer(node.right);
}
}
ret.add(level);
}
return ret;
}
}
方法2:深度优先遍历
- 思路:从根节点开始不断递归左右子树,透传step层数和res输出数组。
- 复杂度分析:时间复杂度
O(n),n是节点的个数。空间复杂度O(n),n是树的高度。
js:
var levelOrder = function(root) {
if(!root) return []
let res = []
dfs(root, 0, res)
return res
};
function dfs(root, step, res){//每层透传当前节点,层数,和输出数组
if(root){
if(!res[step]) res[step] = []//初始化当前层数组
res[step].push(root.val)//当前节点加入当前层数组
dfs(root.left, step + 1, res)//step+1,递归左节点
dfs(root.right, step + 1, res)//step+1,递归右节点
}
}
Java:
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(root != null){
dfs(res, root, 0);
}
return res;
}
private void dfs(List<List<Integer>> res, TreeNode node, int step){
if(res.size() - 1 < step){
res.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
res.get(step).add(node.val);
if(node.left!=null){
dfs(res, node.left, step + 1);
}
if(node.right!=null){
dfs(res, node.right, step + 1);
}
}
}
107. 二叉树的层序遍历 II (medium)
时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(n)
js:
const levelOrderBottom = (root) => {
if (root == null) {
return [];
}
const queue = [];
queue.push(root);
const res = [];
while (queue.length) {
const subRes = [];
const levelSize = queue.length;
for (let i = 0; i < levelSize; i++) {
const cur = queue.shift();
subRes.push(cur.val);
if (cur.left) {
queue.push(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right) {
queue.push(cur.right);
}
}
res.unshift(subRes);//和102不一样的地方 推入res中的方向正好相反
}
return res;
}
java:
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new LinkedList<List<Integer>>();
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> subRes = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
subRes.add(cur.val);
TreeNode left = cur.left, right = cur.right;
if (left != null) {
queue.offer(left);
}
if (right != null) {
queue.offer(right);
}
}
res.add(0, subRes);
}
return res;
}
}
104. 二叉树的最大深度 (easy)
方法1.dfs
- 思路:一个节点的深度等于1加左节点和有节点深度的较大者,用公式表示
h(r)=Math.max(h(r.left), h(right)) + 1,所以可以深度遍历左右子树,返回左右子树的最大深度。 - 复杂度分析:时间复杂度
O(n), 其中 n 为二叉树节点的个数。空间复杂度O(n), 其中n 表示二叉树的高度,最坏的情况下和树的节点数相同
js:
var maxDepth = function(root) {
if(!root) {
return 0;
} else {
const left = maxDepth(root.left);//递归左子树
const right = maxDepth(root.right);//递归右子树
return Math.max(left, right) + 1;//1加左节点和有节点深度的较大者
}
};
Java:
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return 0;
} else {
int left = maxDepth(root.left);
int right = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(left, right) + 1;
}
}
}
方法2.bfs
- 思路:层序遍历二叉树,每层结束的时候depth加1.
- 复杂度分析:时间复杂度
O(n),n 为二叉树的节点个数,每个节点只会被访问一次。空间复杂度O(n),表示队列中存放的元素,最坏情况下和二叉树节点个数一样
Js:
const maxDepth = (root) => {
if (root == null) return 0;
const queue = [root];
let depth = 1;
while (queue.length) {
// 当前层的节点个数
const levelSize = queue.length;
// 逐个让当前层的节点出列
for (let i = 0; i < levelSize; i++) {
// 当前出列的节点
const cur = queue.shift();
// 左右子节点入列
if (cur.left) queue.push(cur.left);
if (cur.right) queue.push(cur.right);
}
// 当前层所有节点已经出列,如果队列不为空,说明有下一层节点,depth+1
if (queue.length) depth++;
}
return depth;
};
Java:
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
int depth = 0;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int levelSize = queue.size();
for(int i = 0; i < levelSize; i++){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if(node.left != null){
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
depth++;
}
return depth;
}
}
111. 二叉树的最小深度 (easy)
方法1.dfs
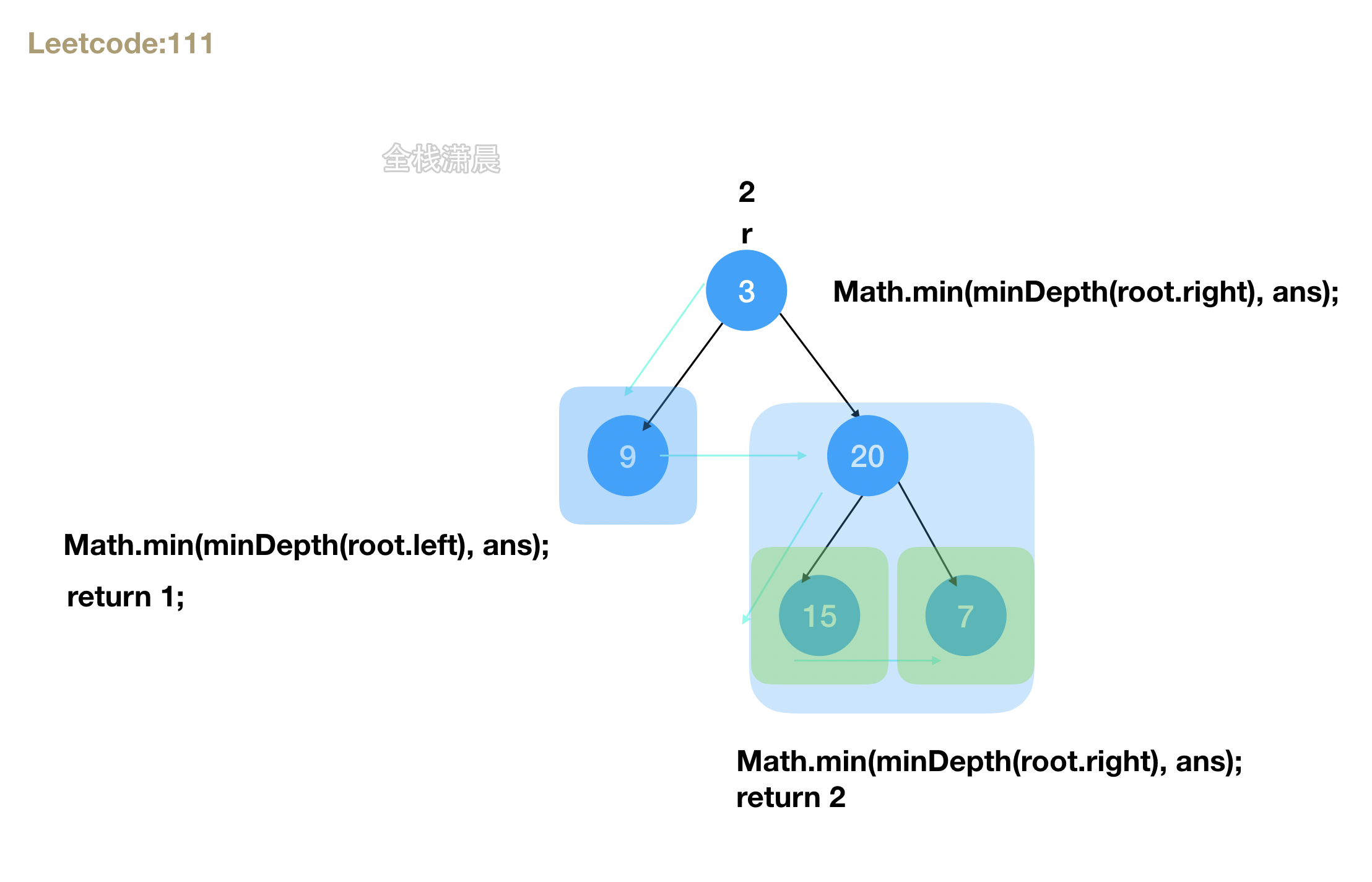
- 思路:深度优先遍历左右子树,分解成子问题,树的最小深度等于左右子树最小深度+1
- 复杂度分析:时间复杂度
O(n), 其中 n 为二叉树节点的个数。空间复杂度O(n), 其中n 表示二叉树的高度,最坏的情况下树呈现链状,和树的节点数相同,平均情况下树的高度与节点数的对数正相关,空间复杂度为O(logn)
js:
var minDepth = function(root) {
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
if(root.left == null && root.right == null) {//遍历到叶子结点终止
return 1;
}
let ans = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER;
if(root.left != null) {
ans = Math.min(minDepth(root.left), ans);//递归左子树,找到左子树的最小深度
}
if(root.right != null) {
ans = Math.min(minDepth(root.right), ans);//递归右子树,找到右子树的最小深度
}
return ans + 1;//最小深度等于左右子树最小深度+1
};
Java:
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
if(root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return 1;
}
int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if(root.left != null) {
ans = Math.min(minDepth(root.left), ans);
}
if(root.right != null) {
ans = Math.min(minDepth(root.right), ans);
}
return ans + 1;
}
}
方法2.bfs
- 思路:广度优先遍历二叉树,每一层深度+1,遇到第一个叶子结点终止,此时的深度就是最小深度
- 复杂度分析:时间复杂度
O(n),n 为二叉树的节点个数,每个节点只会被访问一次。空间复杂度O(n),表示队列中存放的元素,最坏情况下和二叉树节点个数一样
js:
var minDepth = function(root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
let q = [root];
//root本身就是一层,所以深度初始化为1
let depth = 1;
while(q.length){
let len = q.length;
for(let i=0; i<len; i++){
let curr = q.shift();
//判断是当前否是叶子节点
if(curr.left == null && curr.right == null){
return depth;
}
//如果不是叶子结点,就将其相邻节点加入队列
if(curr.left){
q.push(curr.left);
}
if(curr.right){
q.push(curr.right);
}
}
depth++;
}
return depth;
};
Java:
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int depth = 0;
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int sz = q.size();
depth++;
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
TreeNode cur = q.poll();
if (cur.left == null && cur.right == null) {
return depth;
}
if (cur.left != null) {
q.offer(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
q.offer(cur.right);
}
}
}
return depth;
}
}
127. 单词接龙 (hard)
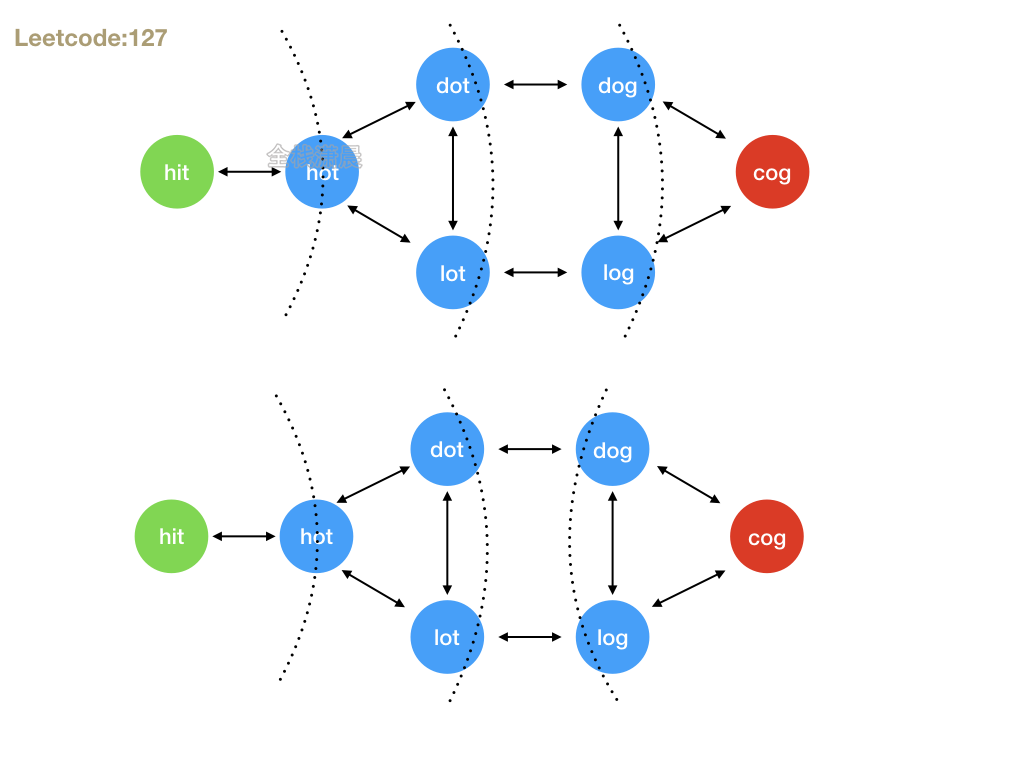
- 思路:bfs,循环beginWord,对每个字符替换26个小写字符,看新生成的单词是否在wordList里面,如果存在就是一个合法的路径,直到新生成的单词是endWord,循环完成还是没到达endWord就返回0。双向bfs思路一样,只不过是从两边向中间靠拢,判断新生成的单词是否在另一个方向走过的路径中。
方法1:bfs
js:
const ladderLength = (beginWord, endWord, wordList) => {
const wordSet = new Set(wordList);
const queue = [];
queue.push([beginWord, 1]);//开始单词和层级加入队列
while (queue.length) {
const [word, level] = queue.shift()//出队 进行bfs
if (word == endWord) {//和endword相等返回层级
return level;
}
for (let i = 0; i < word.length; i++) { //循环单词列表
for (let c = 97; c <= 122; c++) { //循环26个小写字符
//得到新的单词
const newWord = word.slice(0, i) + String.fromCharCode(c) + word.slice(i + 1);
if (wordSet.has(newWord)) { //检查wordset包不包括新生成的单词 避重复入列
queue.push([newWord, level + 1]); //新单词加入队列
wordSet.delete(newWord); //避死循环
}
}
}
}
return 0; // bfs结束,始终没有遇到终点
};
方法2:双向bfs
js:
var ladderLength = function(beginWord, endWord, wordList) {
let wordSet = new Set(wordList)
if (!wordSet.has(endWord)) return 0
//从beginWord到endWord
let begSet = []
//从endWord到beginWord
let endSet = []
begSet.push(beginWord)
endSet.push(endWord)
let n = 1//层级
while(begSet.length > 0){//开始遍历单词
const nextBegins = []//bfs下一层级的单词数组
//步数少数对换一下,让走的慢的在走几步
if(begSet.length > endSet.length){
let q = begSet
begSet = endSet
endSet = q
}
//循环begSet
for(let k = 0; k < begSet.length;k++){
let m = begSet[k]
for(let i = 0; i < m.length; i++){
for (let c = 97; c <= 122; c++){
//生成新词
let newm = m.slice(0, i) + String.fromCharCode(c) + m.slice(i + 1);
if(endSet.includes(newm)){//相遇
return n + 1
}
if( wordSet.has(newm)){
nextBegins.push(newm) //下一层bfs的单词数组
wordSet.delete(newm) //防止重复
}
}
}
}
begSet = nextBegins
n++ //层级+1
}
return 0
};
297. 二叉树的序列化与反序列化 (hard)
方法1.递归dfs

- 思路:深度优先遍历,按根,左,右 返回字符串,方便反序列化的时候从根节点开始构建,递归左右子树,直到遇见了null节点。
- 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(n),每个节点访问一次,n是树的节点个数。空间复杂度O(n),最坏情况下递归深度是n
js:
const serialize = (root) => {
if (root == null) { //遇到null 返回‘X’进行标示
return 'X';
}
const left = serialize(root.left); //序列化左子树
const right = serialize(root.right); //序列化右子树
return root.val + ',' + left + ',' + right; //按根,左,右 返回字符串
};
const deserialize = (data) => {
const list = data.split(','); //字符串转数组
const buildTree = (list) => { //构建树
const rootVal = list.shift(); //第一个元素
if (rootVal == "X") { //如果是X,返回null
return null;
}
const root = new TreeNode(rootVal); //如果不是X就创建节点
root.left = buildTree(list); //构建左子树
root.right = buildTree(list); //构建右子树
return root; //返回构建的节点
};
return buildTree(list);
};
方法2:bfs
- 思路:广度优先遍历节点,不断子节点不断入队,按照根左右的顺序序列化和反序列化
- 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(n),每个节点访问一次,n是树的节点个数。空间复杂度O(n),队列的空间
js:
const serialize = (root) => {
const queue = [root];
let res = [];
while (queue.length) {
const node = queue.shift(); //出队
if (node) { //node存在 推入根左右
res.push(node.val);
queue.push(node.left);
queue.push(node.right);
} else { //如果不存在 推入‘x’
res.push('X');
}
}
return res.join(','); //数组转成字符串
}
const deserialize = (data) => {
if (data == 'X') return null;
const list = data.split(','); //字符串转数组
const root = new TreeNode(list[0]); //从队首开始构建
const queue = [root]; //根节点加入队列
let cursor = 1; //遍历到了第几个节点
while (cursor < list.length) { //当队列没遍历完时
const node = queue.shift(); //出队
const leftVal = list[cursor]; //左节点的值
const rightVal = list[cursor + 1]; //右节点的值
if (leftVal != 'X') { //不是空节点
const leftNode = new TreeNode(leftVal); //构建左节点
node.left = leftNode; //左节点挂在父节点的left下
queue.push(leftNode); //自己入列 构建以自己为根的子树
}
if (rightVal != 'X') {
const rightNode = new TreeNode(rightVal);
node.right = rightNode;
queue.push(rightNode);
}
cursor += 2; //构建的节点数+2
}
return root; //返回根
};
226. 翻转二叉树 (easy)
方法1:递归
- 思路:递归左右子树,反转左右节点
- 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(n),树的每个节点都会遍历一遍。空间复杂度O(n),递归栈空间,最坏的情况下,和节点的个数n相同
js:
var invertTree = function(root) {
if (root === null) {//递归终止条件
return null;
}
const left = invertTree(root.left);//递归左子树
const right = invertTree(root.right);//递归右子树
//交换左右节点
root.left = right;
root.right = left;
return root;
};
java:
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
TreeNode left = invertTree(root.left);
TreeNode right = invertTree(root.right);
root.left = right;
root.right = left;
return root;
}
}
100. 相同的树(easy)
方法1.dfs递归
- 思路:递归比较左右子树
- 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(n),n是节点较少的树中的节点个数,递归有一个节点为null,另一个不为null就停止递归,空间复杂度O(n),递归深度不会超过节点个数
js:
var isSameTree = function(p, q) {
if(p == null && q == null) //都是null表示相同
return true;
if(p == null || q == null) //只有一个是null表示不同
return false;
if(p.val != q.val) //节点的值不同
return false;
return isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right);//递归左右子树
};
java:
class Solution {
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(p == null && q == null)
return true;
if(p == null || q == null)
return false;
if(p.val != q.val)
return false;
return isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right);
}
}
方法2bfs:
- 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(n),n是节点较少的树中的节点个数,空间复杂度O(n),队列的空间不会超过节点较少的树中的节点个数
js:
var isSameTree = function(p, q) {
let pQ = [p], qQ = [q], res = true
while (pQ.length) {
pNode = pQ.shift()
qNode = qQ.shift()
if (pNode === null && qNode === null) {
res = true
} else if (pNode === null || qNode === null) {
res = false
break
} else {
if (pNode.val !== qNode.val) {
res = false
break
} else {
pQ.push(pNode.left)
pQ.push(pNode.right)
qQ.push(qNode.left)
qQ.push(qNode.right)
}
}
}
return res
};
java:
class Solution {
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
Queue<TreeNode> pQ = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
Queue<TreeNode> qQ = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
pQ.offer(p);
qQ.offer(q);
boolean res = true;
while (!pQ.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode pNode = pQ.poll();
TreeNode qNode = qQ.poll();
if (pNode == null && qNode == null) {
res = true;
} else if (pNode == null || qNode == null) {
res = false;
break ;
} else {
if (pNode.val != qNode.val) {
res = false;
break ;
} else {
pQ.offer(pNode.left);
pQ.offer(pNode.right);
qQ.offer(qNode.left);
qQ.offer(qNode.right);
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
101. 对称二叉树 (easy)
方法1.dfs递归
- 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(n),每个节点遍历一次,空间复杂度O(n),递归栈深度,最深不超过n
js:
var isSymmetric = function(root) {
if(!root) return true
const isMirror = (l, r) => {
if(!l && !r) return true; //两个空节点也为镜像
if(
l && r && l.val === r.val && //左节点和右节点相同,左子树和右子树也对称则返回true
isMirror(l.left, r.right) &&
isMirror(l.right, r.left)
) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
return isMirror(root.left, root.right)
};
java:
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return isMirror(root, root);
}
public boolean isMirror(TreeNode l, TreeNode r) {
if (l == null && r == null) {
return true;
}
if (l == null || r == null) {
return false;
}
return l.val == r.val && isMirror(l.left, r.right) && isMirror(l.right, r.left);
}
}
方法2.bfs
- 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(n),每个节点遍历一次,空间复杂度O(n),队列的空间
js:
function isSymmetric(root) {
const isMirror = (l, r) => {
const queue = [l, r];
while (queue.length) {
const u = queue.shift();
const v = queue.shift();
if (!u && !v) continue; //两个空节点也为镜像
//左右节点只有一个节点为空,或者值不相同返回false
if (!u || !v || u.val !== v.val) return false;
queue.push(u.left, v.right); //加入左节点的左子树,右节点的右子树
queue.push(v.left, u.right); //加入右节点的左子树,左节点的右子树
}
return true;
};
return isMirror(root.left, root.right);
}
java:
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return isMirror(root, root);
}
public boolean isMirror(TreeNode u, TreeNode v) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.offer(u);
queue.offer(v);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
u = queue.poll();
v = queue.poll();
if (u == null && v == null) {
continue;
}
if ((u == null || v == null) || (u.val != v.val)) {
return false;
}
queue.offer(u.left);
queue.offer(v.right);
queue.offer(u.right);
queue.offer(v.left);
}
return true;
}
}
112. 路径总和 (easy)
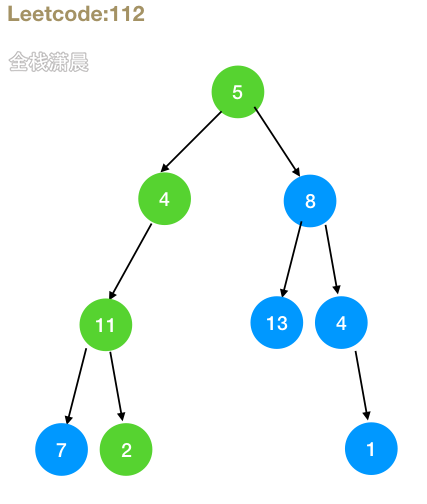
- 思路:递归左右子树,不断让sum减去当前节点的值。左右子树有一个返回true就找到了一条这样的路径
- 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(n),n是节点个数,每个节点遍历一次。空间复杂度O(n),取决于递归栈空间,最坏的情况下是O(n)
js:
const hasPathSum = (root, sum) => {
if (root == null) {//递归终止条件
return false;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {//遍历到叶子节点
return sum - root.val == 0; //sum正好减少到了0 返回ture 否则返回false
}
//递归左右子树,有一个返回true就找到了一条这样的路径
return hasPathSum(root.left, sum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, sum - root.val);
}
java:
class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if (root == null) {
return false;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return sum == root.val;
}
return hasPathSum(root.left, sum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, sum - root.val);
}
}
437. 路径总和 III (medium)
方法1:dfs
- 思路:递归左右子树,在递归的子阶段中,继续以该节点为根节点继续进行路径的寻找
- 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(n^2),所有节点都要遍历一边,还要寻找以该节点为根的子树中是否存在符合条件的路径。空间复杂度O(n),递归空间
js:
var pathSum = function(root, targetSum) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
let ret = rootSum(root, targetSum);//以root为根节点的树中寻找路径
ret += pathSum(root.left, targetSum);//递归左子树,在左子树中寻找路径
ret += pathSum(root.right, targetSum);//递归右子树,在左子树中寻找路径
return ret;
};
const rootSum = (root, targetSum) => {
let ret = 0;
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
const val = root.val;
if (val === targetSum) {
ret++;
}
//以root.left为根节点,targetSum - val为寻找的路径和,继续寻找路径
ret += rootSum(root.left, targetSum - val);
//以root.right为根节点,targetSum - val为寻找的路径和,继续寻找路径
ret += rootSum(root.right, targetSum - val);
return ret;
}
java:
class Solution {
public int pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int ret = rootSum(root, targetSum);
ret += pathSum(root.left, targetSum);
ret += pathSum(root.right, targetSum);
return ret;
}
public int rootSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
int ret = 0;
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int val = root.val;
if (val == targetSum) {
ret++;
}
ret += rootSum(root.left, targetSum - val);
ret += rootSum(root.right, targetSum - val);
return ret;
}
}
方法2:前缀和
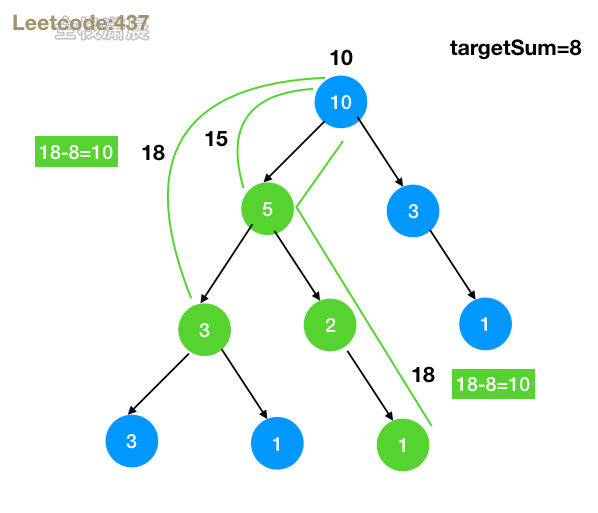
- 思路:记录从根节点到该节点的路径和curr,在递归左右子树,看之前遍历过的路径中是否存在以
curr - targetSum为 路径和的路径,如果存在,那么从根节点到当前节点的路径 减去 这条路径 就是符合条件的路径之一,看图 - 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(n),二叉树中的节点只遍历一遍。空间复杂度O(n),递归栈深度。
js:
var pathSum = function(root, targetSum) {
const prefix = new Map();//存放前缀和 和它的路径数量
prefix.set(0, 1);//初始化前缀和是0的个数
return dfs(root, prefix, 0, targetSum);
}
const dfs = (root, prefix, curr, targetSum) => {//curr指到达当前节点的路径上的和
if (root == null) {//空节点就没有路径了,返回0
return 0;
}
let ret = 0;
curr += root.val;//加上当前节点
ret = prefix.get(curr - targetSum) || 0;//获取以curr - targetSum的前缀和的数量
prefix.set(curr, (prefix.get(curr) || 0) + 1);//在prefix中增加curr的前缀和的数量
ret += dfs(root.left, prefix, curr, targetSum);//递归左子树 加上左子树前缀和为targetSum的路径数
ret += dfs(root.right, prefix, curr, targetSum);//递归右子树 加上右子树前缀和为targetSum的路径数
prefix.set(curr, (prefix.get(curr) || 0) - 1);//节点递归完毕,回溯curr的前缀和数量 避免重复计算
return ret;
}
java:
class Solution {
public int pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
HashMap<Long, Integer> prefix = new HashMap<>();
prefix.put(0L, 1);
return dfs(root, prefix, 0, targetSum);
}
public int dfs(TreeNode root, Map<Long, Integer> prefix, long curr, int targetSum) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int ret = 0;
curr += root.val;
ret = prefix.getOrDefault(curr - targetSum, 0);
prefix.put(curr, prefix.getOrDefault(curr, 0) + 1);
ret += dfs(root.left, prefix, curr, targetSum);
ret += dfs(root.right, prefix, curr, targetSum);
prefix.put(curr, prefix.getOrDefault(curr, 0) - 1);
return ret;
}
}
257. 二叉树的所有路径 (easy)
方法1:dfs
- 思路:递归左右子树,直到叶子节点,递归的过程中不断透传path,递归的每一层连接上当前节点的值
- 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(n),每个节点遍历一次。空间复杂度O(n),递归栈空间
js:
var binaryTreePaths = function(root) {
const paths = [];
const dfs = (root, path) => {//传入递归的节点和路径数组
if (root) {
path += root.val.toString();//加入当前节点
//叶子结点就将所有连接起来的节点字符串加入paths中 也就是其中一条路径
if (root.left === null && root.right === null) {
paths.push(path);
} else {
path += "->"; //不是叶子节点继续递归左右子树
dfs(root.left, path);
dfs(root.right, path);
}
}
}
dfs(root, "");
return paths;
};
java:
class Solution {
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
List<String> paths = new ArrayList<String>();
dfs(root, "", paths);
return paths;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root, String path, List<String> paths) {
if (root != null) {
StringBuffer path1 = new StringBuffer(path);
path1.append(Integer.toString(root.val));
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
paths.add(path1.toString());
} else {
path1.append("->");
dfs(root.left, path1.toString(), paths);
dfs(root.right, path1.toString(), paths);
}
}
}
}
方法2:bfs
- 思路:用队列辅助进行广度优先遍历,不断将左右子节点加入队列,直到叶子节点
- 复杂度:同方法1
js:
var binaryTreePaths = function(root) {
const res = [];
if (root === null) {
return res;
}
const nodes = [root];
const paths = [root.val.toString()];
while (nodes.length) {
const node = nodes.shift();
const path = paths.shift();
if (node.left === null && node.right === null) {//叶子节点
res.push(path);
} else {
if (node.left !== null) {//左节点不为空 加入队列
nodes.push(node.left);
paths.push(path + "->" + node.left.val.toString());
}
if (node.right !== null) {//右节点不为空 加入队列
nodes.push(node.right);
paths.push(path + "->" + node.right.val.toString());
}
}
}
return res;
};
java:
class Solution {
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<String>();
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
Queue<TreeNode> nodeQueue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
Queue<String> pathQueue = new LinkedList<String>();
nodeQueue.offer(root);
pathQueue.offer(Integer.toString(root.val));
while (!nodeQueue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = nodeQueue.poll();
String path = pathQueue.poll();
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
res.add(path);
} else {
if (node.left != null) {
nodeQueue.offer(node.left);
pathQueue.offer(new StringBuffer(path).append("->").append(node.left.val).toString());
}
if (node.right != null) {
nodeQueue.offer(node.right);
pathQueue.offer(new StringBuffer(path).append("->").append(node.right.val).toString());
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
199. 二叉树的右视图 (medium)
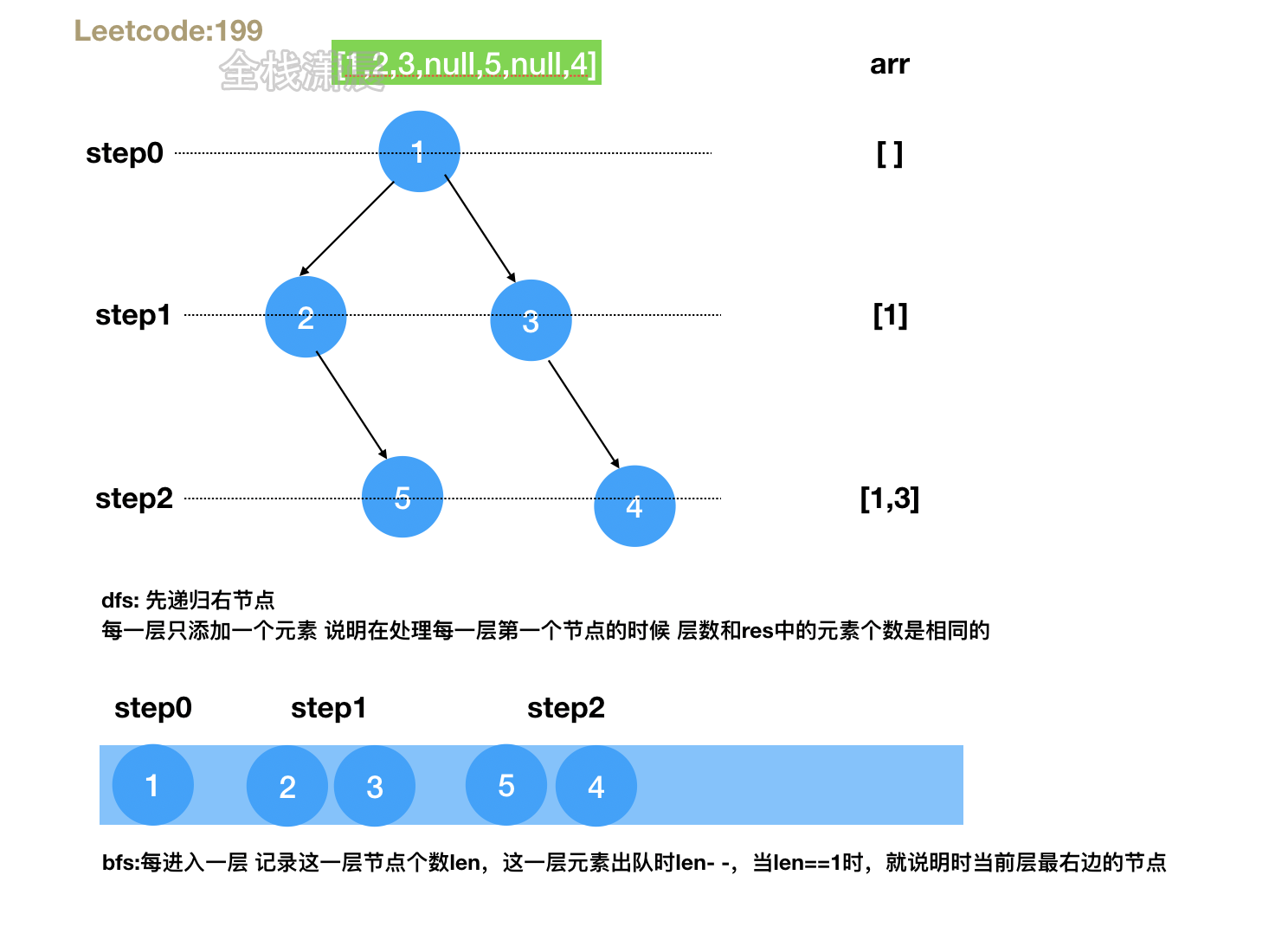
方法1:dfs
- 思路:深度优先遍历,先递归右节点 让它在下一层先被处理,当res长度和step相等时 当前节点就是这一层的右节点,加入数组中
- 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(n),每个节点遍历一次。空间复杂度O(n),递归栈空间
js:
var rightSideView = function (root) {
function dfs(root, step, res) {//传入根节点 层数 右视的节点的数组
if (root) {
if (res.length === step) {
res.push(root.val); //当res长度和step相等时 当前节点就是这一层的右节点 加入数组中
}
dfs(root.right, step + 1, res); //先递归右节点 让它在下一层先被处理
dfs(root.left, step + 1, res);
}
}
if (!root) return [];
let arr = [];
dfs(root, 0, arr);
return arr;
};
java:
class Solution {
List<Integer> res;
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
res = new LinkedList<>();
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
dfs(root, 0);
return res;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root, int depth) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
if (depth == res.size()) {
res.add(root.val);
}
dfs(root.right, depth+1);
dfs(root.left, depth+1);
}
}
方法2:bfs
- 思路:广度优先遍历,记录每一层的节点个数,出队之后让长度减1,当当前层长度等于1时 说明是最边的节点。
- 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(n),每个节点遍历一次。空间复杂度O(n),队列的空间
js:
var rightSideView = function (root) {
if (!root) return [];
let queue = [root]; //广度优先遍历的队列 首先加入root
let arr = []; //存放右视的节点
while (queue.length > 0) {
let len = queue.length;
while (len) {
let node = queue.shift(); //取出队列第一个元素
if (len === 1) arr.push(node.val); //当当前层长度等于1时 说明是最边的节点
if (node.left) queue.push(node.left); //继续向队列中添加左右节点
if (node.right) queue.push(node.right);
len--;//出队之后 当前层长度减1
}
}
return arr;
};
java:
class Solution {
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new LinkedList<>();
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
TreeNode curr = null;
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
curr = queue.poll();
if (curr.left != null) {
queue.offer(curr.left);
}
if (curr.right != null) {
queue.offer(curr.right);
}
}
res.add(curr.val);//或者在换一种思路,循环完当前层之后,最后出队的就是当前层最右边的一个
}
return res;
}
}